Mixtec

The Mixtec (or Mixteca) are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples inhabiting the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla in a region known as La Mixteca. The Mixtecan languages form an important branch of the Otomanguean linguistic family.
The term Mixtec (Mixteco in Spanish) comes from the Nahuatl word Mixtecapan, or "place of the cloud-people." The area in which Mixtec is spoken is known as the Mixteca. The Mixtecs call themselves ñuu savi, ñuu djau, ñuu davi, naa savi, etc., depending on the local variant of their language, the sa'an davi, da'an davi or tu'un savi; in his history of the Mixtec, Kevin Terraciano uses the term Ñudzahui, which he translates "people of the rain place."
Contents |
Overview
In pre-Columbian times, the Mixtec were one of the major civilizations of Mesoamerica. Important ancient centres of the Mixtec include the ancient capital of Tilantongo, as well as the sites of Achiutla, Cuilapan, Huajuapan, Mitla, Tlaxiaco, Tututepec, Juxtlahuaca, and Yucuñudahui. The Mixtec also made major constructions at the ancient city of Monte Albán (which had originated as a Zapotec city before the Mixtec gained control of it). The work of Mixtec artisans who produced work in stone, wood, and metal were well regarded throughout ancient Mesoamerica.
At the height of the Aztec Empire, many Mixtecs paid tribute to the Aztecs, but not all Mixtec towns became vassals. They put up resistance to Spanish rule until they were subdued by the Spanish and their central Mexican allies led by Pedro de Alvarado.
Today, Mixtecs have migrated to various parts of both Mexico and the United States. In recent years a large exodus of indigenous peoples from Oaxaca, such as the Zapotec and Triqui, have emerged as one of the most numerous groups of Amerindians in the United States. Large Mixtec communities exist in the border cities of Tijuana, Baja California, San Diego, California and Tucson, Arizona. Mixtec communities are generally described as trans-national or trans-border because of their ability to maintain and reaffirm social ties between their native homelands and diasporic community. (See: Mixtec transnational migration.)
Geography
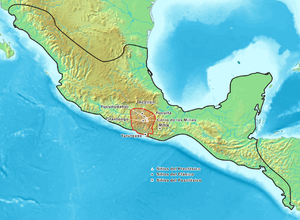
The Mixtec area, both historically and currently, corresponds roughly to the western half of the state of Oaxaca, with some Mixtec communities extending into the neighboring state of Puebla to the north-west and also the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec people and their homelands are often subdivided into three geographic and cultural areas: The Mixteca Alta or Highland Mixtec living in the mountains in, around, and to the west of the Valley of Oaxaca; the Mixteca Baja or Lowland Mixtec living to the north and west of these highlands, and the Mixteca de la Costa or Coastal Mixtec living in the southern plains and the coast of the Pacific Ocean. For most of Mixtec history the Mixteca Alta was the dominant political force, with the capitals of the Mixtec nation located in the central highlands. The valley of Oaxaca itself was often a disputed border region, sometimes dominated by the Mixtec and sometimes by their neighbors to the east, the Zapotec.
An ancient Coixtlahuaca Basin cave site known as the Colossal Natural Bridge is an important sacred place for the Mixtec.
Language, codices, and artwork
The Mixtecan languages (in their many variants) were estimated to be spoken by about 300,000 people at the end of the 20th century, although the majority of Mixtec speakers also had at least a working knowledge of the Spanish language. Some Mixtecan languages are called by names other than Mixtec, particularly Cuicatec (Cuicateco), and Triqui (or Trique).

The Mixtec are well-known in the anthropological world for their Codices, or phonetic pictures in which they wrote their history and genealogies in deerskin in the "fold-book" form. The best known story of the Mixtec Codices is that of Lord Eight Deer, named after the day in which he was born, whose personal name is Jaguar Claw, and whose epic history is related in several codices, including the Codex Bodley and Codex Zouche-Nuttall. He successfully conquered and united most of the Mixteca region.

They were also known for their exceptional mastery of jewelry, in which gold and turquoise figure prominently. The production of Mixtec goldsmiths formed an important part of the tribute the Mixtecs had to pay to the Aztecs during parts of their history.
Further reading
- The Mixtecs of Colonial Oaxaca: Ñudzahui History, Sixteenth Through Eighteenth Centuries, Kevin Terraciano, Stanford University Press, 2001
- The Mixtec Kings and Their People, Ronald Spores, University of Oklahoma Press, 1967
- The Cloud People: Divergent Evolution of the Mixtec and Zapotec Civilizations, Flannery, K. and Marcus, J. (eds.), Percheron Press, 2003.
- Stories in Red and Black: Pictorial Histories of the Aztec and Mixtec, Boone, E. H., University of Texas Press, 2000.
- Presencias de la Cultura Mixteca (Memorias de la Primera Semana de la Cultura Mixteca), Ignacio Ortiz Castro (ed.), Universidad Tecnológica de la Mixteca, 2002.
- La Tierra del Sol y de la Lluvia (Memorias de la Segunda Semana de la Cultura Mixteca), Ignacio Ortiz Castro (ed.), Universidad Tecnológica de la Mixteca, 2003.
- Personajes e Instituciones del Pueblo Mixteco (Memorias de la Tercera Semana de la Cultura Mixteca), Ignacio Ortiz Castro (ed.), Universidad Tecnológica de la Mixteca, 2004.
- Pasado y Presente de la Cultura Mixteca (Memorias de la Cuarta Semana de la Cultura Mixteca), Ignacio Ortiz Castro (ed.), Universidad Tecnológica de la Mixteca, 2005.
- Nuu Savi (Nuu Savi - Pueblo de Lluvia), Miguel Ángel Chávez Guzman (compilador), Juxtlahuaca.org, 2005.
- Joyce, Arthur A. (2010). Mixtecs, Zapotecs and Chatinos: Ancient peoples of Southern Mexico. Wiley Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-6312-0977-5.
See also
- Indigenous people of Oaxaca
External links
- A Mixtec Bibliography
- The Mixtec World
- Mundo Mixteca-from Universidad Tecnológica de la Mixteca (in Spanish)
- Mixtecan Language (including a number of modern variants, in English and Spanish)
- Reading Ancient Scripts- (with links to Learning How to Read Mixtec Codices)
- Other artifacts from Tomb 7 in Monte Alban
| Americas | Paleo-Indians · Genetic history · Archaeology of the Americas · Indigenous peoples of the Americas | |||
| North America | North American pre-Columbian cultures · Chichimeca · Hopewell tradition · Mississippian culture · | |||
| Mesoamerica | Mesoamerican pre-Columbian chronology – Capacha – Cholula – Coclé – Epi-Olmec – Huastec – Izapa – Mixtec – Olmec – Pipil – Quelepa – Shaft tomb tradition – Teuchitlan – Tarascan – Teotihuacan – Tlatilco – Toltec – Totonac – Veracruz – Xochipala – Zapotec | |||
| South America | South American Indigenous people – pre-Columbian chronology – Cañaris – Chachapoya – Chancay – Chavín – Chimu – El Abra – Hydraulic culture of mounds (Bolivia) – Las Vegas – Lima – La Tolita (Tumaco) – Manteño-Guancavilca – Mapuche – Moche – Mollo – Muisca (Chibchas) – Nariño – Nazca – Norte Chico – Quimbaya – San Agustin – Shuar – Sican – Taino – Tairona – Tiwanaku – Tierradentro – Valdivia – Wari | |||
| The Aztec Empire | The Maya civilization | The Inca Empire (Inca civilization) |
||
| Language | Nahuatl language | Mayan languages | Quechua | |
| Writing | Aztec writing | Mayan writing | Quipu | |
| Religion | Aztec religion | Maya religion | Inca religion | |
| Mythology | Aztec mythology | Maya mythology | Inca mythology | |
| Calendar | Aztec calendar | Maya calendar | ||
| Society | Aztec society | Maya society | Inca society | |
| Infrastructure | Chinampas | Maya architecture | Inca architecture (road system) Incan agriculture |
|
| History | Aztec history | Inca history | ||
| People | Moctezuma I Moctezuma II Cuitlahuac Cuauhtémoc |
K'inich Janaab' Pakal Uaxaclajuun Ub'aah K'awiil Jasaw Chan K'awiil I |
Manco Capac Pachacutec Atahualpa Manco Inca |
|
| Conquest | Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (Hernán Cortés) |
Spanish conquest of Yucatán (Francisco de Montejo) Spanish conquest of Guatemala (Pedro de Alvarado) |
Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire (Francisco Pizarro) |
|
| See also | ||||
| Portal:Indigenous peoples of North America – Columbian exchange – Mesoamerican writing systems – Native American cuisine – Native American pottery – Population history of American indigenous peoples – Pre-Columbian art – Painting in the Americas before Colonization | ||||