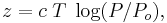Altimeter

An altimeter is an instrument used to measure the altitude of an object above a fixed level. The measurement of altitude is called altimetry, which is related to the term bathymetry, the measurement of depth underwater.
Contents |
Pressure altimeter
Altitude can be determined based on the measurement of atmospheric pressure. The greater the altitude, the lower the pressure. When a barometer is supplied with a nonlinear calibration so as to indicate altitude, the instrument is called a pressure altimeter or barometric altimeter. A pressure altimeter is the altimeter found in most aircraft, and skydivers use wrist-mounted versions for similar purposes. Hikers and mountain climbers use wrist-mounted or hand-held altimeters, in addition to other navigational tools such as a map, magnetic compass, or GPS receiver.
The calibration of an altimeter is of the form
where c is a constant, T is the absolute temperature, P is the pressure at altitude z, and Po is the pressure at sea level. The constant c depends on the acceleration of gravity and the molar mass of the air.
Use in hiking and climbing
An altimeter, used along with a topographic map, can help to verify one's location. It is more reliable, and often more accurate, than a GPS receiver for measuring altitude; GPS may be unavailable, for example, when one is deep in a canyon, or may give wildly inaccurate altitudes when all available satellites are near the horizon. Because the barometric pressure changes with the weather, hikers must periodically recalibrate their altimeters when they reach a known altitude, such as a trail junction or peak marked on a topographical map.
Use in aircraft

In it, an aneroid barometer measures the atmospheric pressure from a static port outside the aircraft. Air pressure decreases with an increase of altitude—approximately 100 hectopascals per 800 meters or one inch of mercury per 1000 feet near sea level.
The altimeter is calibrated to show the pressure directly as an altitude above mean sea level, in accordance with a mathematical model defined by the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA). Older aircraft used a simple aneroid barometer where the needle made less than one revolution around the face from zero to full scale. Modern aircraft use a "sensitive altimeter" which has a primary needle that makes multiple revolutions, and one or more secondary needles that show the number of revolutions, similar to a clock face. In other words, each needle points to a different digit of the current altitude measurement.
On a sensitive altimeter, the sea level reference pressure can be adjusted by a setting knob. The reference pressure, in inches of mercury in Canada and the US and hectopascals (previously millibars) elsewhere, is displayed in the Kollsman window, visible at the right side of the aircraft altimeter shown here. This is necessary, since sea level reference atmospheric pressure varies with temperature and the movement of pressure systems in the atmosphere.
In aviation terminology, the regional or local air pressure at mean sea level (MSL) is called the QNH or "altimeter setting", and the pressure which will calibrate the altimeter to show the height above ground at a given airfield is called the QFE of the field. An altimeter cannot, however, be adjusted for variations in air temperature. Differences in temperature from the ISA model will, therefore, cause errors in indicated altitude.
Radar altimeter
A radar altimeter measures altitude more directly, using the time taken for a radio signal to reflect from the surface back to the aircraft. The radar altimeter is used to measure height above ground level during landing in commercial and military aircraft. Radar altimeters are also a component of terrain avoidance warning systems, warning the pilot if the aircraft is flying too low, or if there is rising terrain ahead. Radar altimeter technology is also used in terrain-following radar allowing fighter aircraft to fly at very low altitude.
Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers can also determine altitude by trilateration with four or more satellites. In aircraft, altitude determined using autonomous GPS is not precise or accurate enough to supersede the pressure altimeter without using some method of augmentation. In hiking and climbing, it is not uncommon to find that the altitude measured by GPS is off by as much as a thousand meters, if all the available satellites happen to be close to the horizon.
Other modes of transport
The altimeter is an instrument optional in off-road vehicles to aid in navigation. Some high-performance luxury cars which were never intended to leave paved roads, such as the Duesenberg in the 1930s, have also been equipped with altimeters.
Hikers and mountaineers use hand-held or wrist-mounted barometric altimeters, as do skydivers.
Diesel submarines have altimeters installed on them to monitor vacuum being pulled in the event the snorkel closes while the diesels are running consequently sucking the air out of the boat.
Measuring air pressure
The local atmospheric pressure or ambient pressure is displayed in the Kollsman window of a sensitive altimeter, when it is adjusted to read zero altitude.[2]
Satellites
A number of satellites (see links) use advanced dual-band radar altimeters to measure height from a spacecraft. That measurement, coupled with orbital elements (possibly augmented by GPS), enables determination of the terrain. The two different wavelengths of radio waves used permit the altimeter to automatically correct for varying delays in the ionosphere.
Spaceborne radar altimeters have proven to be superb tools for mapping ocean-surface topography, the hills and valleys of the sea surface. These instruments send a microwave pulse to the ocean’s surface and time how long it takes to return. A microwave radiometer corrects any delay that may be caused by water vapor in the atmosphere. Other corrections are also required to account for the influence of electrons in the ionosphere and the dry air mass of the atmosphere. Combining these data with the precise location of the spacecraft makes it possible to determine sea-surface height to within a few centimetres (about one inch). The strength and shape of the returning signal also provides information on wind speed and the height of ocean waves. These data are used in ocean models to calculate the speed and direction of ocean currents and the amount and location of heat stored in the ocean, which, in turn, reveals global climate variations.
See also
- Flight instruments
- Flight level
- seasat, TOPEX/Poseidon are satellites that deployed extremely accurate altimeters
- United Airlines Flight 389, an accident attributed to misreading of an altimeter
- Turkish Airlines Flight 1951, an accident attributed to a malfunctioning radio altimeter
- Jason-1, Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2 are current satellite missions that use altimeters to measure sea surface height
External links
- MS5561C Micro Altimeter for GPS, 1m resolution
- History of the Kollsman altimeter
- A Flash 8 based simulator for altimeter errors caused by variations in temperature and pressure
- The use of altimeters in height measurement - for hillwalkers
- Compact digital pressure sensor for altimeters
- Early use of barometers on surveys
- The altimeter and the types of altitude
- Evolution of the Modern Altimeter - Flight archive
- Altimeter Guide and History
References
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||