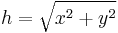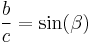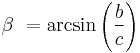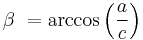Hypotenuse
.png)
A hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle. The length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
For example, if one of the other sides has a length of 3 meters (when squared, 9 m²) and the other has a length of 4 m (when squared, 16 m²), then their squares add up to 25 m². The length of the hypotenuse is the square root of this, or 5 m.
The word hypotenuse derives from the Greek ὑποτείνουσα (hypoteinousa), a combination of hypo- ("under") and teinein ("to stretch"). [1] The word ὑποτείνουσα was used for the hypotenuse of a triangle by Plato in the Timeus 54d and by many other ancient authors.
Contents |
Calculating the hypotenuse

Usually the length of the hypotenuse is calculated using the square root function derived from the Pythagorean theorem. Setting x = c1 and y = c2 to avoid subscripts:
In mathematical notation;
Many computer languages support the ISO C standard function hypot(x,y), which returns the value above. The function is designed not to fail where the straightforward calculation might overflow or underflow and can be slightly more accurate.
Some scientific calculators provide a function to convert from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates. This gives both the length of the hypotenuse and the angle the hypotenuse makes with the base line (c1 above) at the same time when given x and y. The angle returned will normally be that given by atan2(y,x).
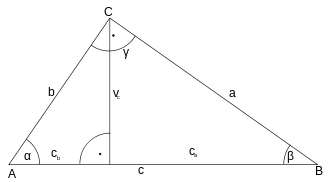
Properties

Orthographic projections:
- The length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the lengths of the orthographic projections of both catheti.
- The square of the length of a cathetus equals the product of the lengths of its orthographic projection on the hypotenuse times the length of this.
-
- b² = a · m
- c² = a · n
- Also, the length of a cathetus b is the proportional mean between the lengths of its projection m and the hypotenuse a.
-
- a/b = b/m
- a/c = c/n
Trigonometric rates
By means of trigonometric rates, can obtain the value of two acute angles, 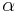 and
and 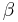 , of the right triangle.
, of the right triangle.
Known the length of the hypotenuse  and of the a cathetiy
and of the a cathetiy 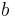 , the rate between both is:
, the rate between both is:
Therefore, the trigonometric inverse function is:
In which 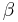 is the value of the opposite of the catheti
is the value of the opposite of the catheti 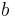 .
.
The adjoining angle of the catheti 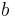 , will be
, will be 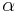 = 90º –
= 90º – 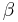
Also, can obtain the value of the angle 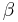 thru the equation:
thru the equation:
In which  is the other catheti.
is the other catheti.
See also
- Cathetus
- Triangle
- Space diagonal
- Nonhypotenuse number
- Taxicab geometry
- Trigonometry
Notes
- ↑ Schwartzman, Steven The Words of Mathematics, An Etymological Dictionary of Mathematical Terms used in English, published by the Mathematical Association of America. A folk etymology with no basis in Ancient Greek calls the hypotenuse a support in the manner of a prop or buttress derived from a combination of hypo- ("under") and tenuse ("side"), but tenuse does not mean "side". Anderson, Raymond (1947). Romping Through Mathematics. Faber. pp. 52.
References
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Hypotenuse" from MathWorld.