International Standard Serial Number
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is a unique eight-digit number used to identify a print or electronic periodical publication.[1] Periodicals published in both print and electronic form may have two separate ISSNs, a print ISSN (p-ISSN) and an electronic ISSN (e-ISSN or eISSN). The ISSN system was first drafted as an ISO international standard in 1971 and published as ISO 3297 in 1975.[2] The ISO subcommittee TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for the standard.
Contents |
Code format
The format of the ISSN is an eight digit number, divided by a hyphen into two four-digit numbers.[1] The last digit, which may be 0–9 or an X, is a check digit. The ISSN of the journal Hearing Research, for example, is 0378-5955, the check digit is 5.
To calculate the check digit, the following algorithm may be used:
- Calculate the sum of the first seven digits of the ISSN multiplied by its position in the number, counting from the right — that is, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, and 2, respectively:
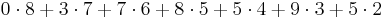
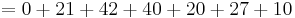
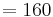 .
.
- The modulus 11 of this sum is then calculated: divide the sum by 11 and determine the remainder.
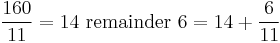 .
.
- If there is no remainder the check digit is 0, otherwise the remainder value is subtracted from 11 to give the check digit:
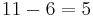
- 5 is the check digit.
- An upper case X in the check digit position indicates a check digit of 10.
To confirm the check digit, calculate the sum of all eight digits of the ISSN multiplied by its position in the number, counting from the right (if the check digit is X, then add 10 to the sum). The modulus 11 of the sum must be 0.
Code assignment
ISSN codes are assigned by a network of ISSN National Centres, usually located at national libraries and coordinated by the ISSN International Centre based in Paris. The International Centre is an intergovernmental organization created in 1974 through an agreement between UNESCO and the French government. The International Centre maintains a database of all ISSNs assigned worldwide, the ISDS Register (International Serials Data System) otherwise known as the ISSN Register. The ISSN Register contains ISSN codes and descriptions for more than one million periodicals[3] with around 50,000 new records added yearly.
Comparison to other identifiers
ISSN and ISBN codes are similar in concept, where ISBNs are assigned to individual books. An ISBN might be assigned for particular issues of a periodical, in addition to the ISSN code for the periodical as a whole. An ISSN, unlike the ISBN code, is an anonymous identifier associated with a periodical title, containing no information as to the publisher or its location. For this reason a new ISSN is assigned to a periodical each time it undergoes a major title change.
Since the ISSN applies to an entire periodical a new identifier, the Serial Item and Contribution Identifier, was built on top of it to allow references to specific volumes, articles, or other identifiable components (like the table of contents).
Availability
The ISSN Register is not freely available for interrogation on the web but is available by subscription. There are several routes to the identification and verification of ISSN codes for the general public.
- the print version of a periodical typically will include the ISSN code as part of the publication information
- most periodical websites contain ISSN code information
- derivative lists of publications will often contain ISSN codes; these can be found through on-line searches with the ISSN code itself or periodical title
- WorldCat permits searching their catalog by ISSN by entering "issn:"+ISSN code in the query field. One can also go directly to an ISSN's record by appending it to http://www.worldcat.org/ISSN/, e.g. http://www.worldcat.org/ISSN/1021-9749. This does not query the ISSN Register itself but rather shows whether any Worldcat library holds an item with the given ISSN.
Use in URNs
An ISSN can be encoded as a Uniform Resource Name, (URN) by prefixing it with "urn:issn:".[4] For example Rail could be referred to as "urn:issn:1534-0481". If the checksum digit is "X" then it is always encoded in uppercase in a URN.
See also
- ASIN (Amazon Standard Identification Number, a proprietary)
- CODEN (serial publication identifier currently used by libraries; replaced by the ISSN for new works)
- DOI (Digital Object Identifier)
- ISAN (International Standard Audiovisual Number)
- ISBN (International Standard Book Number)
- ISMN (International Standard Music Number)
- ISRC (International Standard Recording Code)
- ISWC (International Standard Musical Work Code)
- LCCN (Library of Congress Control Number)
- OCLC (Online Computer Library Center)
- SICI (Serial Item and Contribution Identifier)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "What is an ISSN?". ISSN International Center.
- ↑ ISSN International Center. (2008). "ISSN and ISO standards".
- ↑ The one million milestone was reached in 2001 according to the ISSN statistics information page. Retrieved 2005-07-17.
- ↑ Using The ISSN (International Serial Standard Number) as URN (Uniform Resource Names) within an ISSN-URN Namespace — RFC 3044
External links
- Search by title to find an ISSN
- ISSN International Centre
- ISSN Manual. Cataloging Part (pdf)
- What is an ISSN-L?
- United States Library of Congress: How U.S. publishers can obtain an ISSN
- British Library: Getting an ISSN in the U.K.
- Bibliothèque nationale de France: Getting an ISSN in France
- Deutsche Nationalbibliothek: Getting an ISSN in Germany
|
|||||||