Bopomofo
| Bopomofo | |
| Type | Semi-syllabary (letters for onsets and rimes; diacritics for tones) |
|---|---|
| Spoken languages | Chinese languages, Formosan languages |
| Created by | Commission on the Unification of Pronunciation |
| Time period | 1913 to the present, now used as ruby characters in Taiwan for Chinese, and as the principal script for Formosan |
| Parent systems | (Chinese) → Oracle Bone Script → Seal Script → Clerical Script → Bopomofo |
| Sister systems | Simplified Chinese, Kanji, Hanja, Chữ Nôm, Khitan script |
| ISO 15924 | Bopo |
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | |
| Bopomofo | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese: | 注音符號 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese: | 注音符号 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese romanization |
|---|
| Mandarin for Standard Mandarin Hanyu Pinyin (ISO standard) EFEO Gwoyeu Romatzyh Spelling conventions Latinxua Sin Wenz Mandarin Phonetic Symbols II Chinese Postal Map Romanization Tongyong Pinyin Wade-Giles Yale Legge romanization Simplified Wade Comparison chart |
| Cantonese for Standard Cantonese Guangdong Romanization Hong Kong Government Jyutping Meyer-Wempe Sidney Lau S. L. Wong (phonetic symbols) S. L. Wong (romanisation) Standard Cantonese Pinyin Standard Romanization Yale Barnett-Chao |
| Wu Long-short (romanization) |
| Min Nan for Taiwanese, Amoy, and related Pe̍h-oē-jī For Hainanese Hainanhua Pinyin Fang'an For Teochew Peng'im |
| Min Dong for Fuzhou dialect Foochow Romanized |
| Hakka for Moiyan dialect Kejiahua Pinyin Fang'an For Siyen dialect Phak-fa-sṳ |
| See also: General Chinese (Chao Yuenren) Cyrillization Xiao'erjing Bopomofo Romanisation in Singapore Romanisation in the ROC (Taiwan) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
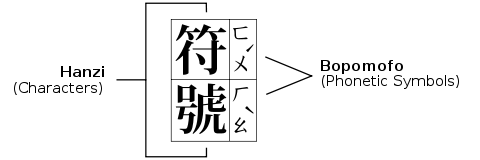
Bopomofo or Zhuyin Fuhao, often abbreviated zhuyin, is a phonetic system for transcribing Chinese, especially Mandarin, for people learning to read, write or speak Mandarin. This semi-syllabary is currently in wide use in the Republic of China of Taiwan (see Uses). Consisting of 37 letters and 4 tone marks, it is a comprehensive system that can transcribe all the possible sounds in Mandarin.
Although often thought of as an alphabet, bopomofo is not based on consonants and vowels but on syllable onsets and rimes, based on the Chinese rime tables but with diacritics rather than separate rimes for the tones. As in an alphabet, the consonants (onsets) are represented by distinct letters. These constitute 21 of bopomofo's 37. However, excluding the medial glide, each rime also has a distinct letter, which conflates vowels, diphthongs, and final consonants. For example, luan is written ㄌㄨㄢ (l-u-an), where the last letter ㄢ represents the entire final -an. These finals constitute the other 16 letters of bopomofo. (However, final -p, -t, -k, which are not found in Mandarin, are written as subscript letters after a final that represents only the vowel.)
In everyday speech, bopomofo may also be referred to as bopomo, both this name and bopomofo name comes from the first letters in the alphabet (ㄅㄆㄇㄈ). In official documents, it is occasionally called the "Mandarin Phonetic Symbols I" (國語注音符號第一式), abbreviated as the "MPS I" (注音一式); however, this official name is almost never used in English. Either chu-yin or the Mandarin Phonetic Symbols (without the numeral suffix) is preferred in official translations. [1] [2] The Roman numeral serves to distinguish it from its lesser known counterpart, the MPS II, a romanization system invented around the same period but now defunct (c.f. Romanization of Chinese in Taiwan).
Contents |
History
The Commission on the Unification of Pronunciation, led by Woo Tsin-hang from 1912 to 1913, created a system called Guóyīn Zìmǔ (國音字母 "National Pronunciation Letters") or Zhùyīn Zìmǔ (註音字母 or 注音字母 "Sound-annotating Letters")[1] which is based on Zhang Binglin's shorthands. For differences with the Zhang system, see Commission on the Unification of Pronunciation. A draft was released on July 11, 1913 by the Republic of China National Ministry of Education, but it was not officially proclaimed until November 23, 1928.[1] zhùyīn zìmǔ was renamed zhùyīn fúhào in April 1930. According to John DeFrancis in The Chinese Language: Fact and Fantasy:
The symbols were initially called Zhùyīn Zìmǔ ("Phonetic Alphabet"); later they were also called Guóyīn Zìmǔ ("National Phonetic Alphabet"). The fear that they might be considered an alphabetic system of writing independent of characters led in 1930 to their being renamed Zhùyīn Fúhào ("Phonetic Symbols").[3]
The use of bopomofo continued after 1949 in the Republic of China on Taiwan. In mainland China, bopomofo was superseded by the pinyin system promulgated by the People's Republic of China, although the pronunciation of words in standard dictionaries are sometimes given in both pinyin and bopomofo.
Taiwan's Education Ministry has attempted for many years to phase out the use of bopomofo in favor of a system based on Latin characters (such as Hanyu Pinyin, which will be the only legal standard starting in 2009). However, this transition has been extremely slow due to the difficulty in teaching elementary school teachers a new Latin-based system.
Modern uses
Input method
Bopomofo can be used as an input method for Chinese characters. It is one of the few input methods that can be found on most modern personal computers without the user having to download or install any additional software. It is also one of the few input methods that can be used for inputting Chinese characters on certain cell phones.


On-screen translations
On-screen Chinese translation software can be used in several ways. For students learning Chinese, bopomofo is one way for them to learn how to pronounce Mandarin.
Compared to pinyin, bopomofo's more compact alphabet makes it easier for some students--without remembering special pronunciation rules. Since the bopomofo characters are similar, and sometimes identical to, Chinese characters, students learning bopomofo are also making incremental steps to learn reading and writing Chinese.

Origin of the letters
The zhuyin letters were created by Zhang Binglin, and mainly taken from ancient or cursive Chinese characters, or parts of such characters, the modern readings of which contain the sound that each letter represents.
| Zhuyin | Origin | |
|---|---|---|
| ㄅ | b | From 勹, the top portion 包 bāo |
| ㄆ | p | From 攵, the combining form of 攴 pū |
| ㄇ | m | From 冂, the archaic form of the radical 冖 mì |
| ㄈ | f | From 匚 fāng |
| ㄪ | v, vo | From 万 wàn, dialectically vàn |
| ㄉ | d | From the archaic form of 刀 dāo. Compare the bamboo form |
| ㄊ | t | From 𠫓 tú, the upside-down 子 seen at the top of 充 |
| ㄋ | n | From |
| ㄌ | l | Calligraphic form of 力 lì |
| ㄍ | g | From the obsolete character 巜 guài 'river' |
| ㄎ | k | From 丂 kǎo |
| ㄫ | ng | From 兀 wù, dialectically ngō |
| ㄏ | h | From 厂 hàn |
| ㄐ | j | From the archaic character 丩 jīu |
| ㄑ | q | From the archaic character ㄑ quǎn, graphic root of the character 巛 chuān (modern 川) |
| ㄬ | ny | From 广 iǎn, dialectically nyiǎn |
| ㄒ | x | From 丅, a seal form of 下 xià. |
| ㄓ | zh | From |
| ㄔ | ch | From the radical 彳 chì |
| ㄕ | sh | From the old character 𡰣 shī |
| ㄖ | r | A semi-cursive form of 日 rì |
| ㄗ | z | From the radical 卩 jié, dialectically zié |
| ㄘ | c | Variant of 七 qī, dialectically ciī. Compare semi-cursive form |
| ㄙ | s | From the old character 厶 sī, which was later replaced by its compound 私 sī. |
| ㄧ | i, y | From 一 yī |
| ㄨ | u, w | From 㐅, ancient form of 五 wǔ. |
| ㄩ | ü, yu, iu | From the ancient character 凵 qū, which remains as a radical |
| ㄚ | a | From 丫 yā |
| ㄛ | o | From the obsolete character 𠀀 hē, inhalation, the reverse of 丂 kǎo, which is preserved as a phonetic in the compound 可 kě.[4] |
| ㄜ | e | Derived from its allophone in Standard Mandarin, ㄛ o |
| ㄝ | e, eh | From 也 yě. Compare the Warring States bamboo form |
| ㄞ | ai | |
| ㄟ | ei | From 乁 yí, an obsolete character meaning 移 yí "to move". |
| ㄠ | ao | From 幺 yāo |
| ㄡ | ou | From 又 yòu |
| ㄢ | an | From the obsolete character ㄢ hàn "to bloom", preserved as a phonetic in the compound 犯 fàn |
| ㄣ | en | From 乚 yǐn |
| ㄤ | ang | From 尢 wāng |
| ㄥ | eng | From 厶, an obsolete form of 厷 gōng |
| ㄦ | er | From 儿, the bottom portion of 兒 ér used as a cursive form |
| ㄭ | ih | ( |
The bopomofo characters usually are represented in typographic fonts as if drawn with an ink brush (as in Regular Script). They are encoded in Unicode in the bopomofo block, in the range U+3105..U+312D.
Stroke order
Stroke direction and order of zhuyin letters. Note that ㄖ is written with three strokes, unlike its ancestral character 日, which has four. The letters ㄓ and 市 are incorrect: both have four strokes, not three and five.
Uses
These phonetic symbols sometimes appear as ruby characters printed next to the Chinese characters in young children's books, and in editions of classical texts (which frequently use characters that are uncommon in modern writing). In advertisements, these phonetic symbols are sometimes used to write certain particles (e.g., ㄉ instead of 的); other than this, one seldom sees these letters used in mass media adult publications except as a pronunciation guide (or index system) in dictionary entries. Bopomofo letters are also mapped to the ordinary Latin character keyboard (1 = bo, q = po, a = mo, and so forth) used in one method for inputting Chinese text when using a computer.
Unlike pinyin, the sole purpose for bopomofo in elementary education is to teach Standard Mandarin pronunciation to children. Grade one textbooks of all subjects (including Mandarin) are entirely in bopomofo. After that year, Chinese character texts are given in annotated form (as a phonetic guide next to hanzi. Around grade four, presence of bopomofo annotation is greatly reduced, remaining only in the new character section. Schoolchildren learn the letters so that they can decode pronunciations given in a Chinese dictionary, and also so that they can find how to write words for which they know only the sounds.
Pinyin, on the other hand, is multipurpose. Besides being a pronunciation notation, pinyin is used widely in publications in mainland China. Some books from mainland China are published purely in pinyin with not even a single Chinese character. Those books are targeted to minority tribal groups or Westerners who know spoken Mandarin but have not yet learned written Chinese characters. There are also many books, which have both hanzi and pinyin (as a phonetic guide). Pinyin is the sole standard in mainland China for romanising Chinese (mainly Mandarin-speaking) geographical and personal names, the pinyin-based romanisation of most Chinese names has become standard in English as well.
Bopomofo is also used to write some of the aboriginal languages of Taiwan, such as Atayal [2], Seediq [3], Paiwan [4], or Tao [5]. For these it is a primary writing system, not an ancillary system as it is for Chinese.
For non-native speakers of Mandarin Chinese, bopomofo can be useful as a learning tool. Because it does not use romanization, confusion over "Latin alphabet" sounds and "Chinese" sounds is not an issue. As well bopomofo's formation of initials and finals to form syllables is more straightforward than pinyin's. However, for one not familiar with bopomofo, it can be more difficult to first understand the proper pronunciations. With its own keyboard layout, it is also less easily used to enter Chinese by people using a standard Latin-based keyboard.
It is also the basis for Chinese Braille.
Writing
| Tone | bopomofo | Pinyin |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | ¯ |
| 2 | ˊ | ´ |
| 3 | ˇ | ˇ |
| 4 | ˋ | ˋ |
| neutral | ˙ | none |
Bopomofo letters are written like Chinese characters, including the general order of strokes and positioning. They are always placed to the right of the Chinese characters, whether the characters are arranged vertically or horizontally. Technically, these are Ruby characters. Very rarely do they appear on top of Chinese characters when written horizontally as furigana would be written above kanji in a Japanese text. Because a syllable block contains usually two or three bopomofo letters (which themselves fit in a square format) stacked on top of each other, the blocks are rectangular.
Heres an example with the word "bottle".
|
or |
|
The tone marks were taken up by Hanyu Pinyin, except that the first tone has no tone marker and the neutral tone is denoted with a dot, while Hanyu Pinyin has a first-tone mark and generally omits the dot. (Tongyong Pinyin on Taiwan uses identical tone marks to bopomofo.) The neutral-tone dot is the only mark to be placed on top of the vertical bopomofo syllable block; the remaining three are in a vertical strip to the right of the character.
Tone mark symbols used in Bopomofo: <ˊ> 2nd tone, <ˇ> 3rd tone, <ˋ> 4th tone, <˙> 5th or neutral tone.
The tone marks are sometimes given in Regular Script style, matching the associated Chinese characters, and have the same basic shape as do those of the pinyin tone symbols. However, they vary in detail. The thickened end of bopomofo's second (rising) tone is always at the lower left, whereas the second tone mark in the pinyin system is a straight line of uniform width. The third tone mark displays the greatest variation.

bopomofo's tone symbolization was used in the ROC-sponsored romanizations created by the Mandarin Promotion Council. The tone symbols in that system were identical with the bopomofo tone symbols, except that they were not in Regular Style calligraphy, but in a Western font face and so resemble the tone symbols used in pinyin.
Most bopomofo letters are written in the same stroke order as Chinese characters. However, because they are an alphabet, some are written faster. For example, both zh (ㄓ) and r (ㄖ) are written in three strokes. (![]() ;
; ![]() )
)
Bopomofo vs. tongyong pinyin & Hanyu pinyin
Bopomofo and pinyin are based on the same Mandarin pronunciations, hence there is a mostly 1-to-1 mapping between the two systems. In the table below, the 'bopomofo' and 'pinyin' columns show equivalency.
- 【】represents the form used in combination with other letters.
A comparison between pinyin and bopomofo for Standard Mandarin can also be done by comparing the transcription of various syllables at Comparison of Chinese Phonetic Systems.

| Initials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bopomofo | Hanyu Pinyin | Tongyong Pinyin[5] | Wade-Giles | Example(Bopomofo, Pinyin) |
| ㄅ | b | b | p | 八 (ㄅㄚ, bā) |
| ㄆ | p | p | p' | 杷 (ㄆㄚˊ, pá) |
| ㄇ | m | m | m | 馬 (ㄇㄚˇ, mǎ) |
| ㄈ | f | f | f | 法 (ㄈㄚˇ, fǎ) |
| ㄉ | d | d | t | 地 (ㄉㄧˋ, dì) |
| ㄊ | t | t | t' | 提 (ㄊㄧˊ, tí) |
| ㄋ | n | n | n | 你 (ㄋㄧˇ, nǐ) |
| ㄌ | l | l | l | 利 (ㄌㄧˋ, lì) |
| ㄍ | g | g | k | 告 (ㄍㄠˋ, gào) |
| ㄎ | k | k | k' | 考 (ㄎㄠˇ, kǎo) |
| ㄏ | h | h | h | 好 (ㄏㄠˇ, hǎo) |
| ㄐ | j | j | ch | 叫 (ㄐㄧㄠˋ, jiào) |
| ㄑ | q | c | ch' | 巧 (ㄑㄧㄠˇ, qiǎo) |
| ㄒ | x | s | hs | 小 (ㄒㄧㄠˇ, xiǎo) |
| ㄓ | zhi 【zh】 | jhih 【jh】 | chih 【ch】 | 主 (ㄓㄨˇ, zhǔ) |
| ㄔ | chi 【ch】 | chih 【ch】 | ch'ih 【ch'】 | 出 (ㄔㄨ, chū) |
| ㄕ | shi 【sh】 | shih 【sh】 | shih 【sh】 | 束 (ㄕㄨˋ, shù) |
| ㄖ | ri 【r】 | rih 【r】 | jih 【j】 | 入 (ㄖㄨˋ, rù) |
| ㄗ | zi 【z】 | zih 【z】 | tzû 【ts】 | 在 (ㄗㄞˋ, zài) |
| ㄘ | ci 【c】 | cih 【c】 | tz'û 【ts'】 | 才 (ㄘㄞˊ, cái) |
| ㄙ | si 【s】 | sih 【s】 | ssû 【s】 | 塞 (ㄙㄞ, sāi) |
| Finals | ||||
| Bopomofo | Hanyu Pinyin | Tongyong Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Example(Bopomofo, Hanyu) |
| ㄚ | a | a | a | 大 (ㄉㄚˋ, dà) |
| ㄛ | o | o | o | 多 (ㄉㄨㄛ, duō) |
| ㄜ | e | e | e | 得 (ㄉㄜˊ, dé) |
| ㄝ | ê | e | eh | 爹 (ㄉㄧㄝ, diē) |
| ㄞ | ai | ai | ai | 晒 (ㄕㄞˋ, shài) |
| ㄟ | ei | ei | ei | 誰 (ㄕㄟˊ, shéi) |
| ㄠ | ao | ao | ao | 少 (ㄕㄠˇ, shǎo) |
| ㄡ | ou | ou | ou | 收 (ㄕㄡ, shōu) |
| ㄢ | an | an | an | 山 (ㄕㄢ, shān) |
| ㄣ | en | en | en | 申 (ㄕㄣ, shēn) |
| ㄤ | ang | ang | ang | 上 (ㄕㄤˋ, shàng) |
| ㄥ | eng | eng | eng | 生 (ㄕㄥ, shēng) |
| ㄦ | er | er | erh | 而 (ㄦˊ, ér) |
| ㄧ | yi 【i】 | yi 【i】 | yi 【i】 | 逆 (ㄋㄧˋ, nì) |
| yin 【in】 | yin 【in】 | yin 【in】 | 音 (ㄧㄣ, yīn) | |
| ying 【ing】 | ying 【ing】 | ying 【ing】 | 英 (ㄧㄥ, yīng) | |
| ㄨ | wu 【u】 | wu 【u】 | wu 【u】 | 努 (ㄋㄨˇ, nǔ) |
| wen 【un】 | wun 【un】 | wen 【un】 | 文 (ㄨㄣˊ, wén) | |
| weng 【ong】 | wong 【ong】 | ng 【ung】 | 翁 (ㄨㄥ, wēng) | |
| ㄩ | yu 【u, ü】 | yu 【u, yu】 | yü 【ü】 | 女 (ㄋㄩˇ, nǚ) |
| yun 【un】 | yun 【un, yun】 | yün 【ün】 | 韻 (ㄩㄣˋ, yūn) | |
| yong 【iong】 | yong | yung 【iung】 | 永 (ㄩㄥˇ, yǒng) | |
Another comparison table
| IPA | ɑ | ɔ | ɤ | aɪ | eɪ | ɑʊ | ɤʊ | an | ən | ɑŋ | ɤŋ | ɑɻ | ʊŋ | i | iɛ | iɤʊ | iɛn | ɪn | ɪŋ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinyin | a | o | e | ai | ei | ao | ou | an | en | ang | eng | er | ong | yi | ye | you | yan | yin | ying |
| Tongyong Pinyin | a | o | e | ai | ei | ao | ou | an | en | ang | eng | er | ong | yi | ye | you | yan | yin | ying |
| Wade-Giles | a | o | o/ê | ai | ei | ao | ou | an | ên | ang | êng | êrh | ung | i | yeh | yu | yen | yin | ying |
| Zhuyin | ㄚ | ㄛ | ㄜ | ㄞ | ㄟ | ㄠ | ㄡ | ㄢ | ㄣ | ㄤ | ㄥ | ㄦ | ㄨㄥ | ㄧ | ㄧㄝ | ㄧㄡ | ㄧㄢ | ㄧㄣ | ㄧㄥ |
| example | 阿 | 哦 | 俄 | 艾 | 黑 | 凹 | 偶 | 安 | 恩 | 昂 | 冷 | 二 | 中 | 一 | 也 | 又 | 言 | 音 | 英 |
| IPA | u | uɔ | ueɪ | uan | uən | uʊn | uɤŋ | uʊŋ | y | yɛ | yɛn | yn | iʊŋ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinyin | wu | wo | wei | wan | wen | weng | yu | yue | yuan | yun | yong | ||
| Tongyong Pinyin | wu | wo | wei | wan | wun | wong | yu | yue | yuan | yun | yong | ||
| Wade-Giles | wu | wo | wei | wan | wên | wêng | yü | yüeh | yüan | yün | yung | ||
| Zhuyin | ㄨ | ㄨㄛ | ㄨㄟ | ㄨㄢ | ㄨㄣ | ㄨㄥ | ㄩ | ㄩㄝ | ㄩㄢ | ㄩㄣ | ㄩㄥ | ||
| example | 五 | 我 | 位 | 完 | 文 | 翁 | 玉 | 月 | 元 | 云 | 用 | ||
| IPA | p | pʰ | m | fəŋ | fʊŋ | tiou | tuei | tʰ | ny | ly | kəɻ | kʰ | xə |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinyin | b | p | m | feng | diu | dui | t | nü | lü | ger | k | he | |
| Tongyong Pinyin | b | p | m | fong | diou | duei | t | nyu | lyu | ger | k | he | |
| Wade-Giles | p | p' | m | fêng | tiu | tui | t' | nü | lü | kêrh | k' | ho | |
| Zhuyin | ㄅ | ㄆ | ㄇ | ㄈㄥ | ㄉㄧㄡ | ㄉㄨㄟ | ㄊ | ㄋㄩ | ㄌㄩ | ㄍㄜㄦ | ㄎ | ㄏㄜ | |
| example | 玻 | 婆 | 末 | 封 | 丟 | 兌 | 特 | 女 | 旅 | 歌儿 | 可 | 何 | |
| IPA | tɕiɛn | tɕyʊŋ | tɕʰɪn | ɕyɛn | ʈʂə | ʈʂɚ | ʈʂʰə | ʈʂʰɚ | ʂə | ʂɚ | ʐə | ʐɚ | tsə | tsuɔ | tsɨ | tsʰə | tsʰɨ | sə | sɨ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinyin | jian | jiong | qin | xuan | zhe | zhi | che | chi | she | shi | re | ri | ze | zuo | zi | ce | ci | se | si |
| Tongyong Pinyin | jian | jyong | cin | syuan | jhe | jhih | che | chih | she | shih | re | rih | ze | zuo | zih | ce | cih | se | sih |
| Wade-Giles | chien | chiung | ch'in | hsüan | chê | chih | ch'ê | ch'ih | shê | shih | jê | jih | tsê | tso | tzŭ | ts'ê | tz'ŭ | sê | szŭ |
| Zhuyin | ㄐㄧㄢ | ㄐㄩㄥ | ㄑㄧㄣ | ㄒㄩㄢ | ㄓㄜ | ㄓ | ㄔㄜ | ㄔ | ㄕㄜ | ㄕ | ㄖㄜ | ㄖ | ㄗㄜ | ㄗㄨㄛ | ㄗ | ㄘㄜ | ㄘ | ㄙㄜ | ㄙ |
| example | 件 | 窘 | 秦 | 宣 | 哲 | 之 | 扯 | 赤 | 社 | 是 | 惹 | 日 | 仄 | 左 | 字 | 策 | 次 | 色 | 斯 |
| IPA | ma˥˥ | ma˧˥ | ma˨˩˦ | ma˥˩ | ma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinyin | mā | má | mǎ | mà | ma |
| Tongyong Pinyin | ma | má | mǎ | mà | må |
| Wade-Giles | ma1 | ma2 | ma3 | ma4 | ma0 |
| Zhuyin | ㄇㄚ | ㄇㄚˊ | ㄇㄚˇ | ㄇㄚˋ | ㄇㄚ・ |
| example (traditional/simplfied) | 媽/妈 | 麻/麻 | 馬/马 | 罵/骂 | 嗎/吗 |

Chinese dialects and languages other than Standard Mandarin
Three letters formerly used in non-standard dialects of Mandarin are now also used to write other Chinese languages as well. (Some bopomofo fonts do not contain these letters; see External links for PDF pictures.)
| Char | Pinyin |
|---|---|
| 万 | v |
| 兀 | ng |
| 广 | ny |
In addition, diacritics were used to create new letters for Min-nan and Hakka.
| Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | Char | Pinyin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ㆠ | bb* | ㆦ | oo [ɔ] | ㆬ | syllabic m | ㆲ | ong | |||
| ㆡ | zz* | ㆧ | onn [õ] | ㆭ | syllabic ng | ㆳ | Innn ?? | |||
| ㆢ | jj* | ㆨ | ir [ɨ] | ㆮ | ainn [aĩ] | ㆴ | Final p | |||
| ㆣ | gg* | ㆩ | ann [ã] | ㆯ | aunn [aũ] | ㆵ | Final t | |||
| ㆤ | ee [e] | ㆪ | inn [ĩ] | ㆰ | am | ㆶ | Final k | |||
| ㆥ | enn [ẽ] | ㆫ | unn [ũ] | ㆱ | om | ㆷ | Final h [ʔ] |
*These are the "muddy" initials found in Minnan and Wu dialects.
See Taiwanese for the two additional tone marks required to write these languages.
See also
- Furigana
- Zhuyin table
- Chinese language
- Mandarin Chinese
- Standard Mandarin
- Pinyin
- Chinese input methods for computers
- Ruby character
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 The Republic of China government, Government Information Office. "Taiwan Yearbook 2006: The People & Languages". "Also available at [1]"
- ↑ Taiwan Headlines. "Taiwan Headlines:". The Republic of China government.
- ↑ John DeFrancis. The Chinese Language: Fact and Fantasy. Honolulu, HI, USA: University of Hawaii Press, 1984. p. 242.
- ↑ "Unihan data for U+ 20000".
- ↑ Tongyong Pinyin is being phased out of use.
External links
- Unicode reference glyphs for bopomofoPDF (69.6 KB) & extended bopomofoPDF (61.6 KB)
- Mandarin Dictionary (need Chinese font for Big5 encoding)
- Chinese Romanization Converter - Convert between Hanyu Pinyin, Wade-Giles, Gwoyeu Romatzyh and other known or (un-)common Romanization systems.
- Bopomofo -> Wade-Giles -> Pinyin -> Word List
- NPA->IPA National Phonetic Alphabet (bopomofo) spellings of words transliterated into the International Phonetic Alphabet (The vowel values have been verified against the official IPA site. See [6] )
- Bopomofo to Pinyin converter and reverse
- bopomofo syllable chart, with Hanyu Pinyin equivalents
- Pinyin Annotator Add bopomofo (bopomofo) or pinyin on top of any Chinese text. Prompts alternative pronunciations to homonyms. Has the option of exporting into OpenOffice Writer for further editing.
- [7] online keyboard for bopomofo which can turn it into Chinese characters
|
|||||||||||