Mucous membrane
| Mucous membran | |
|---|---|
 |
|
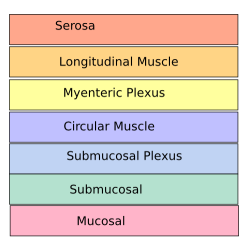
| Layers: serosa longitudinal muscle myenteric plexus circular muscle submucosal plexus submucosal mucosal |
|
 |
|
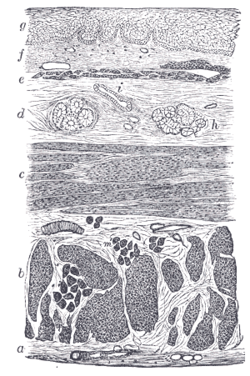
| Section of the human esophagus. Moderately magnified. The section is transverse and from near the middle of the gullet. a. Fibrous covering. b. Divided fibers of longitudinal muscular coat. c. Transverse muscular fibers. d. Submucous or areolar layer. e. Muscularis mucosae. f. Mucous membrane, with vessels and part of a lymphoid nodule. g. Stratified epithelial lining. h. Mucous gland. i. Gland duct. m’. Striated muscular fibers cut across. |
|
| Latin | tunica mucosa |
| Gray's | subject #242 1110 |
| Dorlands/Elsevier | Mucous membrane |
The mucous membranes (or mucosae; singular mucosa) are linings of mostly endodermal origin, covered in epithelium, which are involved in absorption and secretion. They line cavities that are exposed to the external environment and internal organs. They are at several places continuous with skin: at the nostrils, the mouth, the lips, the eyelids, the ears, the genital area, and the anus. The sticky, thick fluid secreted by the mucous membranes and glands is termed mucus. The term mucous membrane refers to where they are found in the body and not every mucous membrane secretes mucus.
Body cavities featuring mucous membrane include most of the respiratory system. The glans penis (head of the penis) and glans clitoridis, along with the inside of the prepuce (foreskin) and the clitoral hood, are mucous membranes. The urethra is also a mucous membrane. The secreted mucus traps the pathogens in the body, preventing any further activities of diseases.
Contents |
Components
- Epithelium
- Lamina propria
- Smooth muscle/Muscularis mucosa/ (GI tract)
Some examples of mucosa
- Buccal mucosa
- Esophageal mucosa
- Gastric mucosa
- Intestinal mucosa
- Nasal mucosa
- Olfactory mucosa
- Oral mucosa
- Bronchial mucosa
- Uterine mucosa
- Endometrium is the mucosa of the uterus
- Penile mucosa
Additional images
 Wall of the ureter. |
 Section of mucous membrane of human stomach, near the cardiac orifice. |
 General structure of the gut wall showing the Mucosa. |
See also
- Mucin
- Mucocutaneous boundary
- Mucociliary clearance
- Mucosal immune system
External links
- mucosa at eMedicine Dictionary
- Organology at UC Davis Digestive/mammal/system1/system4 - "Mammal, whole system (LM, Low)"
- MeSH Mucous+Membrane
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |