Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences.
In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA metabolism. Methylation of heavy metals can also occur outside of biological systems. Chemical methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts.
Contents |
Biological methylation
Epigenetics
Methylation contributing to epigenetic inheritance can occur through either DNA methylation or protein methylation.
DNA methylation in vertebrates typically occurs at CpG sites (cytosine-phosphate-guanine sites, that is, where a cytosine is directly followed by a guanine in the DNA sequence). This methylation results in the conversion of the cytosine to 5-methylcytosine. The formation of Me-CpG is catalyzed by the enzyme DNA methyltransferase. The bulk of mammalian DNA has about 40% of CpG sites methylated, but there are certain areas, known as CpG islands, that are GC-rich (made up of about 65% CG residues), wherein none are methylated. These are associated with the promoters of 56% of mammalian genes, including all ubiquitously expressed genes. One to two percent of the human genome are CpG clusters, and there is an inverse relationship between CpG methylation and transcriptional activity.
Protein methylation typically takes place on arginine or lysine amino acid residues in the protein sequence.[1] Arginine can be methylated once (monomethylated arginine) or twice, with either both methyl groups on one terminal nitrogen (asymmetric dimethylated arginine) or one on both nitrogens (symmetric dimethylated arginine) by peptidylarginine methyltransferases (PRMTs). Lysine can be methylated once, twice or three times by lysine methyltransferases. Protein methylation has been most-studied in the histones. The transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine to histones is catalyzed by enzymes known as histone methyltransferases. Histones that are methylated on certain residues can act epigenetically to repress or activate gene expression.[2][3] Protein methylation is one type of post-translational modification.
Embryonic development
In early mammalian development, the genome within the germ cells is demethylated, while chromosomes in the remaining cells retain the parental methylation patterns. De novo methylation of the germ cells occurs, modifying and adding epigenetic information to the genome based on the sex of the individual [4]. By blastula stage, the methylation is complete. This process is referred to as "reprogramming"[5]. The importance of methylation was shown in knockout mutants without DNA methyltransferase, which all died at the morula stage.
Postnatal development
Increasing evidence is revealing a role of methylation in the interaction of environmental factors with genetic expression. Differences in maternal care during the first 6 days of life in the rat induce differential methylation patterns in some promoter regions and, thus, influencing gene expression.[6] Furthermore, even-more-dynamic processes such as interleukin signaling have been shown to be regulated by methylation.[7]
Cancer
The pattern of methylation has recently become an important topic for research. Studies have found that in normal tissue, methylation of a gene is mainly localised to the coding region, which is CpG-poor. In contrast, the promoter region of the gene is unmethylated, despite a high density of CpG islands in the region.
Neoplasia is characterized by "methylation imbalance" where genome-wide hypomethylation is accompanied by localized hypermethylation and an increase in expression of DNA methyltransferase.[8] The overall methylation state in a cell might also be a precipitating factor in carcinogenesis as evidence suggests that genome-wide hypomethylation can lead to chromosome instability and increased mutation rates.[9] The methylation state of some genes can be used as a biomarker for tumorigenesis. For instance, hypermethylation of the pi-class glutathione S-transferase gene (GSTP1) appears to be a promising diagnostic indicator of prostate cancer.[10]
In cancer, the dynamics of genetic and epigenetic gene silencing are very different. Somatic genetic mutation leads to a block in the production of functional protein from the mutant allele. If a selective advantage is conferred to the cell, the cells expand clonally to give rise to a tumor in which all cells lack the capacity to produce protein. In contrast, epigenetically mediated gene silencing occurs gradually. It begins with a subtle decrease in transcription, fostering a decrease in protection of the CpG island from the spread of flanking heterochromatin and methylation into the island. This loss results in gradual increases of individual CpG sites, which vary between copies of the same gene in different cells.[11]
Bacterial host defense
In addition, adenosine or cytosine methylation is part of the restriction modification system of many bacteria. Bacterial DNAs are methylated periodically throughout the genome. A methylase is the enzyme that recognizes a specific sequence and methylates one of the bases in or near that sequence. Foreign DNAs (which are not methylated in this manner) that are introduced into the cell are degraded by sequence-specific restriction enzymes. Bacterial genomic DNA is not recognized by these restriction enzymes. The methylation of native DNA acts as a sort of primitive immune system, allowing the bacteria to protect themselves from infection by bacteriophage. These restriction enzymes are the basis of restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) testing, used to detect DNA polymorphisms.
Methylation in chemistry
The term methylation in organic chemistry refers to the alkylation process used to describe the delivery of a CH3 group.[12] This is commonly performed using electrophilic methyl sources - iodomethane, dimethyl sulfate, dimethyl carbonate, or less commonly with the more powerful (and more dangerous) methylating reagents of methyl triflate or methyl fluorosulfonate (magic methyl), which all react via SN2 nucleophilic substitution. For example a carboxylate may be methylated on oxygen to give a methyl ester, an alkoxide salt RO− may be likewise methylated to give an ether, ROCH3, or a ketone enolate may be methylated on carbon to produce a new ketone.
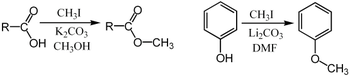
On the other hand, the methylation may involve use of nucleophilic methyl compounds such as methyllithium (CH3Li) or Grignard reagents (CH3MgX). For example, CH3Li will methylate acetone, adding across the carbonyl (C=O) to give the lithium alkoxide of tert-butanol:

Purdie methylation
Purdie methylation is a specific method for the methylation at oxygen of carbohydrates using iodomethane and silver oxide [13]
See also
- Bisulfite sequencing - the biochemical method used to determine the presence or absence of methyl groups on a DNA sequence
References
- ↑ Christopher Walsh (2006). "Chapter 5 - Protein Methylation". Posttranslational modification of proteins: expanding nature's inventory. Roberts and Co. Publishers. ISBN 0-9747077-3-2.. http://www.roberts-publishers.com/walsh/chapter5.pdf.
- ↑ Grewal SI, Rice JC (2004). "Regulation of heterochromatin by histone methylation and small RNAs". Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16 (3): 230–8. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2004.04.002. PMID 15145346. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0955067404000535.
- ↑ Nakayama J, Rice JC, Strahl BD, Allis CD, Grewal SI (2001). "Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly". Science 292 (5514): 110–3. doi:10.1126/science.1060118. PMID 11283354. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11283354.
- ↑ Carroll, Sean B.; Wessler, Susan R.; Griffiths, Anthony J. F.; Lewontin, Richard C. (2008). Introduction to genetic analysis (9th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and CO. p. 403. ISBN 0-7167-6887-9.
- ↑ Mann MR, Bartolomei MS (2002). "Epigenetic reprogramming in the mammalian embryo: struggle of the clones". Genome Biol. 3 (2): 1003.1–.4. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-2-reviews1003. PMID 11864375. PMC 139014. http://genomebiology.com/1465-6906/3/REVIEWS1003.
- ↑ Weaver IC (2007). "Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior and pharmacological intervention. Nature versus nurture: let's call the whole thing off". Epigenetics 2 (1): 22–8. doi:10.4161/epi.2.1.3881. PMID 17965624. http://www.landesbioscience.com/journals/epi/abstract.php?id=3881.
- ↑ Bird A (2003). "Il2 transcription unleashed by active DNA demethylation". Nat. Immunol. 4 (3): 208–9. doi:10.1038/ni0303-208. PMID 12605226.
- ↑ Baylin SB, Herman JG, Graff JR, Vertino PM, Issa JP (1998). "Alterations in DNA methylation: a fundamental aspect of neoplasia". Adv. Cancer Res. 72: 141–96. doi:10.1016/S0065-230X(08)60702-2. PMID 9338076.
- ↑ Chen RZ, Pettersson U, Beard C, Jackson-Grusby L, Jaenisch R (1998). "DNA hypomethylation leads to elevated mutation rates". Nature 395 (6697): 89–93. doi:10.1038/25779. PMID 9738504.
- ↑ Nakayama M, Gonzalgo ML, Yegnasubramanian S, Lin X, De Marzo AM, Nelson WG (2004). "GSTP1 CpG island hypermethylation as a molecular biomarker for prostate cancer". J. Cell. Biochem. 91 (3): 540–52. doi:10.1002/jcb.10740. PMID 14755684.
- ↑ Jones PA, Baylin SB (2002). "The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer". Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 (6): 415–28. doi:10.1038/nrg816. PMID 12042769.
- ↑ March, Jerry; Smith, Michael W. (2001). March's advanced organic chemistry: reactions, mechanisms, and structure. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-58589-0.
- ↑ Purdie T, Irvine JC (1903). "The alkylation of sugars". J. Chem. Soc. 83: 1021–37. doi:10.1039/CT9038301021.
External links
- http://www.methdb.de/ DNA Methylation Database
- deltaMasses Detection of Methylations after Mass Spectrometry
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||