Western Europe
Western Europe at its most general meaning means the countries in the West of Europe. The concept at different times has had different meanings, at times including political and cultural considerations as well as geographical. Since the end of WWII, the term is commonly used to describe the affluent, mixed-capitalist democracies, allied with the United States via NATO.
Contents |
Classical antiquity and medieval origins
The earliest known distinctions between east and west in Europe originate in the history of the Roman Republic. As Roman domain expanded a cultural and linguistical division appeared between the mainly Greek-speaking eastern provinces which had formed the highly urbanized Hellenistic civilization. In contrast, the western territories largely adopted the Latin language. This cultural and linguistic division was eventually reinforced by the later political east-west division of the Roman Empire
The division between these two spheres was enhanced during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages by a number of events. The Western Roman Empire collapsed starting the Early Middle Ages. By contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire, mostly known as Byzantine Empire, managed to survive and even to thrive for another 1000 years. The rise of the Frankish Empire in the west, and in particular the Great Schism that formally divided Eastern Orthodoxy and Roman Catholicism, enhanced the cultural and religious distinctiveness between Eastern and Western Europe.
The conquest of the Byzantine Empire, center of the Eastern Orthodox Church, by the Muslim Ottoman Empire in the 15th century, and the gradual fragmentation of the Holy Roman Empire (which had replaced the Frankish Empire) led to a change of the importance of Roman Catholic/Protestant vs. Eastern Orthodox concept in Europe.
Historical events like the Renaissance, the Protestant Reformation by Martin Luther and the Counter-Reformation of the Catholic Church, the Age of Enlightenment, the French Revolution and the Industrial Revolution are considered to be common experiences which have shaped Western European culture and identity. During the Age of Discovery, most of the Western European countries colonized Africa, Asia, South and North America. All these historical events and cultural developments have influence over the Western European concept.
The Cold War

During the final stages of WWII the future of Europe was decided between the Allies in the 1945 Yalta Conference, between the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Winston Churchill, the President of the United States, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin.
Post-war Europe would be divided into two major spheres: the "West", influenced by the United States, and the Eastern Bloc, dominated by the Soviet Union. With the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided by the Iron Curtain.
This term had been used during World War II by German Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels and later Count Lutz Schwerin von Krosigk in the last days of the war; however, its use was hugely popularised by Winston Churchill, who used it in his famous "Sinews of Peace" address March 5, 1946 at Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri:
| “ | From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject, in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and in some cases increasing measure of control from Moscow. | ” |
Although some countries were officially neutral, they were classified according to the nature of their political and economical systems. This division has largely defined the popular perception and understanding of Western Europe and its borders with Eastern Europe till this day.
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe, in the view accepted after the second World War, was mainly composed of all the European countries liberated and then occupied by the Soviet army. It included the German Democratic Republic, widely known as East Germany, formed by the Soviet occupation zone of Germany. All the countries in Eastern Europe had communist regimes imposed upon them. Most of these countries were officially independent from the Soviet Union, but the practical extent of this independence was quite limited. In some matters many of them were little more than client-states of the Soviet Union.
Currently, the borders of Eastern Europe are a topic of debate, especially because of the countries and people of Western culture[1], identifying themselves with Central Europe.
- Most of these countries were members of the military Warsaw pact and its economical twin COMECON. First and foremost was the Soviet Union (which by itself included Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, etc). Other countries dominated by the Soviet Union were the German Democratic Republic, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Romania.
- The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (formed after WWII and before its later dismemberment) was not a member of the Warsaw Pact. It was a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement, an organization created in an attempt to avoid being assigned to any of the two blocs. It was demonstratively independent from the Soviet Union for most of the Cold War period, but because of its communist regime it was widely regarded part of the Eastern/communist bloc.
- Albania broke with the Soviet Union in the early 1960s as a result of the Sino-Soviet split, aligning itself instead with China. Despite this, it had a communist regime and thus was considered part of the Eastern/communist bloc. Hi peoples:)
Western Europe
At the end of the World War II almost all countries of Western Europe received economical assistance from the United States through the Marshall Plan. Most joined NATO and/or the European Community or its rival, the European Free Trade Association.
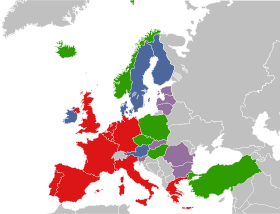
Western Europe was composed of:
- United Kingdom and France, one of the several victors of the war.
- The Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg countries who had been occupied by Nazi Germany and subsequently liberated by the Western Allies.
- The Federal Republic of Germany, widely known as West Germany, which had been formed by the three occupation zones of Germany belonging to the Western Allies (USA, UK, and France). The whole of Germany is now regarded as Western Europe
- Italy, a former Axis Power who had surrendered and been occupied by the Western Allies.
- The Republic of Ireland gained its independence in 1922 from the United Kingdom. It remained neutral during the war. It never joined NATO but it joined the European Union in 1973.
- The Nordic countries were a peculiar case. Denmark and Norway had been conquered by Nazi Germany but were not liberated by the allies. During the war Iceland, then still united with Denmark under a common king, had been invaded and occupied by the United Kingdom and the United States without any casualties by either side. In fact Iceland proclaimed its full independence during the war.
- Sweden had managed to remain neutral throughout the war.
- Finland had been invaded by the Soviet Union and it had been defeated, but was not conquered or occupied. (for further details see: Continuation War). The peace treaty between Finland and the Soviet Union stipulated that the Soviet Union would annex Eastern parts of Finland, and that Finland would have non-threatening relations with the Soviet Union (see also: Moscow Armistice).
- Austria and Switzerland were also a peculiar case. Austria had been incorporated into Nazi Germany through the Anschluss before the war, while Switzerland had managed to remain neutral throughout WWII. After the war both of them remained neutral, in the case of Austria through the Austrian State Treaty. Austria later joined the European Union but not NATO. Switzerland declined membership of NATO and the European Union and joined EFTA instead.
Other countries also became increasingly part of Western Europe.
- Countries who were under the rule of dictators or authoritarian regimes, Portugal, Spain, and Greece became parliamentarian democracies in the mid-1970s. The first two are situated in the geographic south-west of Europe, while the last one is located in the south-east of it. They joined the European Union after the polical changes at home. Spain and Greece joined NATO in the process, but Portugal was indeed a founding member of NATO (1949) and EFTA (1960), during the Estado Novo regime (1932-1974).
- The European microstates of Vatican City, San Marino, Monaco, Andorra and Liechtenstein are considered part of Western Europe but they are mainly overlooked. Many of these states have special agreements and treaties with the European Union.
- The legal status of many of the Overseas territories in Europe (Gibraltar, Channel Islands, Faroe Islands, etc) are peculiar and vary from case to case. Despite all that, they are also considered part of Western Europe.
- Malta is generally considered part of Western Europe.[2]
Later political developments
The world changed dramatically with the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989. The Federal Republic of Germany peacefully absorbed the Democratic Republic of Germany, leading to the German reunification. COMECON and the Warsaw Pact were dissolved, and in 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist. Several countries which had been part of the Soviet Union regained their full independence.
Although the term Western Europe was largely defined of the Cold War, it still remains much in use. The term is commonly used in the media and in everyday use both in "western" and other regions of Europe.
Western Europe has increasingly less to do with the European Union. The 1995, 2004, and 2007 enlargements saw many post-communist countries joining the EU, and a view that Europe is divided strictly into the West and the East is sometimes considered patronising or pejorative by many in the countries of Central Europe.
Present time
Definition used by the United Nations Statistics Division

The United Nations Statistics Division considers Western Europe to consist of the following nine countries,[3] except in the case of United Nations Regional Groups, in which the term also includes northern and southern Europe:
However, it should be noticed that this statistical division was designed during the Cold War period. According to the UN Statistics Division, the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories by the United Nations[4].
Definition used in the CIA World Factbook

The present definition, as geographically defined by the CIA World Factbook[5] includes: Western Europe:
Southwestern Europe:
Western European Union
Member countries of the Western European Union:
See also
- Western European Union
- Western world
- First World
- New Europe
- Old Europe
- Marshall Plan
- Central Europe
References and notes
- The Making of Europe, ISBN 0-14-015409-4, by Robert Bartlett
- Crescent and Cross, ISBN 1-84212-753-5, by Hugh Bicheno
- The Normans, ISBN 0-7524-2881-0, by Trevor Rowley
- 1066 The Year of the Three Battles, ISBN 0-7126-6672-9, by Frank McLynn
- ↑ O. Halecki, The Limits and Divisions of European History, Sheed & Ward, London and New York 1950, Chapter VII
- ↑ United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Western Europe
- ↑ United Nations Statistics Division - Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings
- ↑ http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
External links
- The European sub-regions according to the UN
- Western Europe according to UNESCO
- Teaching about Western Europe
- Western Europe.info
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||