Rho (letter)
 |
|||||
| Greek alphabet | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Αα Alpha | Νν Nu | ||||
| Ββ Beta | Ξξ Xi | ||||
| Γγ Gamma | Οο Omicron | ||||
| Δδ Delta | Ππ Pi | ||||
| Εε Epsilon | Ρρ Rho | ||||
| Ζζ Zeta | Σσς Sigma | ||||
| Ηη Eta | Ττ Tau | ||||
| Θθ Theta | Υυ Upsilon | ||||
| Ιι Iota | Φφ Phi | ||||
| Κκ Kappa | Χχ Chi | ||||
| Λλ Lambda | Ψψ Psi | ||||
| Μμ Mu | Ωω Omega | ||||
| Obsolete letters | |||||
| Other characters | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Greek diacritics | |||||
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ϱ) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic Rêš "head" (see Resh). Its uppercase form is not to be confused with the Roman letter P.
Rho is generally classed as a liquid (together with lambda and sometimes the nasals mu and nu), which has important implications for morphology. It is pronounced similarly to the letter r in languages with a Latin-derived alphabet. In polytonic orthography a rho at the beginning of a word is conventionally written with a rough breathing (equivalent to h) — ῥ — and a double rho within a word is written with a smooth breathing over the first rho and a rough breathing over the second — ῤῥ — apparently reflecting an aspirated or voiceless pronunciation in Ancient Greek, hence the various Greek-derived English words which start with rh or contain rrh. The name of the letter is written in Greek as ῥῶ (polytonic) or ρω/ρο (monotonic).
Letters that arose from rho include Roman R and Cyrillic Er (Р).
If a person is a former Rhodes Scholar, they are entitled to use the Greek letter rho. If used, the symbol should precede the name. (citation, http://www.ox.ac.uk/gazette/calendar/style.pdf)
Common notational uses
The characters Ρ, ρ and ϱ are also used outside its Greek alphabetical context in Science, and Mathematics.
- In Physics
- to represent Density (ρ)
- to represent Momentum (Ρ)
- to represent Resistivity (ρ)
- In Mathematics
- to represent the Radius in a system of spherical polar coordinates
- to represent the correlation coefficient of a population parameter
- to represent the Spectral radius of a matrix
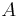 denoted as
denoted as 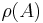
- to represent a Plastic number
- In Economics to represent the discount rate of future pence cash flows
- In Molecular Biology to represent the Rho protein responsible for termination of RNA synthesis. In such occasions, it is often represented as ϱ ("rho symbol" U+03F1), to avoid confusion with the Latin letter p
- In Programming
- For LaTeX, the symbols are
P(Ρ),\rho(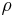 ), and
), and \varrho(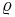 )
) - The lower-case rho ρ has a special meaning in the APL programming language
- For LaTeX, the symbols are
See also
- Р, р - Er (Cyrillic)
- П, п - Pe (Cyrillic)
- R, r - Latin
- P, p - Latin