Centrosome

(1) nucleolus
(2) nucleus
(3) ribosomes (little dots)
(4) vesicle
(5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
(6) Golgi apparatus
(7) Cytoskeleton
(8) smooth ER
(9) mitochondria
(10) vacuole
(11) cytoplasm
(12) lysosome
(13) centrioles within centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. It was discovered by Edouard Van Beneden in 1883 [1] and was described and named in 1888 by Theodor Boveri.[2] The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells.[3] Fungi and plants use other MTOC structures to organize their microtubules.[4][5] Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not necessary.[6]
Centrosomes are composed of two orthogonally arranged centrioles surrounded by an amorphous mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring[7] including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based on a nine triplet microtubule assembled in a cartwheel structure, and contains centrin, cenexin and tektin.[8]
Contents |
Roles of the centrosome
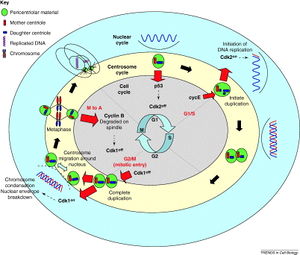
Centrosomes are often associated with the nuclear membrane during interphase of the cell cycle. In mitosis the nuclear membrane breaks down and the centrosome nucleated microtubules can interact with the chromosomes to build the mitotic spindle.
The mother centriole, the one that was inherited from the mother cell, also has a central role in making cilia and flagella.[8]
The centrosome is copied only once per cell cycle so that each daughter cell inherits one centrosome, containing two centrioles. The centrosome replicates during the S phase of the cell cycle. During the prophase of mitosis, the centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell. The mitotic spindle then forms between the two centrosomes. Upon division, each daughter cell receives one centrosome. Aberrant numbers of centrosomes in a cell have been associated with cancer. Doubling of a centrosome is similar to DNA replication in two respects: the semiconservative nature of the process and the action of cdk2 as a regulator of the process.[9] But the processes are essentially different in that centrosome doubling does not occur by template reading and assembly. The mother centriole just aids in the accumulation of materials required for the assembly of the daughter centriole.[10]
Interestingly, centrosomes are not required for the progression of mitosis. When the centrosomes are irradiated by a laser, mitosis proceeds normally with a morphologically normal spindle. Moreover, development of the fruit fly Drosophila is largely normal when centrioles are absent due to a mutation in a gene required for their duplication.[11] In the absence of the centrosome the microtubules of the spindle are focused by motors allowing the formation of a bipolar spindle. Many cells can completely undergo interphase without centrosomes.[8]
Although centrosomes are not required for mitosis or survival of the cell, they are required for survival of the organism. Acentrosomal cells lack radial arrays of astral microtubules. They are also defective in spindle positioning and in ability to establish a central localization site in cytokinesis. The function of centrosome in this context is hypothesized to ensure the fidelity of cell division as it is not necessary but greatly increases the efficacy. Some cell types arrest in the following cell cycle when centrosomes are absent. This is not a universal phenomenon.
When the nematode C. elegans egg is fertilized the sperm delivers a pair of centrioles. These centrioles will form the centrosomes which will direct the first cell division of the zygote and this will determine its polarity. It is not yet clear whether the role of the centrosome in polarity determination is microtubule dependent or independent.
Evolution of the centrosome
The evolutionary history of the centrosome and the centriole has been traced for some of the signature genes, e.g. the centrins[3]. Centrins participate in calcium signaling and are required for centriole duplication.[12] There exist two main subfamilies of centrins, both of which are present in the early-branching eukaryote Giardia intestinalis. Centrins have therefore been present in the common ancestor of eukaryotes. Conversely, they have no recognizable homologs in archea and bacteria and are thus part of the "eukaryotic signature genes." Although there are studies on the evolution of the centrins and centrioles[3],[13] no studies have been published on the evolution of the pericentriolar material.
It is evident that some parts of the centrosome are highly diverged in the model species Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. For example, both species have lost one of the centrin subfamilies that are usually associated with centriole duplication. Drosophila melanogaster mutants that lack centrosomes can even develop to morphologically normal adult flies, which then die shortly after birth because their sensory neurons lack cilia.[11] Thus, these flies have evolved functionally redundant machinery, which is independent of the centrosomes.
Centrosome Associated Nucleotides
Research in 2006[14] indicated that centrosomes from Surf clam eggs contain RNA sequences. The sequences identified were found in "few to no" other places in the cell, and do not appear in existing genome databases. One identified RNA sequence contains a putative RNA polymerase, leading to the hypothesis of an RNA based genome within the centrosome. However, subsequent research has shown that centrosome do not contain their own DNA-based genomes. While it was confirmed that RNA molecules associate with centrosomes, the sequences have still been found within the nucleus. Furthermore, centrosomes can form de novo after having been removed (e.g. by laser irradiation) from normal cells.[13]
References
- ↑ PMID 12226736 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Boveri, Theodor (1888). Zellen-Studien II: Die Befruchtung und Teilung des Eies von Ascaris megalocephala.. Jena: Gustav Fischer Verlag. http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/29952.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 PMID 17977464 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 12224551 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 15473833 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 16546079 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 1967194 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 PMID 11567874 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 11371338 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 17463247 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ 11.0 11.1 PMID 16814722 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 12176356 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ 13.0 13.1 PMID 19196504 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 16754862 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||