Weimar Republic
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The term Weimar Republic (Weimarer Republik, IPA: [ˈvaɪmarɐ repuˈbliːk]) is used by historians to signify the democratic and republican period of Germany from 1919 to 1933.
Following World War I, the republic emerged from the German Revolution in November 1918. In 1919 a national assembly convened in the city of Weimar, where a new constitution for the German Reich was written, to be adopted on 11 August. This attempt to re-establish Germany as a liberal democracy failed with the ascent of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in 1933. Although technically the 1919 Weimar constitution was not invalidated until after World War II, the legal measures taken by the Nazi government in February and March 1933, commonly known as Gleichschaltung, destroyed the mechanisms of a true democracy. Therefore 1933 is usually seen as the end of the Weimar Republic and as the beginning of Hitler's "Third Reich".
The name Weimar Republic was never used officially during its existence. Despite its political form, the new republic was still known as Deutsches Reich in German. This phrase was commonly translated into English as German Empire, although the German word reich has a broader range of connotations than the English Empire, so the name is most often translated to the German Reich in English. The common short form remains Germany.
History
Controlled revolution: the establishment of the Republic (1918–1919)
From 1916 onwards, the 1871 German Empire had effectively been governed by the military headed by the Oberste Heeresleitung (OHL, Supreme Army Command) with the Chief of Staff Paul von Hindenburg. When it became apparent that World War I was lost, the OHL demanded that a civil government be installed in order to meet a key peace talk condition from United States President Woodrow Wilson. Any attempt to continue the war after Bulgaria had left the Central Powers would have only caused German territories to be militarily occupied by the victors. The new Reichskanzler Prince Max von Baden thus offered a cease-fire to U.S. President Wilson on 3 October 1918. On 28 October 1918, the 1871 constitution was finally amended to make the Reich a parliamentary monarchy, which the government had refused for half a century: the Chancellor was henceforth responsible to Parliament, the Reichstag, and no longer to the Kaiser.
The plan to transform Germany into a constitutional monarchy similar to Britain quickly became obsolete as the country slid into a state of near-total chaos. Germany was flooded with soldiers returning from the front, many of them wounded physically and psychologically. Violence was rampant, as the forces of the political right and left fought not only each other, but among themselves.
| History of Germany |
|---|
 |
| Ancient times |
| Germanic peoples |
| Migration Period |
| Frankish Empire |
| Medieval times |
| East Francia |
| Kingdom of Germany |
| Holy Roman Empire |
| Eastward settlement |
| Sectionalism |
| Building a nation |
| Confederation of the Rhine |
| German Confederation |
| German Revolutions of 1848 |
| North German Confederation |
| Unification of Germany |
| The German Reich |
| German Empire |
| World War I |
| Weimar Republic |
| Nazi Germany |
| World War II |
| Post-war Germany since 1945 |
| Occupation + Ostgebiete |
| Expulsion of Germans |
| FRG + GDR |
| German reunification |
| Present day Germany |
| Federal Republic of Germany |
| Topical |
| Military history of Germany |
| Territorial changes of Germany |
| Timeline of German history |
| History of the German language |
Rebellion broke out when on 29 October, the military command, without consultation with the government, ordered the German High Seas Fleet to sortie. This was not only entirely hopeless from a military standpoint, but was also certain to bring the peace negotiations to a halt. The crews of two ships in Wilhelmshaven mutinied. When the military arrested about 1,000 seamen and had them transported to Kiel, the Wilhelmshaven mutiny turned into a general rebellion that quickly swept over most of Germany. Other seamen, soldiers and workers, in solidarity with the arrested, began electing worker and soldier councils (Arbeiter- und Soldatenräte) modelled after the soviets of the Russian Revolution of 1917, and seized military and civil powers in many cities. On 7 November, the revolution had reached Munich, causing King Ludwig III of Bavaria to flee.
In contrast to Russia one year earlier, the councils were not controlled by communists. Most of their members were social democrats. Still, with the emergence of the Soviet Russia, the rebellion caused great fear in the establishment down to the middle classes. The country seemed to be on the verge of a communist revolution.
At the time, the traditional political representation of the working class, the Social Democratic Party was divided: a faction that called for immediate peace negotiations and leaned towards a socialist system had founded the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD) in 1917. In order not to lose their influence, the remaining Majority Social Democrats (MSPD), who supported the war efforts and a parliamentary system, decided to put themselves at the front of the movement, and on 7 November, demanded that Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicate. When he refused, Prince Max of Baden simply announced that he had done so and frantically attempted to establish a regency under another member of the House of Hohenzollern. On 9 November 1918, the German Republic was proclaimed by MSPD member Philipp Scheidemann at the Reichstag building in Berlin, to the fury of Friedrich Ebert, the leader of the MSPD, who still hoped to preserve the monarchy. Two hours later a Free Socialist Republic was proclaimed, 2 kilometers away, at the Berliner Stadtschloss. The proclamation was issued by Karl Liebknecht, co-leader (with Rosa Luxemburg) of the communist Spartacist League, which had allied itself with the USPD in 1917.
On 9 November, in a legally questionable act, Reichskanzler Prince Max of Baden transferred his powers to Friedrich Ebert, who, shattered by the monarchy's fall, reluctantly accepted. It was apparent, however, that this act would not be sufficient to satisfy Liebknecht and his followers, so a day later, a coalition government called "Council of People's Commissioners" (Rat der Volksbeauftragten) was established, consisting of three MSPD and three USPD members. Led by Ebert for the MSPD and Hugo Haase for the USPD it ought to act as collective head of state. Although the new government was confirmed by the Berlin worker and soldier council, it was opposed by the Spartacist League. Ebert called for a National Congress of Councils, which took place from 16 December to 20 December 1918, and in which the MSPD had the majority. Ebert thus managed to enforce quick elections for a National Assembly to produce a constitution for a parliamentary system, marginalizing the movement that called for a socialist republic (see below).
On 11 November an Armistice was signed at Compiègne by German representatives. It effectively ended military operations between the Allies and Germany. It amounted to German demilitarization, without any concessions by the Allies; the naval blockade would continue until complete peace terms were agreed.
From November 1918 through January 1919, Germany was governed by the Council of People's Commissioners. It was extraordinarily active, and issued a large number of decrees. At the same time, its main activities were confined to certain spheres: the eight-hour workday, domestic labour reform, agricultural labour reform, right of civil-service associations, local municipality social welfare relief (split between Reich and States) and important national health insurance, re-instatement of demobilised workers, protection from arbitrary dismissal with appeal as a right, regulated wage agreement, and Universal suffrage from 20 years of age in all classes of elections — local and national. Occasionally the name "Die Deutsche Sozialdemokratische Republik" (The German Social-Democratic Republic) appeared in leaflets and on posters from this era, although this was never the official name of the country.
The Reichswehr and the Revolution
To ensure that his fledgling government was able to maintain control over the country, Ebert made an uneasy pact with the OHL, now led by Ludendorff's successor General Wilhelm Groener. This Ebert-Groener pact stipulated that the government would not attempt to reform the Army so long as the army swore to protect the state. On the one hand, this agreement symbolised the acceptance of the new government by the military, assuaging concern among the middle classes; on the other hand, it was considered a betrayal of worker interests by the radical left wing, and infuriated the right wing who believed democracy to be weak. The new model Reichswehr armed forces, limited by the Treaty of Versailles to 100,000 army soldiers and 15,000 seamen, remained fully under the control of the German officer class despite its nominal re-organisation. As an independent and conservative group in Weimar, it wielded a large amount of influence over the fate of the republic.
This also marked one of several steps that caused the permanent split in the working class' political representation into the SPD and Communists. The eventual fate of the Weimar Republic derived significantly from the general political incapacity of the German labour movement. The several strands within the central mass of the socialist movement adhered more to sentimental loyalty to alliances arising from chance than to any recognition of political necessity. Combined action on the part of the socialists was impossible without action from the millions of workers who stood midway between the parliamentarians and the ultra-leftists who supported the workers councils. Confusion made acute the danger of extreme right and extreme left engaging in virulent conflict.
The split became final after Ebert called upon the OHL for troops to put down another Berlin army mutiny on 23 November 1918, in which soldiers had captured the city's garrison commander and closed off the Reichskanzlei where the Council of People's Commissioners was situated. The ensuing street fighting was brutal with several dead and injured on both sides. This caused the left wing to call for a split with the MSPD which, in their view, had joined with the Anti-Communist military to suppress the Revolution. The USPD thus left the Council of People's Commissioners after only seven weeks. In December, the split deepened when the Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands (KPD) was formed out of a number of radical left-wing groups, including the radical left wing of the USPD and the Spartacist League group.
In January, more armed attempts at establishing communism, known as the Spartacist uprising, by the Spartacist League and others in the streets of Berlin were put down by paramilitary Freikorps units consisting of volunteer soldiers. Bloody street fights culminated in the beating and shooting deaths of Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht after their arrests on 15 January. With the affirmation of Ebert, those responsible were not tried before a court martial, leading to lenient sentences, which made Ebert unpopular amongst the radical leftists.

The National Assembly elections took place 19 January, 1919. In this time, the radical left-wing parties, including the USPD and KPD, were barely able to get themselves organized, leading to a solid majority of seats for the MSPD moderate forces. To avoid the ongoing fights in Berlin, the National Assembly convened in the city of Weimar, giving the future Republic its unofficial name. The Weimar Constitution created a republic under a semi-presidential system with the Reichstag elected by proportional representation. The Socialist and (Non-Socialist) Democratic parties obtained a solid 80 per cent of the vote.
During the debates in Weimar, fighting continued. A Soviet republic was declared in Munich, but was quickly put down by Freikorps and remnants of the regular army. The fall of the Munich Soviet Republic to these units, many of which were situated on the extreme right, resulted in the growth of far-right movements and organizations in Bavaria, including the Nazis, Organisation Consul, and societies of exiled Russian Monarchists. Sporadic fighting continued to flare up around the country. In eastern provinces, forces loyal to Germany's fallen Monarchy fought the republic, while militias of Polish nationalists fought for independence: Great Poland Uprising in Provinz Posen and three Silesian Uprisings in Upper Silesia.
The socialist roots of Weimar

Lost by Germany after World War I; Annexed by neighbouring countries Lost by Germany after World War I; Administered by the League of Nations Germany (1919-1935)
The carefully thought-out social and political legislation introduced during the revolution was generally unappreciated by the German working classes. The two goals sought by the government, democratization and social protection of the working class, were never achieved. This has been attributed to a lack of pre-war political experience on the part of the Social Democrats. The government had little success in confronting the twin economic crises following the war.
The permanent economic crisis was a result of lost pre-war industrial exports, the loss of supplies in raw materials and food stuffs from Alsace-Lorraine, Polish districts and the colonies along with worsening debt balances and reparations payments. Military-industrial activity had almost ceased, although controlled demobilisation kept unemployment at around one million. The fact that the Allies continued to blockade Germany until after the Treaty of Versailles did not help matters, either.
The allies permitted only low import levels of goods that most Germans could not afford. After four years of war and famine, many German workers were exhausted, physically impaired and discouraged. Millions were disenchanted with capitalism and hoping for a new era. Meanwhile the currency devalued.
The German peace delegation in France signed the Treaty of Versailles accepting mass reductions of the German military, unrealistically heavy war reparations payments, and the controversial "War Guilt Clause". Adolf Hitler later blamed the republic and its democracy for the oppressive terms of this treaty, though most current historians disregard the "stab-in-the-back" myth Hitler advocated for his own personal political gain. See also: French-German enmity.
The Republic's first Reichspräsident ("Reich President"), Friedrich Ebert of the SPD, signed the new German constitution into law on 11 August 1919.
Internal conflict (1919–1923)


The Republic was under great pressure from both left and right-wing extremists. The radical left accused the ruling Social Democrats of having betrayed the ideals of the workers' movement by preventing a communist revolution. Right-wing extremists were opposed to any democratic system, preferring an authoritarian state like the 1871 Empire. To further undermine the Republic's credibility the extremists of the right (especially certain members of the former officer corps) also blamed an alleged conspiracy of Socialists and Jews for Germany's defeat in World War I (see Dolchstoßlegende).
For the next five years Germany's large cities suffered political violence between left-wing and right-wing groups, both of which committed violence and murder against innocent civilians and against each other, resulting in many deaths. The worst of the violence was between right-wing paramilitaries called the Freikorps and pro-Communist militias called the Red Guards, both of which admitted ex-soldiers into their ranks.
The first challenge to the Weimar Republic came when a group of communists and anarchists took over the Bavarian government in Munich and declared the creation of the Bavarian Soviet Republic. The communist rebel state was quickly put down one month later when Freikorps units were brought in to battle the leftist rebels.
The Kapp Putsch took place on 13 March 1920, involving a group of 5000 Freikorps troops who gained control of Berlin and installed Wolfgang Kapp (a right-wing journalist) as chancellor. The national government fled to Stuttgart and called for a general strike. While Kapp's vacillating nature did not help matters, the strike crippled Germany's ravaged economy and the Kapp government collapsed after only four days on 17 March.
Inspired by the general strikes, a communist uprising began in the Ruhr region when 50,000 people formed a "Red Army" and took control of the province. The regular army and the Freikorps ended the uprising on their own authority. Other communist rebellions were put down in March 1921 in Saxony and Hamburg.
In 1922, Germany signed a treaty - the Treaty of Rapallo - with Russia, and disarmament was brought to a halt. Under the Treaty of Versailles Germany could only have 100,000 soldiers and no conscription, Naval forces reduced to 15,000 men, 12 destroyers, 6 battleships, and 6 cruisers, no submarines or aircraft. The Treaty with Russia worked in secret, as the treaty allowed Germany to train military personnel, and Russia gained the benefits of German military technology. This was against the Treaty of Versailles, but Russia had pulled out of World War I against the Germans due to the 1917 Russian Revolution and was looked down on by the League of Nations. Germany seized the chance to make an ally.
By 1923, the Republic claimed it could no longer afford the reparations payments required by the Versailles treaty, and the government defaulted on some payments. In response, French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr region, Germany's most productive industrial region at the time, taking control of most mining and manufacturing companies in January 1923. Strikes were called, and passive resistance was encouraged. These strikes lasted eight months, further damaging the economy and increasing the expense of imports. The strike meant no goods were being produced. This infuriated the French, who began to kill and exile protestors in the region.
Since striking workers were paid benefits by the state, much additional currency was printed, fueling a period of hyperinflation. The 1920s German inflation started when Germany had no goods with which to trade. The government printed money to deal with the crisis; this allowed Germany to pay war loans and reparations with worthless marks and helped formerly great industrialists to pay back their own loans. This also led to pay raises for workers and for businessmen who wanted to profit from it. Circulation of money rocketed, and soon the Germans discovered their money was worthless. The value of the Papiermark had declined from 4.2 per US dollar at the outbreak of World War I to 1 million per dollar by August 1923. This gave the Republic's opponents something else to criticise it for. On 15 November 1923, a new currency, the Rentenmark, was introduced at the rate of 1 trillion (1,000,000,000,000) Papiermark for 1 Rentenmark. Know as a Monetary reset. At that time, 1 U.S. dollar was equal to 4.2 Rentenmark. Reparation payments resumed, and the Ruhr was returned to Germany under the Locarno Pact, which defined a border between Germany, France and Belgium.
Further pressure from the right came in 1923 with the Beer Hall Putsch, also called the Munich Putsch, staged by Adolf Hitler in Munich. In 1920, the German Workers' Party had become the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP), nicknamed the Nazi Party, and would become a driving force in the collapse of Weimar. Hitler was named chairman of the party in July 1921. On 8 November 1923, the Kampfbund, in a pact with Erich Ludendorff, took over a meeting by Bavarian prime minister Gustav von Kahr at a beer hall in Munich. Ludendorff and Hitler declared a new government, planning to take control of Munich the following day. The 3,000 rebels were thwarted by 100 policemen. Hitler was arrested and sentenced to five years in prison, a minimum sentence for the charge and he served less than eight months before his release and even then in a comfortable cell. Following the failure of the Beer Hall Putsch, his imprisonment and subsequent release, Hitler focused on legal methods of gaining power.
Golden Era (1923–1929)
Gustav Stresemann was Reichskanzler for 100 days in 1923, and served as foreign minister from 1923-1929, a period of relative stability for the Weimar Republic when there were fewer uprisings and the beginnings of economic recovery.
As chancellor, Stresemann had to restore law and order in certain towns in Germany such as Spandau and Krustin, where the 'Black Reichswehr' (a section of the freikorps) held a mutiny. Saxony and Thuringia allowed KPD members into their governments, and a new nationalist leader in Bavaria called for Bavarian independence and told his army to disobey orders from Berlin. Streseman persuaded Ebert to issue Article 48 to resolve the situation and brought the Freikorps to settle the situation. However the use of violence against political activities led the SPD (Social Democratic Party) to remove themselves from his coalition which finally led to the ending of his chancellorship.
Stresemann's first move as foreign minister was to issue a new currency, the Rentenmark, to halt the extreme hyperinflation crippling German society and the economy. It was successful because Stresemann refused to issue more currency, the cause of the inflationary spiral. In addition the currency was based on land, and restored confidence into the economy. With this achieved, a permanent currency - the Reichsmark - was introduced in 1926. Hans Luther was also appointed as Finance minister who helped balance the budget by dismissing 700 000 public employees.
In 1924 the Dawes Plan was created, an agreement between American banks and the German government, in which the American banks lend money to Germany, to help them pay reparations. Other foreign achievements were the evacuation of the Ruhr in 1925, and the 1925 Treaty of Berlin. This reinforced the Treaty of Rapollo in 1922, and improved relations between the USSR and Germany. Also in this year, Germany was admitted to the League Of Nations, which gave her a good international stance and the ability to veto legislation after Stresemann's insistence on entering as a permanent member. They also made agreements over its western border, though nothing was fixed on the Eastern borders. However, this progress was funded by overseas loans, increasing the nation's debts, while overall trade decreased and unemployment rose. Stresemann's reforms did not relieve the underlying weaknesses of Weimar but gave the appearance of a stable democracy.
The 1920s saw a massive cultural revival in Germany. It was, arguably, the most innovative period of cultural change in Germany.
Innovative street theatre brought plays to the public, the cabaret scene and promiscuity became very popular. Women were americanised, wearing makeup, short hair, smoking and breaking out of tradition. Music was created with a practical purpose, such as Schoenberg's 'atonality' and there was a new type of architecture taught at 'Bauhaus' schools. Art reflected the new ideas of the time with artists such as Grosz being fined for defaming the military and for blasphemy.
There was a lot of opposition to this Weimar culture shock, especially from conservatives. For instance, in 1930 Wilhelm Frick banned jazz performances and removed modern art from museums, as well as a new law being introduced to prevent teenagers from buying pulp fiction or pornography.
Despite the progress during these years, Stresemann was criticized by opponents for his policy of "fulfilment", or compliance with the terms of the Versailles Treaty, and by the German people after the invasion of the Ruhr, in which he agreed to pay the reparations set by the treaty in order for the French troops to evacuate.
In 1929, Stresemann's death marked the end of the "Golden Era" of the Weimar Republic. He died at the age of 51, four years after receiving the 1926 Nobel Peace Prize.
The Republic crumbles and Hitler's support rises (1930–1932)
Loss of credibility
The last years of the Weimar Republic were stamped by even more political instability than in the previous years and the administrations of Chancellors Brüning, Papen, Schleicher and Hitler (from 30 January to 23 March 1933) were all Presidentially-appointed dictatorships. This meant they used the President's power to rule without consulting the Reichstag (German parliament). On 29 March 1930, the finance expert Heinrich Brüning had been appointed the successor of Chancellor Müller by Reichspräsident Paul von Hindenburg after months of political lobbying by General Kurt von Schleicher on behalf of the military. The new government was expected to lead a political shift towards conservatism, based on the emergency powers granted to the Reichspräsident by the constitution, since it had no majority support in the Reichstag.
After an unpopular bill to reform the Reich's finances was left unsupported by the Reichstag, Hindenburg established the bill as an emergency decree based on Article 48 of the constitution. On 18 July 1930, the bill was again invalidated by a slim majority in the Reichstag with the support of the SPD, KPD, the (then small) NSDAP and DNVP. Immediately afterwards, Brüning submitted to the Reichstag the president's decree that it would be dissolved.
The Reichstag general elections on 14 September 1930 resulted in an enormous political shift: 18.3% of the vote went to the Nazis, five times the percentage compared to 1928. This increased legislative representation of the NSDAP had devastating consequences for the Republic. There was no longer a moderate majority in the Reichstag even for a Great Coalition of moderate parties, and this encouraged the supporters of the Nazis to force their claim to power with increasing violence and terror. After 1930, the Republic slid more and more into a state of potential civil war.
From 1930 to 1932, Brüning attempted to reform the devastated state without a majority in Parliament, governing with the help of the President's emergency decrees. During that time, the Great Depression reached its low point. In line with liberal economic theory that less public spending would spur economic growth, Brüning drastically cut state expenditures, including in the social sector. He expected and accepted that the economic crisis would, for a while, deteriorate before things would improve. Among others, the Reich completely halted all public grants to the obligatory unemployment insurance (which had been introduced only in 1927), which resulted in higher contributions by the workers and fewer benefits for the unemployed. This was understandably an unpopular move on his part.
The economic downturn lasted until the second half of 1932, when there were first indications of a rebound. By this time though, the Weimar Republic had lost all credibility with the majority of Germans. While scholars greatly disagree about how Brüning's policy should be evaluated, it can safely be said that it contributed to the decline of the Republic. Whether there were alternatives at the time remains the subject of much debate.
The bulk of German capitalists and land-owners originally gave support to the conservative experiment: not from any personal liking for Brüning, but believing the conservatives would best serve their interests. As, however, the mass of the working class and also of the middle classes turned against Brüning, more of the great capitalists and landowners declared themselves in favour of his opponents - Hitler and Hugenberg. By late 1931 conservatism as a movement was dead, and the time was coming when Hindenburg and the Reichswehr would drop Brüning and come to terms with Hugenberg and Hitler. Hindenburg himself was no less a supporter of an anti-democratic counter-revolution represented by Hugenberg and Hitler.[2]
On 30 May, 1932, Brüning resigned after no longer having Hindenburg's support. Five weeks earlier, Hindenburg had been re-elected Reichspräsident with Brüning's active support, running against Hitler (the president was directly elected by the people while the Reichskanzler was not).
Franz von Papen calls for elections
Hindenburg then appointed Franz von Papen as new Reichskanzler. Von Papen lifted the ban on the SA, imposed after the street riots, in an unsuccessful attempt to secure the backing of Hitler.
Von Papen was closely associated with the industrialist and land-owning classes and pursued an extreme Conservative policy along Hindenburg's lines. He appointed as Reichswehr Minister Kurt von Schleicher and all of the members of the new cabinet were of the same political opinion as Hindenburg. This government was to be expected to assure itself of the co-operation of Hitler. Since the Republicans and Socialists were not yet ready to take action and the Conservatives had shot their political bolt, Hitler and Hindenburg were certain to achieve power.
Elections of July 1932
Since most parties opposed the new government, von Papen had the Reichstag dissolved and called for new elections. The general elections on 31 July 1932 yielded major gains for the KPD and the Nazis, who won 37.2% of the vote, supplanting the Social Democrats as the largest party in the Reichstag.
July 1932 resulted in the question as to what part the now immense Nazi Party would play in the Government of the country. The Nazi party owed its huge increase to an influx of workers, unemployed, despairing peasants, and middle-class people. The millions of radical adherents at first forced the Party towards the Left. They wanted a renewed Germany and a new organisation of German society. The left of the Nazi party strove desperately against any drift into the train of such capitalist and feudal reactionaries. Therefore Hitler refused ministry under Papen, and demanded the chancellorship for himself, but was rejected by Hindenburg on 13 August 1932. There was still no majority in the Reichstag for any government; as a result, the Reichstag was dissolved and elections took place once more in the hope that a stable majority would result.
November and 'Socialist General' Schleicher
The 6 November 1932 elections yielded 33.1% for the Nazis[3], two million voters less than in the previous election. Franz von Papen stepped down and was succeeded by General Kurt von Schleicher as Reichskanzler on 3 December. Schleicher, a political army officer, had developed in an atmosphere of semi-obscurity and intrigue that encompassed the Republican military policy. He had for years been in the camp of those supporting the Conservative counter-revolution. Schleicher's bold and unsuccessful plan was to build a majority in the Reichstag by uniting the Trade Unionist left wings in the various parties, including that of the Nazis led by Gregor Strasser. This did not prove successful either.
In this brief Presidential Dictatatorship entr'acte, Schleicher took the role of 'Socialist General', and entered into relations with the Christian Trade Unions, the Left Nazis and even with the Social Democrats. Schleicher's plan was for a sort of Labour Government under his Generalship. It was an utterly un-workable idea as the Reichswehr officers were hardly prepared to follow Schleicher on this path and the working class had a natural distrust of their future allies. Equally, Schleicher aroused hatred amongst the great capitalists and landowners by these plans. The SPD and KPD could have achieved success building on a Berlin transport strike.

Hitler learned from von Papen that the general had no authority to abolish the Reichstag parliament, whereas any majority of seats did. The cabinet (under a previous interpretation of Article 48) ruled without a sitting Reichstag, which could vote only for its own dissolution. Hitler also learned that all past crippling Nazi debts were to be relieved by German big business.
On 22 January, Hitler's efforts to persuade Oskar von Hindenburg (the President's son) included threats to bring criminal charges over estate taxation irregularities at the President's Neudeck estate (although 5000 extra acres were soon allotted to Hindenburg's property). Out maneuvered by von Papen and Hitler on plans for the new cabinet, and having lost Hindenburg's confidence, Schleicher asked for new elections. On 28 January von Papen described Hitler to Paul von Hindenburg as only a minority part of an alternative, von Papen-arranged government. The four great political movements, the SPD, KPD, Centre, and the Nazis were in opposition.
On 29 January Hitler and von Papen thwarted a last-minute threat of an officially-sanctioned Reichswehr takeover, and on 30 January 1933 Hindenburg accepted the new Papen-Nationalist-Hitler coalition with the Nazis holding only three of eleven Cabinet seats. Later that day, the first cabinet meeting was attended by only two political parties, representing a minority in the Reichstag: The Nazis and the DNVP led by Alfred Hugenberg (196 + 52 seats). Eyeing the Catholic Centre Party's 70 (+ 20 BVP) seats, Hitler refused their leader's demands for constitutional "concessions" (amounting to protection) and planned for dissolution of the Reichstag.
Hindenburg, despite his misgivings about the Nazis' goals and about Hitler as a person, reluctantly agreed to Papen's theory that, with Nazi popular support on the wane, Hitler could now be controlled as chancellor. The date dubbed Machtergreifung (seizure of power) by the Nazi propaganda is commonly seen as the beginning of Nazi Germany.
Hitler's chancellorship and the death of the Weimar Republic (1933)
Hitler was sworn in as Chancellor on the morning of 30 January 1933 in what some observers later described as a brief and indifferent ceremony. By early February, a mere week after Hitler's assumption of the chancellorship, the government had begun to clamp down on the opposition. Meetings of the left-wing parties were banned and even some of the moderate parties found their members threatened and assaulted. Measures with an appearance of legality suppressed the Communist Party in mid-February and included the plainly illegal arrests of Reichstag deputies.
Reichstag Fire
The Reichstag Fire on 27 February was blamed by Hitler's government on the Communists and Hitler used the ensuing state of emergency to obtain the assent of President von Hindenburg to issue the Reichstag Fire Decree the following day. The decree invoked Article 48 of the Weimar Constitution and suspended a number of constitutional protections of civil liberties, allowing the Nazi government to take swift action against political meetings, arresting and killing the Communists.
Reichstag election of March 5
Hitler and the Nazis exploited the German state's broadcasting and aviation facilities in a massive attempt to sway the electorate, but this election — the last multi-party election to take place until the end of the Third Reich twelve years later — yielded a scant majority of 16 seats for the coalition. At the Reichstag elections, which took place on 5 March, the NSDAP obtained seventeen million votes. The Communist, Socialist and Catholic Centre votes stood firm.
Hitler addressed disparate interest groups, stressing the necessity for a definitive solution to the perpetual instability of the Weimar Republic. He now blamed Germany's problems on the Communists, even threatening their lives on 3 March. Former Chancellor Heinrich Brüning proclaimed that his Centre Party would resist any constitutional change and appealed to the President for an investigation of the Reichstag fire. Hitler's successful plan was to induce what remained of the now Communist-depleted Reichstag to grant him, and the Government, the authority to issue decrees with the force of law. The hitherto Presidential Dictatorship hereby was to give itself a new legal form.
On 15 March the first cabinet meeting was attended by the two coalition parties, representing a minority in the Reichstag: The Nazis and the DNVP led by Alfred Hugenberg (196 + 52 seats). According to the Nuremberg Trials this cabinet meeting's first order of business was how at last to achieve the complete counter-revolution by means of the constitutionally-allowed Enabling Act, requiring two-thirds parliamentary majority. This Act would, and did, bring Hitler and the NSDAP unfettered dictatorial powers.
Hitler cabinet meeting in mid-March
At the meeting of the new cabinet on 15 March, Hitler introduced the Enabling Act, which would have authorised the cabinet to enact legislation without the approval of the Reichstag. Meanwhile, the only remaining question for the Nazis was whether the Catholic Centre Party (Zentrum) would support the Enabling Act in the Reichstag, thereby providing the two-thirds majority required to ratify a law that amended the constitution. Hitler expressed his confidence to win over the Centre's votes. Hitler is recorded at the Nuremberg Trials as being sure of eventual Centre Party Germany capitulation and thus rejecting of the DNVP's suggestions to "balance" the majority through further arrests, this time of socialists. Hitler however assured his coalition partners that arrests would resume after the elections and, in fact, some 26 SPD Socialists were physically removed. After meeting with Centre leader Monsignor Ludwig Kaas and other Centre Trade Union leaders daily and denying them a substantial participation in the government, negotiation succeeded in respect of guarantees towards Catholic civil-servants and education issues.
At the last internal Centre meeting prior to the debate on the Enabling Act, Kaas expressed no preference or suggestion on the vote, but as a way of mollifying opposition by Centre members to the granting of further powers to Hitler, Kaas somehow arranged for a letter of constitutional guarantee from Hitler himself prior to his voting with the centre en bloc in favor of the Enabling Act. This guarantee was not ultimately given. Kaas, the party's chairman since 1928, had strong connections to the Vatican Secretary of State, later Pope Pius XII. In return for pledging his support for the act, Kaas would use his connections with the Vatican to set in train and draft the Holy See's long desired Reichskonkordat with Germany (only possible with the co-operation of the Nazis).
Ludwig Kaas is considered along with von Papen as being one of the two most important political figures in the creation of a National Socialist dictatorship.[4]
Enabling Act negotiations
On 20 March negotiation began between Hitler and Frick on one side and the Catholic Centre Party (Zentrum) leaders — Kaas, Stegerwald and Hackelsburger — on the other. The aim was to settle on conditions under which Centre would vote in favor of the Enabling Act. Because of the Nazis' narrow majority in the Reichstag, Centre's support was necessary to receive the required two-thirds majority vote. On 22 March, the negotiations concluded; Hitler promised to continue the existence of the German states, agreed not to use the new grant of power to change the constitution, and promised to retain Zentrum members in the civil service. Hitler also pledged to protect the Catholic confessional schools and to respect the concordats signed between the Holy See and Bavaria (1924), Prussia (1929) and Baden (1931). Hitler also agreed to mention these promises in his speech to the Reichstag before the vote on the Enabling Act.
Ceremonial opening of the Reichstag in Potsdam on March 21
The ceremonial opening of the Reichstag on 21 March was held at the Garrison Church in Potsdam, a shrine of Prussianism, in the presence of many Junker landowners and representatives of the imperial military caste. This impressive and often emotional spectacle — orchestrated by Joseph Goebbels — aimed to link Hitler's government with Germany's imperial past and portray National Socialism as a guarantor of the nation's future. The ceremony helped convince the "old guard" Prussian military elite of Hitler's homage to their long tradition and, in turn, produced the relatively convincing view that Hitler's government had the support of Germany's traditional protector — the Army. Such support would publicly signal a return to conservatism to curb the problems affecting the Weimar Republic, and that stability might be at hand. In a cynical and politically adroit move, Hitler bowed in respectful humility before President and Field Marshal von Hindenburg.
Passage of the Enabling Act by the Reichstag on March 23
The Reichstag Government convened on 23 March 1933, and in the midday opening, Hitler made a historic speech, appearing outwardly calm and conciliatory. It is most noticeable for its abrupt reversal of the Nazi Party's hardline stance against Christianity and particularly Catholicism (needs reference). Hitler presented an appealing prospect of respect towards Christianity by paying tribute to the Christian faiths as "essential elements for safeguarding the soul of the German people". He promised to respect their rights and declared his government's "ambition is a peaceful accord between Church and State" and that he hoped "to improve our friendly relations with the Holy See." This speech aimed especially at the future recognition by the named Holy See and therefore to the votes of the Centre Party addressing many concerns Kaas had voiced during the previous talks. Kaas is considered to have had a hand therefore in the drafting of the speech.[4] Kaas is also reported as voicing the Holy See's desire for Hitler as bulwark against atheistic Russian nihilism previously as early as May 1932.[5]
In the debate prior to the vote on the Enabling Act, Hitler orchestrated the full political menace of his paramilitary forces like the storm troopers in the streets to intimidate reluctant Reichstag deputies into approving the Enabling Act. The Communists' 81 seats had been empty since the Reichstag Fire Decree and other lesser known procedural measures, thus excluding their anticipated "No" votes from the balloting. Otto Wels, the leader of the Social Democrats, whose seats were similarly depleted from 120 to below 100, was the only speaker to defend democracy and in a futile but brave effort to deny Hitler the two-thirds majority, he made a speech critical of the abandonment of democracy to dictatorship. At this Hitler could no longer restrain his wrath.[6]
In his retort to Wels, Hitler abandoned earlier pretence at calm statesmanship and delivered a characteristic screaming diatribe, promising to exterminate all Communists in Germany and threatening Wels' Social Democrats as well. Meanwhile Hitler's promised written guarantee to Monsignor Kaas was being typed up, it was asserted to Kaas, and thereby Kaas was persuaded to silently deliver the Centre bloc's votes for the Enabling Act anyway.
Aftermath
The passing of the Enabling Act gave Hitler and his government sweeping powers to legislate without the Reichstag's approval, and to make foreign policy decisions and deviate from the constitution where they saw fit. Hitler would use these powers to remove all opposition to the dictatorship he wished to create. The decrees issued by Hitler's cabinet within succeeding weeks rapidly stripped Germans of their rights, removed all non-Nazi members of the Civil Service, and banned all other political parties and unions, ushering in the Third Reich.
The NSDAP movement had rapidly passed the power of the majority Nationalist Ministers to control. Unchecked by the police, the S.A indulged in acts of terrorism throughout Germany. Communists, Social Democrats, and the Centre were ousted from public life everywhere. The violent persecution of Jews began, and by the summer 1933 the NSDAP felt itself so invincible that it did away with all the other parties, as well as trades unions. The Nationalist Party was among those suppressed. The NSDAP ruled alone in Germany. The Reichswehr had, however, remained completely untouched by all these occurrences. It was still the same State within a State that it had been in the Weimar Republic. Similarly, the private property of wealthy industrialists and landowners was untouched, whilst the administrative and judicial machinery was only very slightly tampered with.[2]
Reasons for the Weimar Republic's failure
The reasons for the Weimar Republic's collapse are the subject of continuing debate. It may have been doomed from the beginning since even moderates disliked it and extremists on both the left and right loathed it. Germany had no democratic traditions and Weimar democracy was widely seen as chaotic. And since Weimar politicians had been blamed for the "stab in the back" myth that was then widely believed in Germany as the real cause of the surrender of the German army in World War I, the popular legitimacy of the government was on shaky ground.
No single reason can explain the failure of the Weimar Republic. The most commonly asserted causes can be grouped into three categories: economic problems, institutional problems and the roles of specific individuals.
Economic problems
The Weimar Republic had some of the most serious economic problems ever experienced by any Western democracy in history. Rampant hyperinflation, massive unemployment and a large drop in living standards were primary factors. In 1923-29 there was a short period of economic recovery, but the Great Depression of the 1930s led to a worldwide recession. Germany was particularly affected because it depended heavily on American loans. In 1926, about 2 million Germans were unemployed - this rose to around 6 million in 1932. Many blamed the Weimar Republic. This was made apparent when political parties on both right and left wanting to disband the Republic altogether made any democratic majority in Parliament impossible.
The Weimar Republic was severely affected by the Great Depression triggered by the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The crash and subsequent economic stagnation led to increased demands on Germany to repay the debts owed to the United States. As the Weimar Republic was very fragile in all of its existence, the depression proved to be devastating, and played a major role in the NSDAP's takeover.
The Treaty of Versailles was considered by most Germans to be a punishing and degrading document because it forced them to surrender resource-rich areas and pay massive amounts of compensation. These punitive reparations caused consternation and resentment, although the actual economic damage resulting from the Treaty of Versailles is difficult to determine. While the official reparations were considerable Germany ended up paying only a fraction of them. However, the reparations did damage Germany's economy by discouraging market loans, which forced the Weimar government to finance its deficit by printing more money, causing rampant hyperinflation. In addition, the rapid disintegration of Germany in 1919, due to the return of a disillusioned army, the rapid change from possible victory in 1918 to defeat in 1919, and the political chaos may have caused a psychological imprint on Germans that could lead to extreme nationalism, shown by Hitler.
Most historians agree that many industrial leaders identified the Weimar Republic with labour unions and with the Social Democrats, who had established the Versailles concessions of 1918/1919. Although some did see Hitler as a means to abolish the latter, the Republic was already unstable before any industry leaders were supporting Hitler. Even those who supported Hitler's appointment often did not want Nazism in its entirety and considered Hitler a temporary solution in their efforts to abolish the Republic. Industry support alone cannot explain Hitler's enthusiastic support by large segments of the population, including many workers who had turned away from the left.
Institutional problems
It is widely agreed that the 1919 constitution had several weaknesses, making the eventual establishment of a dictatorship likely but it is unknown whether a different constitution could have prevented the Third Reich. However, the 1949 West German constitution (the Grundgesetz) is generally viewed as a strong response to these flaws.
- The institution of the Reichspräsident was frequently considered as an Ersatzkaiser ("substitute emperor"), an attempt to replace the Kaiser (who resigned and fled in 1918) with a similarly strong institution meant to diminish party politics. Article 48 of the constitution gave the President power to "take all necessary steps" if "public order and security are seriously disturbed or endangered". Although this was intended as an emergency clause, it was often used before 1933 to issue decrees without the support of Parliament (see above) and also made Gleichschaltung easier. For example, the Reichstag Fire Decree was issued on the basis of Article 48.
- The use of almost pure proportional representation meant any party with a small amount of support could gain entry into the Reichstag. This led to many small parties, some extremist, building political bases within the system (In 1949, four years after the Second World War the electoral law was changed and only parties with 5% or more of the total vote would be allowed to enter the Bundestag). Yet, it has to be noted that the Reichstag of the monarchy was fractioned to a similar degree although being elected by majority vote under a first-past-the-post system.
- The Reichstag could remove the Reichskanzler from office even if it was unable to agree on a successor. This "Motion of No Confidence" led to many chancellors in quick succession, adding to the Republic's instability (see Chancellor of Germany for a list). As a result, the 1949 Grundgesetz stipulates that a chancellor may only be voted down by Parliament if a successor is elected at the same time (see Constructive Vote of No Confidence).
- The constitution provided that in the event of the president's death or resignation, the Reichskanzler would assume that office (and crucially possess its powers) pending election of a new president. This allowed Hitler to easily unite the offices of Reichskanzler and Reichspräsident after Hindenburg's death in 1934. However, by this time the dictatorship was already firmly installed and this clause alone cannot be blamed for Nazism.
Role of individuals
Some historians prefer to consider individuals and the decisions they made. This brings up the problematic question of what alternatives were available at the time and leads to speculation and hypothesis.
Brüning's economic policy from 1930-1932 has been the subject of much debate. It caused many Germans to identify the Republic with cuts in social spending and extremely liberal economics. Whether there were alternatives to this policy during Great Depression is an open question.
Paul von Hindenburg became Reichspräsident in 1925. He represented the older authoritarian 1871 Empire, and it is hard to label him as a democrat in support of the 1919 Republic, but he was never a Nazi. During his later years (at well over 80 years old), he was also senile. A president with solid democratic beliefs may not have allowed the Reichstag to be circumvented with the use of Article 48 decrees and might have avoided signing the Reichstag Fire Decree. Hindenburg waited one and a half days before he appointed Hitler as Reichskanzler on 30 January 1933, which indicates some hesitance. Some claim Nazism would have lost much public support if Hitler had not been named chancellor.
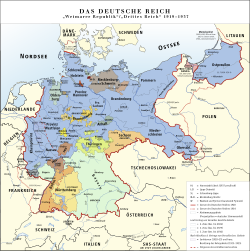
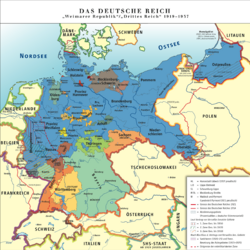
Constituent states of Germany during the Weimar period
Prior to World War I, the constituent states of the German Empire were 22 smaller monarchies, three city-states and the Imperial territory of Alsace-Lorraine. After the territorial losses of the Treaty of Versailles and the revolution of 1918, the remaining states continued as republics. The former Ernestine duchies continued briefly as republics before merging to form the state of Thuringia in 1920, except for Saxe-Coburg, which became part of Bavaria.

| State | Capital | |
|---|---|---|
| Anhalt | Dessau | |
| Baden | Karlsruhe | |
| Bavaria (Bayern) | Munich | |
| Brunswick (Braunschweig) | Braunschweig | |
| Hesse (Hessen / Hessen-Darmstadt) | Darmstadt | |
| Lippe | Detmold | |
| Mecklenburg-Schwerin | Schwerin | |
| Mecklenburg-Strelitz | Neustrelitz | |
| Oldenburg | Oldenburg | |
| Prussia (Preußen) | Berlin | |
| Saxe-Coburg (Sachsen-Coburg) - to Bavaria in 1920 | Coburg | |
| Saxony (Sachsen) | Dresden | |
| Schaumburg-Lippe | Bückeburg | |
| Thuringia (Thüringen) - from 1920 | Weimar | |
| Waldeck-Pyrmont - to Prussia in 1921/1929 | Arolsen | |
| Württemberg | Stuttgart | |
| City-states | ||
| Bremen | ||
| Hamburg | ||
| Lübeck | ||
| States merged to form Thuringia in 1920 | ||
| Reuss | Gera | |
| Saxe-Altenburg (Sachsen-Altenburg) | Altenburg | |
| Saxe-Gotha (Sachsen-Gotha) | Gotha | |
| Saxe-Meiningen (Sachsen-Meiningen) | Meiningen | |
| Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) | Weimar | |
| Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt | Rudolstadt | |
| Schwarzburg-Sondershausen | Sondershausen | |
These states were gradually de facto abolished under the Nazi regime via the Gleichschaltung process, as the states were largely re-organised into Gaue. However, the city-state of Lübeck was formally incorporated into Prussia in 1937 following the Greater Hamburg Act - apparently motivated by Hitler's personal dislike for the city. Most of the remaining states were formally dissolved by the Allies at the end of World War II and ultimately re-organised into the modern states of Germany.
Citations
- ↑ "Das Deutsche Reich im Überblick". Wahlen in der Weimarer Republik. Retrieved on 2007-04-26.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Rosenberg, Arthur (1936). A History of The German Republic. London: Methuen.
- ↑ Evans, Richard J. (2004). The Coming of the Third Reich. New York: The Penguin Press. pp. 446. ISBN 1594200041.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 von Klemperer, Klemens (1992). German Resistance Against Hitler:The Search for Allies Abroad 1938-1945. Oxford: OUP / Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-821940-7.
- ↑ Mowrer, Edgar Ansel (1970). Triumph and Turmoil. London: Allen & Unwin. pp. 209. ISBN 0049200267.
- ↑ Shirer, William L. (1960). The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-72868-7.
References
- Abraham, David (1986). The Collapse of the Weimar Republic: Political Economy and Crisis (2nd Edition ed.). New Jersey: Holmes & Meier Publishers. ISBN 0-8419-1084-7.
- Allen, William Sheridan (1984). The Nazi seizure of Power: the experience of a single German town, 1922-1945. New York, Toronto: F. Watts. ISBN 0-531-09935-0.
- Berghahn, V. R. (1982). Modern Germany. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-34748-3.
- Bookbinder, Paul (1996). Weimar Germany: the Republic of the Reasonable. Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press. ISBN 0-7190-4286-0.
- Bracher, Karl Dietrich (1971) (in German). Die Auflösung der Weimarer Republik; eine Studie zum Problem des Machtverfalls in der Demokratie. Villingen, Schwarzwald: Ring-Verlag.
- Broszat, Martin (1987). Hitler and the Collapse of Weimar Germany. Leamington Spa, New York: Berg. ISBN 0-85496-509-2.
- Childers, Thomas (1983). The Nazi Voter: The Social Foundations of Fascism in Germany, 1919-1933. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-1570-5.
- Craig, Gordon A. (1980). Germany 1866-1945 (Oxford History of Modern Europe). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-502724-8.
- Dorpalen, Andreas (1964). Hindenburg and the Weimar Republic. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press.
- Eschenburg, Theodor (1972) "The Role of the Personality in the Crisis of the Weimar Republic: Hindenburg, Brüning, Groener, Schleicher" pages 3-50 from Republic to Reich The Making Of The Nazi Revolution edited by Hajo Holborn, New York: Pantheon Books.
- Feuchtwanger, Edgar (1993). From Weimar to Hitler: Germany, 1918-33. London: Macmillan. ISBN 0-333-27466-0.
- Gay, Peter (1968). Weimar Culture: The Outsider as Insider. New York: Harper & Row.
- Gordon, Mel (2000). Volutpuous Panic: The Erotic World of Weimar Berlin. New York: Feral House.
- Hamilton, Richard F. (1982). Who Voted for Hitler?. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-09395-4.
- James, Harold (1986). The German Slump: Politics and Economics, 1924-1936. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-821972-5.
- Kaes, Anton; Jay, Martin; Dimendberg, Edward (eds.) (1994). The Weimar Republic Sourcebook. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-06774-6.
- Kolb, Eberhard (1988). The Weimar Republic. P.S. Falla (translator). London: Unwin Hyman. ISBN 0-04-943049-1.
- Mommsen, Hans (1991). From Weimar to Auschwitz. Philip O'Connor (translator). Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-03198-3.
- Mowrer, Edgar Angel (1933). Germany Puts The Clock Back. London.
- Mowrer, Edgar Angel (1970). Triumph and Turmoil. George Allen & Unwin. ISBN 0049200267.
- Nicholls, Anthony James (2000). Weimar And The Rise Of Hitler. New York: St. Martin's Press,. ISBN 0-312-23350-7.
- Peukert, Detlev (1992). The Weimar Republic: the Crisis of Classical Modernity. New York: Hill and Wang. ISBN 0-8090-9674-9.
- Rosenberg, Arthur (1936). A History of The German Republic. London: Methuen.
- Turner, Henry Ashby (1996). Hitler's Thirty Days To Power: January 1933. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-40714-0.
- Turner, Henry Ashby (1985). German Big Business and the Rise of Hitler. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-503492-9.
- Wheeler-Bennett, John (2005). The Nemesis of Power: German Army in Politics, 1918-1945. New York: Palgrave Macmillan Publishing Company. ISBN 1-4039-1812-0.
External links
- The Constitution of the German Reich (Weimar constitution) of 11th August 1919 (English)
- PSM Data Bank
- documents (German)
See also
- Weimar culture
- Inflation in the Weimar Republic
- Gleichschaltung
- Centre Party Germany
- Franz von Papen
- Weimar Constitution
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||