Hyena
| Hyenas Fossil range: 26–0 Ma Early Miocene-recent |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Brown hyena (Parahyaena brunnea) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Hyaenidae Gray, 1821 |
| Living Genera | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The Hyaenidae (pronounced /haɪˈɛnɨdiː/) is a mammalian family of order Carnivora. The Hyaenidae family, native to both African and Asian continents, consists of four living species, the Striped Hyena and Brown Hyena (genus Hyaena), the Spotted Hyena (genus Crocuta), and the Aardwolf (genus Proteles).
Contents |
Evolution
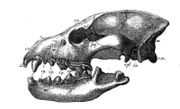
Hyenas seem to have originated 26 million years ago from arboreal ancestors bearing similarities to the modern Banded Palm Civet. Plioviverrops, one of the earliest hyenas, was a lithe civet-like creature that inhabited Eurasia 20-22 million years ago. Details from the middle ear and dental structure marked it as a primitive hyena. This genus proved successful, its descendants flourishing with more pointed jowls and racier legs, much as the Canidae had done in North America.
Fifteen million years ago, dog-like hyenas flourished, with 30 different species being identified. Unlike some of their modern descendants, these hyenas were not specialized bone-crushers, but were more nimble, wolf-like animals. The dog-like hyenas had canid-like molars, allowing them to supplement their carnivorous diet with vegetation and invertebrates.[1]
Five to seven million years ago, the hyenas were outcompeted by canids traveling from North America to Eurasia via the Bering land bridge.The ancestral aardwolves survived by having adapted themselves to an insectivorous diet to which few canids had specialized. Some hyenas evolved bone-crushing teeth, which allowed them to avoid competition with the canids, resulting in the hyenas eventually outcompeting a family of similarly built bone-crushers called "percrocutoids". The percrocutoids became extinct 7 million years ago, coinciding exactly with the rise of bone-crushing hyena species.
Unlike the canids who flourished in the newly colonized Eurasian continent, only one hyena species, the cheetah-like Chasmaporthetes, managed to cross to North America. It became extinct 1.5 million years ago.[1]
The peak diversity of the Hyenidae was during the Pleistocene, with 4 genera and 9 species of hyena.[2] The bone-crushing hyenas became the Old World's dominant scavengers, managing to take advantage of the amount of meat left over from the kills of sabre-toothed cats. One such species was Pachycrocuta, a 200 kg (440 lb) mega-scavenger that could crush elephant bones.[1] As the sabre-toothed cats began to die out and be replaced by short-fanged felids that were more efficient eaters, more hyenas began to hunt for themselves and began evolving into new species, the modern Spotted Hyena being among them.[3]
Genera of the Hyaenidae (extinct and recent)

The list follows McKenna and Bells Classification of Mammals for prehistoric genera (1997)[4] and Wozencraft (2005) in Wilson and Reeders Mammal Species of the World for extant genera.[5] The Percrocutids are, in contrast to McKenna and Bell's classification, not included as a subfamily into the Hyaenidae, but as the separate family Percrocutidae. Furthermore, the living brown hyena and its closest extinct relatives are not included in the genus Pachycrocuta, but in the genus Hyaena. The Protelinae (Aardwolves) are not treated as a separate subfamily, but included in the Hyaeninae.
- Family Hyaenidae
-
- †Tongxinictis (Middle Miocene of Asia)
- †Subfamily Ictitheriinae
- †Herpestides (Early Miocene of Africa and Eurasia)
- †Plioviverrops (including Jordanictis, Protoviverrops, Mesoviverrops; Early Miocene to Early Pliocene of Europe, Late Miocene of Asia)
- †Ictitherium (=Galeotherium; including Lepthyaena, Sinictitherium, Paraictitherium; Middle Miocene of Africa, Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Eurasia)
- †Thalassictis (including Palhyaena, Miohyaena, Hyaenictitherium, Hyaenalopex; Middle to Late Miocene of Asia, Late Miocene of Africa and Europe)
- †Hyaenotherium (Late Miocene to ?Early Pliocene of Eurasia)
- †Miohyaenotherium (Late Miocene of Europe)
- †Lychyaena (Late Miocene of Eurasia)
- †Tungurictis (Middle Miocene of Africa and Eurasia)
- †Proictitherium (Middle Miocene of Africa and Asia, Middle to Late Miocene of Europe)
- Subfamily Hyaeninae
- †Palinhyaena (Late Miocene of Asia)
- †Ikelohyaena (Early Pliocene of Africa)
- Hyaena (=Euhyaena, =Hyena; including brown Hyena, Pliohyaena, Pliocrocuta, Anomalopithecus) Early Pliocene (?Middle Miocene) to Recent of Africa, Late Pliocene (?Late Miocene) to Late Pleistocene of Europe, Late Pliocene to recent in Asia
- †Hyaenictis (Late Miocene of Asia?, Late Miocene of Europe, Early Pliocene (?Early Pleistocene) of Africa)
- †Leecyaena (Late Miocene and/or Early Pliocene of Asia)
- †Chasmaporthetes (=Ailuriaena; including Lycaenops, Euryboas; Late Miocene to Early Pleistocene of Eurasia, Early Pliocene to Late pliocene or Early Pleistocene of Africa, Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of North America)
- †Pachycrocuta (Pliocene and Pleistocene of Eurasia and Africa)
- †Adcrocuta (Late Miocene of Eurasia)
- Crocuta (=Crocotta; including Eucrocuta; Late Pliocene to recent of Africa, Late Pliocene to Late Pleistocene of Eurasia)
- Subfamily Protelinae
- Proteles (=Geocyon; Pleistocene to Recent of Africa)
-
Appearance

Although hyenas bear some physical resemblance to canids, they make up a separate biological family that is most closely related to Herpestidae (the family of mongooses and meerkats), thereby falling within the Feliformia. All species have a distinctly bear-like gait, due to their front legs being longer than their back legs. The Aardwolf, Striped Hyena, and Brown Hyena have striped pelts and manes lining the top of their necks which erect when frightened. The Spotted Hyena's fur is considerably shorter and spotted rather than striped.
Teeth
Spotted Hyenas and, to a lesser extent, Striped and Brown Hyenas, have powerful carnassial teeth adapted for cutting flesh and premolars for crushing bone. Spotted Hyenas have a strong bite proportional to their size, but the view that they have the strongest bite is a myth; and a number of other animals (including the Tasmanian devil) are proportionately stronger.[6][7] The Aardwolf has greatly reduced cheek teeth, sometimes absent in the adult, but otherwise has the same dentition as the other three species.[8] The dental formula for all hyena species is: 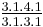
Labiolingually, their mandibles are much stronger at the canine teeth than in canids, reflecting the fact that hyenas crack bones with both their anterior dentition and premolars, unlike canids which do so with their post-carnassial molars.[9] Like felids, hyenas lack the rearward molars of canids and vivverids. By organising their teeth so that the bone-crushing premolars do not interfere with the meat-slicing carnassials to the rear, hyenas can crush bone without blunting the carnassials' blades.[1]
Ecology
Spotted Hyena societies are more complex than those of other carnivorous mammals and have been reported to be remarkably similar to those of cercopithecine primates in respect to group size, structure, competition, and cooperation.[10] One indication of hyena intelligence is that they will move their killed prey closer together to protect them from scavengers. Another indication is their strategic hunting methods.[11]
Reproduction
The majority of hyena species show little sexual dimorphism, with males being only slightly larger than the females. The Spotted Hyena is an exception to this, with females larger than males. One unusual feature of the Spotted Hyena is that females have an enlarged clitoris, called a pseudo-penis, demi-penis, or sometimes mistakenly referred to as a nanophallus. Female hyenas give birth, copulate, and urinate through their protruding genitalia, which stretches to allow the male penis to enter for copulation; it also stretches during birth. The anatomical position of the genitalia gives females complete control over which males are allowed to mate with them.
Researchers originally thought that one cause of this characteristic of the genitals was androgens that were introduced to the fetus very early on in its development. However, it was discovered that when the androgens were held back from the female fetus, the development of her genitalia was not altered.[12] Spotted Hyenas have a matriarchal social structure[13] that some biologists speculate evolved because it is in the best interests of the female hyena to dominate the male hyena as it provides no assistance in rearing the cubs.[13]
Marking and excretion
All species excrete an oily, yellow substance from their anal glands onto objects to mark their territories. When scent marking the anal pouch is turned inside out, or everted. Hyenas also do this as a submissive posture to more dominant hyenas. Genitals, the anal area and the anal glands are sniffed during greeting behavior in which each hyena lifts its leg and allows the other to sniff its anal sacks and genitals. All four species maintain latrines far from the main denning area where dung is deposited. Scent marking is also done by scraping the ground with the paws, which deposits scent from glands on the bottoms of the feet. Hyenas do not raise their legs when urinating as male or dominant canids do.[14]
Hyenas can carry strains of rabies, but do not develop symptoms.[15][16]
Habitat and distribution
Three of the four species of hyena are restricted to sub-Saharan Africa, where they live in environments such as savannah, bushland and desert. The fourth species, the Striped Hyena, is found in northern and eastern Africa as well as in Asia from the Middle East to India.
Dietary habits
Except for the aardwolf, all living hyena species are hunters and scavengers.[17]
Unlike the canids, hyenas do not regurgitate or carry back food in their stomachs for their young[14] because of the speed with which the food is digested by the adults.[1]
They have extremely strong jaws in relation to their body size and have a very powerful digestive system with highly acidic fluids, making them capable of eating and digesting their entire prey, including skin, teeth, horns and bones. Hair and hooves are usually regurgitated. Because their digestive system deals very well with bacteria, they have no aversion to and readily eat carrion.
The Spotted Hyena is primarily a predator, unlike some of its cousins. Spotted Hyenas are successful pack hunters of small to large sized ungulates, and are the most abundant carnivores in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Because the aardwolf is a specialized feeder of termites, it lacks the size and physical power of its cousins.
In culture
Many cultures, including those in Africa, have historically viewed the hyena negatively, associating them with gluttony, uncleanliness and cowardice.
Part of their bad reputation may stem from the hyena's tendency to scavenge graves for food. They are one of the few creatures naturally suited for this, due to their ability to devour and digest every part of a carcass, including bone.[2] The word hyena is derived from the Greek hyaina, meaning "pig", and has a long association with cruelty, treachery and greed.[18]
In Malawi, in the local language large hyenas reputed to be a man-eater were called lipwereri and the ordinary hyena was called a fisi.[19] The Bouda is a mythical tribe reputed to house members able to transform into hyenas.[20] Belief in "Werehyenas" is so entrenched within the traditional lore of the Bornu people of north-eastern Nigeria, that their language even contains a special word, bultungin, which translates as "I change myself into a hyena".[21]
The haunting laughter-like calls of the Spotted Hyena inspired the idea in local cultures that they could imitate human voices and call their victims by name. Hyenas are also associated with divination and sometimes thought of as tools of demons and witches. In African folklore, witches and sorcerers are thought to ride hyenas or even turn into them.
Early naturalists thought hyenas were hermaphrodites or commonly practiced homosexuality, largely due to the female Spotted Hyena's unique urogenital system. According to early writings such as Ovid's Metamorphoses and the Physiologus, the hyena continually changed its sex and nature from male to female and back again. In Paedagogus, Clement of Alexandria noted that the hyena (along with the hare) was "quite obsessed with sexual intercourse." Many Europeans associated the hyena with sexual deformity, prostitution and deviant sexual behavior.
Hyenas (usually "Laughing Hyenas") have been used in animated movies many times as well as having been rendered in live action films, commonly cast as hysterical and unhinged villains. Examples include Shenzi, Banzai and Ed from the Disney animated film The Lion King, Dick and Bo from Kimba the White Lion, one ball-playing individual in Bedknobs and Broomsticks, Harley Quinn's pets, Bud and Lou, and the laughing Hyena in Lady and the Tramp.
In the 2009 Disneynature film The Crimson Wing, the Hyena is seen as one of the villains as it viciously and violently kills one of the flamingos that tries to escape along with all the other flamingos. In the film, the Hyena, along with the Storks are compared as classic storybook and Disney villains.
See also
- Crocotta
- Hyena butter
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Macdonald, David (1992). The Velvet Claw. New York: Parkwest. p. 256. ISBN 0563208449.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Hyaenidae". http://www.lioncrusher.com/family.asp?family=Hyaenidae. Retrieved 2007-05-31.
- ↑ Denis-Huot, Christine & Denis-Huot, Michel (2003). The Art of being a Lion. p. 224. ISBN 158663707X.
- ↑ Malcolm C. McKenna, Susan K. Bell: Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level in Columbia University Press, New York 1997, 631 Seiten, ISBN 0-231-11013-8
- ↑ Wozencraft, W. Christopher (16 November 2005). "Order Carnivora (pp. 532-628)". In Wilson, Don E., and Reeder, DeeAnn M., eds. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2 vols. (2142 pp.). pp. 532–548. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.bucknell.edu/msw3.
- ↑ Ancient Worlds News - Marsupial has the deadliest bite - 04/04/2005.
- ↑ Wroe, S, McHenry, C, and Thomason, J. (2005). "Bite club: comparative bite force in big biting mammals and the prediction of predatory behaviour in fossil taxa.". Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 272 (1563): 619–625. doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2986. PMID 15817436.
- ↑ Richardson, Philip K.R. & Bearder, Simon (1984). Macdonald, D.. ed. The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File. pp. 154–159. ISBN 0-87196-871-1.
- ↑ Therrien, François (2005). "Mandibular force profiles of extant carnivorans and implications for the feeding behaviour of extinct predators". Journal of Zoology 267 (3): 249–270. doi:10.1017/S0952836905007430.
- ↑ Holekamp, Jay; Sharleen T. Sakai & Barbara L. Lundrigan (2007). "The spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) as a model system for study of the evolution of intelligence". Journal of Mammalogy 88 (3): 545–554. doi:10.1644/06-MAMM-S-361R1.1.
- ↑ Lind, Hans. "Bogen om Dyrepsykologi".
- ↑ Meredith, Dennis (2002). "The Paradoxical Predator". Duke Magazine 88 (3). http://www.dukemagazine.duke.edu/dukemag/issues/030402/predator.html.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Social Hierarchies Feeding Behavior in the Spotted Hyena.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Kruuk, Hans (1972). The Spotted Hyena: A study of predation and social behavior. New York: Parkwestk. p. 335. ISBN 0563208449.
- ↑ Jordan Lite (2008-10-08). "Hyenas Carry Rabies but Don't Develop Symptoms.". Scientific American. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=hyenas-carry-rabies-but-d. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Hyenas able to laugh off the threat of rabies". Edinburgh Evening News. 2001-12-11. http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_7832/is_2001_Dec_11/ai_n32991633/?tag=content;col1. Retrieved 2010-04-25.
- ↑ Rohland, Nadin; Pollack, Joshua L.; Nagel, Doris; Beauval, Cédric; Airvaux, Jean; Pääbo, Svante; Hofreiter, Michael (2005). "The population history of extant and extinct hyenas". Molecular Biology and Evolution 22 (12): 2435–2443. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi244. PMID 16120805. http://mbe.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/22/12/2435.
- ↑ Online etymology dictionary: Hyena
- ↑ Clarke, James (1969). Man is the prey: an investigation into the motives and habits of man's natural enemies. p. 163. ISBN 233960872.
- ↑ "The spotted hyena from Aristotle to the Lion King: reputation is everything - In the Company of Animals". Stephen E. Glickman. http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-17909878.html. Retrieved 2007-05-22.
- ↑ lycaon
External links
- IUCN Conservation Union Hyaendiae Specialist Group
- Hyena: Wildlife summary from the African Wildlife Foundation
- Robin M. Weare's Hyena pages
- A mechanism for virilization of female spotted hyenas in utero
- evolution of the family
- Quick Guide - Spotted hyena (deals with intelligence and social interaction)
- Hyenas- Sociable and Smart
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
