Zamboanga Peninsula
For Air strikes in the Zamboanga Peninsula see Air strikes in the Zamboanga Peninsula.
 |
|
| Regional center | Pagadian City, Zamboanga del Sur |
|---|---|
| Population | 3,230,094 |
| – Density | 218.0 per km² |
| Area | 14,810.7 km² |
| Divisions | |
| – Provinces | 3 |
| – Cities | 5 |
| – Municipalities | 67 |
| – Barangays | 1,904 |
| – Cong. districts | 8 |
| Languages | Zamboangueño/Chavacano, Cebuano, Subanon, others |
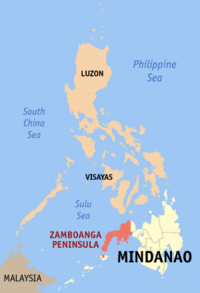
Zamboanga Peninsula is both a peninsula and an administrative region in the Philippines. Designated as Region IX, the region consists of three provinces, namely, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, and Zamboanga Sibugay, and the chartered city of Zamboanga City at the south-eastern tip. The region was previously known as Western Mindanao before the enactment of Executive Order No. 36 on September 19, 2001.
Contents |
History
Province
After the United States annexed the Spanish East Indies in 1898, Zamboanga was briefly independent as the Republic of Zamboanga. It became a part of the Moro Province, which consisted of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago. The name and status of Moro province soon changed to the Department of Mindanao and Sulu on August 16, 1916, that caused Zamboanga to become a province.
On 1942, the occupied by the Japanese Imperial forces taken in Zamboanga Peninsula
On 1945, the liberation at Zamboanga Peninsula by defenders of the Philippine and United States forces against the Japanese Imperial forces during the World War II.
On June 6, 1952, the province was divided into two provinces, Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur, while the chartered City of Zamboanga became an independent city.
Region
Together with the Sulu Archipelago, the provinces that formerly made up Zamboanga province were organized into Region IX by order of Presidential Decree No. 1 as part of the Integrated Reorganization Plan of President Ferdinand Marcos.
Between 1975 to 1989 the old Region IX (Western Mindanao) was divided into two sub-regions by Presidential Decree No. 773 dated August 21, 1975.
Sub-Region IX-A consisted of Basilan, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi with Jolo, Sulu as the sub-regional center.
Sub-Region IX-B consisted of the provinces of Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur, with the chartered city of Zamboanga City as the sub-regional center.
Present
In 2001, Zamboanga Sibugay, was created from the province of Zamboanga del Sur.
During the same year, the residents of Basilan opted to join the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) in a plebiscite. However, the citizens of the capital, Isabela, did not want to join so the city remained a part of this region with the as a result of Executive Order No. 36.
In 2006, Zamboanga City was re-labeled from "City of Flowers" to "Asia's Latin City". The new label is the brainchild of Mayor Celso L. Lobregat believing that this was a more relevant and significant label given the fact that the people of Zamboanga speak Chavacano, a local dialect composed of Eighty percent (80%) Spanish words and the remaining Twenty percent (20%) a mixture of other local dialects such as Visayan, Ilonggo, Subanon, Yakan and Tausug.
Political divisions

| Province/City | Capital | Population (2007) |
Area (km²) |
Pop. density (per km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zamboanga del Norte | Dipolog City | 907,238 | 6,618.0 | 137.0 |
| Zamboanga del Sur | Pagadian City | 914,278 | 3,480.7 | 262.6 |
| Zamboanga Sibugay | Ipil | 546,186 | 3,087.9 | 176.8 |
| Zamboanga City | — | 774,407 | 1,483.4 | 522.0 |
| Isabela City¹ | — | 87,985 | 140.7 | 625.3 |
Component cities
- Dapitan City, Zamboanga del Norte
- Dipolog City, Zamboanga del Norte
- Isabela City¹, Basilan
- Pagadian City, Zamboanga del Sur
¹ Isabela City is a component city and capital of the province of Basilan. Isabela City continues be under the jurisdiction of Basilan for the administration of provincially-devolved services and functions. But for the administration of regional services, the city is part of the Zamboanga Peninsula Region despite the rest of Basilan being under the authority of the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao.
Geography
Zamboanga Peninsula lies between the Moro Gulf, part of the Celebes Sea, and the Sulu Sea. Along the shores of the peninsula are numerous bays and islands. Its territory consists of the three Zamboanga provinces and Zamboanga City, as well as the Northern Mindanao province of Misamis Occidental. The peninsula is connected to the main part of Mindanao through an isthmus situated between Panguil Bay and Pagadian Bay. The boundary between the peninsula and the mainland is artificially marked by the border between the provinces of Zamboanga del Sur and Lanao del Norte.
Resources
The region has vast forest resources and previously used to export logs, lumber, veneer and plywood. Mineral deposits include gold, chromite, coal, iron, lead, and manganese. Among its non-metallic reserves are coal, silica, salt, marble, silica sand, and gravel. Its fishing grounds are devoted to commercial and municipal fishing. It has also aqua farms for brackish water and freshwater fishes.
Cities
Zambaoanga Peninsula has five cities: Dipolog City, Dapitan City, Isabela City, Pagadian City, and the highly-urbanized city of Zamboanga. Isabela City is actually part of the island-province of Basilan to the south of the peninsula, and is that province's capital.
The cities of Zamboanga, Dipolog and Pagadian serve as the centers of trade, commerce and education in the region. Zamboanga City, known for its Fort Pilar, is a tourist destination besides being considered as the busiest city in western Mindanao.
The city of Dapitan is the place of Jose Rizal's exile. It is also known for the old St. James Parish and the beautiful beach resort of Dakak.
The city of Dipolog is also known as the "gate way to western Mindanao " and the "orchid city" of the Philippines . A place that continues to exude an atmosphere of primeval charm amidst a growing presence of modern-day sophistication: a land where peace-loving and genial people proudly celebrate their rich culture and colorful history. A city whose rich natural wonders beckon everyone to its natural shores.
Economy
It has the first export-processing zone in Mindanao. Farming and fishing are the main economic activities of the region. It also has rice and corn mills, oil processing, coffee berry processing and processing of latex from rubber. Its home industries include rattan and furniture craft, basket making, weaving and brass work.
External links
- Zamboanga City, Daily
- Zamboanga Online News
- The Official Website of Zamboanga Today Newspaper
- FILIPINO-TURKISH TOLERANCE SCHOOL
|
|||||||||||