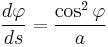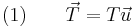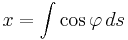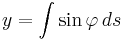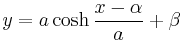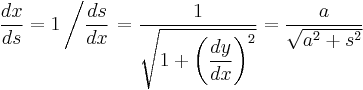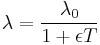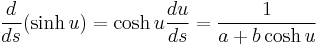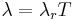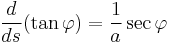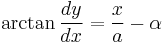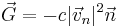Catenary

In physics and geometry, the catenary is the curve that an idealised hanging chain or cable assumes when supported at its ends and acted on only by its own weight. The curve is the graph of the hyperbolic cosine function, and has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola (though mathematically quite different). Its surface of revolution, the catenoid, is a minimal surface and is the shape assumed by a soap film bounded by two parallel circular rings.
Contents |
History
The word catenary is derived from the Latin word catena, which means "chain". Huygens first used the term catenaria in a letter to Leibniz in 1690. However, Thomas Jefferson is usually credited with the English word catenary.[1] The curve is also called the "alysoid," "chainette."[2], or, particularly in the material sciences, "funicular."[3]
It is often stated[4] that Galileo thought that the curve followed by a hanging chain is a parabola. A careful reading of his book Two new sciences[5] shows this to be an oversimplification. Galileo discusses the catenary in two places; in the dialog of the Second Day he states that a hanging chain resembles a parabola. But later, in the dialog of the Fourth Day, he gives more details, and states that a hanging cord is approximated by a parabola, correctly observing that this approximation improves as the curvature gets smaller and is almost exact when the elevation is less than 45o. That the curve followed by a chain is not a parabola was proven by Joachim Jungius (1587–1657) and published posthumously in 1669.[6][7]
The application of the catenary to the construction of arches is due to Robert Hooke, who discovered it in the context of the rebuilding of St Paul's Cathedral,[8] possibly having seen Huygens' work on the catenary. (Some much older arches are also approximate catenaries.)
In 1671, Hooke announced to the Royal Society that he had solved the problem of the optimal shape of an arch, and in 1675 published an encrypted solution as a Latin anagram[9] in an appendix to his Description of Helioscopes,[10] where he wrote that he had found "a true mathematical and mechanical form of all manner of Arches for Building." He did not publish the solution of this anagram[11] in his lifetime, but in 1705 his executor provided it as Ut pendet continuum flexile, sic stabit contiguum rigidum inversum, meaning "As hangs a flexible cable so, inverted, stand the touching pieces of an arch."
In 1691 Gottfried Leibniz, Christiaan Huygens, and Johann Bernoulli derived the equation in response to a challenge by Jakob Bernoulli. David Gregory wrote a treatise on the catenary in 1697.[7]
Euler proved in 1744 that the catenary is the curve which, when rotated about the x-axis, gives the surface of minimum surface area (the catenoid) for the given bounding circle.[2]
The inverted catenary arch
.jpg)


Hooke discovered that the catenary is the ideal curve for an arch of uniform density and thickness which supports only its own weight. When the centerline of an arch is made to follow the curve of an up-side-down (i.e. inverted) catenary, the arch endures almost pure compression, in which no significant bending moment occurs inside the material. If the arch is made of individual elements (e.g., stones) whose contacting surfaces are perpendicular to the curve of the arch, no significant shear forces are present at these contacting surfaces. (Shear stress is still present inside each stone, as it resists the compressive force along the shear sliding plane.) The thrust (including the weight) of the arch at its two ends is tangent to its centerline.

Catenary arches are often used in the construction of kilns. In this construction technique, the shape of a hanging chain of the desired dimensions is transferred to a form which is then used as a guide for the placement of bricks or other building material.[13][14]
However the conditions for a catenary to be the ideal arch are almost never fulfilled: arches usually support more than their own weight, and on the rare occasions when they are freestanding they are sometimes not of uniform thickness. The ideal shape for an arch supporting a large weight is more like a parabola than a catenary. As a result, there are very few arches that have been deliberately built as catenaries, though there are quite a few incorrect claims that various arches are catenaries.

The Gateway Arch in Saint Louis, Missouri, United States is sometimes said to be an (inverted) catenary, but this is incorrect[15]. It is close to a more general curve called a flattened catenary, with equation y=Acosh(Bx). (A catenary would have AB=1.) A catenary is the ideal shape for a freestanding arch of constant thickness, but the gateway arch is not of constant thickness as it gets narrower near the top. According the U.S. National Historic Landmark nomination for the arch, it is a "weighted catenary" instead. Its shape corresponds to the shape that a weighted chain, having lighter links in the middle, would form.[16]
Simple suspension bridges

Free-hanging chains follow the catenary curve, but suspension bridge chains or cables do not hang freely since they support the weight of the bridge. In most cases the weight of the cable is negligible compared with the weight being supported. When the force exerted is uniform with respect to the length of the chain, as in a simple suspension bridge, the result is a catenary.

When the force exerted is uniform with respect to horizontal distance, as in a suspension bridge, the result is a parabola.[17]
When suspension bridges are constructed, the suspension cables initially sag as the catenary curve, before being tied to the deck below, and then gradually assume a parabolic curve as additional connecting cables are tied to connect the main suspension cables with the bridge deck below.
Anchoring of marine objects
The catenary form given by gravity is taken advantage of in its presence in heavy anchor rodes. An anchor rode (or anchor line) usually consists of chain and/or cable. Anchor rodes are used by ships, oilrigs, docks, wind turbines and other marine assets which must be anchored to the seabed.
Particularly with larger vessels, the catenary curve given by the weight of the rode presents a lower angle of pull on the anchor or mooring device. This assists the performance of the anchor and raises the level of force it will resist before dragging. With smaller vessels and in shallow water it is less effective.[18]
The catenary curve in this context is only fully present in the anchoring system when the rode has been lifted clear of the seabed by the vessel's pull, as the seabed obviously affects its shape while it supports the chain or cable. There is also typically a section of rode above the water and thus unaffected by buoyancy, creating a slightly more complicated curve.
Mathematical description
Equation

The equation (up to translation and rotation) of a catenary in Cartesian coordinates has the form
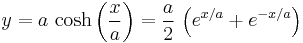 ,
,
where 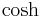 is the hyperbolic cosine function.
is the hyperbolic cosine function.
The Whewell equation for the catenary is
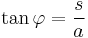 .
.
Differentiating gives
and eliminating  gives the Cesàro equation:
gives the Cesàro equation:
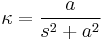 .
.
Other properties
All catenary curves are similar to each other. Changing the parameter a is equivalent to a uniform scaling of the curve.[19]
A parabola rolled along a straight line traces out a catenary (see roulette) with its focus [2].
Square wheels can roll perfectly smoothly if the road has evenly spaced bumps in the shape of a series of inverted catenary curves. The wheels can be any regular polygon save for a triangle, but one must use the correct catenary, corresponding correctly to the shape and dimensions of the wheels.[20]
A charge in a uniform electric field moves along a catenary (which tends to a parabola if the charge velocity is much less than the speed of light c).
The surface of revolution with fixed radii at either end that has minimum surface area is a catenary revolved about the x-axis.
Derivation
We assume that the path followed by the chain is given parametrically by 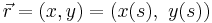 where
where  represents arc length and
represents arc length and 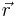 is the position vector. This is the natural parameterization and has the property that
is the position vector. This is the natural parameterization and has the property that 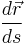 is the unit tangent vector,
is the unit tangent vector, 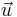 . The derivation of the curve for an optimal arch is similar except that the forces of tension become forces of compression and everything is inverted.
. The derivation of the curve for an optimal arch is similar except that the forces of tension become forces of compression and everything is inverted.
It is now possible to derive two equations which together define the shape of the curve and the tension of the chain at each point. This is done by a careful inspection of the various forces acting on a small segment of the chain and using the fact that these forces must be in balance if the chain is in static equilibrium.
First, let 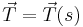 be the force of tension as a function of
be the force of tension as a function of  . The chain is flexible so it can only exert a force parallel to itself. Since tension is defined as the force that the chain exerts on itself,
. The chain is flexible so it can only exert a force parallel to itself. Since tension is defined as the force that the chain exerts on itself, 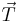 must be parallel to the chain. In other words,
must be parallel to the chain. In other words,
where  is the magnitude of
is the magnitude of 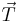 , a positive scalar function of
, a positive scalar function of  .
.
Second, let 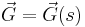 be the external force per unit length acting on a small segment of a chain as a function of
be the external force per unit length acting on a small segment of a chain as a function of  . The forces acting on the segment of the chain between
. The forces acting on the segment of the chain between  and
and 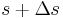 are the force of tension
are the force of tension 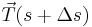 at one end of the segment, the nearly opposite force
at one end of the segment, the nearly opposite force 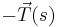 at the other end, and the external force acting on the segment which is approximately
at the other end, and the external force acting on the segment which is approximately 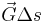 . These forces must balance so
. These forces must balance so
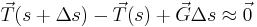 .
.
Divide by 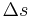 and take the limit as
and take the limit as 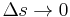 to obtain
to obtain
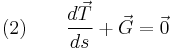 .
.
Note that, up till now, no assumptions have been made regarding the force 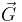 , so equations (1) and (2) can be used as the starting point in the analysis of a flexible chain acting under any external force. The next step is to put in the specific expression for
, so equations (1) and (2) can be used as the starting point in the analysis of a flexible chain acting under any external force. The next step is to put in the specific expression for 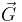 and solve the resulting equations.
and solve the resulting equations.
In this case, 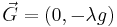 where the chain has constant mass per unit length
where the chain has constant mass per unit length  and the only external force acting on the chain is that of a uniform gravitational field
and the only external force acting on the chain is that of a uniform gravitational field 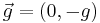 . So we have
. So we have
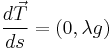 .
.
Integrating we get,
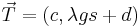 .
.
Note that at the minimum the curve is horizontal and 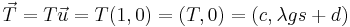 . So
. So  is the tension of the chain at its lowest point this point occurs at
is the tension of the chain at its lowest point this point occurs at 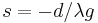 . The point from which
. The point from which  is measured is arbitrary, so pick this point to be the minimum, giving
is measured is arbitrary, so pick this point to be the minimum, giving 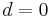 . The equation becomes
. The equation becomes
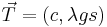 .
.
Note that the horizontal component of the tension is a constant.
From here, we can continue the derivation in two ways.
Alternative 1
If  is the tangential angle of the curve then
is the tangential angle of the curve then 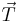 is parallel to
is parallel to 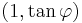 so
so
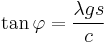 .
.
Write 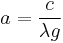 to combine constants and obtain the Whewell equation for the curve,
to combine constants and obtain the Whewell equation for the curve,
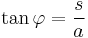 .
.
In general, parametric equations can be obtained from a Whewell equation by integrating:
To find these integrals, make the substitution 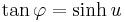 (or
(or 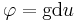 where
where 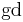 is the Gudermannian function).
is the Gudermannian function).
Then 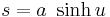 and
and
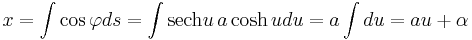
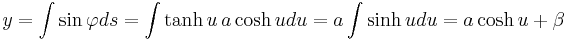 .
.
We can eliminate u to obtain
where 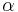 and
and 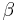 are constants to be determined, along with
are constants to be determined, along with 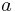 , by the boundary conditions of the problem. Usually these conditions include two points from which the chain is being suspended and the length of the chain.
, by the boundary conditions of the problem. Usually these conditions include two points from which the chain is being suspended and the length of the chain.
Alternative 2
From
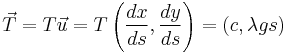 ,
,
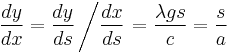 ,
,
where 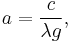 same as before. Then
same as before. Then
and
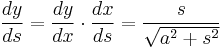 .
.
The integrals of the right hand sides of these equations can be found using standard techniques giving
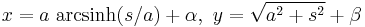 .
.
Again, 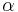 and
and 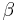 are constants to be determined, along with
are constants to be determined, along with 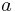 , by the boundary conditions of the problem.
, by the boundary conditions of the problem.
Variations
Elastic Catenary
In an elastic catenary, the cable replaced by a spring and is no longer assumed to be of fixed density, but is allowed to stretch in accordance with Hooke's Law. In this case, the mass per unit length is no longer constant but can be given as
where 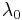 is the mass per unit length for the chain in its relaxed state and
is the mass per unit length for the chain in its relaxed state and 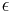 is the spring constant. As in the earlier derivation,
is the spring constant. As in the earlier derivation,
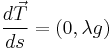 .
.
So the horizontal component of 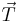 ,
, 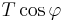 is a constant c. Putting this into the equation for density produces
is a constant c. Putting this into the equation for density produces
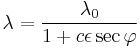 .
.
Then the equation for the vertical component of 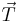 is
is
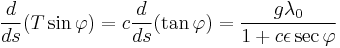 ,
,
or, combining constants,
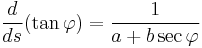 .
.
Using the substitution 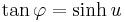 gives
gives
or
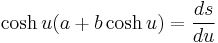 .
.
Parametric equations can be obtained by integrating:
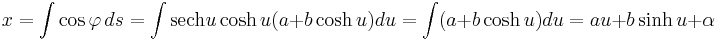 ,
,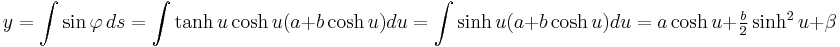 .
.
When b = 0, corresponding to a completely inelastic cable, this is simply the catenary. When a = 0, corresponding to the case there the cable essentially has length 0 in its relaxed state, similar to a Slinky, this is a parabola. When a and b are both >0 then the curve is intermediate between a catenary and a parabola.
Equal resistance catenary
In an equal resistance catenary, cable is strengthened according to the magnitude of the tension at each point, so its resistance to breaking is constant along its length. Assuming that the strength of the cable is proportional to its density, the mass per unit length can be given as
where 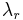 is the mass per unit length per unit of tension force required for the chain to resist breaking. As in the earlier derivation,
is the mass per unit length per unit of tension force required for the chain to resist breaking. As in the earlier derivation,
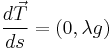 .
.
So the horizontal component of 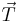 ,
, 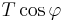 is a constant c. Putting this into the equation for density produces
is a constant c. Putting this into the equation for density produces
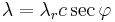 .
.
Then the equation for the vertical component of 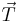 is
is
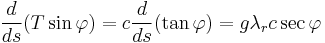 ,
,
or, combining constants,
or
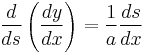 .
.
Multiplying both sides by 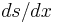 gives
gives
![\frac{d^2y}{dx^2} = \frac{1}{a} \left(\frac{ds}{dx}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{a} \left[1+\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^2\right]](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/7d19da6a533c15f233cf91ef8ce64df0.png) .
.
This can be reduced to a differential equation of degree one using separation of variables to obtain
or
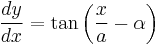 .
.
Another integration produces
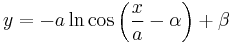 .
.
Towed cables
Instead of gravity, we assume we have a cylindrical cable that is acted on by drag forces due to the movement of some surrounding fluid (e.g. air or water). The velocity relative to the cable is assumed to be a constant 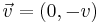 . (Velocity is assumed to be vertical here to preserve similarities with the gravitational case.) To compute the force due to drag, write
. (Velocity is assumed to be vertical here to preserve similarities with the gravitational case.) To compute the force due to drag, write 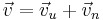 where
where 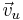 and
and 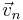 respectively are the components parallel to and orthogonal to the cable. The cable is assumed to be smooth so the force on the cable due to
respectively are the components parallel to and orthogonal to the cable. The cable is assumed to be smooth so the force on the cable due to 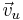 is taken to be negligible. The force acting on the cable, following the Drag equation is
is taken to be negligible. The force acting on the cable, following the Drag equation is
where  is a constant depending on the density of the fluid, the diameter of the cable, and the Drag coefficient. If
is a constant depending on the density of the fluid, the diameter of the cable, and the Drag coefficient. If 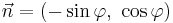 denotes the unit normal vector, then
denotes the unit normal vector, then
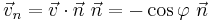 .
.
So
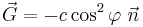 .
.
From equations (1) and (2) above,
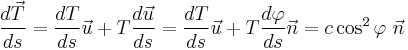 .
.
Setting the coefficients of 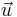 and
and 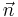 equal produces
equal produces
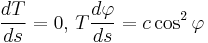 .
.
So T is a constant in this case and combining constants in the second equation gives
which is one of the equations for the catenary given above. This is a case where a different expression for the force acting on the chain/cable produce the same curve but a different expression for tension.
In applications, the force of gravity and additional terms in the force due to drag may be added to the expression for force, yielding equations that must be solved numerically.
See also
- Overhead lines
- Roulette (curve) - an elliptic/hyperbolic catenary
- Troposkein - the shape of a spun rope
References
- ↑ "Catenary" at Math Words
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 MathWorld
- ↑ e.g.: Shodek, Daniel L. (2004). Structures (5th ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 22. ISBN 9780130488794. OCLC 148137330.
- ↑ For example Lockwood p. 124
- ↑ Galileo Galilei (1914). Dialogues concerning two new sciences. Trans. Henry Crew & Alfonso de Salvio. Macmillan. pp. 149, 290. http://books.google.com/books?id=SPhnaiERbWcC.
- ↑ Swetz, Faauvel, Bekken, "Learn from the Masters," 1997, MAA ISBN 0-88385-703-0, pp.128-9
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lockwood p. 124
- ↑ "Monuments and Microscopes: Scientific Thinking on a Grand Scale in the Early Royal Society" by Lisa Jardine
- ↑ cf. the anagram for Hooke's law, which appeared in the next paragraph.
- ↑ Arch Design
- ↑ The original anagram was "abcccddeeeeeefggiiiiiiiiillmmmmnnnnnooprrsssttttttuuuuuuuux": the letters of the Latin phrase, alphabetized.
- ↑ Hymers, Paul (2005). Planning and Building a Conservatory. New Holland. p. 36. ISBN 1843309106.
- ↑ Minogue, Coll; Sanderson, Robert (2000). Wood-fired Ceramics: Contemporary Practices. University of Pennsylvania. p. 42. ISBN 0812235142.
- ↑ Peterson, Susan; Peterson, Jan (2003). The Craft and Art of Clay: A Complete Potter's Handbook. Laurence King. p. 224. ISBN 1856693546.
- ↑ Osserman, Robert (2010), "Mathematics of the Gateway Arch", Notices of the American Mathematical Society 57 (2): 220–229, ISSN 0002-9920, http://www.ams.org/notices/201002/index.html
- ↑ Laura Soullière Harrison (1985) (PDF), National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Jefferson National Expansion Memorial Gateway Arch / Gateway Arch; or "The Arch", National Park Service, http://pdfhost.focus.nps.gov/docs/NHLS/Text/87001423.pdf, retrieved 2009-06-21 and Accompanying one photo, aerial, from 1975PDF (578 KB)
- ↑ Paul Kunkel (June 30, 2006). "Hanging With Galileo". Whistler Alley Mathematics. http://whistleralley.com/hanging/hanging.htm. Retrieved March 27, 2009.
- ↑ Chain, Rope, and Catenary - Anchor Systems For Small Boats
- ↑ http://xahlee.org/SpecialPlaneCurves_dir/Catenary_dir/catenary.html
- ↑ "Roulette: A Comfortable Ride on an n-gon Bicycle" by Borut Levart, Wolfram Demonstrations Project, 2007.
- Lockwood, E.H. (1961). "Chapter 13: The Tractrix and Catenary". A Book of Curves. Cambridge. http://www.archive.org/details/bookofcurves006299mbp.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Catenary" from MathWorld.
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Catenary", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Curves/Catenary.html.
- "Chaînette" at Encyclopédie des Formes Mathématiques Remarquables
- "Chaînette élastique" at Encyclopédie des Formes Mathématiques Remarquables
- "Courbe de la corde à sauter" at Encyclopédie des Formes Mathématiques Remarquables
External links
- "Catenary of equal resistance" at Encyclopédie des Formes Mathématiques Remarquables
- "Catenary" at Visual Dictionary of Special Plane Curves
- Hanging With Galileo - mathematical derivation of formula for suspended and free-hanging chains; interactive graphical demo of parabolic vs. hyperbolic suspensions.
- Catenary Demonstration Experiment - An easy way to demonstrate the Mathematical properties of a cosh using the hanging cable effect. Devised by Jonathan Lansey
- Horizontal Conveyor Arrangement - Diagrams of different horizontal conveyor layouts showing options for the catenary section both supported and unsupported
- Catenary curve derived - The shape of a catenary is derived, plus examples of a chain hanging between 2 points of unequal height, including C program to calculate the curve.
- Cable Sag Error Calculator - Calculates the deviation from a straight line of a catenary curve and provides derivation of the calculator and references.
- Hexagonal Geodesic Domes - Catenary Domes, an article about creating catenary domes