Human pharynx
| Human pharynx |
 |
| Head and neck. |
 |
| Pharynx |
| Gray's |
subject #244 1141 |
| Artery |
pharyngeal branches of ascending pharyngeal artery, ascending palatine, descending palatine, pharyngeal branches of inferior thyroid |
| Vein |
pharyngeal veins |
| Nerve |
pharyngeal plexus |
| MeSH |
Pharynx |
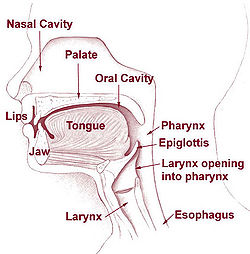
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the neck and throat situated immediately posterior to (behind) the mouth and nasal cavity, and cranial, or superior, to the esophagus, larynx, and trachea.
Functions
The pharynx is part of the digestive system and respiratory system of many organisms.
Because both food and air pass through the pharynx, a flap of connective tissue called the epiglottis closes over the trachea when food is swallowed to prevent choking or aspiration. In humans the pharynx is important in vocalization.
Parts
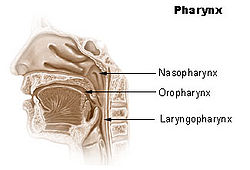
The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections:
Nasopharynx
The nasopharynx region extends between the internal nares and the soft palate and lies superior to the oral cavity. Some lymphoid tissue—the pharyngeal tonsils or the adenoids—are located in the posterior wall. The Eustachian tubes, or auditory tubes, which connect the middle ear to the pharynx, open into the nasopharynx. The opening opens and closes, equalizing the air pressure in the middle ear to that of the atmosphere. This is needed for proper conduction of sound.
Oropharynx
The oropharynx lies behind the oral cavity. The anterior wall consists of the base of the tongue and the epiglottic vallecula; the lateral wall is made up of the tonsil, tonsillar fossa, and tonsillar (faucial) pillars; the superior wall consists of the inferior surface of the soft palate and the uvula.
Laryngopharynx
The laryngopharynx, also known as the hypopharynx, roughly corresponds to the levels between C4 to C6, it includes the pharyngo-esophageal junction (postcricoid area), the piriform sinus, and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Like the oropharynx above it, the hypopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium.
It lies inferior to the upright epiglottis and extends to the larynx, where the respiratory and digestive pathways diverge.
At that point, the laryngopharynx is continuous with the esophagus posteriorly. The esophagus conducts food and fluids to the stomach; air enters the larynx anteriorly. During swallowing, food has the "right of way", and air passage temporarily stops.
Gallery
|
|
Organs of the digestive system.
|
The entrance to the larynx, viewed from behind.
|
Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx.
|
The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind.
|
References
- Stedman's/LWW 1551471
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn, Seventh Edition.
- TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours Sobin LH & Wittekind Ch (eds)Sixth edition UICC 2002 ISBN 0-471-22288-7
See also
External links
|
Human systems and organs |
|
TA 2-4:
MS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fibrous joint · Cartilaginous joint · Synovial joint
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA 5-11:
splanchnic/
viscus |
|
mostly
Thoracic
|
|
|
|
mostly
Abdominopelvic
|
|
|
Mouth ( Salivary gland, Tongue) · upper GI ( Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Esophagus, Stomach) · lower GI ( Small intestine, Appendix, Colon, Rectum, Anus) · accessory ( Liver, Biliary tract, Pancreas)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TA 12-16 |
|
|
Blood
(Non-TA) |
|
|
| general anatomy: systems and organs, regional anatomy, , , superficial anatomy of limbs |
|
|
Head and neck, upper RT: Nose (TA A06.1, GA 10.992) |
|
| External nose |
Ala of nose
nasal cartilages (of the septum, Greater alar, Lesser alar, Lateral nasal, Accessory nasal, Vomeronasal)
|
|
| Nasal cavity |
|
Openings
|
Nasal vestibule · Nostril · Posterior nasal apertures
|
|
|
Lateral wall
|
Nasal concha/meati: Superior nasal concha · Middle nasal concha · Inferior nasal concha · Superior nasal meatus · Middle nasal meatus · Inferior nasal meatus
Sphenoethmoidal recess · Ethmoid bulla · Agger nasi · Ethmoidal infundibulum · Semilunar hiatus · Maxillary hiatus
|
|
|
Medial wall
|
Nasal septum · Vomeronasal organ
|
|
|
Mucous membrane
|
Olfactory mucosa
|
|
|
| Paranasal sinuses |
Maxillary sinus · Sphenoidal sinuses · Frontal sinus · Ethmoid sinus
|
|
| Naso-pharynx |
Pharyngeal opening of auditory tube (Salpingopharyngeal fold, Salpingopalatine fold, Torus tubarius) · Pharyngeal tonsil · Pharyngeal recess
|
|
|
|
anat(n, x, l, c)/phys/devp
|
noco(c)/cong/tumr, sysi/, injr
|
|
|
|
|
|
Head and neck anatomy, digestive system: Mouth anatomy (TA A05.1-2, GA 11.1110-2, 1125-1141) |
|
| Mouth |
|
|
|
Vestibule
|
Lip (Upper, Lower, Vermilion border, Frenulum of lower lip, Philtrum)
Cheek (Buccal fat pad)
|
|
|
OC proper
|
|
Palate/
roof of mouth
|
Hard palate · Soft palate · Palatine raphe · Incisive papilla
|
|
|
Gingiva
|
Interdental papilla · Gingival sulcus · Gingival margin
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parotid gland/Parotid duct · Submandibular gland/Submandibular duct · Sublingual gland/Major sublingual duct
|
|
|
Teeth
|
see tooth anatomy
|
|
|
|
dorsum (Taste bud, Median sulcus, Terminal sulcus, Foramen cecum, Lingual tonsils) · underside (Frenulum, Fimbriated fold, Sublingual caruncle) · Anterior · Posterior · Glossoepiglottic folds · Lingual septum
|
|
|
Oro-pharynx/
fauces |
Oropharyngeal isthmus/Isthmus of the fauces
Soft palate (Uvula, Palatoglossal arch, Palatopharyngeal arch, Plica semilunaris of the fauces)
Tonsillar fossa
Palatine tonsil
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anatomy of torso, digestive system: Gastrointestinal tract, excluding mouth (TA A05.3-7, GA 11.1141) |
|
| Upper GI |
|
|
Piriform sinus
spaces: Peripharyngeal space (Retropharyngeal space, Parapharyngeal space) · Retrovisceral space (Retropharyngeal space, Danger space) · Prevertebral space
Pterygomandibular raphe · Pharyngeal raphe · Buccopharyngeal fascia · Pharyngobasilar fascia
Pharyngeal muscles
|
|
|
|
UES · LES · Esophageal glands
Serosa / Adventitia · Muscular layer · Submucosa · Mucosa (Muscularis mucosa)
|
|
|
|
by region: Greater curvature · Lesser curvature (Angular incisure) · Cardia · Body · Fundus · Pylorus (Pyloric antrum, Pyloric canal)
by layer: Serosa · Muscular layer (Pyloric sphincter) · Submucosa · Gastric mucosa (Muscularis mucosa, Gastric rugae, Gastric pits, Gastric gland/Cardiac glands/Fundic glands/Pyloric glands)
|
|
|
| Lower GI |
|
|
|
Layers
|
Serosa · Subserosa · Muscular layer · Circular folds · Submucosa · Mucosa (Muscularis mucosa, Peyer's patches, Intestinal villus, Intestinal gland) |
|
|
|
Suspensory muscle, Major duodenal papilla, Minor duodenal papilla, Duodenal cap • Duodenojejunal flexure • Brunner's glands
|
|
|
|
no substructures
|
|
|
Ileum
|
Terminal ileum • Ileocecal valve
|
|
|
|
|
|
Layers
|
Serosa · Subserosa · Muscular layer · Submucosa · Mucosa |
|
|
Cecum
|
|
|
|
|
ascending colon, hepatic flexure, transverse colon, splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon
continuous (taenia coli, haustra, epiploic appendix)
|
|
|
|
Transverse folds of rectum • Rectal ampulla
|
|
|
Anal canal
|
Anal columns • Anal valves • Anal sinuses • Pectinate line
Sphincter ani internus muscle • Intersphincteric groove • Sphincter ani externus muscle
Anus
|
|
|
|
|
|
anat(t, g, p)/phys/devp/cell/
|
|
proc, drug(A2A/2B/3/4//6/7/14/16), blte
|
|
|
|






