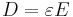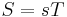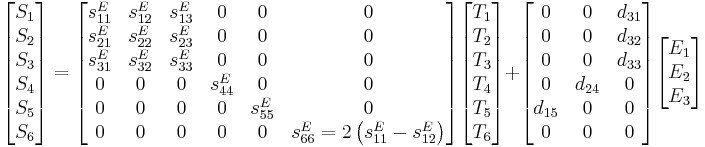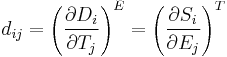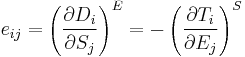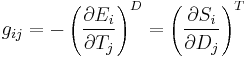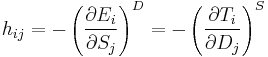Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in solid materials having no crystalline center of symmetry (notably crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA and various proteins)[1]because of an applied electromechanical interaction. The word piezoelectricity is derived from Greek origin; meaning electricity resulting from pressure. Piezoelectricity is the direct result of the piezoelectric effect.
The piezoelectric effect is an electromechanical interaction between the electrical and mechanical states in solid materials which have no crystalline center of symmetry[2]. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process in that materials exhibiting the direct piezoelectric effect (the internal generation of electrical charge resulting from an applied mechanical force) also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect (the internal generation of a mechanical force resulting from an applied electrical force). For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measureable piezoelectricity when it’s static structure is deformed to about 0.1% of the original dimension. Conversely, lead zirconate titanate crystals will change about 0.1% of their static dimension when an external electric field is applied to the material.
Piezoelectricity is found in useful applications such as the production and detection of sound, generation of high voltages, electronic frequency generation, microbalances, and ultra fine focusing of optical assemblies. It is also the basis of a number of scientific instrumental techniques with atomic resolution, the scanning probe microscopies such as STM, AFM, MTA, SNOM, etc., and everyday uses such as acting as the ignition source for cigarette lighters and push-start propane barbecues.
Contents |
History
Discovery and early research
The pyroelectric effect, where a material generates an electric potential in response to a temperature change, was studied by Carl Linnaeus and Franz Aepinus in the mid-18th century. Drawing on this knowledge, both René Just Haüy and Antoine César Becquerel posited a relationship between mechanical stress and electric charge; however, experiments by both proved inconclusive.
The first demonstration of the direct piezoelectric effect was in 1880 by the brothers Pierre Curie and Jacques Curie. They combined their knowledge of pyroelectricity with their understanding of the underlying crystal structures that gave rise to pyroelectricity to predict crystal behavior, and demonstrated the effect using crystals of tourmaline, quartz, topaz, cane sugar, and Rochelle salt (sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate). Quartz and Rochelle salt exhibited the most piezoelectricity.

The Curies, however, did not predict the converse piezoelectric effect. The converse effect was mathematically deduced from fundamental thermodynamic principles by Gabriel Lippmann in 1881.[3] The Curies immediately confirmed the existence of the converse effect, and went on to obtain quantitative proof of the complete reversibility of electro-elasto-mechanical deformations in piezoelectric crystals.
For the next few decades, piezoelectricity remained something of a laboratory curiosity. More work was done to explore and define the crystal structures that exhibited piezoelectricity. This culminated in 1910 with the publication of Woldemar Voigt's Lehrbuch der Kristallphysik (textbook on crystal physics), which described the 20 natural crystal classes capable of piezoelectricity, and rigorously defined the piezoelectric constants using tensor analysis.
World War I and post-war
The first practical application for piezoelectric devices was sonar, first developed during World War I. In France in 1917, Paul Langevin and his coworkers developed an ultrasonic submarine detector. The detector consisted of a transducer, made of thin quartz crystals carefully glued between two steel plates, and a hydrophone to detect the returned echo. By emitting a high-frequency chirp from the transducer, and measuring the amount of time it takes to hear an echo from the sound waves bouncing off an object, one can calculate the distance to that object.
The use of piezoelectricity in sonar, and the success of that project, created intense development interest in piezoelectric devices. Over the next few decades, new piezoelectric materials and new applications for those materials were explored and developed.
Piezoelectric devices found homes in many fields. Ceramic phonograph cartridges simplified player design, were cheap and accurate, and made record players cheaper to maintain and easier to build. The development of the ultrasonic transducer allowed for easy measurement of viscosity and elasticity in fluids and solids, resulting in huge advances in materials research. Ultrasonic time-domain reflectometers (which send an ultrasonic pulse through a material and measure reflections from discontinuities) could find flaws inside cast metal and stone objects, improving structural safety.
World War II and post-war
During World War II, independent research groups in the United States, Russia, and Japan discovered a new class of man-made materials, called ferroelectrics, which exhibited piezoelectric constants many times higher than natural materials. This led to intense research to develop barium titanate and later lead zirconate titanate materials with specific properties for particular applications.
One significant example of the use of piezoelectric crystals was developed by Bell Telephone Laboratories. Following World War I, Frederick R. Lack, working in radio telephony in the engineering department, developed the “AT cut” crystal, a crystal that operated through a wide range of temperatures. Lack's crystal didn't need the heavy accessories previous crystal used, facilitating its use on aircraft. This development allowed Allied air forces to engage in coordinated mass attacks through the use of aviation radio.
Development of piezoelectric devices and materials in the United States was kept within the companies doing the development, mostly due to the wartime beginnings of the field, and in the interests of securing profitable patents. New materials were the first to be developed — quartz crystals were the first commercially exploited piezoelectric material, but scientists searched for higher-performance materials. Despite the advances in materials and the maturation of manufacturing processes, the United States market had not grown as quickly. Without many new applications, the growth of the United States' piezoelectric industry suffered.
In contrast, Japanese manufacturers shared their information, quickly overcoming technical and manufacturing challenges and creating new markets. Japanese efforts in materials research created piezoceramic materials competitive to the U.S. materials, but free of expensive patent restrictions. Major Japanese piezoelectric developments include new designs of piezoceramic filters for radios and televisions, piezo buzzers and audio transducers that can connect directly to electronic circuits, and the piezoelectric igniter, which generates sparks for small engine ignition systems (and gas-grill lighters) by compressing a ceramic disc. Ultrasonic transducers that transmit sound waves through air had existed for quite some time, but first saw major commercial use in early television remote controls. These transducers now are mounted on several car models as an echolocation device, helping the driver determine the distance from the rear of the car to any objects that may be in its path.
Mechanism
The nature of the piezoelectric effect is closely related to the occurrence of electric dipole moments in solids. The latter may either be induced for ions on crystal lattice sites with asymmetric charge surroundings (as in BaTiO3 and PZTs) or may directly be carried by molecular groups (as in cane sugar). The dipole density or polarization (dimensionality [Cm/m3] ) may easily be calculated for crystals by summing up the dipole moments per volume of the crystallographic unit cell.[4] As every dipole is a vector, the dipole density P is also a vector or a directed quantity. Dipoles near each other tend to be aligned in regions called Weiss domains. The domains are usually randomly oriented, but can be aligned during poling (not the same as magnetic poling), a process by which a strong electric field is applied across the material, usually at elevated temperatures.
Of decisive importance for the piezoelectric effect is the change of polarization P when applying a mechanical stress. This might either be caused by a re-configuration of the dipole-inducing surrounding or by re-orientation of molecular dipole moments under the influence of the external stress. Piezoelectricity may then manifest in a variation of the polarization strength, its direction or both, with the details depending on 1. the orientation of P within the crystal, 2. crystal symmetry and 3. the applied mechanical stress. The change in P appears as a variation of surface charge density upon the crystal faces, i.e. as a variation of the electrical field extending between the faces, since the units of surface charge density and polarization are the same, C/m2] = [Cm/m3]. However, piezoelectricity is not caused by a change in charge density on the surface, but by dipole density in the bulk. For example, a 1 cm3 cube of quartz with 2 kN (500 lbf) of correctly applied force can produce a voltage of 12500 V.[5]
Piezoelectric materials also show the opposite effect, called converse piezoelectric effect, where the application of an electrical field creates mechanical deformation in the crystal.
Mathematical description
Piezoelectricity is the combined effect of the electrical behavior of the material:
where D is the electric charge density displacement (electric displacement), ε is permittivity and E is electric field strength, and
where S is strain, s is compliance and T is stress.
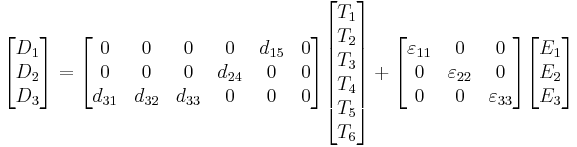
These may be combined into so-called coupled equations, of which the strain-charge form is:
![\{S\} = \left [s^E \right ]\{T\}+[d^t]\{E\}](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/efb5e2aaf1489c25e42bed45f96f9e8b.png)
![\{D\} = [d]\{T\}+\left [ \varepsilon^T \right ] \{E\}](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/70a492348ab079857832462a23dfb025.png) ,
,
where ![[d]](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/55bbeb5fefa388fc850000a090efc0eb.png) is the matrix for the direct piezoelectric effect and
is the matrix for the direct piezoelectric effect and ![[d^t]](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/d7d9045fa870eb6f063228c4ad6224b2.png) is the matrix for the converse piezoelectric effect. The superscript E indicates a zero, or constant, electric field; the superscript T indicates a zero, or constant, stress field; and the superscript t stands for transposition of a matrix.
is the matrix for the converse piezoelectric effect. The superscript E indicates a zero, or constant, electric field; the superscript T indicates a zero, or constant, stress field; and the superscript t stands for transposition of a matrix.
The strain-charge for a material of the 4mm (C4v) crystal class (such as a poled piezoelectric ceramic such as tetragonal PZT or BaTiO3) as well as the 6mm crystal class may also be written as (ANSI IEEE 176):
where the first equation represents the relationship for the converse piezoelectric effect and the latter for the direct piezoelectric effect.[6]
Although the above equations are the most used form in literature, some comments about the notation are necessary. Generally D and E are vectors, that is, Cartesian tensor of rank-1; and permittivity ε is Cartesian tensor of rank 2. Strain and stress are, in principle, also rank-2 tensors. But conventionally, because strain and stress are all symmetric tensors, the subscript of strain and stress can be re-labeled in the following fashion: 11 → 1; 22 → 2; 33 → 3; 23 → 4; 13 → 5; 12 → 6. (Different convention may be used by different authors in literature. Say, some use 12 → 4; 23 → 5; 31 → 6 instead.) That is why S and T appear to have the "vector form" of 6 components. Consequently, s appears to be a 6 by 6 matrix instead of rank-4 tensor. Such a re-labeled notation is often called Voigt notation.
In total, there are 4 piezoelectric coefficients, 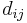 ,
, 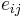 ,
, 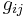 , and
, and 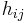 defined as follows:
defined as follows:
where the first set of 4 terms correspond to the direct piezoelectric effect and the second set of 4 terms correspond to the converse piezoelectric effect [7]. A formalism has been worked out for those piezoelectric crystals, for which the polarization is of the crystal-field induced type, that allows for the calculation of piezoelectrical coefficients 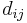 from electrostatic lattice constants or higher-order Madelung constants [4].
from electrostatic lattice constants or higher-order Madelung constants [4].
Crystal classes

Of the thirty-two crystal classes, twenty-one are non-centrosymmetric (not having a centre of symmetry), and of these, twenty exhibit direct piezoelectricity (the 21st is the cubic class 432). Ten of these represent the polar crystal classes, which show a spontaneous polarization without mechanical stress due to a non-vanishing electric dipole moment associated with their unit cell, and which exhibit pyroelectricity. If the dipole moment can be reversed by the application of an electric field, the material is said to be ferroelectric.
- Polar crystal classes: 1, 2, m, mm2, 4, 4 mm, 3, 3m, 6, 6 mm.
- Piezoelectric crystal classes: 1, 2, m, 222, mm2, 4, 4, 422, 4 mm, 42m, 3, 32, 3m, 6, 6, 622, 6 mm, 62m, 23, 43m.
For polar crystals, for which P ≠ 0 holds without applying a mechanical load, the piezoelectric effect manifests itself by changing the magnitude or the direction of P or both. For the non-polar, but piezoelectric crystals, on the other hand, a polarization P different from zero is only elicited by applying a mechanical load. For them the stress can be imagined to transform the material from a non-polar crystal class (P =0) to a polar one [4], having P ≠ 0.
Materials
Many materials, both natural and man-made, exhibit piezoelectricity:
Naturally-occurring crystals
- Berlinite (AlPO4), a rare phosphate mineral that is structurally identical to quartz
- Cane sugar
- Quartz
- Rochelle salt
- Topaz
- Tourmaline-group minerals
Other natural materials
- Bone: Dry bone exhibits some piezoelectric properties. Studies of Fukada et al. showed that these are not due to the apatite crystals, which are centrosymmetric, thus non-piezoelectric, but due to collagen. Collagen exhibits the polar uniaxial orientation of molecular dipoles in its structure and can be considered as bioelectret, a sort of dielectric material exhibiting quasipermanent space charge and dipolar charge. Potentials are thought to occur when a number of collagen molecules are stressed in the same way displacing significant numbers of the charge carriers from the inside to the surface of the specimen. Piezoelectricity of single individual collagen fibrils was measured using piezoresponse force microscopy, and it was shown that collagen fibrils behave predominantly as shear piezoelectric materials [8].
The piezoelectric effect is generally thought to act as a biological force sensor.[9][10] This effect was exploited by research conducted at the University of Pennsylvania in the late 1970s and early 1980s, which established that sustained application of electrical potential could stimulate both resorption and growth (depending on the polarity) of bone in-vivo.[11] Further studies in the 1990s provided the mathematical equation to confirm long bone wave propagation as to that of hexagonal (Class 6) crystals.[12]
Man-made crystals
- Gallium orthophosphate (GaPO4), a quartz analogic crystal
- Langasite (La3Ga5SiO14), a quartz analogic crystal
Man-made ceramics

The family of ceramics with perovskite or tungsten-bronze structures exhibits piezoelectricity:
- Barium titanate (BaTiO3)—Barium titanate was the first piezoelectric ceramic discovered.
- Lead titanate (PbTiO3)
- Lead zirconate titanate (Pb[ZrxTi1−x]O3 0<x<1)—more commonly known as PZT, lead zirconate titanate is the most common piezoelectric ceramic in use today.
- Potassium niobate (KNbO3)
- Lithium niobate (LiNbO3)
- Lithium tantalate (LiTaO3)
- Sodium tungstate (Na2WO3)
- Ba2NaNb5O5
- Pb2KNb5O15
Lead-free piezoceramics
More recently, there is growing concern regarding the toxicity in lead-containing devices driven by the result of restriction of hazardous substances directive regulations. To address this concern, there has been a resurgence in the compositional development of lead-free piezoelectric materials.
- Sodium potassium niobate (NaKNb). In 2004, a group of Japanese researchers led by Yasuyoshi Saito discovered a sodium potassium niobate composition with properties close to those of PZT, including a high
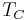 .[13]
.[13] - Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) is also a promising candidate for the replacement of lead-based ceramics.
- Sodium niobate NaNbO3
So far, neither the environmental impact nor the stability of supplying these substances have been confirmed.
Polymers
- Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): PVDF exhibits piezoelectricity several times greater than quartz. Unlike ceramics, where the crystal structure of the material creates the piezoelectric effect, in polymers the intertwined long-chain molecules attract and repel each other when an electric field is applied.
Applications
Piezoelectric crystals are now used in numerous ways:
High voltage and power sources
Direct piezoelectricity of some substances like quartz, as mentioned above, can generate potential differences of thousands of volts.
- The best-known application is the electric cigarette lighter: pressing the button causes a spring-loaded hammer to hit a piezoelectric crystal, producing a sufficiently high voltage electric current that flows across a small spark gap, thus heating and igniting the gas. The portable sparkers used to light gas grills or stoves work the same way, and many types of gas burners now have built-in piezo-based ignition systems.
- A similar idea is being researched by DARPA in the United States in a project called Energy Harvesting, which includes an attempt to power battlefield equipment by piezoelectric generators embedded in soldiers' boots. However, these energy harvesting sources by association have an impact on the body. DARPA's effort to harness 1-2 watts from continuous shoe impact while walking were abandoned due to the impracticality and the discomfort from the additional energy expended by a person wearing the shoes. Other energy harvesting ideas include harvesting the energy from human movements in train stations or other public places.[14][15]
- A piezoelectric transformer is a type of AC voltage multiplier. Unlike a conventional transformer, which uses magnetic coupling between input and output, the piezoelectric transformer uses acoustic coupling. An input voltage is applied across a short length of a bar of piezoceramic material such as PZT, creating an alternating stress in the bar by the inverse piezoelectric effect and causing the whole bar to vibrate. The vibration frequency is chosen to be the resonant frequency of the block, typically in the 100 kilohertz to 1 megahertz range. A higher output voltage is then generated across another section of the bar by the piezoelectric effect. Step-up ratios of more than 1000:1 have been demonstrated. An extra feature of this transformer is that, by operating it above its resonant frequency, it can be made to appear as an inductive load, which is useful in circuits that require a controlled soft start.[16] These devices can be used in DC-AC inverters to drive cold cathode fluorescent lamps. Piezo transformers are some of the most compact high voltage sources.
Sensors

The principle of operation of a piezoelectric sensor is that a physical dimension, transformed into a force, acts on two opposing faces of the sensing element. Depending on the design of a sensor, different "modes" to load the piezoelectric element can be used: longitudinal, transversal and shear.
Detection of pressure variations in the form of sound is the most common sensor application, e.g. piezoelectric microphones (sound waves bend the piezoelectric material, creating a changing voltage) and piezoelectric pickups for Acoustic-electric guitars. A piezo sensor attached to the body of an instrument is known as a contact microphone.
Piezoelectric sensors especially are used with high frequency sound in ultrasonic transducers for medical imaging and also industrial nondestructive testing (NDT).
For many sensing techniques, the sensor can act as both a sensor and an actuator – often the term transducer is preferred when the device acts in this dual capacity, but most piezo devices have this property of reversibility whether it is used or not. Ultrasonic transducers, for example, can inject ultrasound waves into the body, receive the returned wave, and convert it to an electrical signal (a voltage). Most medical ultrasound transducers are piezoelectric.
In addition to those mentioned above, various sensor applications include:
- Piezoelectric elements are also used in the detection and generation of sonar waves.
- Power monitoring in high power applications (e.g. medical treatment, sonochemistry and industrial processing).
- Piezoelectric microbalances are used as very sensitive chemical and biological sensors.
- Piezos are sometimes used in strain gauges.
- Piezoelectric transducers are used in electronic drum pads to detect the impact of the drummer's sticks.
- Automotive engine management systems use piezoelectric transducers to detect detonation by sampling the vibrations of the engine block and also to detect the precise moment of fuel injection (needle lift sensors).
- Ultrasonic piezo sensors are used in the detection of acoustic emissions in acoustic emission testing.
- Crystal earpieces are sometimes used in old or low power radios
Actuators

As very high electric fields correspond to only tiny changes in the width of the crystal, this width can be changed with better-than-micrometer precision, making piezo crystals the most important tool for positioning objects with extreme accuracy — thus their use in actuators. Multilayer ceramics, using layers thinner than 100 microns, allow reaching high electric fields with voltage lower than 150 V. These ceramics are used within two kinds of actuators: direct piezo actuators and Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators. While direct actuator's stroke is generally lower than 100 microns, amplified piezo actuators can reach millimeter strokes.
- Loudspeakers: Voltage is converted to mechanical movement of a piezoelectric polymer film.
- Piezoelectric motors: piezoelectric elements apply a directional force to an axle, causing it to rotate. Due to the extremely small distances involved, the piezo motor is viewed as a high-precision replacement for the stepper motor.
- Piezoelectric elements can be used in laser mirror alignment, where their ability to move a large mass (the mirror mount) over microscopic distances is exploited to electronically align some laser mirrors. By precisely controlling the distance between mirrors, the laser electronics can accurately maintain optical conditions inside the laser cavity to optimize the beam output.
- A related application is the acousto-optic modulator, a device that scatters light off of sound waves in a crystal, generated by piezoelectric elements. This is useful for fine-tuning a laser's frequency.
- Atomic force microscopes and scanning tunneling microscopes employ converse piezoelectricity to keep the sensing needle close to the probe[18].
- Inkjet printers: On many inkjet printers, piezoelectric crystals are used to drive the ejection of ink from the inkjet print head towards the paper.
- Diesel engines: high-performance common rail diesel engines use piezoelectric fuel injectors, first developed by Robert Bosch GmbH, instead of the more common solenoid valve devices.
- Active control of vibration using amplified actuators.
- X-ray shutters.
- XY stages for micro scanning used in infrared cameras.
Frequency standard
The piezoelectrical properties of quartz are useful as standard of frequency.
- Quartz clocks employ a tuning fork made from quartz that uses a combination of both direct and converse piezoelectricity to generate a regularly timed series of electrical pulses that is used to mark time. The quartz crystal (like any elastic material) has a precisely defined natural frequency (caused by its shape and size) at which it prefers to oscillate, and this is used to stabilize the frequency of a periodic voltage applied to the crystal.
- The same principle is critical in all radio transmitters and receivers, and in computers where it creates a clock pulse. Both of these usually use a frequency multiplier to reach the megahertz and gigahertz ranges.
Piezoelectric motors

Types of piezoelectric motor include:
- The travelling-wave motor used for auto-focus in reflex cameras
- Inchworm motors for linear motion
- Rectangular four-quadrant motors with high power density (2.5 watt/cm3) and speed ranging from 10 nm/s to 800 mm/s.
- Stepping piezo motor, using stick-slip effect.
All these motors, except the stepping stick-slip motor work on the same principle. Driven by dual orthogonal vibration modes with a phase difference of 90°, the contact point between two surfaces vibrates in an elliptical path, producing a frictional force between the surfaces. Usually, one surface is fixed causing the other to move. In most piezoelectric motors the piezoelectric crystal is excited by a sine wave signal at the resonant frequency of the motor. Using the resonance effect, a much lower voltage can be used to produce a high vibration amplitude.
Stick-slip motor works using the inertia of a mass and the friction of a clamp. Such motors can be very small. Some are used for camera sensor displacement, allowing anti shake function.
Reduction of vibrations and noise
Different teams of researchers have been investigating ways to reduce vibrations in materials by attaching piezo elements to the material. When the material is bent by a vibration in one direction, the vibration-reduction system responds to the bend and sends electric power to the piezo element to bend in the other direction. Future applications of this technology are expected in cars and houses to reduce noise.
In a demonstration at the Material Vision Fair in Frankfurt in November 2005, a team from TU Darmstadt in Germany showed several panels that were hit with a rubber mallet, and the panel with the piezo element immediately stopped swinging.
Piezoelectric ceramic fiber technology is being used as an electronic damping system on some HEAD tennis rackets.[19]
Infertility treatment
In people with previous total fertilization failure, piezoelectric activation of oocytes together with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) seems to improve fertilization outcome.[20]
See also
- Charge amplifier
- Electronic component
- Electret
- Electrostriction
- Energy harvesting, methods of converting other forms of energy to electricity.
- Ferroelectricity
- Flexoelectricity
- Magnetostriction
- Piezomagnetism
- Piezosurgical
- Piezoresistive effect
- Sonomicrometry
- Surface acoustic wave
- Triboluminescence
References
- ↑ Holler, F. James; Skoog, Douglas A; Crouch, Stanley R (2007). "Chapter 1". Principles of Instrumental Analysis (6th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 9. ISBN 9780495012016.
- ↑ Gautschi, G (2002). Piezoelectric Sensorics: Force, Strain, Pressure, Acceleration and Acoustic Emission Sensors, Materials and Amplifiers.. Springer.
- ↑ Lippman, G. (1881). "Principe de la conservation de l'électricité" (in French). Annales de chimie et de physique 24: 145. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k348640.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 M. Birkholz (1995). "Crystal-field induced dipoles in heteropolar crystals – II. physical significance". Z. Phys. B 96: 333–340. doi:10.1007/BF01313055.
- ↑ Sensor Sense: Piezoelectric Force Sensors
- ↑ Damjanovic, Dragan (1998). "Ferroelectric, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of ferroelectric thin films and ceramics". Reports on Progress in Physics 61: 1267–1324. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/61/9/002.
- ↑ Kochervinskii, V (July 2003). "Piezoelectricity in Crystallizing Ferroelectric Polymers". Crystallography Reports 48 (4): 649–675. doi:10.1134/1.1595194.
- ↑ M. Minary-Jolandan, and Min-Feng Yu, Nanotechnology 20 (2009) 085706 (6pp)
- ↑ Lakes, Roderic. "Electrical Properties of Bone: A Review". University of Wisconsin–Madison. http://silver.neep.wisc.edu/~lakes/BoneElectr.html.
- ↑ Becker, Robert O; Marino, Andrew A (1982). "Chapter 4: Electrical Properties of Biological Tissue (Piezoelectricity)". Electromagnetism & Life. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-87395-560-9. http://www.ortho.lsuhsc.edu/Faculty/Marino/EL/EL4/Piezo.html.
- ↑ Pollack, S.R; Korostoff, E., Starkebaum, W. y Lannicone, W (1979). ed. Brighton, C.T., Black, J. and Pollack, S.R.. ed. "Micro-electrical studies of stress-generated potentials in bone.". Electrical Properties of Bone and Cartilage (New York City: Grune & Stratton, Inc).
- ↑ Fotiadis, D.I; Foutsitzi, G., and Massalas, C.V (1999). "Wave propagation modeling in human long bones". Acta Mechanica 137: 65–81. doi:10.1007/BF01313145. http://www.springerlink.com/content/tr43l7562581u4q8.
- ↑ Saito, Yasuyoshi; Takao, Hisaaki; Tanil, Toshihiko; Nonoyama, Tatsuhiko; Takatoril Kazumasa; Homma, Takahiko; Nagaya, Toshiatsu; Nakamura, Masaya (2004-11-04). "Lead-free piezoceramics". Nature (Nature Publishing Group) 432 (7013): 81–87. doi:10.1038/nature03028. PMID 15516921. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v432/n7013/abs/nature03028.html.
- ↑ Richard, Michael Graham (2006-08-04). "Japan: Producing Electricity from Train Station Ticket Gates". TreeHugger. Discovery Communications, LLC. http://www.treehugger.com/files/2006/08/japan_ticket_gates.php.
- ↑ Wright, Sarah H (2007-07-25). "MIT duo sees people-powered "Crowd Farm"". MIT news. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/2007/crowdfarm-0725.html.
- ↑ Phillips, James R (2000-08-10). "Piezoelectric Technology: A Primer". eeProductCenter. TechInsights. http://www.techonline.com/community/ed_resource/feature_article/8277.
- ↑ How Rocket-Propelled Grenades Work by Shane Speck
- ↑ The scanning mechanism for ROSETTA/MIDAS from an engineering model to the flight model
- ↑ "Isn’t it amazing how one smart idea, one chip and an intelligent material has changed the world of tennis?". HEAD. http://www.head.com/tennis/technology.php?region=eu&tag=intelligence. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
- ↑ Baltaci V, Ayvaz OU, Unsal E, et al. (May 2009). "The effectiveness of intracytoplasmic sperm injection combined with piezoelectric stimulation in infertile couples with total fertilization failure". Fertil. Steril.. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.107. PMID 19464000.
International standards
- ANSI-IEEE 176 (1987) Standard on Piezoelectricity
- IEEE 177 (1976) Standard Definitions & Methods of Measurement for Piezoelectric Vibrators
- IEC 444 (1973) Basic method for the measurement of resonance freq & equiv series resistance of quartz crystal units by zero-phase technique in a pi-network
- IEC 302 (1969) Standard Definitions & Methods of Measurement for Piezoelectric Vibrators Operating over the Freq Range up to 30 MHz
External links
- Gautschi, Gustav H., 2002, Piezoelectric Sensorics, Springer, ISBN 3-540-42259-5,
- Fundamentals of Piezoelectrics
- Piezo motor based microdrive for neural signal recording
- History of Piezoelectricity
- Research on new Piezoelectric materials
- Piezo Equations
- Piezo in Medical Design
- Video demonstration of Piezoelectricity
- DoITPoMS Teaching and Learning Package – Piezoelectric Materials
- Piezo Motor Types