Bulgarian language
| Bulgarian | ||
|---|---|---|
| Български език Bălgarski ezik |
||
| Spoken in | ||
| Region | The Balkans | |
| Total speakers | 9 million[1][2] | |
| Ranking | 61 | |
| Language family | Indo-European
|
|
| Writing system | Cyrillic alphabet | |
| Official status | ||
| Official language in | ||
| Recognised minority language in | ||
| Regulated by | Institute of Bulgarian at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (Институт по български език към Българската академия на науките (БАН)) | |
| Language codes | ||
| ISO 639-1 | bg | |
| ISO 639-2 | bul | |
| ISO 639-3 | bul | |
| Linguasphere | ||
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | ||
Bulgarian (български език, pronounced [ˈbɤɫɡɐrski ɛˈzik]) is an Indo-European language, a member of the Slavic linguistic group.
Bulgarian demonstrates several linguistic innovations that set it apart from all other Slavic languages except the Macedonian language, such as the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article (see Balkan linguistic union), the lack of a verb infinitive, and the retention and further development of the Proto-Slavic verb system. Various verb forms exist to express unwitnessed, retold, and doubtful action. Estimates of the number of people around the world who speak Bulgarian fluently range from about 8.5 million[2] to 9 million.[1] The Bulgarian language is mutually intelligible with the Macedonian language.[3]
Contents |
History
The development of the Bulgarian language may be divided into several historical periods.
- Prehistoric period - occurred between the Slavonic migration to eastern Balkans and the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius to Great Moravia in the 860s.
- Old Bulgarian (9th to 11th century, also referred to as Old Church Slavonic) - a literary norm of the early southern dialect of the Common Slavic language from which Bulgarian evolved. It was used by Saints Cyril and Methodius and their disciples to translate the Bible and other liturgical literature from Greek into Slavic.
- Middle Bulgarian (12th to 15th century) - a literary norm that evolved from the earlier Old Bulgarian, after major innovations were accepted. It was a language of rich literary activity and the official administration language of the Second Bulgarian Empire.
- Modern Bulgarian - dates from the 16th century onwards, undergoing general grammar and syntax changes in the 18th and 19th centuries. Present-day written Bulgarian language was standardized on the basis of the 19th-century Bulgarian vernacular. The historical development of the Bulgarian language can be described as a transition from a highly synthetic language (Old Bulgarian) to a typical analytic language (Modern Bulgarian) with Middle Bulgarian as a midpoint in this transition.

Bulgarian was the first "Slavic" language attested in writing. As Slavic linguistic unity lasted into late antiquity, in the oldest manuscripts this language was initially referred to as языкъ словяньскъ, "the Slavic language". In the Middle Bulgarian period this name was gradually replaced by the name языкъ блъгарьскъ, the "Bulgarian language". In some cases, the name языкъ блъгарьскъ was used not only with regard to the contemporary Middle Bulgarian language of the copyist but also to the period of Old Bulgarian. A most notable example of anachronism is the Service of St. Cyril from Skopje (Скопски миней), a 13th century Middle Bulgarian manuscript from northern Macedonia according to which St. Cyril preached with "Bulgarian" books among the Moravian Slavs. The first mention of the language as the "Bulgarian language" instead of the "Slavonic language" comes in the work of the Greek clergy of the Bulgarian Archbishopric of Ohrid in the 11th century, for example in the Greek hagiography of Saint Clement of Ohrid by Theophylact of Ohrid (late 11th century).
During the Middle Bulgarian period, the language underwent dramatic changes, losing the Slavonic case system, but preserving the rich verb system (while the development was exactly the opposite in other Slavic languages) and developing a definite article. Consequently, modern Bulgarian is about as far from Russian as Swedish is from German. It was influenced by proto-Bulgar and its non-Slavic neighbors in the Balkan linguistic union (mostly grammatically) and later also by Turkish, which was the official language of the Ottoman Empire, in the form of the Ottoman Turkish language, mostly lexically. As a national revival occurred towards the end of the period of Ottoman rule (mostly during the 19th century), a modern Bulgarian literary language gradually emerged which drew heavily on Church Slavonic/Old Bulgarian (and to some extent on literary Russian, which had preserved many lexical items from Church Slavonic) and later reduced the number of Turkish and other Balkanic loans. Today one difference between Bulgarian dialects in the country and literary spoken Bulgarian is the significant presence of Old Bulgarian words and even word forms in the latter. Russian loans are distinguished from Old Bulgarian ones on the basis of the presence of specifically Russian phonetic changes, as in оборот (turnover, rev), непонятен (incomprehensible), ядро (nucleus) and others. As usual in such cases, many other loans from French, English and the classical languages have subsequently entered the language as well.
Modern Bulgarian was based essentially on the Eastern dialects of the language, but its pronunciation is in many respects a compromise between East and West Bulgarian (see especially the phonetic sections below).
Dialects

The language is mainly split into two broad dialect areas, based on the different reflexes of the Common Slavic yat vowel (Ѣ). This split, which occurred at some point during the Middle Ages, led to the development of Bulgaria's:
- Western dialects (informally called твърд говор/tvurd govor - "hard speech")
- the former yat is pronounced "e" in all positions. e.g. млеко (mlekò) – milk, хлеб (hleb) – bread.[4]
- Eastern dialects (informally called мек говор/mek govor – "soft speech")
- the former yat alternates between "ya" and "e": it is pronounced "ya" if it is under stress and the next syllable does not contain a front vowel (e or i) — e.g. мляко (mlyàko), хляб (hlyab), and "ye" otherwise — e.g. млекар (mlekàr) – milkman, хлебар (hlebàr) – baker. This rule obtains in most Eastern dialects, although some have "ya", or a special "open e" sound, in all positions.
The literary language norm, which is generally based on the Eastern dialects, also has the Eastern alternating reflex of yat. However, it has not incorporated the general Eastern umlaut of all synchronic or even historic "ya" sounds into "e" before front vowels — e.g. поляна (polyana) vs полени (poleni) "meadow – meadows" or even жаба (zhaba) vs жеби (zhebi) "frog – frogs", even though it co-occurs with the yat alternation in almost all Eastern dialects that have it (except a few dialects along the yat border, e.g. in the Pleven region).[5]
More examples of the yat umlaut in the literary language are:
- mlyàko (milk) [n.] → mlekàr (milkman); mlèchen (milky), etc.
- syàdam (sit) [vb.] → sedàlka (seat); sedàlishte (seat, e.g. of government), etc.
- svyat (holy) [adj.] → svetètz (saint); svetìlishte (sanctuary), etc.
Until 1945, Bulgarian orthography did not reveal this alternation and used the original Old Slavic Cyrillic letter yat (Ѣ), which was commonly called двойно е (dvoyno e) at the time, to express the historical yat vowel or at least root vowels displaying the ya – e alternation. The letter was used in each occurrence of such a root, regardless of the actual pronunciation of the vowel: thus, both mlyako and mlekar were spelled with (Ѣ). Among other things, this was seen as a way to "reconcile" the Western and the Eastern dialects and maintain language unity at a time when much of Bulgaria's Western dialect area was controlled by Serbia and Greece, but there were still hopes and occasional attempts to recover it. With the 1945 orthographic reform, this letter was abolished and the present spelling was introduced, reflecting the alternation in pronunciation.
This had implications for some grammatical constructions:
- The third person plural pronoun and its derivatives. The original pronoun before 1945 was spelledтѣ (tě) – "they", and all its derivatives took this as the root. After the orthographic change, the pronoun and all its derivatives were given an equal share of soft and hard spellings:
- "they" – те (te) → "them" – тях (tyah);
- "their(s)" – tehen (masc.); tyahna (fem.); tyahno (neut.); tehni (plur.)
- adjectives received the same treatment as тѢ :
- "whole" – tsyal → "the whole...": tseliyat (masc.); tsyalata (fem.); tsyaloto (neut.); tselite (plur.)
Sometimes, with the changes, words began to be spelled as other words with different meanings, e.g.:
- свѣт (svět) – "holy" became свят (svyat), spelt and pronounced the same as свят – "world".
- тѣ (tě) – "they" became те (te), the same as the second person direct object pronoun те – "you".
In spite of the literary norm regarding the yat vowel, many people living in Western Bulgaria, including the capital Sofia, will fail to observe its rules. While the norm requires the realizations vidyal vs videli (he has seen; they have seen), some natives of Western Bulgaria will preserve their local dialect pronunciation with "e" for all instances of "yat" (e.g. videl, videli). Others, attempting to adhere to the norm, will actually use the "ya" sound even in cases where the standard language has "e" (e.g. vidyal, vidyali). The latter hypercorrection is called свръхякане ("svrah-yakane" ≈"over-softening").
Relationship to Macedonian
Most sources in and out of Bulgaria before the Second World War referred to the southern Slavonic dialect continuum covering the area of today's Republic of Macedonia as a group of Bulgarian dialects.[6][7][8][9][10][11] The local variants of the name of the language are balgàrtski, bolgàrtski, bulgàrtski[12], bògartski, bogàrtski, bùgarski or bugàrski.
After WWII, the question about the Bulgarian character of the language in the territory of the Republic of Macedonia was put aside in the name of Bulgarian-Yugoslavian friendship under the pressure of the Soviet Union. After 1958 when the pressure from Moscow decreased, Sofia turned back to the view that the Macedonian language did not exist as a separate language.
Alphabet
In 886 AD, the Bulgarian Empire introduced the Glagolitic alphabet which was devised by the Saints Cyril and Methodius in the 850s. The Glagolitic alphabet was gradually superseded in later centuries by the Cyrillic alphabet, developed around the Preslav Literary School, Bulgaria in the beginning of the 10th century.
Several Cyrillic alphabets with 28 to 44 letters were used in the beginning and the middle of the 19th century during the efforts on the codification of Modern Bulgarian until an alphabet with 32 letters, proposed by Marin Drinov, gained prominence in the 1870s. The alphabet of Marin Drinov was used until the orthographic reform of 1945 when the letters yat (Ѣ, ѣ [æː], called "double e"), and yus (Ѫ, ѫ [ɔ̃], called "big yus" or "ъ кръстато") were removed from the alphabet, reducing the number of letters to 30.
Nowadays the Bulgarian language is written in the Cyrillic script .
With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on January 1, 2007, Cyrillic became the third official alphabet of the EU.
The following table gives the letters of the Bulgarian alphabet, along with the IPA values for the sound of each letter:
| Bulgarian alphabet | ISO 9 | Official transliteration | IPA* | Name of Letter | English equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| А а | A a | A a | /a/ or /ɐ/ | a | a as in "adorable" |
| Б б | B b | B b | /b/ | бъ | b as in "bug" |
| В в | V v | V v | /v/ | въ | v as in "vet" |
| Г г | G g | G g | /ɡ/ or /ɟ/ | гъ | g as in "god" |
| Д д | D d | D d | /d/ | дъ | d as in "dog" |
| Е е | E e | E e | /ɛ/ | е | e as in "best" |
| Ж ж | Ž ž | Zh zh | /ʒ/ | жъ | s as in "treasure" |
| З з | Z z | Z z | /z/ | зъ | z as in "zoo" |
| И и | I i | I i | /i/ | и | ee as in "see" |
| Й й | J j | Y y | /j/ | и кратко | y as in "yes" |
| К к | K k | K k | /k/ or /c/ | къ |
c as in "cat" |
| Л л | L l | L l | /l/, /ɫ/, /ʎ/ | лъ |
l as in "call" |
| М м | M m | M m | /m/ | мъ | m as in "man" |
| Н н | N n | N n | /n/ | нъ | n as in "normal" |
| О о | O o | O o | /ɔ/ or /o/ | о | o as in "order" |
| П п | P p | P p | /p/ | пъ | p as in "pet" |
| Р р | R r | R r | /r/ | ръ | r as in "restaurant" |
| С с | S s | S s | /s/ | съ | s as in "sound" |
| Т т | T t | T t | /t/ | тъ | t as in "top" |
| У у | U u | U u | /u/ or /o/ | y | оо as in "tool" |
| Ф ф | F f | F f | /f/ | фъ | f as in "food" |
| Х х | H h | H h | /x/ | хъ | ch as in Scottish "loch" |
| Ц ц | C c | Ts ts | /t͡s/ | цъ | ts as in "fits" |
| Ч ч | Č č | Ch ch | /t͡ʃ/ | чъ | ch as in "chip" |
| Ш ш | Š š | Sh sh | /ʃ/ | шъ | sh as in "shot" |
| Щ щ | Št št1 | Sht sht | /ʃt/ | щъ | sht as in "shtick" |
| Ъ ъ | Ă ă1 | A a | /ɤ̞/, /ə/ or /ɐ/ | ер голям | u as in "turn" |
| Ь ь | J j1 | Y y | /j/ | ер малък | combined with <о> as ьо, for a pronunciation like yo in "yoyo"
less often with e as ьe, pronounced like ye in "yet" |
| Ю ю | Ju ju1 | Yu yu | /ju/ | ю | u as in "menu" |
| Я я | Ja ja1 | Ya ya | /ʝa/ | я | ya as in "yarn" |
* See Wikipedia:IPA for Bulgarian and Macedonian for details.
1 The romanizations of these characters differ from the current version, ISO 9:1995, as it was never officially adopted as a Bulgarian standard.
Most letters in the Bulgarian alphabet stand for just one specific sound. Three letters stand for the single expression of combinations of sounds, namely щ (sht), ю (yu), and я (ya). Two sounds do not correspond to separate letters, but are expressed as the combination of two letters, namely дж (/dʒ/) and дз (/dz/). The letter ь marks the softening (palatalization) of any consonant before /ɔ/ .
The names of the letters are simple representations of their phonetic values, with all consonants being followed by /ə/ — thus the alphabet goes: /a/ - /bə/ - /və/, etc. Й is known as "и-kratko" (short /i/), Ъ as "er-golyam" (large Er), and Ь as "er-maluk" (small Er). When saying the alphabet fast, people often omit to say Й and Ь, and pronounce Ъ simply as /ə/.
For the transliteration of Bulgarian into the Latin alphabet (romanization), see Romanization of Bulgarian.
Phonology
Vowels
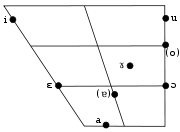
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | и /i/ | у /u/ | |
| Mid | е /ɛ/ | ъ /ɤ/[note 1] | о /ɔ/ |
| Low | а /a/, (/ɐ/) |
Bulgarian's six vowels may be grouped in three pairs according to their backness: front, central and back. All vowels are relatively lax, as in most other Slavic languages, and unlike the tense vowels, for example, in the Germanic languages. Unstressed vowels tend to be shorter and weaker compared to their stressed counterparts, and the corresponding pairs of open and closed vowels approach each other with a tendency to merge, above all as low (open and open-mid) vowels are raised and shift towards the high (close and close-mid) ones. However, the coalescence is not always complete. The vowels are often distinguished in emphatic or deliberately distinct pronunciation, and reduction is strongest in colloquial speech. Besides that, some linguists distinguish two degrees of reduction, as they have found that a clearer distinction tends to be maintained in the syllable immediately preceding the stressed one. The complete merger of the pair /a/ - /ɤ/ is regarded as most common, while the status of /ɔ/ vs /u/ is less clear. A coalescence of /ɛ/ and /i/ or even /e/ is not allowed in formal speech and is regarded as a provincial (East Bulgarian) dialect feature; instead, unstressed /ɛ/ is both raised and centralized, approaching ъ /ɤ/.[13] The /ɤ/ vowel itself does not exist as a phoneme in other Slavic languages. It is often transcribed as /ə/, also in this article.
Semivowels
The Bulgarian language possesses one semivowel: /j/, being equivalent to y in English like in yes. It is expressed graphically with the letter й, as in най /naj/ ("most"), тролей /trɔlɛj/ ("trolleybus"), except when it precedes /a/ or /u/, in which case the combination of two phonemes is expressed with a single letter, respectively я or ю: (e.g. ютия /jutija/ "(flat) iron").
The semivowel /j/ does not occur after consonants. Thus, after a consonant, я, ю, and ьо signify its palatalisation rather than a semivowel: бял /bʲal/ "white", плюя /plʲuja/ "I spit", льос /lʲɔs/ "loess".
Consonants
Bulgarian has a total of 35 consonant phonemes (see table below). Three additional phonemes can also be found ([xʲ], [d͡z], and [d͡zʲ]), but only in foreign proper names such as Хюстън /xʲustən/ ("Houston"), Дзержински /d͡zɛrʒinski/ ("Dzerzhinsky"), and Ядзя /jad͡zʲa/, the Polish name "Jadzia". They are, however, normally not considered part of the phonetic inventory of the Bulgarian language. According to the criterion of sonority, the Bulgarian consonants may be divided into 12 pairs (voiced<>voiceless). The only consonant without a counterpart is the voiceless velar fricative /x/ . The contrast 'voiced vs. voiceless' is neutralized in word-final position, where all obstruents are pronounced as voiceless (as in most Slavic languages); this neutralization is, however, not reflected in the spelling.
Hard and palatalized consonants
The Bulgarian consonants б /b/, в /v/, г /ɡ/, д /d/, з /z/, к /k/, л /l//ɫ/, м /m/, н /n/, п /p/, р /r/, с /s/, т /t/, ф /f/, ц /t͡s/ can denote both a normal, "hard" pronunciation, as well as a "soft", palatalized one. The hard and the palatalized consonants are considered separate phonemes in Bulgarian. The consonants ж /ʒ/, ш /ʃ/, ч /t͡ʃ/ and дж /d͡ʒ/ do not have palatalized variants, which is probably connected with the fact that they have arisen historically through palatalization in Common Slavonic. These consonants may still be somewhat palatalized in some speakers' pronunciation, but as a rule this is not the case.
The softness of the palatalized consonants is always indicated in writing in Bulgarian. A consonant is palatalized if:
- it is followed by я / ʲa/, ю / ʲu/, or ьо / ʲɔ/. (Note: ь occurs only before о in Bulgarian)
(When я and ю aren't preceded by a consonant, they signal that the vowels /a/ and /u/ are preceded by the semivowel /j/. For /jɔ/, Bulgarian uses "йо", as in Ню Йорк, "New York".)
Even though palatalized consonants are phonemes in Bulgarian, they may in some cases be positionally conditioned, hence redundant. In Eastern Bulgarian dialects, consonants are always allophonically palatalized before the vowels /i/ and /ɛ/. This is not the case in Standard Bulgarian, but that form of the language does have similar allophonic alternations. Thus, к /k/, г /ɡ/ and х /x/ tend to be palatalized before /i/ and /ɛ/, and the realization of the phoneme л /l/ varies along the same principles: one of its allophones, involving a raising of the back of the tongue and a lowering of its middle part (thus similar or, according to some scholars, identical to a velarized lateral), occurs in all positions, except before the vowels /i/ and /ɛ/, where a more "clear" version with a slight raising of the middle part of the tongue occurs. The latter pre-front realization is traditionally (and incorrectly) called "soft l", even though it is not palatalized (and thus isn’t identical to the /lʲ/ signalled by the letters ьо, я and ю). In some Western Bulgarian dialects, this allophonic variation does not exist.
Furthermore, in the speech of many young people the more common and arguably velarized allophone of /l/ is often realized as a labiovelar approximant [w].[14] This phenomenon, colloquially known as мързеливо "л" (lazy "l") in Bulgaria, was first registered in the 1970s and isn't connected to original dialects. Similar developments, termed L-vocalization, have occurred in many languages, including Polish, Serbo-Croatian and certain dialects of English such as Cockney and AAVE.
It is important to point out that even though it is traditionally accepted that palatal and non-palatal consonants are different phonemes, some researchers [15] claim that only the non-palatal consonants can be considered phonemes (with hard and palatalized allophones). The reason for this is that words with a palatal consonant can be considered as having an "underlying" /j/ after the consonant (which is also reflected in the spelling). This palatal approximant makes the consonant palatal through regressive assimilation. This theory is supported by the fact that these palatal allophones do not normally appear in syllable-final position as in other Slavic languages, such as Russian.
Palatalization
During the palatalization of most hard consonants (the bilabial, labiodental and alveolar ones), the middle part of the tongue is lifted towards the palatum, resulting in the formation of a second articulatory centre whereby the specific palatal "clang" of the soft consonants is achieved. The articulation of alveolars /l/, /n/ and /r/, however, usually does not follow that rule; the palatal clang is achieved by moving the place of articulation further back towards the palatum so that /ʎ/, /ɲ/ and /rʲ/ are actually alveopalatal (postalvelolar) consonants. Soft /ɡ/ and /k/ (/ɡʲ/ and /kʲ/, respectively) are articulated not on the velum but on the palatum and are considered palatal consonants.
Table
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental/ Alveolar |
Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | hard | /m/ | /n/ | |||||||||
| soft | /mʲ/ | /ɲ/ | ||||||||||
| Plosive | hard | /p/ | /b/ | /t/ | /d/ | /k/ | /ɡ/ | |||||
| soft | /pʲ/ | /bʲ/ | /tʲ/ | /dʲ/ | /kʲ/ | /ɡʲ/ | ||||||
| Affricate | hard | /t͡s/ | /t͡ʃ/ | /d͡ʒ/ | ||||||||
| soft | /t͡sʲ/ | |||||||||||
| Fricative | hard | /f/ | /v/ | /s/ | /z/ | /ʃ/ | /ʒ/ | /x/ | ||||
| soft | /fʲ/ | /vʲ/ | /sʲ/ | /zʲ/ | ||||||||
| Trill | hard | /r/ | ||||||||||
| soft | /rʲ/ | |||||||||||
| Approximant | soft | /j/ | ||||||||||
| Lateral | hard | /l//ɫ/ | ||||||||||
| soft | /ʎ/ | |||||||||||
Word stress
Bulgarian word stress is dynamic. Stressed syllables are louder and longer than unstressed ones. Stress, like Russian and other East Slavic languages, is also lexical rather than fixed as in French, Latin or the West Slavic ones, i.e. it may fall on any syllable of a polysyllabic word and its position may vary in inflection and derivation, for example, мъж /məʃ/ ("man"), мъжът /məˈʒət/ ("the man"). Bulgarian stress is also distinctive: for example, в'ълна /ˈvəlna/ ("wool") and вълн'а /vəlˈna/ ("wave") are only differentiated by stress. Stress usually isn't signified in written text (one notable exception being the single dative female pronoun ѝ ("to her", to differentiate it from simple "и", meaning "and"). It may, however, be indicated in cases with minimal pairs like the above, where disambiguation is needed, or in order to signify the dialectal deviation from the standard language pronunciation. In such cases, stress is signified by placing a grave accent on the vowel of the stressed syllable.[note 2]
Grammar
The parts of speech in Bulgarian are divided in 10 different types, which are categorized in two broad classes: mutable and immutable. The difference is that mutable parts of speech vary grammatically, whereas the immutable ones do not change, regardless of their use. The five classes of mutables are: nouns, adjectives, numerals, pronouns and verbs. Syntactically, the first four of these form the group of the noun or the nominal group. The immutables are: adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, particles and interjections. Verbs and adverbs form the group of the verb or the verbal group.
Nominal morphology
Nouns and adjectives have the categories grammatical gender, number, case (only vocative) and definiteness in Bulgarian. Adjectives and adjectival pronouns agree with nouns in number and gender. Pronouns have gender and number and retain (as in nearly all Indo-European languages) a more significant part of the case system.
Nominal inflection
Gender
There are three grammatical genders in Bulgarian: masculine, feminine and neuter. The gender of the noun can largely be inferred from its ending: nouns ending in a consonant ("zero ending") are generally masculine (for example, град {grad} "city", син {sin} "son", мъж {məzh} "man"); those ending in –а/–я (-a/-ya) (жена {zhena} "woman", дъщеря {dəshterya} "daughter", улица {ulitsa} "street") are normally feminine; and nouns ending in –е, –о are almost always neuter (дете {dete} “child”, езеро {ezero} "lake"), as are those relatively few words (usually loans) that end in –и, –у, and –ю (цунами "tsunami", табу {tabu} "taboo", меню {menyu} "menu"). Perhaps the most significant exception from the above are the relatively numerous nouns that end in a consonant and yet are feminine: these comprise, firstly, a large group of nouns with zero ending expressing quality, degree or an abstraction, including all nouns ending on –ост/–ест -{ost/est} (мъдрост {mədrost} "wisdom", низост {nizost} "vileness", прелест {prelest} "loveliness", болест {bolest} "sickness", любов {lyubov} "love"), and secondly, a much smaller group of irregular nouns with zero ending which define tangible objects or concepts (кръв {krəv} "blood", кост {kost} "bone", вечер {vecher} "evening", нoщ (nosht) "night").
The plural forms of the nouns do not express their gender as clearly as the singular ones, but may also provide some clues to it: the ending –и (-i) is more likely to be used with a masculine or feminine noun (факти {fakti} "facts", болести {bolesti} "sicknesses"), while one in –а/–я belongs more often to a neuter noun (езера {ezera} "lakes"). Also, the plural ending –ове (-ove) occurs only in masculine nouns.
Number
Two numbers are distinguished in Bulgarian — singular and plural. A variety of plural suffixes is used, and the choice between them is partly determined by their ending in singular and partly influenced by gender; in addition, irregular declension and alternative plural forms are common. Words ending in –а/–я (which are usually feminine) generally have the plural ending –и, upon dropping of the singular ending. Of nouns ending in a consonant, the feminine ones also use –и, whereas the masculine ones usually have –и for polysyllables and –ове for monosyllables (however, exceptions are especially common in this group). Nouns ending in –о/–е (most of which are neuter) mostly use the suffixes –а, –я (both of which require the dropping of the singular endings) and –та.
With cardinal numbers and related words such as няколко ("several"), masculine nouns use a special count form in –а/–я, which stems from the Proto-Slavonic dual: двама/трима ученика (two/three students) versus тези ученици (these students); cf. feminine две/три/тези жени (two/three/these women) and neuter две/три/тези деца (two/three/these children). However, a recently developed language norm requires that count forms should only be used with masculine nouns that do not denote persons. Thus, двама/трима ученици is perceived as more correct than двама/трима ученика, while the distinction is retained in cases such as два/три молива (two/three pencils) versus тези моливи (these pencils).
Case
- See also: Bulgarian grammar - Case System
Cases exist only in the personal pronouns (as they do in many other modern Indo-European languages), with nominative, accusative, dative and vocative forms. Vestiges are present in the masculine personal interrogative pronoun кой ("who") and in a number of phraseological units and sayings. The major exception are vocative forms, which are still in use for masculine (with the endings -e, -o and -ю) and feminine nouns (-[ь/й]o and -e) in the singular. However, there is a tendency to avoid them in many personal names, as the use of feminine name forms in -[ь/й]o[16] and of the potential vocative forms of foreign names has come to be considered rude or rustic. Thus, "Иване" means "Hey, Ivan", while the corresponding feminine forms "Елено" ("Hey, Elena"), "Маргарито" ("Hey, Margarita") are today seen as rude[16] or, at best, unceremonious, and declining foreign names as in *"Джоне" ("hey, John") or *"Саймъне" ("hey, Simon") could only be considered humorous. Interestingly, the "ban" on constructing vocative forms for foreign names does not apply to names from Classical Antiquity, with the source languages having the vocative case as well: cf "Цезаре" ("Oh Caesar"), "Перикле" ("Oh Pericles"), Зевсе ("Oh Zeus") and even "Афродито" ("Oh Aphrodite").
Case remnants
Some key words do retain their cases, which today are no longer considered nominative, accusative and dative, but rather as being subject, direct object and indirect object parts of speech:
- All personal pronouns — e.g. masculine singular:
- той, {toy} (he) – него, {nègo} (him) – нему, {nèmu} (to him — archaic)[note 3]
- The masculine interrogative pronoun кой, {koy} (who) and all of its derivatives — these, however, are not declined for all masculine nouns, but only when they refer to men:
- кой {koy} (who) – кого {kogò} (whom) – кому {komù} (to whom — very rarely used).[note 4]
- the words някой {nyakoy} (someone) and никой {nikoy} (no one) follow the same pattern as кой {koy};
- всеки {vseki} (everyone) and друг {drug} (someone else) are similar (-иго {-igo}; -иму {-imu}), but extremely rare.
- the relative clauses който {koyto} (who/that), когото {kogoto} (whom/that) and комуто {komuto} (to whom/that) — again, only declined when referring to men — i.e.
- човекът с когото говоря {chovekət, s kogoto govorya} (the man that I'm talking to)
- столът, на който седя {stolət, na koyto sedya} (the chair that I'm sitting on)
- кой {koy} (who) – кого {kogò} (whom) – кому {komù} (to whom — very rarely used).[note 4]
Definiteness (article)
In modern Bulgarian, definiteness is expressed by a definite article which is postfixed to the noun, much like in the Scandinavian languages or Romanian (indefinite: човек, "person"; definite: човекът, "the person") or to the first nominal constituent of definite noun phrases (indefinite: добър човек, "a good person"; definite: добрият човек, "the good person"). There are four singular definite articles. Again, the choice between them is largely determined by the noun's ending in the singular.[17] Nouns that end in a consonant and are masculine use –ът/–ят, when they are grammatical subjects, and –а/–я elsewhere (all four endings are normally pronounced [ə]). Nouns that end in a consonant and are feminine, as well as nouns that end in –а/–я (most of which are feminine, too) use –та. Nouns that end in –е/–о use –то.
The plural definite article is –те for all nouns except for those, whose plural form ends in –а/–я; these get –тa instead. When postfixed to adjectives the definite articles are –ят/–я for masculine gender (again, with the longer form being reserved for grammatical subjects), –та for feminine gender, –то for neuter gender, and –те for plural.
Adjective and numeral inflection
Both groups agree in gender and number with the noun they are appended to. They may also take the definite article as explained above.
Pronouns
Pronouns may vary in gender, number, definiteness and are the only parts of speech that have retained case inflexions. Three cases are exhibited by some groups of pronouns — nominative, accusative and dative. The distinguishable types of pronouns include the following: personal, relative, reflexive, interrogative, negative, indefinitive, summative and possessive.
Verbal morphology and grammar
According to some accounts, the Bulgarian verb can take up to 3,000 distinct forms, as it varies in person, number, voice, aspect, mood, tense and even gender.
Finite verbal forms
Finite verbal forms are simple or compound and agree with subjects in person (first, second and third) and number (singular, plural) in Bulgarian. In addition to that, past compound forms using participles vary in gender (masculine, feminine, neuter) and voice (active and passive) as well as aspect (perfective/aorist and imperfective).
Aspect
Bulgarian verbs express lexical aspect: perfective verbs signify the completion of the action of the verb and form past perfective (aorist) forms; imperfective ones are neutral with regard to it and form past imperfective forms. Most Bulgarian verbs can be grouped in perfective-imperfective pairs (imperfective<>perfective: идвам<>дойда "come", пристигам<>пристигна “arrive”). Perfective verbs can be usually formed from imperfective ones by suffixation or prefixation, but the resultant verb often deviates in meaning from the original. In the pair examples above, aspect is stem-specific and therefore there is no difference in meaning.
In Bulgarian, there is also grammatical aspect. Three grammatical aspects are distinguishable: neutral, perfect and pluperfect. The neutral aspect comprises the three simple tenses and the future tense. The pluperfect is manifest in tenses that use double or triple auxiliary "be" participles like the past pluperfect subjunctive. Perfect constructions use a single auxiliary "be".
Mood
The traditional interpretation is that in addition to the four moods (наклонения, naklonenia) shared by most other European languages - indicative (изявително, izyavitelno), imperative (повелително, povelitelno), subjunctive (подчинително, podchinitelno) and conditional (условно, uslovno) - in Bulgarian there is one more to describe a generalistic category of unwitnessed events - the inferential (преизказно, preízkazno) mood. This view has been challenged in recent years. Admirative and dubitative mood forms, temporally distinct from the inferential, and optative mood forms, temporally but not grammatically distinguishable from the subjunctive, have been identified, bringing the total to eight.
Tense
There are three grammatically distinctive positions in time — present, past and future — which combine with aspect and mood to produce a number of formations. Normally, in grammar books these formations are viewed as separate tenses — i. e. "past imperfect" would mean that the verb is in past tense, in the imperfective aspect, and in the indicative mood (since no other mood is shown). There are more than 40 different tenses across Bulgarian's two aspects and five (or eight) moods.
In the indicative mood, there are three simple tenses:
- Present tense is a temporally unmarked simple form made up of the verbal stem and a complex suffix composed of the thematic vowel /e/, /i/ or /a/ and the person/number ending (пристигам, pristigam, "I arrive/I am arriving"); only imperfective verbs can stand in the present indicative tense independently;
- Past imperfect is a simple verb form used to express an action which is contemporaneous or subordinate to other past actions; it is made up of an imperfective or a perfective verbal stem and the person/number ending (пристигаx, pristigah; пристигнеx, pristigneh, "I was arriving");
- Past aorist is a simple form used to express a temporarily independent, specific past action; it is made up of a perfective or an imperfective verbal stem and the person/number ending (пристигнах, pristignah, "I arrived", четох, chetoh, "I read");
In the indicative there are also the following compound tenses:
- Future tense is a compound form made of the particle ще (shte) and present tense (ще уча, shte ucha, "I will study"); negation is expressed by the construction няма да (nyama da) and present tense (няма да уча, nyama da ucha, or the old-fashioned form "не ще уча", "ne shte ucha" - "I will not study");
- Past future tense is a compound form used to express an action which was to be completed in the past but was future as regards another past action; it is made up of the past imperfect of the verb ща (shta) "will, want", the particle да (da) "to" and the present tense of the verb (щях да уча, shtyah da ucha, "I was going to study");
- Present perfect is a compound form used to express an action which was completed in the past but is relevant for or related to the present; it is made up of the present tense of the verb съм (səm) "be" and the past participle (съм учил, səm uchil, "I have studied");
- Past perfect is a compound form used to express an action which was completed in the past and is relative to another past action; it is made up of the past tense of the verb съм (səm) "be" and the past participle (бях учил, byah uchil, "I had studied");
- Future perfect is a compound form used to express an action which is to take place in the future before another future action; it is made up of the future tense of the verb съм (səm) "be" and the past participle (ще съм учил, shte səm uchil, "I will have studied");
- Past future perfect is a compound form used to express a past action which is future with respect to a past action which itself is prior to another past action; it is made up of the past imperfect of ща (shta) "will, want", the particle да (da) "to", the present tense of the verb съм (səm) "be" (am) and the past participle of the verb (щях да съм учил, shtyah da səm uchil, "I would have studied").
The four perfect constructions above can vary in aspect depending on the aspect of the main-verb participle; they are in fact pairs of imperfective and perfective aspects. Verbs in forms using past participles also vary in voice and gender.
There is only one simple tense in the imperative mood - the present - and there are simple forms only for the second person using the suffixes -и/-й (-i, -y/i) for singular and -ете/-йте (-ete, -yte) for plural; e.g., уча (ucha) "to study": учи (uchi), sg., учете (uchete), pl.; играя (igraya) "to play": играй (igray), играйте (igrayte). There are compound imperative forms for all persons and numbers in the present compound imperative (да играе, da igrae), the present perfect compound imperative (да е играл, da e igral) and the rarely used present pluperfect compound imperative (да е бил играл, da e bil igral).
The conditional mood consists of five compound tenses, most of which are not grammatically distinguishable. The present, future and past conditional use a special past form of the stem би- (bi - "be") and the past participle (бих учил, bih uchil, "I would study"). The past future conditional and the past future perfect conditional coincide in form with the respective indicative tenses.
The subjunctive mood is rarely documented as a separate verb form in Bulgarian, (being, morphologically, a sub-instance of the quasi-infinitive construction with the particle да (da) "to" and a normal finite verb form), but nevertheless it is used regularly. The most common form, often mistaken for the present tense, is the present subjunctive ([пo-добре] да отидa, [po-dobre] da otida, "I had better go"). The difference between the present indicative and the present subjunctive tense is that the subjunctive can be formed by both perfective and imperfective verbs. It has completely replaced the infinitive and the supine from complex expressions (see below). It is also employed to express opinion about possible future events. The past perfect subjunctive ([пo-добре] да бях отишъл, [po-dobre] da byah otishəl, "I had better gone") refers to possible events in the past, which did not take place, and the present pluperfect subjunctive (да съм бил отишъл, da səm bil otishəl), which may be used about both past and future events arousing feelings of incontinence, suspicion, etc. and is impossible to translate in English. This last variety of the subjunctive in Bulgarian is sometimes also called the dubitative mood.
The inferential mood has five pure tenses. Two of them are simple - past aorist inferential and past imperfect inferential - and are formed by the past participles of perfective and imperfective verbs, respectively. There are also three compound tenses - past future inferential, past future perfect inferential and past perfect inferential. All these tenses' forms are gender-specific in the singular. There are also conditional and compound-imperative crossovers. The existence of inferential forms has been attributed to Turkic influences by most Bulgarian linguists. Morphologically, they are derived from the perfect.
Non-finite verbal forms
Bulgarian has the following participles:
- Present active participle (сегашно деятелно причастие) is formed from imperfective stems with the addition of the suffixes –ащ/–ещ/–ящ (четящ, "reading") and is used only attributively;
- Present passive participle (сегашно страдателно причастие) is formed by the addition of the suffixes -им/аем/уем (четим, "that can be read, readable");
- Past active aorist participle (минало свършено деятелно причастие) is formed by the addition of the suffix –л– to perfective stems (чел, "[have] read");
- Past active imperfect participle (минало несвършено деятелно причастие) is formed by the addition of the suffixes –ел/–ал/–ял to imperfective stems (четял, "[have been] reading");
- Past passive aorist participle' (минало свършено страдателно причастие) is formed from aorist/perfective stems with the addition of the suffixes -н/–т (прочетен, "read"; убит, "killed"); it is used predicatively and attributively;
- Past passive imperfect participle' (минало несвършено страдателно причастие) is formed from imperfective stems with the addition of the suffix –н (прочитан, "[been] read"); убивaн, [been] being killed); it is used predicatively and attributively;
- Adverbial participle (деепричастие) is usually formed from imperfective present stems with the suffix –(е)йки (четейки, "while reading"), relates an action contemporaneous with and subordinate to the main verb and is originally a Western Bulgarian form. A more rarely used form is the one using the aorist stem, which implies purpose and is a more recent invention (убиейки, "by killing", as opposed to убивайки, "while killing").
The participles are inflected by gender, number, and definiteness, and are coordinated with the subject when forming compound tenses (see tenses above). When used in attributive role the inflection attributes are coordinated with the noun that is being attributed.
Adverbs
The most productive way to form adverbs is to derive them from the neuter singular form of the corresponding adjective (бързо (fast), силно (hard), странно (strange), although adjectives ending in -ки use the masculine singular form, also in -ки, instead: юнашки (heroically), мъжки (bravely, like a man), майсторски (skilfully). The same pattern is used to form adverbs from the (adjective-like) ordinal numerals, e.g. първо (firstly), второ (secondly), трето (thirdly), and in some cases from (adjective-like) cardinal numerals, e.g. двойно (twice as/double), тройно (three times as), петорно (five times as).
The remaining adverbs are formed in ways that are no longer productive in the language. A small number are original (not derived from other words), for example: тук (here), там (there), вътре (inside), вън (outside), много (very/much) etc. The rest are mostly fossilized case forms, such as:
- archaic locative forms of some adjectives, e.g. добре (well), зле (badly), твърде (too, rather), and nouns горе (up), утре (tomorrow), лете (in the summer);
- archaic instrumental forms of some adjectives, e.g. тихом (quietly), скришом (furtively), слепешком (blindly), and nouns, e.g. денем (during the day), нощем (during the night), редом (one next to the other), духом (spiritually), цифром (in figures), словом (with words); or verbs: тичешком (while running), лежешком (while lying), стоешком (while standing).
- archaic accusative forms of some nouns: днес (today),нощес (tonight) сутрин (in the morning), зимъс (in winter);
- archaic genitive forms of some nouns: довечера (tonight), снощи (last night), вчера (yesterday);
- homonymous and etymologically identical to the feminine singular form of the corresponding adjective used with the definite article: здравата (hard), слепешката (gropingly); the same pattern has been applied to some verbs, e.g. тичешката (while running), лежешката (while lying), стоешката (while standing).
- derived from cardinal numerals by means of a non-productive suffix: веднъж (once), дваж (twice), триж (thrice);
Adverbs can sometimes be reduplicated to emphasize the qualitative or quantitative properties of actions, moods or relations as performed by the subject of the sentence: "бавно-бавно" ("rather slowly"), "едва-едва" ("with great difficulty"), "съвсем-съвсем" ("quite", "thoroughly").
Lexis
Most of the word-stock of modern Bulgarian consists of derivations of some 2,000 words inherited from proto-Slavonic through the mediation of Old and Middle Bulgarian. Thus, the native lexical terms in Bulgarian account for 70% to 75% of the lexicon.
The remaining 25% to 30% are loanwords from a number of languages, as well as derivations of such words. The languages which have contributed most to Bulgarian are Russian and Turkish, and to a lesser extent French. Latin and Greek are the source of many words, used mostly in international terminology. Many of the numerous loanwords from Turkish (and, via Turkish, from Arabic and Persian) which were adopted into Bulgarian during the long period of Ottoman rule, have been substituted with native terms. In addition, both specialized (usually coming from the field of science) and commonplace English words (notably abstract, commodity/service-related or technical terms) have also penetrated Bulgarian since the second half of the 20th century, especially since 1989. A noteworthy portion of this English-derived terminology has attained some unique features in the process of its introduction to native speakers and this has resulted in peculiar derivations that slightly set the newly-formed loanwords apart from the original words (mainly in pronunciation), although many loanwords are completely identical to the source words. A growing number of international neologisms are also being widely adopted.
Syntax
Bulgarian employs clitic doubling, mostly for emphatic purposes. For example, the following constructions are common in colloquial Bulgarian:
- Аз (го) дадох подаръка на Мария.
- (lit. "I gave it the present to Maria.")
- Аз (ѝ го) дадох подаръка на Мария.
- (lit. "I gave her it the present to Maria.")
The phenomenon is practically obligatory in the spoken language in the case of inversion signalling information structure (in writing, clitic doubling may be skipped in such instances, with a somewhat bookish effect):
- Подаръка (ѝ) го дадох на Мария.
- (lit. "The present [to her] it I-gave to Maria.")
- На Мария ѝ (го) дадох подаръка.
- (lit. "To Maria to her [it] I-gave the present.")
Sometimes, the doubling signals syntactic relations, thus:
- Петър и Иван ги изядоха вълците.
- (lit. "Petar and Ivan them ate the wolves.")
- Transl.: "Petar and Ivan were eaten by the wolves".
This is contrasted with:
- Петър и Иван изядоха вълците.
- (lit. "Petar and Ivan ate the wolves")
- Transl.: "Petar and Ivan ate the wolves".
In this case, clitic doubling can be a colloquial alternative of the more formal or bookish passive voice, which would be constructed as follows:
- Петър и Иван бяха изядени от вълците.
- (lit. "Petar and Ivan were eaten by the wolves.")
Clitic doubling is also fully obligatory, both in the spoken and in the written norm, in clauses including several special expressions that use the short accusative and dative pronouns, like играе ми се (I feel like playing), студено ми е (I am cold), боли ме ръката (my arm hurts):
- На мен ми се спи, а на Иван му се играе.
- (lit. "To me to me it-feels-like-sleeping, and to Ivan to him it-feels-like-playing")
- Transl.: "I feel like sleeping, and Ivan feels like playing."
- На нас ни е студено, а на вас ви е топло.
- (lit. "To us to us it-is cold, and to you-plur. to you-plur. it-is warm"
- Transl.: "We are cold, and you are warm."
- Иван го боли гърлото, а мене ме боли главата.
- (lit. Ivan him aches the throat, and me me aches the head)
- Transl.: Ivan has sore throat, and I have a headache.
Except the above examples, clitic doubling is considered inappropriate in a formal context. Bulgarian grammars usually do not treat this phenomenon extensively.
Other features
Questions
Questions in Bulgarian which do not use a question word (such as who? what? etc) are formed with the particle ли after the verb; a subject is not necessary, as the verbal conjugation suggests who is performing the action:
- Идваш - you are coming; Идваш ли? - are you coming?
While the particle ли generally goes after the verb, it can go after a noun or adjective if a contrast is needed:
- Идваш ли с нас? - are you coming with us?;
- С нас ли идваш? - are you coming with us (or going with them)?
A verb is not always necessary, e.g. when presenting a choice:
- Той ли? - "him?"; Жълтият ли? - "the yellow one?"[note 5]
Rhetorical questions can be formed by adding ли to a question word, thus forming a "double interrogative" –
- Кой? - "Who?"; Кой ли?! - "I wonder who(?)"
The same construction +не ("no") is an emphasised positive –
- Кой беше там? - "Who was there?" — Кой ли не! - "Nearly everyone!" (lit. "I wonder who wasn't there!")
Significant verbs
Səm
The verb съм (səm)[note 6] - "to be" is also used as an auxiliary for forming the perfect, the passive and the conditional:
- past tense - udaril səm - I have hit
- passive - udaren səm - I am hit
- past passive - byah udaren - I was hit
- conditional - bih udaril - I would hit
Two alternate forms of съм exist -
- бъда (bə̀da) – interchangeable with съм in most tenses and moods, but never in the present indicative - e.g. iskam da bəda (I want to be), shte bəda tuk (I will be here); in the imperative, only бъда is used – bədi tuk! (be here!);
- бивам (bìvam) – slightly archaic, imperfective form of бъда - e.g. bivashe zaplashen (he used to get threats); in contemporary usage, it is mostly used in the negative to mean "ought not", e.g. ne biva da pushish (you shouldn't smoke).[note 7]
Shte
The impersonal verb щe (shte) (lit. "it wants")[note 8] is used to for forming the (positive) future tense:
- otivam - I am going
- shte otivam - I will be going
The negative future is formed with the invariable construction няма да (nyama da - see "nyama" below) [note 9] :
- nyama da otivam - I will not be going
The past tense of this verb – щях (shtyah) – is conjugated to form the past conditional ("would have" - again, with "da", since it is irrealis):
- shtyah da otida - I would have gone; shteshe da otidesh - you would have gone
Ima and Nyama
The verbs имам (imam) (to have) and нямам (nyamam) (to not have) -
- the third person singular of these two can be used impersonally to mean "there is/there are" or "there isn't/aren't any...",[note 10] e.g. -
- ima vreme (there is still time - compare Spanish "hay");
- nyama nikoy (there is no one there).
- The impersonal form няма (nyama) is used in the negative future - see shte, above.
- nyama used on its own can mean simply "I won't" - a simple refusal to a suggestion or instruction.
Diminutives and augmentatives
Diminutive
- See also: Diminutive#Bulgarian
Usually done by adding "-che", "-tse" or "-(ch)ka". The gender of the word is thus changed, usually to the neuter:
- kolà (car) → kolìchka (pram/baby's buggy)
- kotka/kote (cat) → kotentse (kitten)
- Affectionate Form
Sometimes proper nouns and words referring to friends or family members can have a diminutive ending added to show affection. These constructions are all referred to as "na galeno" (lit. "caressing" form):
- mayka (mother) → maychitse; tatko (father) → tatentse
Such words can be used both from parent to child, and vice-versa, as can -
- batko (big brother) → batentse; priyatel (friend) → priyatelche.
Personal names are shortened and made neuter:
- Georgi → Gosho/Gotse, Mihail → Misho, Angel → Gele/Acho, Ivan → Vanko, Vasil → Vasko
- Anna → Ani, Irina → Reni
There is an interesting trend (which is comparatively modern, although it might well have deeper, dormant roots) where the feminine ending "-ka" and the definite article suffix "-ta" ("the") are added to male names – note that this is affectionate and not at all insulting (in fact, the endings are not even really considered as being "feminine"):
- Ivan → Vànkata, Acho → Àchkata.
The female equivalent would be to add the neuter ending "-to" to the diminutive form:
- Nadia → Nadeto, Sonia → Soncheto
Augmentative
This is to present words to sound larger - usually by adding "-shte":
- chovek (person) → chovechishte (huge person) (note the root change k→ch)
Some words only exist in an augmentative form - e.g.
- zrelishte "(awesome) spectacle" (from the old Slavic root "to see")
- svlachishte "landslide" - from svlicham "to drag down"
Conjunctions and particles
- "But"
In Bulgarian, there are several conjunctions all translating into English as "but", which are all used in distinct situations. They are но (no), ама (amà), а (a), ами (amì), and ала (alà) (and обаче (obache) — "however", identical in use to но).
While there is some overlapping between their uses, in many cases they are specific. For example, ami is used for a choice — ne tova, ami onova — "not this one, but that one" (comp. Spanish sino), while ama is often used to provide extra information or an opinion — kazah go, ama sgreshih — "I said it, but I was wrong". Meanwhile, a provides contrast between two situations, and in some sentences can even be translated as "although", "while" or even "and" — az rabotya, a toy blee — "I'm working, and he's daydreaming".
Very often, different words can be used to alter the emphasis of a sentence — e.g. while "pusha, no ne tryabva" and "pusha, a ne tryabva" both mean "I smoke, but I shouldn't", the first sounds more like a statement of fact ("...but I mustn't"), while the second feels more like a judgement ("...but I oughtn't"). Similarly, az ne iskam, ama toy iska and az ne iskam, a toy iska both mean "I don't want to, but he does", however the first emphasises the fact that he wants to, while the second emphaseses the wanting rather than the person.
Ala is interesting in that, while it feels archaic, it is often used in poetry and frequently in children's stories, since it has quite a moral/ominous feel to it.
Some common expressions use these words, and some can be used alone as interjections:
- da, ama ne (lit. "yes, but no") — means "you're wrong to think so".
- ama can be tagged onto a sentence to express surprise: ama toy spi! — "he's sleeping!"
- ами! — "you don't say!", "really!"
Vocative particles
Bulgarian has several abstract particles which are used to strengthen a statement. These have no precise translation in English.[note 11] The particles are strictly informal and can even be considered rude by some people and in some situations. They are mostly used at the end of questions or instructions.
- бе (be) - the most common particle. It can be used to strengthen a statement or, sometimes, to indicate derision of an opinion, aided by the tone of voice. (Originally purely masculine, it can now be used towards both men and women.)
- kazhi mi, be - tell me (insistence); taka li, be? - is that so? (derisive); vyarno li, be? - you don't say!.
- де (de) - expresses urgency, sometimes pleading.
- stavay, de! - come on, get up!
- ма (ma) (feminine only) - originally simply the feminine counterpart of be, but today perceived as rude and derisive (compare the similar evolution of the vocative forms of feminine names).
- бре (bre, masculine), мари(mari, feminine) - similar to be and ma, but archaic. Although informal, can sometimes be heard being used by older people.
Modal Particles
These are "tagged" on to the beginning or end of a sentence to express the mood of the speaker in relation to the situation. They are mostly interrogative or slightly imperative in nature. There is no change in the grammatical mood when these are used (although they may be expressed through different grammatical moods in other languages).
- нали (nalì) – is a universal affirmative tag, like "isn't it"/"won't you", etc (it is invariable, like the French n'est-ce pas). It can be placed almost anywhere in the sentence, and does not always require a verb:
- shte doydesh, nali? - you are coming, aren't you?; nali iskaha? - didn't they want to?; nali onzi? - that one, right?;
- it can express quite complex thoughts through simple constructions - nali nyamashe? - "I thought you weren't going to!" or "I thought there weren't any!" (depending on context - the verb nyama presents general negation/lacking, see "nyama", above).
- дали (dalì) – expresses uncertainty (if in the middle of a clause, can be translated as "whether") - e.g. dali shte doyde? - "do you think he will come?"
- нима (nimà) – presents disbelief ~"don't tell me that..." - e.g. nima iskash?! - "don't tell me you want to!". It is slightly archaic, but still in use. Can be used on its own as an interjection - nima!
- дано (danò) – expresses hope - shte doyde - "he will come"; dano doyde - "I hope he comes" (comp. Spanish ojalá). Grammatically, dano is entirely separate from the verb nadyavam se - "to hope".
- нека (nèka) – means "let('s)" - e.g. neka doyde - "let him come"; when used in the first person, it expresses extreme politeness: neka da otidem... - "let us go" (in colloquial situations, haide, below, is used instead).
- neka, as an interjection, can also be used to express judgement or even Schadenfreude - neka mu! - "he deserves it!".
Intentional particles
These express intent or desire, perhaps even pleading. They can be seen as a sort of cohortative side to the language. (Since they can be used by themselves, they could even be considered as verbs in their own right.) They are also highly informal.
- хайде (hàide) - "come on", "let's"
- e.g. haide, po-burzo - "faster!"
- я (ya) - "let me" - exclusively when asking someone else for something. It can even be used on its own as a request or instruction (depending on the tone used), indicating that the speaker wants to partake in or try whatever the listener is doing.
- ya da vidya - let me see; ya? or ya! - "let me.../give me..."
- недей (nedèi) (plur. nedèyte) – can be used to issue a negative instruction - e.g. nedey da idvash - "don't come" (nedey + subjunctive). In some dialects, the construction nedey idva (nedey + preterite) is used instead. As an interjection – nedei! - "don't!" (See section on imperative mood).
These particles can be combined with the vocative particles for greater effect, e.g. ya da vidya, be (let me see), or even exclusively in combinations with them, with no other elements, e.g. haide, de! (come on!); nedey, de! (I told you not to!).
Pronouns of Quality
Bulgarian has several pronouns of quality which have no direct parallels in English — kakuv (what sort of); takuv (this sort of); onakuv (that sort of — colloq.); nyakakuv (some sort of); nikakuv (no sort of); vsyakakuv (every sort of); and the relative pronoun kakuvto (the sort of...that...). The adjective ednakuv ("the same") derives from the same radical.[note 12]
Example phrases include:
- kakuv chovek?! — "what person?!"; kakuv chovek e toy? — what sort of person is he?
- ne poznavam takuv — "I don't know any (people like that)" (lit. "I don't know this sort of (person)")
- nyakakvi hora — lit. "some type of people", but the understood meaning is "a bunch of people I don't know"
- vsyakakvi hora — "all sorts of people"
- kakuv iskash? — "which type do you want?"; nikakuv! — "I don't want any!"/"none!"
An interesting phenomenon is that these can be strung along one after another in quite long constructions, e.g. -
| word | literal meaning | sentence | meaning of sentence as a whole |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | edna kola | a car |
| takava | this sort of | edna takava kola... | this car (that i'm trying to describe) |
| nikakva | no sort of | edna takava nikakva kola | this worthless car (that i'm trying to describe) |
| nyakakva | some sort of | edna takava nyakakva nikakva kola | this sort of worthless car (that I'm trying to describe) |
An extreme (colloquial) sentence, with almost no physical meaning in it whatsoever — yet which does have perfect meaning to the Bulgarian ear — would be :
- "kakva e taya takava edna nyakva nikva?!"
- inferred translation — "what kind of no-good person is she?"
- literal translation: "what kind of — is — this one here (she) — this sort of — one — some sort of — no sort of"
— Note: the subject of the sentence is simply the pronoun "taya" (lit. "this one here"; colloq. - "she").
Similar "meaningless" expressions are extremely common in spoken Bulgarian, especially when the speaker is finding it difficult to describe something.
Miscellaneous
- The commonly-cited phenomenon of Bulgarian people shaking their head for "yes" and nodding for "no" is true but, with the influence of Western culture, ever rarer, and almost non-existent among the younger generation. (It should be noted, however, that the shaking and nodding are not identical to the Western gestures. The "nod" for no is actually an upward movement of the head rather than a downward one, while the shaking of the head for yes is not completely horizontal, but also has a slight "wavy" aspect to it.)
- A dental click [ǀ] (similar to the English "tsk") also means "no" (informal), as does ъ-ъ [ʔə-ʔə] (the only occurrence in Bulgarian of the glottal stop). The two are often said with the upward 'nod'.
- Bulgarian has an extensive vocabulary covering family relationships. The biggest range of words is for uncles and aunts – e.g. chicho (your father's brother), vuicho (your mother's brother), svako (your aunt's husband); an even larger amount of synonyms for these three exists in the various dialects of Bulgarian, including kaleko, lelincho, tetin, etc. The words do not only refer to the closest members of the family (such as brat - brother, but batko - older brother), but extend to its furthest reaches, e.g. badjanak (the relationship of the husbands of two sisters to each other).
- As with many Slavic languages, the double negative in Bulgarian is grammatically correct, while some forms of it, when used instead of a single negative form, are grammatically incorrect. The following are literal translations of grammatically correct Bulgarian sentences that utilize a double or multiple negation: "Никой никъде никога нищо не е направил." (multiple negation without the use of a compound double negative form, i.e. using a listing of several successive single negation words) - "Nobody never nowhere nothing did not do." (translated as "nobody has ever done anything, anywhere"); "Никога не съм бил там." (double negation without the use of a compound double negative form, i.e. using a listing of several successive single negation words) - I did not there never go ("[I] have never been there"); Никога никакви чувства не съм имал! - I have not never had no feelings! (I have never had any feelings!). The same applies for Macedonian.
Vocabulary
Comparison with other Slavic languages
| Bulgarian (Български) | Macedonian (Македонски) | Serbian (Српски/Srpski) | Russian (Русский) | Polish (Polski) | English |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| дърво | дрво | дрво/drvo | дерево | drzewo | tree |
| картоф | компир | кромпир/krompir | картофель | ziemniak, kartofel | potato |
| котка | мачка | мачка/mačka | кошка | kot | cat |
| куче, пес | куче, пес | пас/pas | собака, пёс | pies | dog |
| къща, дом | куќа, дом | кућа, дом / kuća, dom | дом | dom | house, home |
| маса | маса | сто/sto | стол | stół | table (furniture) |
| мляко | млеко | млеко/mleko | молоко | mleko | milk |
| стол | стол | столица/stolica | стул | krzesło | chair |
| Bulgarian (Български) | Macedonian (Македонски) | Serbian (Српски/Srpski) | Russian (Русский) | Polish (Polski) | English |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| имам | имам | имам/imam | имею | mam | I have |
| искам, желая | сакам | желим, хоћу/želim, hoću | хочу, желаю | chcę | I want |
| правя,върша | правам, вршам | вршим/vršim | делаю | robię | I do |
| ходя, вървя | одам, врвам | ходам/hodam | хожу | chodzę | I walk |
| говоря, думам, приказвам, казвам | зборувам, говорам | говорим/govorim | говорю | mówię | I talk |
| намирам | наоѓам | налазим/nalazim | нахожу | znajduję | I find |
| ям | јадам, ручам | једем/jedem | ем | jem | I eat |
| пия | пијам | пијем/pijem | пью | piję | I drink |
Common expressions
- Здравей (zdravéy) — Hello
- Здрасти (zdrásti) — Hi [note 13]
- Добро утро (dobró útro) — Good morning
- Добър ден (dóbər dén) — Good day
- Добър вечер (dóbər vécher) — Good evening
- Лека нощ (léka nósht) — Good night
- Довиждане (dovízhdane) — Good-bye
- Как се казваш? (kak se kazvash) — What is your name (informal)?
- Кой си ти? (kóy si ti) [informal, masculine] — Who are you?
- Коя си ти? (kоyá si ti) [informal, feminine] — Who are you?
- Кой сте вие? (kóy ste víe) [formal, masculine]
- Коя сте вие? (kоyá ste víe) [formal, feminine] — Who are you?
(In the above two examples, the formal expression uses a plural verb but a singular pronoun, which allows speakers to distinguish the two grammatical forms.)
- Кои сте вие? (kоí ste víe) [plural form] — Who are you?
- Как си? (kák si) [informal] — How are you?
- Как сте? (kák sté) [formal, and also plural form] — How are you?
- Да (dá) — Yes
- Не (né) — No
- Може би (mózhe bí) — Maybe
- Какво правиш? (kakvó právish) [informal] — What are you doing?
- Какво правите? (kakvó právite) [formal, and also plural form] — What are you doing?
- Добре съм (dobré səm) — I’m fine
- Всичко [най-]хубаво (vsíchko [nay-]húbavo) — All the best
- Поздрави (pózdravi) — Regards
- Благодаря (blagodaryə́) [formal and informal] — Thank you
- Моля (mólya) — Please
- Моля (mólia) — You're welcome
- Извинете! (izvinéte) [formal] — Excuse me!
- Извинявай! (izvinyávai) [informal] — Sorry!
- Обичам те! (obícham te) — I love you!
- Колко е часът? (kólko e chasə́t) — What’s the time?
- Говорите ли…? (govórite li…) — Do you speak…?
- …английски (anglíyski) — English
- …български (bə́lgarski) — Bulgarian
- …немски (némski) — German
- …полски (polski) — Polish
- …руски (ruski) — Russian
- …холандски (holándski) — Dutch
- …гръцки (grə́tski) — Greek
- …сръбски (srə́bski) — Serbian
- …италиански (italiánski) — Italian
- …испански (ispánski) — Spanish
- …френски (frénski) — French
- …японски (yapónski) — Japanese
- …китайски (kitáyski) — Chinese
- …корейски (koréyski) — Korean
- …арабски (arabski) — Arabian
- Ще се видим скоро (shté sé vídim skóro) — We'll see each other soon
- Ще се видим утре (shté sé vídim útre) — We'll see each other tomorrow
Also, some very frequent expressions have been borrowed from other languages. Most of them are somewhat informal.
- Мерси (mersí) — Thank you; from French (although this word is probably even more common than native "Благодаря", it is inappropriate in very official or solemn contexts)
- Чао (cháo) — Bye; from Italian (the informal counterpart of native "Довиждане", this word is more common than the native)
- Cупep (súper) — Super; (from English, colloquial; note - "Super" remains the same regardless of quantity or gender, although an even more colloquial adjective суперски (súperski) does decline as usual)
- Aло (álo) — Hallo on the phone; from French (unlike the above, this word is stylistically neutral).
- Здраве да е! (zdràve da e) — lit. "may there (at least) be health" (used when things have not gone as well as the speaker might have hoped.)
See also
- Ausbausprache – Abstandsprache – Dachsprache
- Balkan sprachbund
- Macedonian language
- Romanization of Bulgarian
- Slavic language (Greece)
- Torlakian dialect
- Swadesh list of Bulgarian words
- Bulgarian name
Notes
- ↑ Sometimes transcribed as /ə/, also in this article.
- ↑ For practical purposes, the grave accent can be combined with letters by pasting the symbol "̀" directly after the designated letter. An alternative is to use the keyboard shortcut Alt + 0300 (if working under a Windows operating system), or to add the decimal HTML code "̀" after the targeted stressed vowel if editing HTML source code. See "Accute accent" diacritic character in Unicode, Unicode character "Cyrillic small letter i with grave" and Unicode character "Cyrillic capital letter i with grave" for the exact Unicode characters that utilize the grave accent. Retrieved 2010-06-21.
- ↑ One should be careful not to confuse these last two with their opposites не го, {ne gò} and не му, {ne mù} - "not...(to) him"! Similar with the feminine: нея, {nèya} (to her) ≠ не я (нея я̀), {ne yà} (not...her)
- ↑ All of these are becoming ever rarer in modern Bulgarian, especially кому {komu} and its derivatives. Instead of this, people often say на кого {na kogo} or even на кой {na koy}; на кой {na koy} itself is even beginning to replace the accusative на кого {na kogo}, although this usage is currently deemed grammatically incorrect and frowned upon.
- ↑ The word или ("either/or") has a similar etymological root: и + ли ("and + ?") - e.g. (или) Жълтият или червеният - "(either) the yellow one or the red one". wiktionary
- ↑ Səm - pronounced similar to English "sum".
- ↑ It is a common reply to the question Kak e? "How are things?" (lit. "how is it?") – biva "alright" (lit. "it (repetitively) is") or Kak si? "How are you?" -bìvam "I'm OK".
- ↑ "Shte" - from the verb щa (shta) - "to want". The present tense of this verb in the sense of "to want" is archaic and only used colloquially. Instead, искам (iskam) is used.
- ↑ Formed from the impersonal verb няма (nyama) (lit. "it does not have") and the subjunctive particle да (da - "that")
- ↑ They can also be used on their own as a reply, with no object following: ima - "there are some"; nyama - "there aren't any" - compare German keine.
- ↑ Perhaps most similar in use is the tag "man", but the Bulgarian particles are more abstract still.
- ↑ Like the demonstratives, these take the same form as pronouns as they do as adjectives — ie. takuv means both "this kind of..." (adj.) and this kind of person/thing (pron., depending on the context).
- ↑ This is a more informal form of Здравей In polite conversation, the "Vi" form is used by both parties: zdraveyte.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Ethnologue". Ethnologue. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=bul. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dalby 2007, Dictionary of Languages)
- ↑ Macedonia: warlords and rebels in the Balkans, John Phillips, I.B.Tauris, 2004, ISBN 186064841X, p. 60.
- ↑ "Стойков, Стойко. 2002 (1962) Българска диалектология. Стр. 101". Promacedonia.org. http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_izt_0.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ↑ "Стойков, Стойко. 2002 (1962) Българска диалектология. Стр. 99". Promacedonia.org. http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_izt_0.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ↑ Mazon, Andre. Contes Slaves de la Macédoine Sud-Occidentale: Etude linguistique; textes et traduction; Notes de Folklore, Paris 1923, p. 4.
- ↑ Селищев, Афанасий. Избранные труды, Москва 1968.
- ↑ Die Slaven in Griechenland von Max Vasmer. Verlag der Akademie der Wissenschaften, Berlin 1941. Kap. VI: Allgemeines und sprachliche Stellung der Slaven Griechenlands.
- ↑ K. Sandfeld, Balkanfilologien (København, 1926, MCMXXVI).
- ↑ Konstantin Josef Jireček, Die Balkanvölker und ihre kulturellen und politischen Bestrebungen, Urania, II, Jg. 13, 27. März 1909, p. 195.
- ↑ Stefan Verković, Описание быта македонских болгар; Топографическо-этнографический очерк Македонии (Петербург, 1889).
- ↑ Шклифов, Благой and Екатерина Шклифова, Български деалектни текстове от Егейска Македония, София 2003, с. 28-36 (Shklifov, Blagoy and Ekaterina Shklifova. Bulgarian dialect texts from Aegean Macedonia Sofia 2003, p. 28-33)
- ↑ Жобов, Владимир (2004) Звуковете в българския език. Стр. 44-45.
- ↑ Жобов, Владимир (2004) Звуковете в българския език. Стр. 65-66.
- ↑ Куон Джин Чой (1998). Фонологичността на признака мекост в съвременния български език. http://liternet.bg/publish1/choi/mekost.htm
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Кръстев, Боримир, 1992. Граматика за всички. Стр.61.
- ↑ Пашов, Петър (1999) Българска граматика. Стр.73-74.
Bibliography
- Comrie, Bernard and Corbett, Greville G. (1993) The Slavonic Languages, London and New York: Routledge ISBN 0-415-04755-2
- International Phonetic Association (1999) Handbook of the International Phonetic Association ISBN 0-521-63751-1
- Бояджиев и др. (1998) Граматика на съвременния български книжовен език. Том 1. Фонетика
- Жобов, Владимир (2004) Звуковете в българския език
- Кръстев, Боримир (1992) Граматика за всички
- Пашов, Петър (1999) Българска граматика
External links
Linguistic reports
Dictionaries
- Bulgarian-English-Bulgarian Online dictionary from SA Dictionary
- Online Dual English-Bulgarian dictionary
- Online automatic translation between Bulgarian, English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish
- Bulgarian Dictionary: from Webster’s Dictionary
- Bulgarian bilingual dictionaries
- Englisch-Bulgarian (Cyrillic) Dictionary
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
