Keynesian economics
| Economics |
 |
|
Economies by region
|
| General categories |
|---|
|
Microeconomics · Macroeconomics |
| Methods |
|
Mathematical (Game theory · Optimization) |
| Fields and subfields |
|
Behavioral · Cultural · Evolutionary |
| Lists |
|
Journals · Publications |
|
Economic ideologies
|
| Business and Economics Portal |
Keynesian economics (pronounced /ˈkeɪnziən/, also called Keynesianism and Keynesian theory) is a macroeconomic theory based on the ideas of 20th century British economist John Maynard Keynes. Keynesian economics argues that private sector decisions sometimes lead to inefficient macroeconomic outcomes and therefore advocates active policy responses by the public sector, including monetary policy actions by the central bank and fiscal policy actions by the government to stabilize output over the business cycle.[1] The theories forming the basis of Keynesian economics were first presented in The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, published in 1936; the interpretations of Keynes are contentious, and several schools of thought claim his legacy.
Keynesian economics advocates a mixed economy—predominantly private sector, but with a large role of government and public sector—and served as the economic model during the latter part of the Great Depression, World War II, and the post-war economic expansion (1945–1973), though it lost some influence following the stagflation of the 1970s. The advent of the global financial crisis in 2007 has caused a resurgence in Keynesian thought. The former British Prime Minister Gordon Brown, President of the United States Barack Obama, and other world leaders have used Keynesian economics through government stimulus programs to assist the economic state of their countries.[2]
Contents |
Overview
According to Keynesian theory, some microeconomic-level actions – if taken collectively by a large proportion of individuals and firms – can lead to inefficient aggregate macroeconomic outcomes, where the economy operates below its potential output and growth rate. Such a situation had previously been referred to by classical economists as a general glut. There was disagreement among classical economists (some of whom believed in Say's Law – that "supply creates its own demand"), on whether a general glut was possible. Keynes contended that a general glut would occur when aggregate demand for goods were insufficient, leading to an economic downturn with unnecessarily high unemployment and losses of potential output. In such a situation, government policies could be used to increase aggregate demand, thus increasing economic activity and reducing unemployment and deflation.
Keynes argued that the solution to the Great Depression was to stimulate the economy ("inducement to invest") through some combination of two approaches: a reduction in interest rates and government investment in infrastructure. Investment by government injects income, which results in more spending in the general economy, which in turn stimulates more production and investment involving still more income and spending and so forth. The initial stimulation starts a cascade of events, whose total increase in economic activity is a multiple of the original investment.[3]
A central conclusion of Keynesian economics is that, in some situations, no strong automatic mechanism moves output and employment towards full employment levels. This conclusion conflicts with economic approaches that assume a strong general tendency towards equilibrium. In the 'neoclassical synthesis', which combines Keynesian macro concepts with a micro foundation, the conditions of general equilibrium allow for price adjustment to eventually achieve this goal. More broadly, Keynes saw his theory as a general theory, in which utilization of resources could be high or low, whereas previous economics focused on the particular case of full utilization.
The new classical macroeconomics movement, which began in the late 1960s and early 1970s, criticized Keynesian theories, while New Keynesian economics have sought to base Keynes's idea on more rigorous theoretical foundations.
Some interpretations of Keynes have emphasized his stress on the international coordination of Keynesian policies, the need for international economic institutions, and the ways in which economic forces could lead to war or could promote peace.[4]
Precursors
Keynes's work was part of a long-running debate within economics over the existence and nature of general gluts. While a number of the policies Keynes advocated (notably government deficit spending) and the theoretical ideas he proposed (effective demand, the multiplier, the paradox of thrift) were advanced by various authors in the 19th and early 20th century, Keynes's unique contribution was to provide a general theory of these, which proved acceptable to the political and economic establishments.
Schools
An intellectual precursor of Keynesian economics was underconsumption theory in classical economics, dating from such 19th century economists as Thomas Malthus, the Birmingham School of Thomas Attwood,[5] and the American economists William Trufant Foster and Waddill Catchings, who were influential in the 1920s and 1930s. Underconsumptionists were, like Keynes after them, concerned with failure of aggregate demand to attain potential output, calling this "underconsumption" (focusing on the demand side), rather than "overproduction" (which would focus on the supply side), and advocating economic interventionism. Keynes specifically discussed underconsumption (which he wrote "under-consumption") in the General Theory, in Chapter 22, Section IV and Chapter 23, Section VII.
Numerous concepts were developed earlier and independently of Keynes by the Stockholm school during the 1930s; these accomplishments were described in a 1937 article, published in response to the 1936 General Theory, sharing the Swedish discoveries.[6]
Concepts
The multiplier dates to work in the 1890s by the Australian economist Alfred De Lissa, the Danish economist Julius Wulff, and the German American economist Nicholas Johannsen,[7] the latter being cited in a footnote of Keynes.[8] Nicholas Johannsen also proposed a theory of effective demand in the 1890s.
The paradox of thrift was stated in 1892 by John M. Robertson in his The Fallacy of Savings, in earlier forms by mercantilist economists since the 16th century, and similar sentiments date to antiquity:[9][10]
Today these ideas, regardless of provenance, are referred to in academia under the rubric of "Keynesian economics", due to Keynes's role in consolidating, elaborating, and popularizing them.
Keynes and the Classics
| Part of the series on |
|
Concepts
Economic theories
Origins
People
Variants
Related topics
Movements
|
Keynes sought to distinguish his theories from and oppose them to "classical economics," by which he meant the economic theories of David Ricardo and his followers, including John Stuart Mill, Alfred Marshall, Francis Ysidro Edgeworth, and Arthur Cecil Pigou. A central tenet of the classical view, known as Say's law, states that "supply creates its own demand". Say's Law can be interpreted in two ways. First, the claim that the total value of output is equal to the sum of income earned in production is a result of a national income accounting identity, and is therefore indisputable. A second and stronger claim, however, that the "costs of output are always covered in the aggregate by the sale-proceeds resulting from demand" depends on how consumption and saving are linked to production and investment. In particular, Keynes argued that the second, strong form of Say's Law only holds if increases in individual savings exactly match an increase in aggregate investment.[11]
Keynes sought to develop a theory that would explain determinants of saving, consumption, investment and production. In that theory, the interaction of aggregate demand and aggregate supply determines the level of output and employment in the economy.
Because of what he considered the failure of the “Classical Theory” in the 1930s, Keynes firmly objects to its main theory—adjustments in prices would automatically make demand tend to the full employment level.
Neo-classical theory supports that the two main costs that shift demand and supply are labor and money. Through the distribution of the monetary policy, demand and supply can be adjusted. If there were more labor than demand for it, wages would fall until hiring began again. If there was too much saving, and not enough consumption, then interest rates would fall until people either cut their savings rate or started borrowing.
Wages and spending
During the Great Depression, the classical theory defined economic collapse as simply a lost incentive to produce, and the mass unemployment as a result of high and rigid real wages.
To Keynes, the determination of wages is more complicated. First, he argued that it is not real but nominal wages that are set in negotiations between employers and workers, as opposed to a barter relationship. Second, nominal wage cuts would be difficult to put into effect because of laws and wage contracts. Even classical economists admitted that these exist; unlike Keynes, they advocated abolishing minimum wages, unions, and long-term contracts, increasing labor-market flexibility. However, to Keynes, people will resist nominal wage reductions, even without unions, until they see other wages falling and a general fall of prices.
He also argued that to boost employment, real wages had to go down: nominal wages would have to fall more than prices. However, doing so would reduce consumer demand, so that the aggregate demand for goods would drop. This would in turn reduce business sales revenues and expected profits. Investment in new plants and equipment—perhaps already discouraged by previous excesses—would then become more risky, less likely. Instead of raising business expectations, wage cuts could make matters much worse.
Further, if wages and prices were falling, people would start to expect them to fall. This could make the economy spiral downward as those who had money would simply wait as falling prices made it more valuable—rather than spending. As Irving Fisher argued in 1933, in his Debt-Deflation Theory of Great Depressions, deflation (falling prices) can make a depression deeper as falling prices and wages made pre-existing nominal debts more valuable in real terms.
Excessive saving

To Keynes, excessive saving, i.e. saving beyond planned investment, was a serious problem, encouraging recession or even depression. Excessive saving results if investment falls, perhaps due to falling consumer demand, over-investment in earlier years, or pessimistic business expectations, and if saving does not immediately fall in step, the economy would decline.
The classical economists argued that interest rates would fall due to the excess supply of "loanable funds". The first diagram, adapted from the only graph in The General Theory, shows this process. (For simplicity, other sources of the demand for or supply of funds are ignored here.) Assume that fixed investment in capital goods falls from "old I" to "new I" (step a). Second (step b), the resulting excess of saving causes interest-rate cuts, abolishing the excess supply: so again we have saving (S) equal to investment. The interest-rate (i) fall prevents that of production and employment.
Keynes had a complex argument against this laissez-faire response. The graph below summarizes his argument, assuming again that fixed investment falls (step A). First, saving does not fall much as interest rates fall, since the income and substitution effects of falling rates go in conflicting directions. Second, since planned fixed investment in plant and equipment is mostly based on long-term expectations of future profitability, that spending does not rise much as interest rates fall. So S and I are drawn as steep (inelastic) in the graph. Given the inelasticity of both demand and supply, a large interest-rate fall is needed to close the saving/investment gap. As drawn, this requires a negative interest rate at equilibrium (where the new I line would intersect the old S line). However, this negative interest rate is not necessary to Keynes's argument.
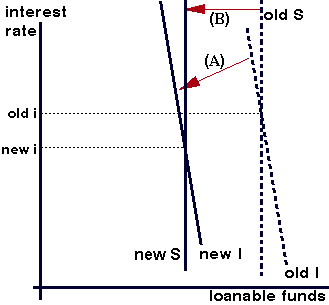
Third, Keynes argued that saving and investment are not the main determinants of interest rates, especially in the short run. Instead, the supply of and the demand for the stock of money determine interest rates in the short run. (This is not drawn in the graph.) Neither changes quickly in response to excessive saving to allow fast interest-rate adjustment.
Finally, because of fear of capital losses on assets besides money, Keynes suggested that there may be a "liquidity trap" setting a floor under which interest rates cannot fall. While in this trap, interest rates are so low that any increase in money supply will cause bond-holders (fearing rises in interest rates and hence capital losses on their bonds) to sell their bonds to attain money (liquidity). In the diagram, the equilibrium suggested by the new I line and the old S line cannot be reached, so that excess saving persists. Some (such as Paul Krugman) see this latter kind of liquidity trap as prevailing in Japan in the 1990s. Most economists agree that nominal interest rates cannot fall below zero, however, some economists (particularly those from the Chicago school) reject the existence of a liquidity trap.
Even if the liquidity trap does not exist, there is a fourth (perhaps most important) element to Keynes's critique. Saving involves not spending all of one's income. It thus means insufficient demand for business output, unless it is balanced by other sources of demand, such as fixed investment. Thus, excessive saving corresponds to an unwanted accumulation of inventories, or what classical economists called a general glut.[12] This pile-up of unsold goods and materials encourages businesses to decrease both production and employment. This in turn lowers people's incomes—and saving, causing a leftward shift in the S line in the diagram (step B). For Keynes, the fall in income did most of the job by ending excessive saving and allowing the loanable funds market to attain equilibrium. Instead of interest-rate adjustment solving the problem, a recession does so. Thus in the diagram, the interest-rate change is small.
Whereas the classical economists assumed that the level of output and income was constant and given at any one time (except for short-lived deviations), Keynes saw this as the key variable that adjusted to equate saving and investment.
Finally, a recession undermines the business incentive to engage in fixed investment. With falling incomes and demand for products, the desired demand for factories and equipment (not to mention housing) will fall. This accelerator effect would shift the I line to the left again, a change not shown in the diagram above. This recreates the problem of excessive saving and encourages the recession to continue.
In sum, to Keynes there is interaction between excess supplies in different markets, as unemployment in labor markets encourages excessive saving—and vice-versa. Rather than prices adjusting to attain equilibrium, the main story is one of quantity adjustment allowing recessions and possible attainment of underemployment equilibrium.
Active fiscal policy
As noted, the classicals wanted to balance the government budget. To Keynes, this would exacerbate the underlying problem: following either policy would raise saving (broadly defined) and thus lower the demand for both products and labor. For example, Keynesians see Herbert Hoover's June 1932 tax increase as making the Depression worse.
Keynes′ ideas influenced Franklin D. Roosevelt's view that insufficient buying-power caused the Depression. During his presidency, Roosevelt adopted some aspects of Keynesian economics, especially after 1937, when, in the depths of the Depression, the United States suffered from recession yet again following fiscal contraction. But to many the true success of Keynesian policy can be seen at the onset of World War II, which provided a kick to the world economy, removed uncertainty, and forced the rebuilding of destroyed capital. Keynesian ideas became almost official in social-democratic Europe after the war and in the U.S. in the 1960s.
Keynes′ theory suggested that active government policy could be effective in managing the economy. Rather than seeing unbalanced government budgets as wrong, Keynes advocated what has been called countercyclical fiscal policies, that is policies which acted against the tide of the business cycle: deficit spending when a nation's economy suffers from recession or when recovery is long-delayed and unemployment is persistently high—and the suppression of inflation in boom times by either increasing taxes or cutting back on government outlays. He argued that governments should solve problems in the short run rather than waiting for market forces to do it in the long run, because "in the long run, we are all dead."[13]
This contrasted with the classical and neoclassical economic analysis of fiscal policy. Fiscal stimulus (deficit spending) could actuate production. But to these schools, there was no reason to believe that this stimulation would outrun the side-effects that "crowd out" private investment: first, it would increase the demand for labor and raise wages, hurting profitability; Second, a government deficit increases the stock of government bonds, reducing their market price and encouraging high interest rates, making it more expensive for business to finance fixed investment. Thus, efforts to stimulate the economy would be self-defeating.
The Keynesian response is that such fiscal policy is only appropriate when unemployment is persistently high, above the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU). In that case, crowding out is minimal. Further, private investment can be "crowded in": fiscal stimulus raises the market for business output, raising cash flow and profitability, spurring business optimism. To Keynes, this accelerator effect meant that government and business could be complements rather than substitutes in this situation. Second, as the stimulus occurs, gross domestic product rises, raising the amount of saving, helping to finance the increase in fixed investment. Finally, government outlays need not always be wasteful: government investment in public goods that will not be provided by profit-seekers will encourage the private sector's growth. That is, government spending on such things as basic research, public health, education, and infrastructure could help the long-term growth of potential output.
A Keynesian economist might point out that classical and neoclassical theory does not explain why firms acting as "special interests" to influence government policy are assumed to produce a negative outcome, while those same firms acting with the same motivations outside of the government are supposed to produce positive outcomes. Libertarians counter that because both parties consent, free trade increases net happiness, but government imposes its will by force, decreasing happiness. Therefore firms that manipulate the government do net harm, while firms that respond to the free market do net good.
In Keynes' theory, there must be significant slack in the labor market before fiscal expansion is justified. Both conservative and some neoliberal economists question this assumption, unless labor unions or the government "meddle" in the free market, creating persistent supply-side or classical unemployment. Their solution is to increase labor-market flexibility, e.g., by cutting wages, busting unions, and deregulating business.
Deficit spending is not Keynesianism. Keynesianism recommends counter-cyclical policies to smooth out fluctuations in the business cycle. An example of a counter-cyclical policy is raising taxes to cool the economy and to prevent inflation when there is abundant demand-side growth, and engaging in deficit spending on labor-intensive infrastructure projects to stimulate employment and stabilize wages during economic downturns. Classical economics, on the other hand, argues that one should cut taxes when there are budget surpluses, and cut spending—or, less likely, increase taxes—during economic downturns. Keynesian economists believe that adding to profits and incomes during boom cycles through tax cuts, and removing income and profits from the economy through cuts in spending and/or increased taxes during downturns, tends to exacerbate the negative effects of the business cycle. This effect is especially pronounced when the government controls a large fraction of the economy, and is therefore one reason fiscal conservatives advocate a much smaller government.
"Multiplier effect" and interest rates
Two aspects of Keynes' model had implications for policy:
First, there is the "Keynesian multiplier", first developed by Richard F. Kahn in 1931. Exogenous increases in spending, such as an increase in government outlays, increases total spending by a multiple of that increase. A government could stimulate a great deal of new production with a modest outlay if:
- The people who receive this money then spend most on consumption goods and save the rest.
- This extra spending allows businesses to hire more people and pay them, which in turn allows a further increase consumer spending.
This process continues. At each step, the increase in spending is smaller than in the previous step, so that the multiplier process tapers off and allows the attainment of an equilibrium. This story is modified and moderated if we move beyond a "closed economy" and bring in the role of taxation: the rise in imports and tax payments at each step reduces the amount of induced consumer spending and the size of the multiplier effect.
Second, Keynes re-analyzed the effect of the interest rate on investment. In the classical model, the supply of funds (saving) determined the amount of fixed business investment. That is, since all savings was placed in banks, and all business investors in need of borrowed funds went to banks, the amount of savings determined the amount that was available to invest. To Keynes, the amount of investment was determined independently by long-term profit expectations and, to a lesser extent, the interest rate. The latter opens the possibility of regulating the economy through money supply changes, via monetary policy. Under conditions such as the Great Depression, Keynes argued that this approach would be relatively ineffective compared to fiscal policy. But during more "normal" times, monetary expansion can stimulate the economy.
Postwar Keynesianism
Keynes's ideas became widely accepted after WWII, and until the early 1970s, Keynesian economics provided the main inspiration for economic policy makers in Western industrialized countries.[14] Governments prepared high quality economic statistics on an ongoing basis and tried to base their policies on the Keynesian theory that had become the norm. In the early era of new liberalism and social democracy, most western capitalist countries enjoyed low, stable unemployment and modest inflation, an era called the Golden Age of Capitalism.
In terms of policy, the twin tools of post-war Keynesian economics were fiscal policy and monetary policy. While these are credited to Keynes, others, such as economic historian David Colander, argue that they are rather due to the interpretation of Keynes by Abba Lerner in his theory of Functional Finance, and should instead be called "Lernerian" rather than "Keynesian".[15]
Through the 1950s, moderate degrees of government demand leading industrial development, and use of fiscal and monetary counter-cyclical policies continued, and reached a peak in the "go go" 1960s, where it seemed to many Keynesians that prosperity was now permanent. In 1971, Republican US President Richard Nixon even proclaimed "we are all Keynesians now".[16] However, with the oil shock of 1973, and the economic problems of the 1970s, modern liberal economics began to fall out of favor. During this time, many economies experienced high and rising unemployment, coupled with high and rising inflation, contradicting the Phillips curve's prediction. This stagflation meant that the simultaneous application of expansionary (anti-recession) and contractionary (anti-inflation) policies appeared to be necessary, a clear impossibility. This dilemma led to the end of the Keynesian near-consensus of the 1960s, and the rise throughout the 1970s of ideas based upon more classical analysis, including monetarism, supply-side economics[16] and new classical economics. At the same time Keynesians began during the period to reorganize their thinking (some becoming associated with New Keynesian economics); one strategy, utilized also as a critique of the notably high unemployment and potentially disappointing GNP growth rates associated with the latter two theories by the mid-1980s, was to emphasize low unemployment and maximal economic growth at the cost of somewhat higher inflation (its consequences kept in check by indexing and other methods, and its overall rate kept lower and steadier by such potential policies as Martin Weitzman's share economy).[17]
Currently, multiple schools of economic thought exist that trace their legacy to Keynes, notably Neo-Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economics, and Post-Keynesian economics. Keynes' biographer Robert Skidelsky writes that the post-Keynesian school has remained closest to the spirit of Keynes' work in following his monetary theory and rejecting the neutrality of money.[18][19]
In the postwar era Keynesian analysis was combined with neoclassical economics to produce what is generally termed the "neoclassical synthesis", yielding Neo-Keynesian economics, which dominated mainstream macroeconomic thought. Though it was widely held that there was no strong automatic tendency to full employment, many believed that if government policy were used to ensure it, the economy would behave as neoclassical theory predicted. This post-war domination by Neo-Keynesian economics was broken during the stagflation of the 1970s. There was a lack of consensus among macroeconomists in the 1980s. However, the advent of New Keynesian economics in the 1990s, modified and provided microeconomic foundations for the neo-Keynesian theories. These modified models now dominate mainstream economics.
Post-Keynesian economists on the other hand, reject the neoclassical synthesis, and more generally, neoclassical economics applied to the macroeconomy. Post-Keynesian economics is a heterodox school which holds that both Neo-Keynesian economics and New Keynesian economics are incorrect, and a misinterpretation of Keynes's ideas. The Post-Keynesian school encompasses a variety of perspectives, but has been far less influential than the other more mainstream Keynesian schools.
Main theories
The two key theories of mainstream Keynesian economics are the IS-LM model of John Hicks, and the Phillips curve; both of these are rejected by Post-Keynesians.
It was with John Hicks that Keynesian economics produced a clear model which policy-makers could use to attempt to understand and control economic activity. This model, the IS-LM model is nearly as influential as Keynes' original analysis in determining actual policy and economics education. It relates aggregate demand and employment to three exogenous quantities, i.e., the amount of money in circulation, the government budget, and the state of business expectations. This model was very popular with economists after World War II because it could be understood in terms of general equilibrium theory. This encouraged a much more static vision of macroeconomics than that described above.
The second main part of a Keynesian policy-maker's theoretical apparatus was the Phillips curve. This curve, which was more of an empirical observation than a theory, indicated that increased employment, and decreased unemployment, implied increased inflation. Keynes had only predicted that falling unemployment would cause a higher price, not a higher inflation rate. Thus, the economist could use the IS-LM model to predict, for example, that an increase in the money supply would raise output and employment—and then use the Phillips curve to predict an increase in inflation.
Criticism
Monetarist criticism
One school began in the late 1940s with Milton Friedman. Instead of rejecting macro-measurements and macro-models of the economy, the monetarist school embraced the techniques of treating the entire economy as having a supply and demand equilibrium. However, because of Irving Fisher's equation of exchange, they regarded inflation as solely being due to the variations in the money supply, rather than as being a consequence of aggregate demand. They argued that the "crowding out" effects discussed above would hobble or deprive fiscal policy of its positive effect. Instead, the focus should be on monetary policy, which was considered ineffective by early Keynesians.
Monetarism had an ideological as well as a practical appeal: monetary policy does not, at least on the surface, imply as much government intervention in the economy as other measures. The monetarist critique pushed Keynesians toward a more balanced view of monetary policy, and inspired a wave of revisions to Keynesian theory.
New classical macroeconomics criticism
Another influential school of thought was based on the Lucas critique of Keynesian economics. This called for greater consistency with microeconomic theory and rationality, and particularly emphasized the idea of rational expectations. Lucas and others argued that Keynesian economics required remarkably foolish and short-sighted behavior from people, which totally contradicted the economic understanding of their behavior at a micro level. New classical economics introduced a set of macroeconomic theories which were based on optimising microeconomic behavior. These models have been developed into the Real Business Cycle Theory, which argues that business cycle fluctuations can to a large extent be accounted for by real (in contrast to nominal) shocks.
Austrian School criticism
Austrian economist Friedrich Hayek criticized Keynesian economic policies for what he called their fundamentally collectivist approach, arguing that such theories encourage centralized planning, which leads to malinvestment of capital, which is the cause of business cycles[20]. Hayek also argued that Keynes' study of the aggregate relations in an economy is fallacious, as recessions are caused by micro-economic factors. Hayek claimed that what starts as temporary governmental fixes usually become permanent and expanding government programs, which stifle the private sector and civil society.
Other Austrian school economists have also attacked Keynesian economics. Henry Hazlitt criticized, paragraph by paragraph, Keynes' General Theory.[21] Murray Rothbard accuses Keynesianism of having "its roots deep in medieval and mercantilist thought."[22]
Methodological disagreement and different results that emerge
Beginning in the late 1950s neoclassical macroeconomists began to disagree with the methodology employed by Keynes and his successors. Keynesians emphasized the dependence of consumption on disposable income and, also, of investment on current profits and current cash flow. In addition Keynesians posited a Phillips curve that tied nominal wage inflation to unemployment rate. To buttress these theories Keynesians typically traced the logical foundations of their model (using introspection) and buttressed their assumptions with statistical evidence.[23] Neoclassical theorists demanded that macroeconomics be grounded on the same foundations as microeconomic theory, profit-maximizing firms and utility maximizing consumers.[23]
The result of this shift in methodology produced several important divergences from Keynesian Macroeconomics:[23]
- Independence of Consumption and current Income (life-cycle permanent income hypothesis)
- Irrelevance of Current Profits to Investment (Modigliani-Miller theorem)
- Long run independence of inflation and unemployment (natural rate of unemployment)
- The inability of monetary policy to stabilize output (rational expectations)
- Irrelevance of Taxes and Budget Deficits to Consumption (Ricardian Equivalence)
Keynesian responses to the critics
The heart of the 'new Keynesian' view rests on microeconomic models that indicate that nominal wages and prices are "sticky," i.e., do not change easily or quickly with changes in supply and demand, so that quantity adjustment prevails. According to economist Paul Krugman, "while I regard the evidence for such stickiness as overwhelming, the assumption of at least temporarily rigid nominal prices is one of those things that works beautifully in practice but very badly in theory."[24] This integration is further spurred by the work of other economists which questions rational decision-making in a perfect information environment as a necessity for micro-economic theory. Imperfect decision making such as that investigated by Joseph Stiglitz underlines the importance of management of risk in the economy.
Over time, many macroeconomists have returned to the IS-LM model and the Phillips curve as a first approximation of how an economy works. New versions of the Phillips curve, such as the "Triangle Model", allow for stagflation, since the curve can shift due to supply shocks or changes in built-in inflation. In the 1990s, the original ideas of "full employment" had been modified by the NAIRU doctrine, sometimes called the "natural rate of unemployment." NAIRU advocates suggest restraint in combating unemployment, in case accelerating inflation should result. However, it is unclear exactly what the value of the NAIRU should be—or whether it even exists.
See also
- Functional finance
- Job guarantee
- Keynesian formula
- Microfoundations
- Military Keynesianism
- New Keynesian economics
- Post-Keynesian economics
- State capitalism
- Underconsumption
- 2008–2009 Keynesian resurgence
References
- ↑ Sullivan, Arthur; Steven M. Sheffrin (2003). Economics: Principles in action. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 0130630853.
- ↑ Chris Giles in London, Ralph Atkins in Frankfurt and Krishna Guha in Washington. "The undeniable shift to Keynes". The Financial Times. http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/c4cf37f4-d611-11dd-a9cc-000077b07658.html. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ↑ Blinder, Alan S. (2002). "Keynesian Economics". The Concise Encyclopedia of Economics. http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/KeynesianEconomics.html. Retrieved 2008-04-09
- ↑ Markwell, Donald (2006). John Maynard Keynes and International Relations: Economic Paths to War and Peace. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198292368
- ↑ Glasner, David (1997). "Attwood, Thomas (1783-1856)". In Glasner, David. Business Cycles and Depressions: An Encyclopedia. Taylor & Francis. p. 22. ISBN 0824009444. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=e1ZEPd_pQnoC&pg=PA22. Retrieved 2009-06-15
- ↑ Ohlin, Bertil (1937). "Some Notes on the Stockholm Theory of Savings and Investment". Economic Journal
- ↑ Dimand, Robert William (1988). The origins of the Keynesian revolution. Stanford: Stanford University Press. p. 117. ISBN 0804715254
- ↑ Keynes, John Maynard (1930). Treatise on Money. London: Macmillan. p. 90
- ↑ Nash, Robert T.; Gramm, William P. (1969). "A Neglected Early Statement the Paradox of Thrift". History of Political Economy 1 (2): 395–400. doi:10.1215/00182702-1-2-395. http://hope.dukejournals.org/cgi/pdf_extract/1/2/395.
- ↑ Robertson, John M. (1892). The Fallacy of Saving. http://www.archive.org/stream/fallacyofsavings00robe/fallacyofsavings00robe_djvu.txt.
- ↑ cf. General Theory, Ch.1,2
- ↑ "The General Glut Controversy". http://cepa.newschool.edu/het/essays/classic/glut.htm
- ↑ Keynes, John Maynard (1924). "The Theory of Money and the Foreign Exchanges". A Tract on Monetary Reform.
- ↑ Fletcher, Gordon (1989). The Keynesian Revolution and Its Critics: Issues of Theory and Policy for the Monetary Production Economy. Palgrave MacMillan. pp. xix — xxi, 88 , 189–191, 234–238, 256–261. ISBN 0312452608.
- ↑ "What eventually became known as textbook Keynesian policies were in many ways Lerner’s interpretations of Keynes's policies, especially those expounded in The Economics of Control (1944) and later in The Economics of Employment (1951). . . . Textbook expositions of Keynesian policy naturally gravitated to the black and white 'Lernerian' policy of Functional Finance rather than the grayer Keynesian policies. Thus, the vision that monetary and fiscal policy should be used as a balance wheel, which forms a key element in the textbook policy revolution, deserves to be called Lernerian rather than Keynesian." (Colander 1984, p. 1573)
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Lewis, Paul (August 15, 1976). "Nixon's Economic Policies Return to Haunt the G.O.P.". New York Times. http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=FB0717FE345E1A738DDDAC0994D0405B868BF1D3
- ↑ Blinder, Alan S. (1987). Hard Heads, Soft Hearts: Tough Minded Economics for a Just Society. New York: Perseus Books. pp. 65–66. ISBN 0201145197.
- ↑ Skidelsky 2009
- ↑ Financial markets, money and the real world, by Paul Davidson, pp. 88–89
- ↑ Hayek, Friedrich (1989). The Collected Works of F.A. Hayek. University of Chicago Press. p. 202. ISBN 978-0-226-32097-7.
- ↑ "The Failure of the 'New Economics': An Analysis of the Keynesian Fallacies". http://www.mises.org/books/failureofneweconomics.pdf
- ↑ Rothbard, Murray (1947). Spotlight on Keynesian Economics. Ludwig von Mises Institute. http://mises.org/story/2950
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Akerlof, George A. (2007). "The Missing Motivation in Macroeconomics". American Economic Review 97 (1): 5–36. doi:10.1257/aer.97.1.5.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul. "There's Something About Macro". http://web.mit.edu/krugman/www/islm.html
Further reading
- Blinder, Alan. "Keynesian Economics". Concise Encyclopedia of Economics. http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/KeynesianEconomics.html.
- Keynes, John Maynard (2004) [1919]. The Economic Consequences of the Peace. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers. ISBN 0765805294. http://socserv2.socsci.mcmaster.ca/~econ/ugcm/3ll3/keynes/peace.htm.
- Keynes, John Maynard (1933-12-31). "An Open Letter to President Roosevelt". New York Times. http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F70A11FB3C5513738DDDA80B94DA415B838FF1D3.
- Keynes, John Maynard (2007) [1936]. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0230004768. http://cepa.newschool.edu/het/essays/keynes/keynescont.htm.
- Lindahl, Erik (1954). "On Keynes' economic system". Economic Record 30: 19–32, 159–171. Especially up to p. 26. — This offers a compact summary of the Keynes equations and their interrelation.
- Donald Markwell, John Maynard Keynes and International Relations: Economic Paths to War and Peace, Oxford University Press, 2006.
- Traill, R.R. (2008). Problems with Economic Rationalism — Psychology, Green-issues, and Jobs. Melbourne: Ondwelle. http://www.ondwelle.com/OSM08.pdf. — Includes a more concise structured version of Lindahl's summary (in Section 2.1 + Appendix), — a discussion of the 2008 financial-crash, — and comments on J.L.Stein's generalization:-
- Stein, Jerome L. (1982). Monetarist, Keynesian & New classical economics. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0631129081.
- Gordon, Robert J. (1990). "What Is New-Keynesian Economics?". Journal of Economic Literature 28 (3): 1115–1171. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2727103.
- Hazlitt, Henry (1959). The Failure of the ‘New Economics’. An Analysis of the Keynesian Fallacies. Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand. http://www.mises.org/books/failureofneweconomics.pdf.
- Colander, David (December 1984). "Was Keynes a Keynesian or a Lernerian?". Journal of Economic Literature 22: 1571–79, argues for the influence of Abba Lerner's interpretation Keynes in "textbook" Keynesianism.
External links
- John Maynard Keynes,The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money,1936
- Works by John Maynard Keynes at Project Gutenberg
- Fonseca, Gonçalo L.. "The Keynesian Revolution". http://cepa.newschool.edu/het/essays/keynes/keynesrev.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-30.
- Why America Must have a Fiscal Stimulus Lawrence Summers, Harvard Kennedy School's Belfer Center
- "We are all Keynesians now" historic piece; macroeconomics in mass publications
- Donald Markwell, Keynes and Australia, Reserve Bank of Australia, 2000 [1]
- Alan Greenspan Speech Alan Greenspan blames Keynesian economics for debilitating the U.S. economy prior to the Presidency of Ronald Reagan.
- Family of Economics http://www.economicsfamily.com
- Norman, Reuben L. Jr. "Theories on the Great Depression: Harris, Sklar and Carlo: Secular Stagnation, Disaccumulation, Monopolies-Overproduction and the Long Waves". http://www.southerndomains.com/SouthernBanks/p5.htm.
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||||||||||||||