Maurya Empire
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive and powerful empire in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC. Originating from the kingdom of Magadha in the Indo-Gangetic plains (modern Bihar, eastern Uttar Pradesh and Bengal) in the eastern side of the Indian subcontinent, the empire had its capital city at Pataliputra (modern Patna).[1][2] The Empire was founded in 322 BC by Chandragupta Maurya, who had overthrown the Nanda Dynasty and rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India taking advantage of the disruptions of local powers in the wake of the withdrawal westward by Alexander the Great's Greek and Persian armies. By 320 BC the empire had fully occupied Northwestern India, defeating and conquering the satraps left by Alexander.
It was one of the world's largest empires in its time. At its greatest extent, the empire stretched to the north along the natural boundaries of the Himalayas, and to the east stretching into what is now Assam. To the west, it probably reached beyond modern Pakistan, annexing Balochistan and much of what is now Afghanistan, including the modern Herat and Kandahar provinces. The Empire was expanded into India's central and southern regions by the emperors Chandragupta and Bindusara, but it excluded a small portion of unexplored tribal and forested regions near Kalinga (modern Orissa). Its decline began 60 years after Ashoka's rule ended, and it dissolved in 185 BC with the foundation of the Sunga Dynasty in Magadha.
Under Chandragupta, the Mauryan Empire conquered the trans-Indus region, which was under Macedonian rule. Chandragupta then defeated the invasion led by Seleucus I, a Greek general from Alexander's army. Under Chandragupta and his successors, both internal and external trade, and agriculture and economic activities, all thrived and expanded across India thanks to the creation of a single and efficient system of finance, administration and security. After the Kalinga War, the Empire experienced half a century of peace and security under Ashoka. Mauryan India also enjoyed an era of social harmony, religious transformation, and expansion of the sciences and of knowledge. Chandragupta Maurya's embrace of Jainism increased social and religious renewal and reform across his society, while Ashoka's embrace of Buddhism has been said to have been the foundation of the reign of social and political peace and non-violence across all of India. Ashoka sponsored the spreading of Buddhist ideals into Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, West Asia and Mediterranean Europe.
Chandragupta's minister Chanakya wrote the Arthashastra, one of the greatest treatises on economics, politics, foreign affairs, administration, military arts, war, and religion ever produced in India. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka are the primary sources of written records of the Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Asoka at Sarnath, is the national emblem of India.
Chanakya and Chandragupta Maurya
A brahmin named Chanakya (real name Vishnugupta, also known as Kautilya) traveled to Magadha, a kingdom that was large and militarily powerful and feared by its neighbors, but was dismissed by its king Dhana, of the Nanda Dynasty. Meanwhile, the conquering armies of Alexander the Great decided against going further eastward, deterred by the prospect of battling Magadha: he returned to Babylon and re-deployed most of his troops west of the Indus river. Soon after Alexander died in Babylonin 323 BCE, his empire fragmented, and local kings declared their independence, leaving several smaller disunited satraps. Chandragupta Maurya deposed Dhana. The Greek generals Eudemus, and Peithon, ruled until around 316 BCE, when Chandragupta Maurya (with the help of Chanakya, who was now his advisor) utterly defeated the Macedonians and consolidated the region under the control of his new seat of power in Magadha.
Chandragupta Maurya's rise to power is shrouded in mystery and controversy. On the one hand, a number of ancient Indian accounts, such as the drama Mudrarakshasa (Poem of Rakshasa - Rakshasa was the prime minister of Magadha) by Visakhadatta, describe his royal ancestry and even link him with the Nanda family. A kshatriya tribe known as the Maurya's are referred to in the earliest Buddhist texts, Mahaparinibbana Sutta. However, any conclusions are hard to make without further historical evidence. Chandragupta first emerges in Greek accounts as "Sandrokottos". As a young man he is said to have met Alexander.[3] He is also said to have met the Nanda king, angered him, and made a narrow escape.[4] Chanakya's original intentions were to train a guerilla army under Chandragupta's command. The Mudrarakshasa of Visakhadutta as well as the Jaina work Parisishtaparvan talk of Chandragupta's alliance with the Himalayan king Parvatka, sometimes identified with Porus (Sir John Marshall "Taxila", p18, and al.)[5][6][7].
Conquest of Magadha
Chanakya encouraged Chandragupta Maurya and his army to take over the throne of Magadha. Using his intelligence network, Chandragupta gathered many young men from across Magadha and other provinces, men upset over the corrupt and oppressive rule of king Dhana, plus resources necessary for his army to fight a long series of battles. These men included the former general of Taxila, other accomplished students of Chanakya, the representative of King Porus of Kakayee, his son Malayketu, and the rulers of small states.
Preparing to invade Pataliputra, Maurya hatched a plan. A battle was announced and the Magadhan army was drawn from the city to a distant battlefield to engage Maurya's forces. Maurya's general and spies meanwhile bribed the corrupt general of Nanda. He also managed to create an atmosphere of civil war in the kingdom, which culminated in the death of the heir to the throne. Chanakya managed to win over popular sentiment. Ultimately Nanda resigned, handing power to Chandragupta, and went into exile and was never heard of again. Chanakya contacted the prime minister, Rakshasas, and made him understand that his loyalty was to Magadha, not to the Magadha dynasty, insisting that he continue in office. Chanakya also reiterated that choosing to resist would start a war that would severely affect Magadha and destroy the city. Rakshasa accepted Chanakya's reasoning, and Chandragupta Maurya was legitimately installed as the new King of Magadha. Rakshasa became Chandragupta's chief advisor, and Chanakya assumed the position of an elder statesman.
|
The approximate extent of the Magadha state in the 5th century BCE. |
 The Nanda Empire at its greatest extent under Dhana Nanda circa 323 BCE. |
 The Maurya Empire when it was first founded by Chandragupta Maurya circa 320 BCE, after conquering the Nanda Empire when he was only about 20 years old. |
|
 Chandragupta extended the borders of the empire southward into the Deccan Plateau circa 300 BC.[9] |
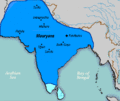 Ashoka the Great extended into Kalinga during the Kalinga War circa 265 BCE, and established superiority over the southern kingdoms. |
Chandragupta Maurya
| Approximate Dates of Mauryan Dynasty | ||||||||||||
| Emperor | Reign start | Reign end | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chandragupta Maurya | 322 BCE | 298 BCE | ||||||||||
| Bindusara | 297 BCE | 272 BCE | ||||||||||
| Asoka The Great | 273 BCE | 232 BCE | ||||||||||
| Dasaratha | 232 BCE | 224 BCE | ||||||||||
| Samprati | 224 BCE | 215 BCE | ||||||||||
| Salisuka | 215 BCE | 202 BCE | ||||||||||
| Devavarman | 202 BCE | 195 BCE | ||||||||||
| Satadhanvan | 195 BCE | 187 BCE | ||||||||||
| Brihadratha | 187 BCE | 185 BCE | ||||||||||
Chandragupta destroyed the Greeks when Seleucus I, ruler of the Seleucid Empire, tried to reconquer the northwestern parts of India, during a campaign in 305 BCE, but failed. The two rulers finally concluded a peace treaty: a marital treaty (Epigamia) was concluded, in which the Greeks offered their Princess for alliance and help from him. Chandragupta snatched the satrapies of Paropamisade (Kamboja and Gandhara), Arachosia (Kandhahar) and Gedrosia (Balochistan), and Seleucus I received 500 war elephants that were to have a decisive role in his victory against western Hellenistic kings at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BCE. Diplomatic relations were established and several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes, Deimakos and Dionysius resided at the Mauryan court.
Chandragupta established a strong centralized state with a complex administration at Pataliputra, which, according to Megasthenes, was "surrounded by a wooden wall pierced by 64 gates and 570 towers— (and) rivaled the splendors of contemporaneous Persian sites such as Susa and Ecbatana." Chandragupta's son Bindusara extended the rule of the Mauryan empire towards southern India. He also had a Greek ambassador at his court, named Deimachus (Strabo 1–70).
Megasthenes describes a disciplined multitude under Chandragupta, who live simply, honestly, and do not know writing:
- " The Indians all live frugally, especially when in camp. They dislike a great undisciplined multitude, and consequently they observe good order. Theft is of very rare occurrence. Megasthenes says that those who were in the camp of Sandrakottos, wherein lay 400,000 men, found that the thefts reported on any one day did not exceed the value of two hundred drachmae, and this among a people who have no written laws, but are ignorant of writing, and must therefore in all the business of life trust to memory. They live, nevertheless, happily enough, being simple in their manners and frugal. They never drink wine except at sacrifices. Their beverage is a liquor composed from rice instead of barley, and their food is principally a rice-pottage." Strabo XV. i. 53-56, quoting Megasthenes[10]
Bindusara
Ashoka the Great
Chandragupta's grandson was Ashokavardhan Maurya, better known as Ashoka the Great (ruled 273- 232 BCE).
As a young prince, Ashoka was a brilliant commander who crushed revolts in Ujjain and Taxila. As monarch he was ambitious and aggressive, re-asserting the Empire's superiority in southern and western India. But it was his conquest of Kalinga which proved to be the pivotal event of his life. Although Ashoka's army succeeded in overwhelming Kalinga forces of royal soldiers and civilian units, an estimated 100,000 soldiers and civilians were killed in the furious warfare, including over 10,000 of Ashoka's own men. Hundreds of thousands of people were adversely affected by the destruction and fallout of war. When he personally witnessed the devastation, Ashoka began feeling remorse, and he cried 'what have I done?'. Although the annexation of Kalinga was completed, Ashoka embraced the teachings of Gautama Buddha, and renounced war and violence. For a monarch in ancient times, this was an historic feat.
Ashoka implemented principles of ahimsa by banning hunting and violent sports activity and ending indentured and forced labor (many thousands of people in war-ravaged Kalinga had been forced into hard labor and servitude). While he maintained a large and powerful army, to keep the peace and maintain authority, Ashoka expanded friendly relations with states across Asia and Europe, and he sponsored Buddhist missions. He undertook a massive public works building campaign across the country. Over 40 years of peace, harmony and prosperity made Ashoka one of the most successful and famous monarchs in Indian history. He remains an idealized figure of inspiration in modern India.
The Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, are found throughout the Subcontinent. Ranging from as far west as Afghanistan and as far south as Andhra (Nellore District), Ashoka's edicts state his policies and accomplishments. Although predominantly written in Prakrit, two of them were written in Greek, and one in both Greek and Aramaic. Ashoka's edicts refer to the Greeks, Kambojas, and Gandharas as peoples forming a frontier region of his empire. They also attest to Ashoka's having sent envoys to the Greek rulers in the West as far as the Mediterranean. The edicts precisely name each of the rulers of the Hellenic world at the time such as Amtiyoko (Antiochus), Tulamaya (Ptolemy), Amtikini (Antigonos), Maka (Magas) and Alikasudaro (Alexander) as recipients of Ashoka's proselytism. The Edicts also accurately locate their territory "600 yojanas away" (a yojanas being about 7 miles), corresponding to the distance between the center of India and Greece (roughly 4,000 miles).[11]
 A representation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka, which was erected around 250 BCE. It is the emblem of India. |
Statuettes of the Maurya period, 4th-3rd century BCE. Musée Guimet. |
Administration
The Empire was divided into four provinces, which one of the four, look like a giant crescents. with the imperial capital at Pataliputra. From Ashokan edicts, the names of the four provincial capitals are Tosali (in the east), Ujjain in the west, Suvarnagiri (in the south), and Taxila (in the north). The head of the provincial administration was the Kumara (royal prince), who governed the provinces as king's representative. The kumara was assisted by Mahamatyas and council of ministers. This organizational structure was reflected at the imperial level with the Emperor and his Mantriparishad (Council of Ministers).
Historians theorize that the organization of the Empire was in line with the extensive bureaucracy described by Kautilya in the Arthashastra: a sophisticated civil service governed everything from municipal hygiene to international trade. The expansion and defense of the empire was made possible by what appears to have been the largest standing army of its time. According to Megasthenes, the empire wielded a military of 600,000 infantry, 30,000 cavalry, and 9,000 war elephants. A vast espionage system collected intelligence for both internal and external security purposes. Having renounced offensive warfare and expansionism, Ashoka nevertheless continued to maintain this large army, to protect the Empire and instill stability and peace across West and South Asia.
Economy
For the first time in South Asia, political unity and military security allowed for a common economic system and enhanced trade and commerce, with increased agricultural productivity. The previous situation involving hundreds of kingdoms, many small armies, powerful regional chieftains, and internecine warfare, gave way to a disciplined central authority. Farmers were freed of tax and crop collection burdens from regional kings, paying instead to a nationally administered and strict-but-fair system of taxation as advised by the principles in the Arthashastra. Chandragupta Maurya established a single currency across India, and a network of regional governors and administrators and a civil service provided justice and security for merchants, farmers and traders. The Mauryan army wiped out many gangs of bandits, regional private armies, and powerful chieftains who sought to impose their own supremacy in small areas. Although regimental in revenue collection, Maurya also sponsored many public works and waterways to enhance productivity, while internal trade in India expanded greatly due to newfound political unity and internal peace.

Under the Indo-Greek friendship treaty, and during Ashoka's reign, an international network of trade expanded. The Khyber Pass, on the modern boundary of Pakistan and Afghanistan, became a strategically important port of trade and intercourse with the outside world. Greek states and Hellenic kingdoms in West Asia became important trade partners of India. Trade also extended through the Malay peninsula into Southeast Asia. India's exports included silk goods and textiles, spices and exotic foods. The Empire was enriched further with an exchange of scientific knowledge and technology with Europe and West Asia. Ashoka also sponsored the construction of thousands of roads, waterways, canals, hospitals, rest-houses and other public works. The easing of many over-rigorous administrative practices, including those regarding taxation and crop collection, helped increase productivity and economic activity across the Empire.
In many ways, the economic situation in the Mauryan Empire is comparable to the Roman Empire of several centuries later. Both had extensive trade connections and both had organizations similar to corporations. While Rome had organizational entities which were largely used for public state-driven projects, Mauryan India, unlike Rome, had numerous private commercial entities. These existed purely for private commerce and developed before the Mauryan Empire itself, while the Romans did not have such pre-existing entities.[13] (See also Economic history of India.)
Religion


Jainism
Emperor Chandragupta Maurya became the first major Indian monarch to initiate a religious transformation at the highest level when he embraced Jainism, a religious movement resented by orthodox Hindu priests who usually attended the imperial court. At an older age, Chandragupta renounced his throne and material possessions to join a wandering group of Jain monks. Chandragupta was a disciple of Acharya Bhadrabahu. It is said that in his last days, he observed the rigorous but self purifying Jain ritual of santhara i.e. fast unto death, at Shravana Belagola in Karnataka. However, his successor, Emperor Bindusara, was an Ajivika and distanced himself from Jain and Buddhist movements. Samprati, the grandson of Ashoka also embraced Jainism. Samrat Samprati was influenced by the teachings of Jain monk Arya Suhasti Suri and he is known to have built 125,000 Jain Temples across India. Some of them are still found in towns of Ahmedabad, Viramgam, Ujjain & Palitana. It is also said that just like Ashoka, Samprati sent messengers & preachers to Greece, Persia & middle-east for the spread of Jainism. But to date no research has been done in this area. Thus, Jainism became a vital force under the Mauryan Rule. Chandragupta & Samprati are credited for the spread of Jainism in Southern India. Lakhs of Jain Temples & Jain Stupas were erected during their reign. But due to lack of royal patronage & its strict principles, along with the rise of Shankaracharya & Ramanujacharya, Jainism, once the major religion of southern India, began to decline.
Buddhism
But when Ashoka embraced Buddhism, following the Kalinga War, he renounced expansionism and aggression, and the harsher injunctions of the Arthashastra on the use of force, intensive policing, and ruthless measures for tax collection and against rebels. Ashoka sent a mission led by his son Mahinda and daughter Sanghamitta to Sri Lanka, whose king Tissa was so charmed with Buddhist ideals that he adopted them himself and made Buddhism the state religion. Ashoka sent many Buddhist missions to West Asia, Greece and South East Asia, and commissioned the construction of monasteries, schools and publication of Buddhist literature across the empire. He is believed to have built as many as 84,000 stupas across India i.e. Sanchi and Mahabodhi Temple, and he increased the popularity of Buddhism in Afghanistan, Thailand and north Asian countries. Ashoka helped convene the Third Buddhist Council of India and South Asia's Buddhist orders, near his capital, a council that undertook much work of reform and expansion of the Buddhist religion.
Brahmanism
While himself a Buddhist, Ashoka retained the membership of Brahmana priests and ministers in his court, and he maintained religious freedom and tolerance although the Buddhist faith grew in popularity with his patronage. Brahmanic society began embracing the philosophy of ahimsa, and given the increased prosperity and improved law enforcement, crime and internal conflicts reduced dramatically. Also greatly discouraged was the caste system and orthodox discrimination, as Brahmanism began to absorb the ideals and values of Jain and Buddhist teachings. Social freedom began expanding in an age of peace and prosperity.
Architectural remains
Architectural remains of the Maurya period are rather few. Remains of a hypostyle building with about 80 columns of a height of about 10 meters have been found in Kumhrar, 5 km from Patna Railway station, and is one of the very few site that has been connected to the rule of the Mauryas in that city. The style is rather reminiscent of Persian Achaemenid architecture.[15]
The grottoes of Barabar Caves, are another example of Mauryan architecture, especially the decorated front of the Lomas Rishi grotto. These were offered by the Mauryas to the Buddhist sect of the Ajivikas.[16]
The most widespread example of Maurya architecture are the Pillars of Ashoka, often exquisitely decorated, with more than 40 spread throughout the sub-continent.
Natural history in the times of the Mauryas
The protection of animals in India became serious business by the time of the Maurya dynasty; being the first empire to provide a unified political entity in India, the attitude of the Mauryas towards forests, its denizens and fauna in general is of interest.
The Mauryas firstly looked at forests as a resource. For them, the most important forest product was the elephant. Military might in those times depended not only upon horses and men but also battle-elephants; these played a role in the defeat of Seleucus, Alexander's governor of the Punjab. The Mauryas sought to preserve supplies of elephants since it was cheaper and took less time to catch, tame and train wild elephants than to raise them. Kautilya's Arthashastra contains not only maxims on ancient statecraft, but also unambiguously specifies the responsibilities of officials such as the Protector of the Elephant Forests:[17]
On the border of the forest, he should establish a forest for elephants guarded by foresters. The Superintendent should with the help of guards...protect the elephants whether along on the mountain, along a river, along lakes or in marshy tracts...They should kill anyone slaying an elephant.
The Mauryas also designated separate forests to protect supplies of timber, as well as lions and tigers, for skins. Elsewhere the Protector of Animals also worked to eliminate thieves, tigers and other predators to render the woods safe for grazing cattle.
The Mauryas valued certain forest tracts in strategic or economic terms and instituted curbs and control measures over them. They regarded all forest tribes with distrust and controlled them with bribery and political subjugation. They employed some of them, the food-gatherers or aranyaca to guard borders and trap animals. The sometimes tense and conflict-ridden relationship nevertheless enabled the Mauryas to guard their vast empire.[18]
When Ashoka embraced Buddhism in the latter part of his reign, he brought about significant changes in his style of governance, which included providing protection to fauna, and even relinquished the royal hunt. He was the first ruler in history to advocate conservation measures for wildlife and even had rules inscribed in stone edicts. The edicts proclaim that many followed the king's example in giving up the slaughter of animals; one of them proudly states:[18]
Our king killed very few animals.—Edict on Fifth Pillar
However, the edicts of Ashoka reflect more the desire of rulers than actual events; the mention of a 100 'panas' (coins) fine for poaching deer in royal hunting preserves shows that rule-breakers did exist. The legal restrictions conflicted with the practices freely exercised by the common people in hunting, felling, fishing and setting fires in forests.[18]
Contacts with the Hellenistic world

Foundation of the Empire
Relations with the Hellenistic world may have started from the very beginning of the Maurya Empire. Plutarch reports that Chandragupta Maurya met with Alexander the Great, probably around Taxila in the northwest:
- "Sandrocottus, when he was a stripling, saw Alexander himself, and we are told that he often said in later times that Alexander narrowly missed making himself master of the country, since its king was hated and despised on account of his baseness and low birth". Plutarch 62-3[19]
Reconquest of the Northwest (c. 310 BCE)
Chandragupta ultimately occupied Northwestern India, in the territories formerly ruled by the Greeks, where he fought the satraps (described as "Prefects" in Western sources) left in place after Alexander (Justin), among whom may have been Eudemus, ruler in the western Punjab until his departure in 317 BCE or Peithon, son of Agenor, ruler of the Greek colonies along the Indus until his departure for Babylon in 316 BCE.
- "India, after the death of Alexander, had assassinated his prefects, as if shaking the burden of servitude. The author of this liberation was Sandracottos, but he had transformed liberation in servitude after victory, since, after taking the throne, he himself oppressed the very people he has liberated from foreign domination" Justin XV.4.12-13[20]
- "Later, as he was preparing war against the prefects of Alexander, a huge wild elephant went to him and took him on his back as if tame, and he became a remarkable fighter and war leader. Having thus acquired royal power, Sandracottos possessed India at the time Seleucos was preparing future glory." Justin XV.4.19[21]
Conflict and alliance with Seleucus (305 BCE)

Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of the Asian portion of Alexander's former empire, conquered and put under his own authority eastern territories as far as Bactria and the Indus (Appian, History of Rome, The Syrian Wars 55), until in 305 BCE he entered in a confrontation with Chandragupta:
- "Always lying in wait for the neighboring nations, strong in arms and persuasive in council, he [Seleucus] acquired Mesopotamia, Armenia, 'Seleucid' Cappadocia, Persis, Parthia, Bactria, Arabia, Tapouria, Sogdia, Arachosia, Hyrcania, and other adjacent peoples that had been subdued by Alexander, as far as the river Indus, so that the boundaries of his empire were the most extensive in Asia after that of Alexander. The whole region from Phrygia to the Indus was subject to Seleucus". Appian, History of Rome, The Syrian Wars 55[22]
Though no accounts of the conflict remain, it is clear that Seleucus fared poorly against the Indian Emperor as he failed in conquering any territory, and in fact, was forced to surrender much that was already his. Regardless, Seleucus and Chandragupta ultimately reached a settlement and through a treaty sealed in 305 BCE, Seleucus, according to Strabo, ceded a number of territories to Chandragupta, including southern Afghanistan and parts of Persia.
Accordingly, Seleucus obtained five hundred war elephants, a military asset which would play a decisive role at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BCE.
Marital alliance
It is generally thought that Chandragupta married Seleucus's daughter, or a Greek Macedonian princess, a gift from Seleucus to formalize an alliance. In a return gesture, Chandragupta sent 500 war-elephants[8][23][24][25][26][27], a military asset which would play a decisive role at the Battle of Ipsus in 302 BC. In addition to this treaty, Seleucus dispatched an ambassador, Megasthenes, to Chandragupta, and later Deimakos to his son Bindusara, at the Mauryan court at Pataliputra (modern Patna in Bihar state). Later Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the ruler of Ptolemaic Egypt and contemporary of Ashoka the Great, is also recorded by Pliny the Elder as having sent an ambassador named Dionysius to the Mauryan court.[28].
Mainstream scholarship asserts that Chandragupta received vast territory west of the Indus, including the Hindu Kush, modern day Afghanistan, and the Balochistan province of Pakistan.[29][30] Archaeologically, concrete indications of Mauryan rule, such as the inscriptions of the Edicts of Ashoka, are known as far as Kandhahar in southern Afghanistan.
| “ | "He (Seleucus) crossed the Indus and waged war with Sandrocottus [Maurya], king of the Indians, who dwelt on the banks of that stream, until they came to an understanding with each other and contracted a marriage relationship." | ” |
| “ | "After having made a treaty with him (Sandrakotos) and put in order the Orient situation, Seleucos went to war against Antigonus." | ” |
|
—Junianus Justinus, Historiarum Philippicarum libri XLIV, XV.4.15 |
||
The treaty on "Epigamia" implies lawful marriage between Greeks and Indians was recognized at the State level, although it is unclear whether it occurred among dynastic rulers or common people, or both. .
Exchange of ambassadors
Seleucus dispatched an ambassador, Megasthenes, to Chandragupta, and later Deimakos to his son Bindusara, at the Mauryan court at Pataliputra (Modern Patna in Bihar state). Later Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the ruler of Ptolemaic Egypt and contemporary of Ashoka, is also recorded by Pliny the Elder as having sent an ambassador named Dionysius to the Mauryan court.[28]
Exchange of presents
Classical sources have also recorded that following their treaty, Chandragupta and Seleucus exchanged presents, such as when Chandragupta sent various aphrodisiacs to Seleucus:
- "And Theophrastus says that some contrivances are of wondrous efficacy in such matters [as to make people more amorous]. And Phylarchus confirms him, by reference to some of the presents which Sandrakottus, the king of the Indians, sent to Seleucus; which were to act like charms in producing a wonderful degree of affection, while some, on the contrary, were to banish love" Athenaeus of Naucratis, "The deipnosophists" Book I, chapter 32[31]
His son Bindusara 'Amitraghata' (Slayer of Enemies) also is recorded in Classical sources as having exchanged present with Antiochus I:
- "But dried figs were so very much sought after by all men (for really, as Aristophanes says, "There's really nothing nicer than dried figs"), that even Amitrochates, the king of the Indians, wrote to Antiochus, entreating him (it is Hegesander who tells this story) to buy and send him some sweet wine, and some dried figs, and a sophist; and that Antiochus wrote to him in answer, "The dry figs and the sweet wine we will send you; but it is not lawful for a sophist to be sold in Greece" Athenaeus, "Deipnosophistae" XIV.67[32]
Greek population in India
Greek population apparently remained in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent under Ashoka's rule. In his Edicts of Ashoka, set in stone, some of them written in Greek, Ashoka describes that Greek population within his realm converted to Buddhism:
- "Here in the king's domain among the Greeks, the Kambojas, the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions in Dharma". Rock Edict Nb13 (S. Dhammika).
Fragments of Edict 13 have been found in Greek, and a full Edict, written in both Greek and Aramaic has been discovered in Kandahar. It is said to be written in excellent Classical Greek, using sophisticated philosophical terms. In this Edict, Ashoka uses the word Eusebeia ("Piety") as the Greek translation for the ubiquitous "Dharma" of his other Edicts written in Prakrit:
- "Ten years (of reign) having been completed, King Piodasses (Ashoka) made known (the doctrine of) Piety (εὐσέβεια, Eusebeia) to men; and from this moment he has made men more pious, and everything thrives throughout the whole world. And the king abstains from (killing) living beings, and other men and those who (are) huntsmen and fishermen of the king have desisted from hunting. And if some (were) intemperate, they have ceased from their intemperance as was in their power; and obedient to their father and mother and to the elders, in opposition to the past also in the future, by so acting on every occasion, they will live better and more happily". (Trans. by G.P. Carratelli [1])
Buddhist missions to the West (c.250 BCE)

Also, in the Edicts of Ashoka, Ashoka mentions the Hellenistic kings of the period as a recipient of his Buddhist proselytism, although no Western historical record of this event remain:
- "The conquest by Dharma has been won here, on the borders, and even six hundred yojanas (5,400-9,600 km) away, where the Greek king Antiochos rules, beyond there where the four kings named Ptolemy, Antigonos, Magas and Alexander rule, likewise in the south among the Cholas, the Pandyas, and as far as Tamraparni (Sri Lanka)." (Edicts of Ashoka, 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika).
Ashoka also claims that he encouraged the development of herbal medicine, for men and animals, in their territories:
- "Everywhere within Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi's [Ashoka's] domain, and among the people beyond the borders, the Cholas, the Pandyas, the Satiyaputras, the Keralaputras, as far as Tamraparni and where the Greek king Antiochos rules, and among the kings who are neighbors of Antiochos, everywhere has Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi, made provision for two types of medical treatment: medical treatment for humans and medical treatment for animals. Wherever medical herbs suitable for humans or animals are not available, I have had them imported and grown. Wherever medical roots or fruits are not available I have had them imported and grown. Along roads I have had wells dug and trees planted for the benefit of humans and animals". 2nd Rock Edict
The Greeks in India even seem to have played an active role in the propagation of Buddhism, as some of the emissaries of Ashoka, such as Dharmaraksita, are described in Pali sources as leading Greek ("Yona") Buddhist monks, active in Buddhist proselytism (the Mahavamsa, XII[33]).
Subhagsena and Antiochos III (206 BCE)
Sophagasenus was an Indian Mauryan ruler of the 3rd century BCE, described in ancient Greek sources, and named Subhagsena or Subhashsena in Prakrit. His name is mentioned in the list of Mauryan princes, and also in the list of the Yadava dynasty, as a descendant of Pradyumna. He may have been a grandson of Ashoka, or Kunala, the son of Ashoka. He ruled an area south of the Hindu Kush, possibly in Gandhara. Antiochos III, the Seleucid king, after having made peace with Euthydemus in Bactria, went to India in 206 BC and is said to have renewed his friendship with the Indian king there:
- "He (Antiochus) crossed the Caucasus and descended into India; renewed his friendship with Sophagasenus the king of the Indians; received more elephants, until he had a hundred and fifty altogether; and having once more provisioned his troops, set out again personally with his army: leaving Androsthenes of Cyzicus the duty of taking home the treasure which this king had agreed to hand over to him". Polybius 11.39
Decline
Ashoka was followed for 50 years by a succession of weaker kings. Brhadrata, the last ruler of the Mauryan dynasty, held territories that had shrunk considerably from the time of emperor Ashoka, although he still upheld the Buddhist faith.
Sunga coup (185 BCE)
Brihadrata was assassinated in 185 BCE during a military parade, by the commander-in-chief of his guard, the Brahmin general Pusyamitra Sunga, who then took over the throne and established the Sunga dynasty. Buddhist records such as the Asokavadana write that the assassination of Brhadrata and the rise of the Sunga empire led to a wave of persecution for Buddhists,[34] and a resurgence of Hinduism. According to Sir John Marshall,[35] Pusyamitra may have been the main author of the persecutions, although later Sunga kings seem to have been more supportive of Buddhism. Other historians, such as Etienne Lamotte[36] and Romila Thapar,[37] among others, have argued that archaeological evidence in favor of the allegations of persecution of Buddhists are lacking, and that the extent and magnitude of the atrocities have been exaggerated.
Establishment of the Indo-Greek Kingdom (180 BCE)
The fall of the Mauryas left the Khyber Pass unguarded, and a wave of foreign invasion followed. The Greco-Bactrian king, Demetrius, capitalized on the break-up, and he conquered southern Afghanistan and Pakistan around 180 BC, forming the Indo-Greek Kingdom. The Indo-Greeks would maintain holdings on the trans-Indus region, and make forays into central India, for about a century. Under them, Buddhism flourished, and one of their kings Menander became a famous figure of Buddhism, he was to establish a new capital of Sagala, the modern city of Sialkot. However, the extent of their domains and the lengths of their rule are subject to much debate. Numismatic evidence indicates that they retained holdings in the subcontinent right up to the birth of Christ. Although the extent of their successes against indigenous powers such as the Sungas, Satavahanas, and Kalingas are unclear, what is clear is that Scythian tribes, renamed Indo-Scythians, brought about the demise of the Indo-Greeks from around 70 BCE and retained lands in the trans-Indus, the region of Mathura, and Gujarat.
| Preceded by Nanda dynasty |
Magadha dynasties | Succeeded by Sunga dynasty |
See also
| Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||||||||
| Timeline: | Northwestern India | Northern India | Southern India | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6th century BCE |
(Persian rule)
(Islamic conquests)
(Islamic Empire) |
|
|
|||||||||
- Magadha Empire
- History of India
Notes
- ↑ Kulke, Hermann; Rothermund, Dietmar (2004), A History of India, 4th edition. Routledge, Pp. xii, 448, ISBN 0415329205, http://www.amazon.com/History-India-Hermann-Kulke/dp/0415329205/.
- ↑ Thapar, Romila (1990), A History of India, Volume 1, New Delhi and London: Penguin Books. Pp. 384, ISBN 0140138358, http://www.amazon.com/History-India-Penguin/dp/0140138358/.
- ↑ :"Androcottus, when he was a stripling, saw Alexander himself, and we are told that he often said in later times that Alexander narrowly missed making himself master of the country, since its king was hated and despised on account of his baseness and low birth." Plutarch 62-3 Plutarch 62-3
- ↑ :"He was of humble origin, but was pushing to acquiring the throne by the superior power of the mind. When after having offensed the king of Nanda by his insolence, he was comdemned to death by the king, he was saved by the speed of his own feet... He gathered bandits and invited Indian to a change of rule." Justin XV.4.15 "Fuit hic humili quidem genere natus, sed ad regni potestatem maiestate numinis inpulsus. Quippe cum procacitate sua Nandrum regem offendisset, interfici a rege iussus salutem pedum ceieritate quaesierat. (Ex qua fatigatione cum somno captus iaceret, leo ingentis formae ad dormientem accessit sudoremque profluentem lingua ei detersit expergefactumque blande reliquit. Hoc prodigio primum ad spem regni inpulsus) contractis latronibus Indos ad nouitatem regni sollicitauit." Justin XV.4.15
- ↑
- "asti tava Shaka-Yavana-Kirata-Kamboja-Parasika-Bahlika parbhutibhih
- Chankyamatipragrahittaishcha Chandergupta Parvateshvara
- balairudidhibhiriva parchalitsalilaih samantaad uprudham Kusumpurama"
- (Sanskrit original, Mudrarakshasa 2).
- ↑ The Hunas mentioned in Mudrarakshasa play (II) of Vishakhadatta are same people as the Harahunas of the Mahabharata (II.32.12). They were located in Herat/Aria according to Dr Moti Chandra and were an earlier branch of the Hunas (See: Geographical and Economic Studies in the Mahābhārata: Upāyana Parva, 1945, p 66, Dr Moti Chandra; Also: Studies in the Geography of Ancient and Medieval India, 1971, p 33, Dr D. C. Sircar.
- ↑ For Harahunas being a group of the Hunas, see also: Early History of Iranians and Atharvaveda, Persica-9, 1980, p 118, Dr Michael Witzel, Harvard University.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (1977), Ancient India, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0436-8
- ↑ Radhakumud Mookerji (1988). Chandragupta Maurya and His Times (p. 39). Motilal Banarsidass Publ. ISBN 81-208-0405-8.
- ↑ Source:Megasthenes fragment XXVII
- ↑ Edicts of Ashoka, 13th Rock Edict, translation S. Dhammika.
- ↑ Reference: "India: The Ancient Past" p.113, Burjor Avari, Routledge, ISBN 0-415-35615-6
- ↑ Khanna, Vikramaditya S. (2005). The Economic History of the Corporate Form in Ancient India. University of Michigan.
- ↑ Source: "Butkara I", Facenna.
- ↑ "L'age d'or de l'Inde Classique", p23
- ↑ "L'age d'or de l'Inde Classique", p22
- ↑ Rangarajan, M. (2001) India's Wildlife History, pp 7.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Rangarajan, M. (2001) India's Wildlife History, pp 8.
- ↑ Plutarch 62-3
- ↑ "(Transitum deinde in Indiam fecit), quae post mortem Alexandri, ueluti ceruicibus iugo seruitutis excusso, praefectos eius occiderat. Auctor libertatis Sandrocottus fuerat, sed titulum libertatis post uictoriam in seruitutem uerterat ; 14 siquidem occupato regno populum quem ab externa dominatione uindicauerat ipse seruitio premebat." Justin XV.4.12-13
- ↑ "Molienti deinde bellum aduersus praefectos Alexandri elephantus ferus infinitae magnitudinis ultro se obtulit et ueluti domita mansuetudine eum tergo excepit duxque belli et proeliator insignis fuit. Sic adquisito regno Sandrocottus ea tempestate, qua Seleucus futurae magnitudinis fundamenta iaciebat, Indiam possidebat." Justin XV.4.19
- ↑ Appian, History of Rome, The Syrian Wars 55
- ↑ Ancient India, (Kachroo ,p.196)
- ↑ The Imperial Gazetteer of India, (Hunter,p.167)
- ↑ The evolution of man and society, (Darlington ,p.223)
- ↑ W. W. Tarn (1940). "Two Notes on Seleucid History: 1. Seleucus' 500 Elephants, 2. Tarmita", The Journal of Hellenic Studies 60, p. 84-94.
- ↑ Partha Sarathi Bose (2003). Alexander the Great's Art of Strategy. Gotham Books. ISBN 1-59240-053-1.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Pliny the Elder, "The Natural History", Chap. 21
- ↑ Vincent A. Smith (1998). Asoka. Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-1303-1.
- ↑ Walter Eugene Clark (1919). "The Importance of Hellenism from the Point of View of Indic-Philology", Classical Philology 14 (4), p. 297-313.
- ↑ Ath. Deip. I.32
- ↑ Athenaeus, "Deipnosophistae" XIV.67
- ↑ Full text of the Mahavamsa Click chapter XII
- ↑ According to the Ashokavadana
- ↑ Sir John Marshall, "A Guide to Sanchi", Eastern Book House, 1990, ISBN 81-85204-32-2, pg.38
- ↑ E. Lamotte: History of Indian Buddhism, Institut Orientaliste, Louvain-la-Neuve 1988 (1958)
- ↑ Asoka and the Decline of the Mauryas by Romila Thapar, Oxford University Press, 1960 P200
References
- Robert Morkot, The Penguin Historical Atlas of Ancient Greece ISBN 0-14-051335-3
- Chanakya, Arthashastra ISBN 0-14-044603-6
- J.F.C. Fuller, The Generalship of Alexander the Great ISBN 0-306-81330-0
External links
- The Mauryan Empire at All Empires
- Livius.org: Maurya dynasty
- Mauryan Empire of India
- Extent of the Empire
- The Mauryan Empire from Britannica
- Ashoka and Buddhism
- Ashoka's Edicts





