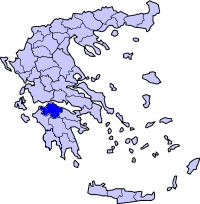
Achaea
| Achaea Prefecture Νομός Αχαΐας |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
| Country: | |
| Capital: | Patras |
| Periphery: | West Greece |
| Population: | 331,316 (2005) Ranked 5th |
| Area: | 3,271.507 km² (1,263 sq.mi.) Ranked 14th |
| Density: | 101 /km² (262 /sq.mi.) Ranked 9th |
| Number of municipalities: | 21 |
| Number of communities: | 2 |
| Postal codes: | 25x xx - 26x xx |
| Area codes: | 261, 269x |
| Licence plate code: | ΑΖ, AX |
| ISO 3166-2 code: | GR-13 |
| Website: | http://www.achaia.gr/ |
Achaea (Greek: Αχαΐα Achaïa, [axaˈia]; Ἀχαία in polytonic orthography) is an ancient province and a present prefecture of Greece, on the northern coast of the Peloponnese, stretching from the mountain ranges of Erymanthus and Cyllene on the south to a narrow strip of fertile land on the north, bordering the Gulf of Corinth, into which the mountain Panachaicus (1,902 m, the northernmost mountain range in the Peloponnese) projects.
Achaea is bounded on the west by the territory of Elis, on the east by that of Sicyon, which, however, was sometimes included in it. The population in 2001 had reached over 300,000.
.svg.png)
Contents |
Geography
Its geography features the Omblos and Marathia mountains to the east, Erymanthos to the centre, Chelmos or Aroania in the southeast, Skollis in the southwest, Movri and Mavros Oros to the west. Rivers ordered from west to east include the Larissos, Tytheos, Parapeiros and Charadros to the northwest and Selinountas, Vouraikos and several others to the east. Most of the forests are in the mountain ranges, though several are in the plains including the extreme west. There are grasslands around the mid-elevation areas and barren lands in the highest areas.
Climate
Achaea has hot summers and mild winters. Sunny days dominate during the summer months in areas near the coast, while the summer can be cloudy and rainy in the mountains. Snow is very common during the winter in the mountains of Erymanthus, Panachaicus and Aroania. Winter high temperatures are around the 10°C mark throughout the low lying areas.
Provinces
- Province of Aigialeia - Aigio
- Province of Kalavryta - Kalavryta
- Province of Patras - Patras
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece.
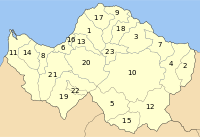
Municipalities and communities
| Municipality | YPES code | Seat (if different) | First existence | Refounded |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aigeira | 0701 | Aigeira | - | - |
| Aigio | 0702 | Aigio | - | - |
| Akrata | 0703 | Akrata | - | 1997 |
| Aroania | 0704 | Psofida | - | - |
| Diakopto | 0706 | Diakopto | - | 1997 |
| Dymi | 0707 | Kato Achaïa | - | 1997 |
| Erineos | 0708 | Kamares | - | 1994 |
| Farres | 0722 | Chalandritsa | - | 1997 |
| Kalavryta | 0709 | Kalavryta | - | 1997 |
| Larissos | 0711 | Metóchi | - | 1997 |
| Lefkasio | 0713 | Kleitoria | - | 1997 |
| Messatida | 0714 | Ovrya | - | 1997 |
| Movri | 0715 | Sageika | - | 1997 |
| Olenia | 0723 | Lousika | - | 1997 |
| Paion | 0716 | Dafni | - | 1997 |
| Paralia | 0717 | Paralia | - | - |
| Patras | 0718 | Patras | 1830 | not refounded |
| Rio | 0719 | Rio | - | - |
| Sympoliteia | 0720 | Rododafni | - | - |
| Tritaia | 0721 | Stavrodromi | 1830s-1910s | 1997 |
| Vrachnaiika | 0705 | Vrachnaiika | - | - |
| Community | YPES code | Seat (if different) | ||
| Kalentzi | 0710 | Ágios Geórgios | - | - |
| Leontio | 0712 | Leontio | - | - |
Former municipalities
- Erymanthia - existed until 1913, it covered the western and the central portions of the Erymanthos mountain range except in the Elis side.
- Panachaia - existed until the late-1940s, it covered the western portion of the Panachaiko mountains hence its name which is the current eastern portion of the city of Patras.
Main towns and cities
Here are the cities ranked by the largest, as of 2003.
- Patra (Patras) 150,000 (est.), (met. about 200,000)
- Aigion 30,000 (est.)
- Rhion
- Ovrya
- Kato Achaia
- Aigeira
- Akrata
- Kalavryta
- Vrachnaiika
- Mintilogi
- Paralia
- Alissos
- Ptéri
- Chalandritsa
- Diakopton/Diacopton
- Psathopyrgos
History
Ancient Achaea
Medieval and modern history
Achaea remained a province of the Byzantine Empire after the fall of the western Roman Empire. However, after the Fourth Crusade several new crusader states were founded in Greece. One of these was the Principality of Achaea, which like the Roman province, covered a much larger area than traditional Achaea.
The Principality of Achaea fell to the Ottoman Empire in the mid-15th century. The area was later invaded by the Venetians in the late-16th and the 17th centuries and later invaded by the Ottomans again.
In 1821, it became part of Greece. During the Greek War of Independence, Aigio was the first city to be liberated by the Greeks and several villages days after as well as the city of Patras. Achaea or Achaia later produced several heroes including Kanaris, Zaimis and Roufos and prime ministers of Greece including Andreas Michalakopoulos as well as some head of states.
In the first years of the country, the prefecture amalgamated to form the prefecture of Achaea-Elis of Achaea and Elis until 1899 and covered an area of around 6,000 km², the older enlarged again in 1909 and did not finally split again until 1936. The area of Mataragka remained historically Ilia until the 1990s along with the area of Vouprasi.
Georgios Mavrommatis (ran in 1828) was the first prefectural head in modern Achaea and Georgios Glarakis was the first leader that ran in the 1830s.
Achaea saw an influx of refugees that arrived from Asia Minor during the Greco Turkish War of 1919-1922. Tens of thousands were relocated to their camps in the suburbs of Patras and a few villages mainly within the coastline. One of the camps was named Prosfygika
After World War II and the Greek Civil War, many of its buildings were rebuilt and this work took several years.
In the 20th century, the area which excluded Metochi reverted from Ilia as the municipality of Kalotychia became Vouprasias. That part had been a part of Ilia, then Elis during the ancient times. Another reorganization reverted Mataranga and Spata into the prefecture of Achaia and the municipality of Larissos.
A mid-1994 late-night (around 3 AM local time) earthquake rumbled the area with a magnitude around 5 on the Richter scale. This was a minor one. It was after another earthquake. A forest fire consumed the northern part of the Panachaicus in the mid-1990s. Many municipalities were recreated between 1994, several more and 1997 and several others in 1998 which revived Tritaia, Movri, Erymanthos, Kalavryta and many more. Every administrative community became municipal and communal districts.
Population

Achaea today has about one-third of its peninsula's inhabitants and two-thirds of Achaia living in the Patra area which is the capital of Achaea and the Peloponnese, and more than half of the population live in the city (municipality). It is also the third largest city in Greece excluding Piraeus. The main industrial area is 20 km south of the city near Fares, and Tsoukoulaiíka and Vrachnaiíka.
Aigion is a seaside city with a city hall and a city square is in its heart. The population is around 30,000.
Culture
Kalavrita is a town situated more than 70 km to the east via the road from Achaea's capital. A few kilometres to its west is a monastery situated on the peak of the hill. Its name is Aghía Lávra. 12 to 20 km east, is Cave Lakes where lakes are inside this brilliant cave. It is open to tourists, and the length is around 300 to 500 m. The mountain hosts the most modern Greek telescope, named Aristarchus (after the ancient Greek astronomer - Aristarchus of Samos) and operated by the National Observatory of Athens A narrow gauge railway track runs for 30 km, mainly as a tourist attraction. The track begins near Kalavrita and ends off Diakopton.
Economy
Patras is one of the main industrial and commerce centers in Greece.
Temeni is a place where the famous spring water Avra (Άυρα) or Aúra is manufactured. It is owned by Tria Epsilon, a division of Coca-Cola Company and a parent.
There are no oil refineries except for a small refinery near Rio.
Transport
There are two main bus terminals in the cities of Patras and Aigio.
The main highways are:
- E55, NW, N-Cen., N
- E65, N, NE
- GR-5, N-Cen., N
- GR-8 (longest), old national road, N, NE
- GR-8A, superhighway/new national road, N, NE
- GR-9, old and new, N-Cen., NW, W
- GR-31 (Aigio - Pteri), NE, E-Cen.
- GR-33, N-Cen., SW, S, SE
- GR-48, N-Cen., N
- GR-62 (Kato Achaia - Araxos), NW (length: 13 km)
- Aigeira-Akrata Road
- Kalavryta-Diakopto Road
- Kalavryta-Kato Kleitoria Road
- Patras By-Pass
- Patras-Kalavryta Road
Pavement began in the 1960s, the 1970s and the 1980s
A bypass which bypasses Patras begun construction in 1990, and extended construction to GR-33 in 1992, Savalia in 1993, East Patra or Patras in 1995, and in 1998 into GR-8. Lights were installed in the early 2000s on the beltway, and opened to traffic on late 2003. It starts from near Roitika and ends just south of Rhion.
GR-8 was the first superhighway, along with GR-5 in the prefecture. The beltway is the second, and the bridge will be the third. Its length now has almost 100 km of superhighway. Its length was only 70 to 75 km until 2003.
The Rio-Antirrio bridge, which started construction in 2000 (though plans had been made throughout the 1990s, and was supposed to begin in those years), opened in mid-2004, connecting the mainland and the Peloponnese. This eliminated much of the ferry service which has been used for about half a century for automobiles. Since then, there is only the rare ferry service in the city of Aigio(n), which is the ferry route to Aghios Nikolaos in Phocis.
A future superhighway between Patras and Pyrgos was announced in the winter of 2003 and will be in plan, but no date has been set.
Communications
Newspapers, fanzines and others
Current newspapers
- Achagiotika Nea - Kato Achaia
- Allagi - Patras
- Elliniki Dimokratia - Patras
- Epi ta proso - Patras
- Evdomada - Patras
- Filodimos - Aigio
- Frouros tis Anatolikis Aigialeias - Akrata and eastern Aigaleia
- Ta Gegonota tis Achaias - Achaea
- I Gnomi - Patras
- Imera - Patras [1]
- Imerisios Kyrix - Patras
- Kosmos tis Patras - Patras
- Paraliaki - Patras
- Pelopas - uncertain
- Patraiki Evdomada - Patras
- Politis ton Patron - Patras - political
- Proodos - Patras
- Proti tis Aigaleias - Aigio and Aigaleia
- Simerini - Patras
- Splats - a fanzine based in Patras
- Sport Week - Patras - sports
- Sportivo west - Patras - sports
- Styx - Akrata
- Symvoulos Epocheiriseon - Patras
- Toxotis - uncertain
Ceased and defunct newspapers
- Achaikos Kyrix - an older newspaper of Patras
- Tachydromos tis Anatolis - Patras, one of the few newspapers that were only published in French
Radio
- ERA Patras - located in Rio next to the Rio Junction with the new GR-9/E55 and the GR-5/E55 and the GR-48/E65
- Super B - Patras
- Top FM - 93 FM
- Ionion FM - 95.8 FM
- Radio Gamma - 96 FM
- Step FM - 97 FM (former)
- MFM
- Radio Aigio - 99.2 FM
- You FM - 100.1 FM (launched in 2006/2007)
- Fasma FM (from Etoloakarnania?)
- ANT1 Radio Patras - somewhere 106 FM
- Mojo FM - 107.9 FM
Television
- Achaia Channel - Patrast
- Patra TV - Patras
- Super B - Patras
- Tele Con - extinct
- Tele Time - regional
- AXION - Aigio
Companies
- Achaiki
- Kronos Supermarkets - Patras
Persons
- Actor, mythological legend
- Alexon, ancient figure
- Timoleon Ambelas, a writer
- Anchialus, mythological legend
- Dimitrios Andrikopoulos-Boukaouris, Mayor of Patras
- Antheia, mythological legend
- Argyra, mythological legend
- Autonous, ancient figure
- Bolina, ancient figure
- Bryson of Achaea, ancient figure
- Anastasios Charalambis General and Prime Minister for one day in 1922.
- Vasileios Christopoulos, an artist
- Danielis, ancient figure
- Kostas Davourlis Footballer of Panachaiki
- Theodoros Deligiannis a Prime Minister of Greece
- Ioannis Diakidis
- Rena Dor, actress
- Dymas, ancient figure
- Eperatus, ancient figure
- Eurypylus
- Spyros Fokas, an actor
- Asimakis Fotilas, a revolutionary leader
- Panagiotakis Fotilas, a revolutionary leader
- Giorgos Giannias, a revolutionary leader
- Dimitrios Gounaris a Prime Minister of Greece
- Helike, ancient queen
- Ion, mythological legend
- Antonios Kalamogdartis, a revolutionary leader
- Athanasios Kanakaris-Roufos, a revolutionary leader
- Panagiotis Karatzas, a revolutionary leader
- Kostas Katsouranis Footballer - European Champion (Euro 2004)
- Konstantinos Konstantopoulos a Mayor of Patras and Prime Minister of Greece
- Andreas Kontogouris, a revolutionary leader
- Nikolaos Kontopoulos
- Christos Laskaris
- Afroditi Laoutari, anactress
- Dimitrios Maximos
- Vassilis Makris, an artist
- Memos Makris, an artist
- Dimitrios Maximos a Prime Minister of Greece
- Melanippus, ancient fiture
- Andreas Michalakopoulos a Prime Minister of Greece
- Andreas Mikroutsikos
- Betty Moschona, an actress
- Molurus, ancient figure
- Thanos Mikroutsikos, an artist
- Myscellus
- Kostis Palamas national Greek poet
- George Papandreou (senior) a Prime Minister of Greece
- Georgios Papadopoulos Leader of the military junta
- Georgios Papandreou (historian), an unrelated historian and linguist
- Anagnostis Petimezas, a revolutionary leader
- Konstantinos Petimezas, a revolutionay leader
- Konstantis Petimezas, a revoltuionary leader
- Nikolaos Petimezas (elder)
- Angelos Roufos
- Benizelos Rouphos a Prime Minister of Greece
- Ioannis Roufos
- Selemnus, mythological legend
- Panagiotis Skagiopoulos
- Sokratis Skartsis, poet
- Konstantinos Skourletis, mayor of Patras
- Markos Sklivaniotis
- Socrates of Achaea, ancient figure
- Sostratus of Dyme, an ancient figure
- Sostratus of Pellene, an ancient Greek Olympian
- Konstantinos Stefanopoulos President of Greece
- Epameinondas Thomopoulos, an artist
- Dimitrios Tofalos Olympic Champion
- Spyridon Vassiliadis, poet
- Xenofon Verykios
- Dimitrios Votsis, mayor of Patras
- Spyros Vrettos, poet
- Alexandros Zaimis a Prime Minister and President of Greece
Sports
There are two skiing resorts, one on the Panachaicus west of the mountain top (elevation around 1700 m) east of Patras, it will be Nafpaktos's closest because of the new bridge (mid-2004) and the other on Aroania, sometimes still called Chelmos, near Kalavrita. It is Kalavrita's closest resort.
Sporting teams
Division rankings were as of the 2005-06 season for most teams, for football (soccer), they are run by the Achaia Football Clubs Association:
- Teams with multiple sporting clubs
- Achaiki - Kato Achaia, third division
- Achaikos Kato Achaias
- Achaios Saravali Patras - Saravali - fourth division
- Achilleas Ovrias FC - Ovrya, fourth division
- Achilleas Patras AC - Patras, fourth division
- Achilleas Kamaron
- AEK Patras FC - Patras, fourth division
- Aetos Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Agiou Dimitriou FC
- Aias Anthoupoli
- Aias Avythiou
- Anagennisi/Aias Sympoliteias - Rododafni
- Apollon Eglykada
- Apollon Patras
- Apolloniada Patras
- Aris Patras
- Aris Valimitika
- Aris Logos
- Arla A.C.
- A.O. Ampelokipi Patras
- A.O. Anagenisi Patras
- Agyia FC - Patras (Agyia), fourth division
- Albatross Glyfadas Patras - Patras, fourth division
- AS Apollo Eglikadas, fourth division
- Aris - fourth division
- Asteras Temenis
- Astrapi Psarofai - Patras (Psarofai), fourth division
- Atlantida Girokomeiou - Patras - third division (as of 2007)
- Atromitos Lappa
- Atromitos Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Atromitos Zarouchleika Patras - Patras (Zarouchleika) - fourth division
- Dafni FC
- Dafni Kalavrita
- Diagoras Vrachneika - Vrachneika
- Diakopto AC - Diakopto - fourth division
- Doxa Chalandritsas FC - Chalandritsa, fourth division
- Doxa Elaionas - Elaionas
- Doxa Paralias - Paralia, fourth division
- Dimi A.O.
- Doxa Niforeika
- Egieas Egion
- Elpida Egklykadas - Egklykada, fourth division
- Esperos Patras
- Ethnikos Aigio
- Ethnikos Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Ethnikos Sageika - Sageika, fourth division
- Faraikos - Farres
- Filia Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Floga Kalamaki
- Floga Rodia - Rodia
- Fostiras Ovrias FC - Ovrya, fourth division
- Galini Patras
- Galaxidi - Demenika
- Ikaros Petrotou
- Ikaros Lakopetras
- Iraklis Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Iraklis Leykas
- Iraklis Zachloritika - Zachloritika
- A.O. Kagkadi
- A.O. Kallithea
- A.O. Kaminia
- A.O. Kalavrita
- A.O. Krini
- A.O. Krini 97
- P.A.O. Kritikon Patras
- Kypros Patron AC - Patras, fourth division
- Posidvn Elikis
- A.E. Limnochori - Limnochori
- Megas Dikefalon
- Metochi F. C. - Metochi
- Milon Ovrias
- NE Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Niforeika F.C. - Niforeika
- Niki Nikoleika - Nikoleika or Nikolaiika
- Niki Proasteio
- NO Patras - Patras, fourth division
- APS Olympiakos - fourth division
- Olympiakos Aigio - Aigio, fourth division
- Olympiakos Kamares - Kamares - fourth division
- Olympiakos Patras - Patras - fourth division
- Olympiacos Soudeneika
- Olympiada
- A.O. Omonia Patras
- Ormi Patras - Patras - fourth division
- Pampatraikos - Patras - third division (as of 2007)
- Panachaiki - Patras, second division
- Panachaikos Souli
- Panaigialeios - fourth division
- Panathinaikos Skagiopouleiou - fourth division
- Panionios Achilleas Agyias AU - Patras (Agyia), fourth division
- P.A.O. Kosmos
- Pelopas Patras
- Perivola A.O.
- APS Patrai - Patras, fourth division
- Patraikos AC - Patras, fourth division
- PAS Patraikos - Patras, fourth division
- EA Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Patreos - Patras, fourth division
- Perivoila F.C.
- Peteinoi F.C.
- Pigasos Begkoulariou FC, fourth division
- Pirsos Patras
- A.O. Polyteknos
- Poseidonos Patras AU - Patras, ceased
- Proodevtiki - fourth division
- A.O. Psilalonia Patras
- A.O. Romanos - Romanos
- Skakistikos Omilos Patras - Patras, fourth division
- Spartakos Ovrya - Ovrya - third division (as of 2007)
- T.A.D. '93 Aigiou
- A.O. Thea - Thea
- Thyella Aigeira - Aigeira
- Thyella Aigio - Aigio
- Thyella - Patras, third division
- Thyella Skiada - third division
- Tritaiikos Stavrodromi - Stavrodromi
- A.O. Vasilikou
- A.O. Vounteni
- A.O. Vouprasio
- A.O. Vouraikos Diakopto
- A.P.S. Zavlani - fourth division
- A.O. Ziria
- Basketball only
- A.O. Skagiopouleio
- Defunct and historic teams
- Foinikas Patras - Patras
- Lefkos Asteras - Patras
- Olympiakos Kato Achaia - Kato Achaia
- Thriamvos Patras - Patras, now part of EPA Patras
Notes
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (Eleventh ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (Eleventh ed.). Cambridge University Press.- Bunson, Matthew (1994). Encyclopedia of the Roman Empire. New York: Facts on File Inc.
External links
|
|||||||