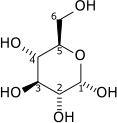
Acetyl-CoA
| Acetyl-CoA |
 |
 |
| Identifiers |
| CAS number |
72-89-9  Y Y |
| PubChem |
444493 |
| ChemSpider |
392413 |
| MeSH |
Acetyl+Coenzyme+A |
O=C(SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)[C@H](O)C(C)(C)COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]3O[C@@H](n2cnc1c(ncnc12)N)[C@H](O)[C@@H]3OP(=O)(O)O)C
|
InChI=1/C23H38N7O17P3S/c1-12(31)51-7-6-25-14(32)4-5-26-21(35)18(34)23(2,3)9-44-50(41,42)47-49(39,40)43-8-13-17(46-48(36,37)38)16(33)22(45-13)30-11-29-15-19(24)27-10-28-20(15)30/h10-11,13,16-18,22,33-34H,4-9H2,1-3H3,(H,25,32)(H,26,35)(H,39,40)(H,41,42)(H2,24,27,28)(H2,36,37,38)/t13-,16-,17-,18+,22-/m1/s1
Key: ZSLZBFCDCINBPY-ZSJPKINUBJ
|
| Properties |
| Molecular formula |
C23H38N7O17P3S |
| Molar mass |
809.57 g/mol |
 Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
| Infobox references |
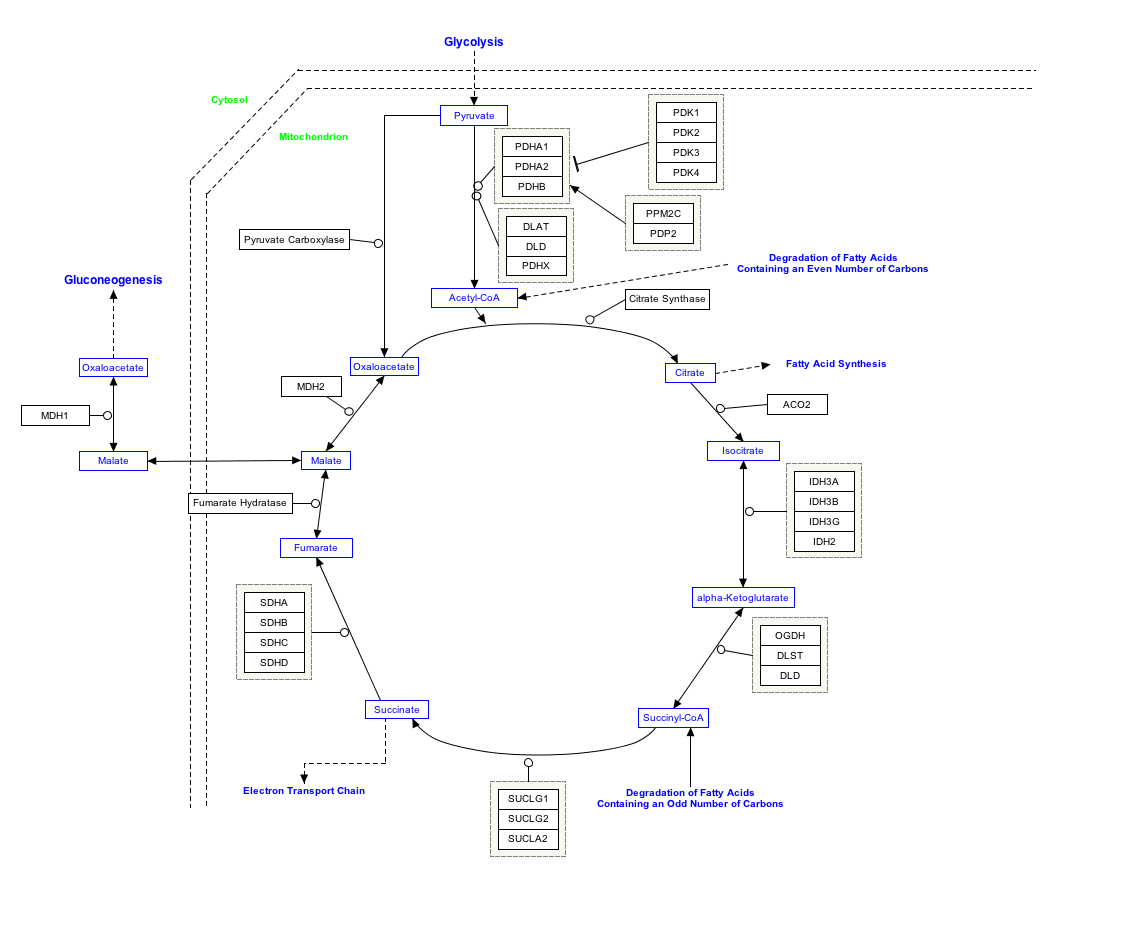
Acetyl coenzyme A or Acetyl-CoA is an important molecule in metabolism, used in many biochemical reactions. Its main use is to convey the carbon atoms within the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. In chemical structure, acetyl-CoA is the thioester between coenzyme A (a thiol) and acetic acid (an acyl group carrier). Acetyl-CoA is produced during the second step of aerobic cellular respiration, pyruvate decarboxylation, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle.
Acetyl-CoA is also an important component in the biogenic synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Choline, in combination with Acetyl-CoA, is catalyzed by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase to produce acetylcholine and a coenzyme a byproduct.
Functions
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and pyruvate formate lyase reactions
The oxidative conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA is referred to as the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. It is catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Other conversions between pyruvate and acetyl-CoA are possible. For example, pyruvate formate lyase disproportionates pyruvate into acetyl-CoA and formic acid. The pyruvate formate lyase reaction does not involve any net oxidation or reduction.
Fatty acid metabolism
In animals, acetyl-CoA is essential to the balance between carbohydrate metabolism and fat metabolism (see fatty acid synthesis). In normal circumstances, acetyl-CoA from fatty acid metabolism feeds into the citric acid cycle, contributing to the cell's energy supply. In the liver, when levels of circulating fatty acids are high, the production of acetyl-CoA from fat breakdown exceeds the cellular energy requirements. To make use of the energy available from the excess acetyl-CoA, ketone bodies are produced which can then circulate in the blood. Therefore, when at rest, both the skeletal and cardiac muscles satisfy their energy requirement mainly through oxidation of ketone bodies.
In some circumstances, this can lead to the presence of very high levels of ketone bodies in the blood, a condition called ketosis. Benign dietary ketosis can safely occur in people following low-carbohydrate diets, which cause fats to be metabolised as a major source of energy. This is different from ketosis brought on as a result of starvation, and from ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition that can affect diabetics.
In plants, de novo fatty acid synthesis occurs in the plastids. Many seeds accumulate large reservoirs of seed oils to support germination and early growth of the seedling before it is a net photosynthetic organism. Fatty acids are incorporated into membrane lipids, the major component of most membranes.
Other reactions
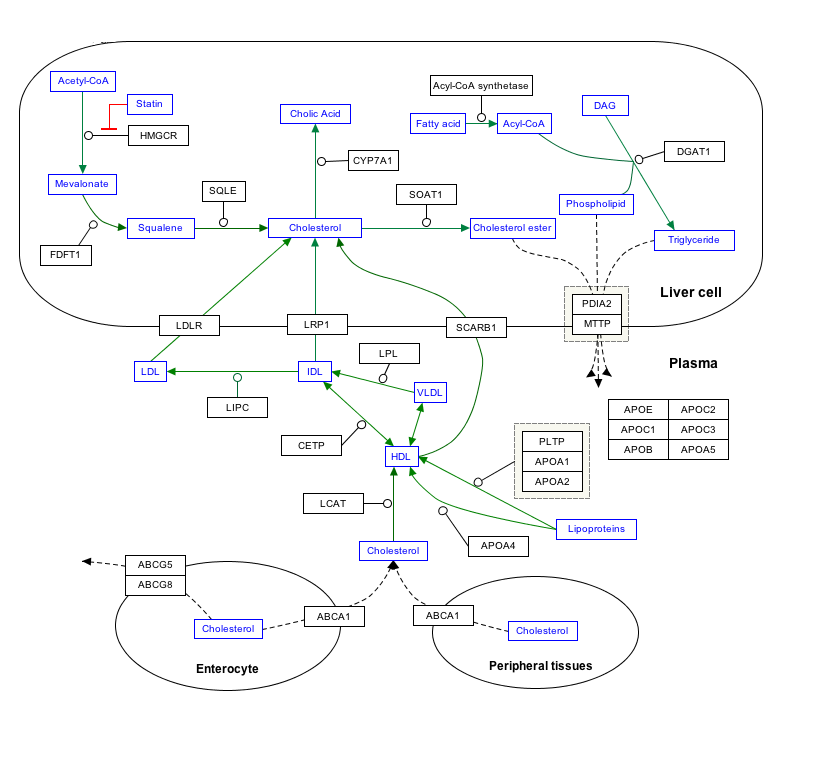
- Two acetyl-CoA can be condensed to create acetoacetyl-CoA, the first step in the HMG-CoA/ mevalonic acid pathway leading to synthesis of isoprenoids. In animals HMG-CoA is a vital precursor to cholesterol and ketone synthesis.
- Acetyl-CoA is also the source of the acetyl group incorporated onto certain lysine residues of histone and non-histone proteins in the post-translational modification acetylation, a reaction catalyzed by acetyltransferases.
- In plants and animals, cytosolic acetyl-CoA is synthesized by ATP citrate lyase [1]. When glucose is abundant in the blood of animals, it is converted via glycolysis in the cytosol to pyruvate, and thence to acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrion. The excess of acetyl-CoA results in production of excess citrate, which is exported into the cytosol to give rise to cytosolic acetyl-CoA.
- Acetyl-CoA can be carboxylated in the cytosol by acetyl-CoA carboxylase, giving rise to malonyl-CoA, a substrate required for synthesis of flavonoids and related polyketides, for elongation of fatty acids to produce waxes, cuticle, and seed oils in members of the Brassica family, and for malonation of proteins and other phytochemicals [2].
- In plants, these include sesquiterpenes, brassinosteroids (hormones), and membrane sterols.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to visit Gene Wiki pages and related Wikipedia articles. The pathway can be downloaded and edited at WikiPathways.
See also
- Citric acid cycle
- HMG-CoA reductase pathway
- Fatty acid metabolism
- Acyl CoA
- Acetyl Co-A synthetase
- Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase
External links
|
Nootropics |
|
| Acetylcholinesterases |
Donepezil • Galantamine • Huperzine A (Huperzia Serrata) • Ladostigil • Rivastigmine • Tacrine
|
|
| Ampakines |
CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • Sunifiram • Unifiram
|
|
| D1 Agonists |
6-Br-APB • A-77636 • Dihydrexidine • Dinapsoline • Doxanthrine • SKF-81297
|
|
| Eugeroics |
|
|
| GABAA α5 Inverse Agonists |
α5IA • L-655,708 • PWZ-029 • Suritozole • TB-21007 • ZK-93426
|
|
| H3 Antagonists |
A-349,821 • ABT-239 • Ciproxifan • GSK-189,254
|
|
| mACh Agonists |
Alvameline • Arecoline • Cevimeline • CI-1017 • Milameline • Sabcomeline • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Xanomeline
|
|
| nACh Agonists |
AR-R17779 • Ispronicline • Nicotine • PNU-282,987 • SSR-180,711 • WAY-317,538 |
|
| Racetams |
Aniracetam • Brivaracetam • Coluracetam • Etiracetam • Fasoracetam • Levetiracetam • Nebracetam • Nefiracetam • Oxiracetam • Phenylpiracetam • Piracetam • Pramiracetam • Rolziracetam • Seletracetam
|
|
| Others |
Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Bilobalide ( Ginkgo Biloba) • Carbenoxolone • Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine • Ensaculin • Fipexide • Idebenone • Latrepirdine • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • S-17092 • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Tricyanoaminopropene • Vinpocetine |
|
|
Cholesterol and steroid metabolic intermediates |
|
| Mevalonate pathway |
|
to HMG-CoA
|
Acetyl-CoA · Acetoacetyl-CoA · HMG-CoA
|
|
|
Ketone bodies
|
Acetone · Acetoacetic acid · beta-Hydroxybutyric acid
|
|
|
to DMAPP
|
Mevalonic acid · Phosphomevalonic acid · 5-Diphosphomevalonic acid · Isopentenyl pyrophosphate · Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
|
|
|
Geranyl-
|
Geranyl pyrophosphate · Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
|
|
|
|
Prephytoene diphosphate · Phytoene
|
|
|
| Non-mevalonate pathway |
|
DOXP · MEP · CDP-ME · CDP-MEP · MEcPP · HMB-PP · IPP · DMAPP
|
|
|
| To Cholesterol |
Farnesyl pyrophosphate · Squalene · 2,3-Oxidosqualene · Lanosterol
Lanosterol · Lathosterol · 7-Dehydrocholesterol · Cholesterol
Lanosterol · Zymosterol · 7-Dehydrodesmosterol · Desmosterol · Cholesterol
|
|
| Steroid |
|
Corticosteroids
(C21 pregnane)
|
|
|
|
Sex steroids
|
|
|
DHEA · Androstenedione/5-Androstenediol · Testosterone · Dihydrotestosterone
DHEA sulfate · Epitestosterone
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nonhuman |
|
Phytosterols
|
Stigmasterol · Brassicasterol
|
|
|
Ergosterols
|
Ergosterol · Ergocalciferol
|
|
|
|
|
mt, r//c/p/i/y, f/s/l/o, a/u, n, h
|
rgcp//y, f/s/l/o, au, n, h,
|
m(A16, C10),i(//c//i/y, /s/o, a/u,n, h)
|
|
biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (alco, glys, glpr) · lipd (fata, phld, strd, gllp, eico, ttpy) · amac · ncbs
|
|
|
| Glucose |
Hexokinase |
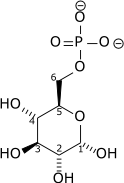
Glucose 6-phosphate |
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase |
Fructose 6-phosphate |
phosphofructokinase-1 |
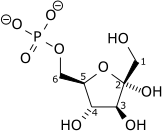
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate |
Fructose bisphosphate aldolase |
 |
ATP |
ADP |
 |
|
|
 |
ATP |
ADP |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
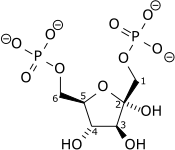
| Dihydroxyacetone phosphate |
|
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate |
Triosephosphate isomerase |
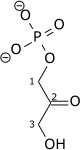
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
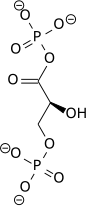
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate |
 |
|
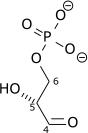 |
|
|
|
 |
NAD+ + Pi |
NADH + H+ |
|
 |
| + |
 |
2 |
 |
2 |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase |
3-Phosphoglycerate |
Phosphoglycerate mutase |
2-Phosphoglycerate |
Phosphopyruvate hydratase(Enolase) |
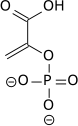
Phosphoenolpyruvate |
Pyruvate kinase |
Pyruvate |
| ADP |
ATP |
|
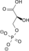 |
|
|
|
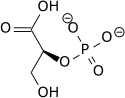 |
|
H2O |
|
 |
ADP |
ATP |
|
 |
 |
2 |
 |
2 |
 |
2 |
 |
2 |
|
|
|
mt, r//c/p/i/y, f/s/l/o, a/u, n, h
|
rgcp//y, f/s/l/o, au, n, h,
|
m(A16, C10),i(//c//i/y, /s/o, a/u,n, h)
|
|
|
|
Amino acid metabolism metabolic intermediates |
|
| K→acetyl-CoA |
|
|
Saccharopine · Allysine · α-Aminoadipic acid · α-Aminoadipate · Glutaryl-CoA · Glutaconyl-CoA · Crotonyl-CoA · β-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA
|
|
|
|
α-Ketoisocaproic acid · Isovaleryl-CoA · 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA · 3-Methylglutaconyl-CoA · HMG-CoA
|
|
|
|
N'-Formylkynurenine · Kynurenine · Anthranilic acid · 3-Hydroxykynurenine · 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid · 2-Amino-3-carboxymuconic semialdehyde · 2-Aminomuconic semialdehyde · 2-Aminomuconic acid · Glutaryl-CoA
|
|
|
| G |
|
|
|
|
3-Phosphoglyceric acid
glycine→ creatine: Glycocyamine · Phosphocreatine · Creatinine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Urocanic acid · Imidazol-4-one-5-propionic acid · Formiminoglutamic acid · Glutamate-1-semialdehyde
|
|
|
|
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid
|
|
|
|
Ornithine · Putrescine · Agmatine
|
|
|
other
|
|
|
|
|
G→propionyl-CoA→
succinyl-CoA
|
|
|
α-Ketoisovaleric acid · Isobutyryl-CoA · Methacrylyl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid · 2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoic acid
|
|
|
|
2,3-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid · 2-Methylbutyryl-CoA · Tiglyl-CoA · 2-Methylacetoacetyl-CoA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
α-Ketobutyric acid
|
|
|
propionyl-CoA→
|
Methylmalonyl-CoA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid · Homogentisic acid · 4-Maleylacetoacetate
|
|
|
|
G→oxaloacetate
|
see urea cycle
|
|
|
| Other |
|
|
Cysteine metabolism
|
Cysteine sulfinic acid
|
|
|
|
|
mt, r//c/p/i/y, f/s/l/o, a/u, n, h
|
rgcp//y, f/s/l/o, au, n, h,
|
m(A16, C10),i(//c//i/y, /s/o, a/u,n, h)
|
|
|
|
|
Cholinergics |
|
|
Receptor ligands |
|
|
mAChR
|
Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 · AC-42 · AC-260,584 · Aceclidine · Acetylcholine · AF30 · AF150(S) · AF267B · AFDX-384 · Alvameline · AQRA-741 · Arecoline · Bethanechol · Butyrylcholine · Carbachol · CDD-0034 · CDD-0078 · CDD-0097 · CDD-0098 · CDD-0102 · Cevimeline · cis-Dioxolane · Ethoxysebacylcholine · LY-593,039 · L-689,660 · LY-2,033,298 · McNA343 · Methacholine · Milameline · Muscarine · NGX-267 · Ocvimeline · Oxotremorine · PD-151,832 · Pilocarpine · RS86 · Sabcomeline · SDZ 210-086 · Sebacylcholine · Suberylcholine · Talsaclidine · Tazomeline · Thiopilocarpine · Vedaclidine · VU-0029767 · VU-0090157 · VU-0152099 · VU-0152100 · VU-0238429 · WAY-132,983 · Xanomeline · YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate · 4-DAMP · Aclidinium Bromide · Anisodamine · Anisodine · Atropine · Atropine Methonitrate · Benactyzine · Benzatropine (Benztropine) · Benzydamine · BIBN 99 · Biperiden · Bornaprine · CAR-226,086 · CAR-301,060 · CAR-302,196 · CAR-302,282 · CAR-302,368 · CAR-302,537 · CAR-302,668 · CS-27349 · Cyclobenzaprine · Cyclopentolate · Darifenacin · DAU-5884 · Dimethindene · Dexetimide · DIBD · Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) · Ditran · EA-3167 · EA-3443 · EA-3580 · EA-3834 · Elemicin · Etanautine · Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) · Flavoxate · Himbacine · HL-031,120 · Ipratropium · J-104,129 · Hyoscyamine · Mamba Toxin 3 · Mamba Toxin 7 · Mazaticol · Mebeverine · Methoctramine · Metixene · Myristicin · N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate · N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate · Orphenadrine · Otenzepad · Oxybutynin · PBID · PD-102,807 · Phenglutarimide · Phenyltoloxamine · Pirenzepine · Piroheptine · Procyclidine · Profenamine · RU-47,213 · SCH-57,790 · SCH-72,788 · SCH-217,443 · Scopolamine (Hyoscine) · Solifenacin · Telenzepine · Tiotropium · Tolterodine · Trihexyphenidyl · Tripitamine · Tropatepine · Tropicamide · WIN-2299 · Xanomeline · Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) · Tricyclic Antidepressants ( Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) · Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) · Typical Antipsychotics ( Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) · Atypical Antipsychotics ( Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)
|
|
|
nAChR
|
Agonists: 5-HIAA · A-84,543 · A-366,833 · A-582,941 · A-867,744 · ABT-202 · ABT-418 · ABT-560 · ABT-894 · Acetylcholine · Altinicline · Anabasine · AR-R17779 · Butyrylcholine · Carbachol · Cotinine · Cytisine · Decamethonium · Desformylflustrabromine · Dianicline · Dimethylphenylpiperazinium · Epibatidine · Epiboxidine · Ethanol · Ethoxysebacylcholine · EVP-4473 · EVP-6124 · Galantamine · GTS-21 · Ispronicline · Lobeline · MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) · Nicotine · NS-1738 · PHA-543,613 · PHA-709,829 · PNU-120,596 · PNU-282,987 · Pozanicline · Rivanicline · Sazetidine A · Sebacylcholine · SIB-1508Y · SIB-1553A · SSR-180,711 · Suberylcholine · TC-1698 · TC-1734 · TC-1827 · TC-2216 · TC-5214 · TC-5619 · TC-6683 · Tebanicline · Tropisetron · UB-165 · Varenicline · WAY-317,538 · XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine · α-Bungarotoxin · α-Conotoxin · Alcuronium · Amantadine · Anatruxonium · Atracurium · Bupropion (Amfebutamone) · Chandonium · Chlorisondamine · Cisatracurium · Coclaurine · Coronaridine · Dacuronium · Decamethonium · Dextromethorphan · Dextropropoxyphene · Dextrorphan · Diadonium · DHβE · Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) · Dipyrandium · Dizocilpine (MK-801) · Doxacurium · Duador · Esketamine · Fazadinium · Gallamine · Hexafluronium · Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) · Ibogaine · Isoflurane · Ketamine · Kynurenic acid · Laudexium (Laudolissin) · Levacetylmethadol · Malouetine · Mecamylamine · Memantine · Methadone · Methorphan (Racemethorphan) · Methyllycaconitine · Metocurine · Mivacurium · Morphanol (Racemorphanol) · Neramexane · Nitrous Oxide · Pancuronium · Pempidine · Pentamine · Pentolinium · Phencyclidine · Pipecuronium · Radafaxine · Rapacuronium · Rocuronium · Surugatoxin · Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) · Thiocolchicoside · Toxiferine · Trimethaphan · Tropeinium · Tubocurarine · Vecuronium · Xenon
|
|
|
|
|
Reuptake inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
CHT Inhibitors
|
Hemicholinium-3 (Hemicholine; HC3) · Triethylcholine
|
|
|
|
Vesicular
|
|
VAChT Inhibitors
|
Vesamicol
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
ChAT inhibitors
|
1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium · 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium · 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole · 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine · Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 · Acryloylcholine · AF64A · B115 · BETA · CM-54,903 · N,N-Dimethylaminoethylacrylate · N,N-Dimethylaminoethylchloroacetate
|
|
|
|
|
|
AChE inhibitors
|
Reversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb · Bendiocarb · Bufencarb · Carbaryl · Carbendazim · Carbetamide · Carbofuran · Chlorbufam · Chloropropham · Ethienocarb · Ethiofencarb · Fenobucarb · Fenoxycarb · Formetanate · Furadan · Ladostigil · Methiocarb · Methomyl · Miotine · Oxamyl · Phenmedipham · Pinmicarb · Pirimicarb · Propamocarb · Propham · Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine · Neostigmine · Phenserine · Physostigmine · Pyridostigmine · Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide · Ambenonium · Donepezil · Edrophonium · Galantamine · Huperzine A · Minaprine · Tacrine · Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate · Azinphos-methyl · Bensulide · Cadusafos · Chlorethoxyfos · Chlorfenvinphos · Chlorpyrifos · Chlorpyrifos-Methyl · Coumaphos · Cyclosarin (GF) · Demeton · Demeton-S-Methyl · Diazinon · Dichlorvos · Dicrotophos · Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) · Diisopropylphosphate · Dimethoate · Dioxathion · Disulfoton · EA-3148 · Echothiophate · Ethion · Ethoprop · Fenamiphos · Fenitrothion · Fenthion · Fosthiazate · GV · Isofluorophate · Isoxathion · Malaoxon · Malathion · Methamidophos · Methidathion · Metrifonate · Mevinphos · Monocrotophos · Naled · Novichok agent · Omethoate · Oxydemeton-Methyl · Paraoxon · Parathion · Parathion-Methyl · Phorate · Phosalone · Phosmet · Phostebupirim · Phoxim · Pirimiphos-Methyl · Sarin (GB) · Soman (GD) · Tabun (GA) · Temefos · Terbufos · Tetrachlorvinphos · Tribufos · Trichlorfon · VE · VG · VM · VR · VX; Others: Demecarium · Onchidal ( Onchidella binneyi)
|
|
|
BChE inhibitors
|
* Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others |
|
|
Precursors
|
Choline (Lecithin) · Citicoline · Cyprodenate · Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) · Glycerophosphocholine · Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) · Phosphatidylcholine · Phosphatidylethanolamine · Phosphorylcholine · Pirisudanol
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Others
|
Acetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin · β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime · Obidoxime · Pralidoxime
|
|
|
|