Heterotroph
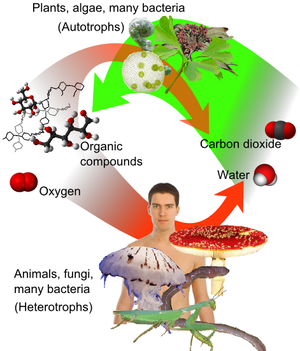
Overview of cycle between
autotrophs and
heterotrophs.
A heterotroph (Greek ἕτερος heteros = "another", "different" and τροφή trophe = "nutrition", "growth") is an organism that uses organic carbon for growth by consuming other organisms.[1] This contrasts with autotrophs, such as plants, which can directly use sources of energy such as light to produce organic substrates from carbon dioxide.
Ecology
Heterotrophs function as consumers in food chains: they obtain organic carbon by eating other heterotrophs or autotrophs. They break down complex organic compounds that are produced by autotrophs.
All animals are heterotrophic, as well as fungi and many bacteria. Some animals, such as corals, form symbiotic relationships with autotrophs and obtain organic carbon in this way. Furthermore, some parasitic plants have also turned fully or partially heterotrophic, while so-called carnivorous plants consume animals to augment their nitrogen supply while remaining autotrophic.
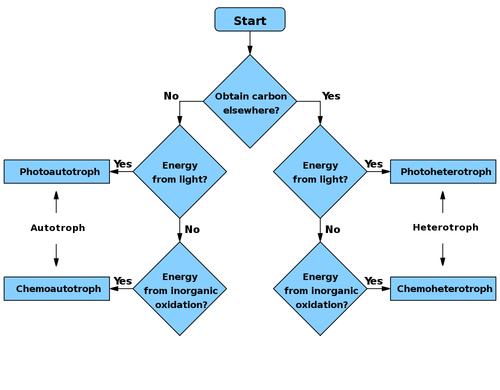
Flowchart to determine if a species is
autotroph, heterotroph, or a subtype
Biologists distinguish two types of heterotroph:
- photoheterotroph — obtains energy from light, but needs carbon in an organic form for growth. These are mostly certain kinds of bacteria.(Plants are photoautotrophs — not heterotrophs at all.)
- chemoheterotroph — needs an organic source of carbon for both energy source and growth. All animals and fungi are chemoheterotrophs.
Organotrophs and Lithotrophs
These terms refer to the chemical reactions that are involved in biosynthetic processes or respiration. Phototrophs and chemotrophs can be either lithotrophic or organotrophic.
- Lithotrophs are either Bacteria or Archaea that feed off of minerals, sometimes near an undersea vent.
- Organotrophs feed off of organic substances. All animals are organoheterotrophs. (All plants are organoautotrophs.)
See also
- Primary nutritional groups
- Auxotrophy
- Saprotrophic nutrition
References
|
Feeding behaviours |
|
| Carnivores |
|
adult
|
Hematophagy · Insectivore · Lepidophagy · Man-eater · Molluscivore · Mucophagy · Myrmecophagy · Ophiophagy · Piscivore · Avivore · Spongivore · Vermivore
|
|
|
reproductive
|
Oophagy · Ovophagy · Paedophagy · Placentophagy · Breastfeeding · Weaning |
|
|
cannibalistic
|
|
|
 |
|
| Herbivores |
Folivore · Frugivore · Graminivore · Granivore · Nectarivore · Palynivore · Xylophagy · Osteophagy
|
|
| Others |
|
|
| Methods |
Apex predator · Bottom feeding · Browsing · Hypercarnivore · Filter feeding · Grazing · Kleptoparasitism · Scavenging · Trophallaxis |
|
| Predation · Antipredator adaptation · Carnivorous plant · Carnivorous fungus · Carnivorous protist · Category:Eating behaviors |
|
|
Modelling ecosystems - trophic components |
|
| General |
Abiotic component · Abiotic stress · Behaviour · Biogeochemical cycle · Biomass · Biotic component · Biotic stress · Carrying capacity · Competition · Ecosystem · Ecosystem ecology · Ecosystem model · Keystone species · List of feeding behaviours · Metabolic theory of ecology · Productivity
|
 |
|
| Producers |
|
|
| Consumers |
Apex predator · Bacterivore · Carnivores · Chemoorganotroph · Foraging · Generalist and specialist species · Herbivores · Heterotroph · Heterotrophic nutrition · Mesopredator release hypothesis · Omnivores · Optimal foraging theory · Predation
|
|
| Decomposers |
Chemoorganoheterotrophy · Decomposition · Detritivores · Detritus
|
|
| Microorganisms |
Bacteriophage · Lithoautotroph · Lithotrophy · Microbial food web · Microbial loop · Microbial metabolism · Phage ecology
|
|
| Food webs |
Cold seeps · Hydrothermal vents · Intertidal · Kelp forests · Lakes · North Pacific Subtropical Gyre · Rivers · San Francisco Estuary · Soil · Tidal pool
|
|
| Trophic effects |
Ascendency · Bioaccumulation · Biomagnification · Cascade effect · Competitive exclusion principle · Copiotrophs · Dominance · Ecological efficiency · Ecological network · Ecological pyramid · Ecological succession · Energy quality · Energy Systems Language · f-ratio · Feed conversion ratio · Feeding frenzy · Mesotrophic soil · Oligotroph · Paradox of the plankton · Trophic cascade · Trophic level · Trophic mutualism · Trophic state index
|
|
| Defense/counter |
Antipredator adaptations · Herbivore adaptations to plant defense · Plant defense against herbivores · Predator avoidance in schooling fish
|
|
|
|
|
Modelling ecosystems - other components |
|
| Population ecology |
Abundance · Allee effect · Depensation · Ecological yield · Effective population size · Intraspecific competition · Logistic function · Malthusian growth model · Maximum sustainable yield · Overpopulation in wild animals · Overexploitation · Population cycle · Population dynamics · Population modeling · Population size · Predator–prey equations · Recruitment · Resilience · Small population size · Stability
|
 |
|
| Species |
Biodiversity · Density-dependent inhibition · Ecological effects of biodiversity · Ecological extinction · Endemic species · Flagship species · Gradient analysis · Indicator species · Introduced species · Invasive species · Latitudinal gradients in species diversity · Minimum viable population · Occupancy-abundance relationship · Population viability analysis · Rapoport's rule · Relative abundance distribution · Relative species abundance · Species diversity · Species homogeneity · Species richness · Species distribution · Species-area curve · Umbrella species
|
|
| Species interaction |
|
|
| Spatial ecology |
Cross-boundary subsidy · Ecocline · Ecotone · Ecotype · Disturbance · Edge effect · Foster's rule · Habitat fragmentation · Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis · Island biogeography · Landscape ecology · Landscape epidemiology · Landscape limnology · Metapopulation · Patch dynamics · Source–sink dynamics
|
|
| Niche |
Ecological niche · Ecological trap · Ecosystem engineer · Environmental niche modelling · Guild · Habitat · Limiting similarity · Niche apportionment models · Niche differentiation
|
|
| Other networks |
Assembly rules · Bateman's principle · Bioluminescence · Ecological collapse · Ecological debt · Ecological deficit · Ecological energetics · Ecological indicator · Ecological threshold · Ecosystem diversity · Emergence · Kleiber's law · Liebig's law of the minimum · Marginal value theorem · Thorson's rule · Xerosere
|
|
| Other |
Allometry · Alternative stable state · Balance of Nature · Biological data visualization · Biogeography · Constructal theory · Ecocline · Ecological economics · Ecological footprint · Ecological forecasting · Ecological humanities · Ecological stoichiometry · Ecopath · Ecosystem based fisheries · Endolith · Evolutionary ecology · Functional ecology · Industrial ecology · Macroecology · Microecosystem · Natural environment · Systems ecology · Theoretical ecology
|
|
| List of ecology topics |
|
|
|




