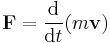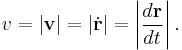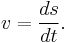Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity (the rate of change of its position); it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero .
Like velocity, speed has the dimensions of a length divided by a time; the SI unit of speed is the meter per second, but the most usual unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometer per hour or, in the USA and the UK, miles per hour.
The fastest possible speed at which energy or information can travel, according to special relativity, is the speed of light in vacuum c = 299,792,458 meters per second, approximately 1079 million kilometers (671 million miles) per hour. Matter cannot quite reach the speed of light, as this would require an infinite amount of energy.
Definition
The speed v is defined as the magnitude of the velocity v, that is the derivative of the position r with respect to time:
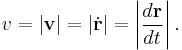
If s is the length of the path traveled until time t, the speed equals the time derivative of s:
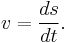
In the special case where the velocity is constant (that is, constant speed in a straight line) this can be simplified to v=s/t. The average speed over a finite time interval is the total distance traveled divided by the time duration.
Expressed in graphical language, the slope of a tangent line of a distance-time graph is the instantaneous speed, and the slope of a chord line of distance-time graph is the average speed over the time interval between the ends of the chord.
Units
Units of speed include:
- Meters per second (symbol m s−1 or m/s), the SI derived unit;
- Kilometers per hour (symbol km/h);
- Miles per hour (symbol mph);
- Knots (nautical miles per hour, symbol kn or kt);
- Feet per second (symbol fps or ft/s);
- Mach number, speed divided by the speed of sound;
- The speed of light in vacuum (symbol c) is one of the natural units:
- c = 299,792,458 m/s.
Conversions between common units of speed
|
m/s |
km/h |
mph |
knot |
ft/s |
| 1 m/s = |
1 |
3.6 |
2.236936 |
1.943844 |
3.280840 |
| 1 km/h = |
0.277778 |
1 |
0.621371 |
0.539957 |
0.911344 |
| 1 mph = |
0.44704 |
1.609344 |
1 |
0.868976 |
1.466667 |
| 1 knot = |
0.514444 |
1.852 |
1.150779 |
1 |
1.687810 |
| 1 ft/s = |
0.3048 |
1.09728 |
0.681818 |
0.592484 |
1 |
(Values in bold face are exact.)
Examples of different speeds
- Speed of a common snail = 0.001 m/s; 0.004 km/h; 0.002 mph (1 millimeter per second).
- A brisk walk = 1.7 m/s; 6.1 km/h; 3.8 mph (5.5 feet per second).
- Olympic sprinters (average speed over 100 metres) = 10 m/s; 36 km/h; 22 mph.
- Speed limit on a French autoroute = 36 m/s; 130 km/h; 80 mph.
- Taipei 101 observatory elevator = 1010 m/min ; 16.7 m/s ; 60.6 km/h; 37.6 mph
- Cruising speed of a Boeing 747-8 = 290 m/s; 1050 km/h; 650 mph; (Mach 0.85)
- The speed of sound in dry air at sea-level pressure and 20 °C (293 kelvin) = 343 ms-1 ≈ 1235 km/h ≈ 768 mph ( = Mach 1 by definition).
- Muzzle velocity of an AK47 assault rifle = 710 m/s; 2,600 km/h; 1,600 mph.
- Muzzle velocity of a paintball marker = 90 m/s; 320 km/h; 200 mph.
- Official flight airspeed record = 980 m/s; 3,530 km/h; 2,194 mph.
- Escape velocity on Earth: 11.2 km/s; 40,000 km/h; 25,000 mph
- Space shuttle on re-entry = 7,800 m/s; 28,000 km/h; 17,500 mph.
- Average orbital speed of planet Earth = 29,783 m/s; 107,218 km/h; 66,623 mph.
- Speed of light in vacuum (symbol c) 299,792,458 m/s (exactly, by definition of meter).
See also
- Air speed
- Land speed
- List of vehicle speed records
- Speedometer
- Typical projectile speeds
- V speeds
References
- Richard P. Feynman, Robert B. Leighton, Matthew Sands. The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Volume I, Section 8-2. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts (1963). ISBN 0-201-02116-1.