United States invasion of Panama
| Invasion of Panama | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Soldiers from the 7th Infantry Division (light) prepare to take La Comandancia in the El Chorrillo neighborhood of Panama City, December 1989. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 16,000+ | 27,684+ | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 100-1000 soldiers killed; 300-4,000 civilians killed | 24 killed, 325 wounded |
||||||
The United States invasion of Panama, codenamed Operation Just Cause, was the invasion of Panama by the United States in December 1989, during the administration of U.S. President George H. W. Bush, and ten years before the Panama Canal was transferred from control of the United States, back to Panama. During the invasion, de facto Panamanian leader, general, and dictator Manuel Noriega was deposed and the Panamanian Defense Force dissolved.
Contents |
Background
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties, which set in motion the process of handing the Panama Canal over to Panamanian control, was signed by President of the United States Jimmy Carter and Omar Torrijos of Panama on September 7, 1977. U.S. relations with Noriega spanned decades from 1959 to the early 1980s, when Noriega served as a U.S. intelligence asset and was on the Central Intelligence Agency's payroll. Noriega's relations with George H. W. Bush may have begun in the 1970s, when Bush was head of the CIA.[1] Noriega had worked to advance U.S. interests in Central America, notably in sabotaging the forces of the socialist government in Nicaragua, the Sandinistas, and the FMLN revolutionaries in El Salvador, receiving a salary upwards of $100,000 per year for his efforts.[2] ; and as he worked with the Drug Enforcement Administration to restrict illegal drug shipments, he was known to work with the drug dealers themselves simultaneously.[1]
During the 1980s, U.S. President Ronald Reagan negotiated with General Noriega, requesting that the Panamanian leader peacefully step down, while pressuring him with several drug-related indictments in U.S. courts. Later negotiations involved dropping the drug-trafficking indictments. In March of 1989, an attempted coup against the government of Panama was resisted by Noriega's forces. In May '89, during the national elections, an alliance of parties opposed to the military dictatorship of Manuel Noriega counted results from the country's election precincts before they were sent to the district centers. Their tally showed their candidate, Guillermo Endara defeating Carlos Duque, candidate of a pro-Noriega coalition, by a nearly 3-to-1 margin. Endara was beaten up by Noriega supporters the next day.[1] Noriega declared the election null and maintained power by force, making him unpopular among Panamanians. Noriega's government insisted that they won the presidential election and irregularities had been on the part of U.S.-backed candidates from opposition parties.[3] Bush called on Noriega to honor the will of the Panamanian people.[1]

The Panamanian Defense Force (PDF), turning its back on Noriega, offered to hand him over to the US; no action was taken.
In October 1989, Noriega foiled a second coup attempt led by major Moisés Giroldi. Pressure mounted on Bush, as the media labeled him a "wimp" for failing to aid Panama amidst his rhetoric.[1][4] Bush declared that the U.S. would not negotiate with a known drug-trafficker and denied having any knowledge of Noriega's involvement with the drug trade prior to his indictment.[5] President Bush's allegations that forces under Noriega's command had shot and killed an unarmed American serviceman, wounded another, arrested and brutally beat a third American serviceman and then brutally interrogated his wife, threatening her with sexual abuse, were cited by US Ambassador Thomas R. Pickering to the United Nations Security Council as sufficient grounds for invasion as an act of self-defense within Article 51 of the UN charter.[6]
In the December 16 incident that led to the killing of American Marine officer Lt. Robert Paz, four U.S. personnel were stopped at a roadblock outside PDF headquarters in the El Chorrillo neighborhood of Panama City. The United States Department of Defense claimed that the servicemen were unarmed and in a private vehicle and that they attempted to flee the scene only after their vehicle was surrounded by a crowd of civilians and PDF troops. The PDF claimed the Americans were armed and on a reconnaissance mission.[7] It was also reported by the Los Angeles Times[8] that "according to American military and civilian sources" the officer killed was a member of the "Hard Chargers", a group whose goal was to agitate members of the PDF. It was also reported that the group's "tactics were well known by ranking U.S. officers" who were frustrated by "Panamanian provocations committed under dictator Manuel A. Noriega", although the group was not officially sanctioned by the military. The Pentagon later denied that such a group ever existed.[9] According to an official U. S. military report "witnesses to the incident, a U.S. naval officer and his wife were assaulted by Panamanian Defense Force soldiers while in police custody".[10]
Justification for the invasion
The official United States justification for the invasion was articulated by President George H. W. Bush on the morning of December 20, a few hours after the start of the operation. Bush listed four reasons for the invasion:[11]
- Safeguarding the lives of U.S. citizens in Panama. In his statement, Bush claimed that Noriega had declared that a state of war existed between the United States and Panama and that he also threatened the lives of the approximately 35,000 US citizens living there. There had been numerous clashes between U.S. and Panamanian forces; one US Marine had been killed a few days earlier and several incidents of harassment of US citizens had taken place.
- Defending democracy and human rights in Panama.
- Combating drug trafficking. Panama had become a center for drug money laundering and a transit point for drug trafficking to the United States and Europe.
- Protecting the integrity of the Torrijos-Carter Treaties. Members of Congress and others in the U.S. political establishment claimed that Noriega threatened the neutrality of the Panama Canal and that the United States had the right under the treaties to intervene militarily to protect the Panama canal.
In regard to one of the reasons set forth by the United States to justify the invasion, namely the Panamanian legislature's declaration of a state of war between the United States and Panama, Noriega insists[12] that this statement referred to a state of war directed by the U.S. against Panama, in the form of what he claimed were harsh economic sanctions and constant, provocative military maneuvers (Operations Purple Storm and Sand Flea)[13] that were prohibited by the Torrijos-Carter Treaties. The U.S. had turned a blind-eye to Noriega's involvement since the 1970s. Noriega was then singled out for direct involvement in these drug trafficking operations. Panama, before the contended 'declaration of war' against the US, had instigated no hostile actions against any other country.
Invasion
The U.S. Army, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Navy and U.S. Marines participated in Operation Just Cause. Ground forces consisted of combat elements of the XVIII Airborne Corps, the 82nd Airborne Division, the 7th Infantry Division (Light), the 75th Ranger Regiment, a Joint Special Operations Task Force, elements of the 5th Infantry Division, 1138th Military Police Company of the Missouri Army National Guard, 193rd Infantry Brigade, 508th Infantry Regiment, 59th Engineer Co. (Sappers), Marine Security Forces Battalion Panama, and elements from the 3rd Battalion, 6th Marine Regiment, Marine Fleet Antiterrorism Security Teams, 2nd Light Armored Infantry Battlion, and 2nd Marine Logistics Group.
The military incursion into Panama began on December 20, 1989, at 0100 local time. The operation involved 57,684 U.S. troops and over 300 aircraft —including the AC-130 Spectre gunship, OA-37B Dragonfly observation and attack aircraft, and the F-117A Nighthawk stealth aircraft flown by the 37th Tactical Fighter Wing, and AH-64 Apache attack helicopter. The invasion of Panama was the first combat deployment for the AH-64, the HMMWV and the F-117A. These were deployed against the 46,000 members of the Panama Defense Force (PDF).[14]
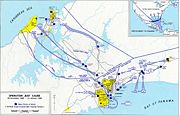
The operation began with an assault of strategic installations such as the civilian Punta Paitilla Airport in Panama City, a PDF garrison and airfield at Rio Hato, where Noriega also maintained a residence, and other military command centers throughout the country. The attack on the central headquarters of the PDF (referred to as La Comandancia) touched off several fires, one of which destroyed most of the adjoining and heavily populated El Chorrillo neighborhood in downtown Panama City.[15] According to eyewitnesses,[16] the houses in this neighborhood were purposefully set on fire by US soldiers in order to arrest PDF soldiers hiding in the area. During the firefight at the Comandancia, the PDF downed two special operations helicopters and forced one AH-6 Little Bird to crash land in the Panama Canal.[17] Fort Amador was secured by elements of the 508th Airborne Infantry and 59th Engineer Company (sappers) in a night time air assault which secured the fort in the early hours of December 20th. Fort Amador was a key position because of its relationship to the large oil farms adjacent to the canal, the Bridge of the Americas over the canal, and the Pacific entrance to the Panama Canal. There where key command and control elements of the PDF stationed at Fort Amador. Furthermore, Fort Amador also had a large US housing Area that need to be secured to prevent the PDF from taking US citizens as hostages. This position also protected the left flank of the attack on the Comadancia and the securing of the neighborhood El Chorrillos, which had many of Noriega's supporters in the form dignity battalions (referred to as Dingbats). A few hours after the invasion began, Guillermo Endara was sworn in at Rodman Naval Base. It is generally agreed that Endara would have been the victor in the presidential election which had been scheduled earlier that year.[18] The 1138th Military Police Company of the Missouri Army National Guard set up a detainee camp at Empire Range to handle the mass of civilian and military detainees. This unit made history by being the first Guard unit called into active service since the Vietnam War. This would not be the last time the unit would be called, as Operation Desert Shield/Storm was looming on the horizon.
Military operations continued for several weeks, mainly against military units of the Panama Army. Noriega remained at large for several days, but realizing he had few options in the face of a massive manhunt, with a one million dollar reward for his capture, he obtained refuge in the Vatican diplomatic mission in Panama City. The US military's psychological pressure on him and diplomatic pressure on the Vatican mission, however, was relentless, as was the playing of loud rock-and-roll music on boomboxes[19] day and night in a densely populated area. It has subsequently become clear, however, that the music was used principally to prevent parabolic microphones from being used to eavesdrop on negotiations, and not as a psychological weapon based around Noriega's supposed loathing of rock music.[20] Noriega finally surrendered to the U.S. military on January 3, 1990. He was immediately put on a military transport plane and extradited to the United States.
While some US Marine units continued their deployment, others that had been deployed since October 3, 1989 began returning on January 12, 1990. Along with units of the 193rd Infantry Brigade, 508th Airborne Infantry and 59th Engineer Company (Sapper), 16th Military Police Brigade, these units continued "police" patrols throughout Panama City, and areas west of the Canal, to restore law and order and support the newly installed government (under the moniker Operation Promote Liberty). One of these units was the 555TH Military Police, who had been in country since December 20, 1989. They had the unique pleasure of fighting the PDF and then training the Panamanian Police Force who were prior PDF.
Casualties
The US lost 24 troops,[21] and 325 were wounded (WIA). The U.S. Southern Command, at that time based on Quarry Heights in Panama, estimated the number of Panamanian military dead at 205, lower than its original estimate of 314. There has been considerable controversy over the number of Panamanian civilian casualties resulting from the invasion. The Southern Command estimated that number at 200.
Physicians for Human Rights[22] in a report issued one year after the invasion,[23] estimated that "at least 300 Panamanian civilians died due to the invasion". The report also concluded that "neither Panamanian nor U.S. governments provided a careful accounting of non-lethal injuries" and that "relief efforts were inadequate to meet the basic needs of thousands of civilians made homeless by the invasion". The report estimated the number of displaced civilians to be over 15,000, whereas the U.S. military provided support for only 3,000 of these. Other estimates have suggested that between 2000 and 5000 civilians died, some arguing that this was a result of use of excessive force and novel weapons by the U.S military.
According to official Pentagon figures 516 Panamanians were killed during the invasion; an internal Army memo estimated the number at 1,000[24]
An Independent Commission of Inquiry on the invasion estimated Panamanian deaths between 1,000 and 4,000[25][26]
Human Rights Watch's 1991 report on Panama in the post-invasion aftermath, stated that even with some uncertainties about the scale of civilian casualties, the figures are "still troublesome" because
"[Panama's civilian deaths] reveal that the 'surgical operation' by American forces inflicted a toll in civilian lives that was at least four-and-a-half times higher than military causalities in the enemy, and twelve or thirteen times higher than the casualties suffered by U.S. troops. By themselves these ratios suggest that the rule of proportionality and the duty to minimize harm to civilians, where doing so would not compromise a legitimate military objective, were not faithfully observed by they invading U.S. forces. For us, the controversy over the number of civilian casualties should not obscure the important debate on the manner in which those people died."[27]
Origin of the name "Operation Just Cause"
Operation plans directed against Panama evolved from plans designed to defend the Canal. They became more aggressive as the situation between the two nations deteriorated. The Prayer Book series of plans included rehearsals for a possible clash (Operation Purple Storm) and missions to secure US sites (Operation Bushmaster). Eventually these plans became Operation Blue Spoon, which was renamed by President Bush as Just Cause.
The name "Just Cause" has been used primarily by the United States military for planning and historical purposes and by other U.S. entities such as the State Department. The Panamanian name for the Operation is "The Invasion" (La Invasión).
In recent years, the naming of U.S. military operations has been the source of some controversy, both internationally and domestically (see Operation Enduring Freedom). At the time operations to depose Noriega were being planned, U.S. military operations were given meaningless names. Just Cause was planned under the name Blue Spoon, and the invasion itself incorporated elements of the Operation Nifty Package and Operation Acid Gambit plans. The name Blue Spoon was later changed to Just Cause for aesthetic and public relations reasons. The post-invasion occupation and reconstruction was titled Operation Promote Liberty.
Local and international reactions
The invasion of Panama provoked international outrage. Some countries charged that the United States committed an act of aggression by invading Panama and was trying to conceal a new manifestation of its interventionist policy of force in Latin America. On 29 December, the General Assembly of the United Nations voted 75–20 with 40 abstentions to condemn the invasion as a flagrant violation of international law.[28]
On December 22 the Organization of American States passed a resolution deploring the invasion and calling for withdrawal of U.S. troops, in addition to a separate resolution condemning the violation of the diplomatic status of the Nicaraguan Embassy in Panama by US Special Forces who had entered the building.[29] At the UN Security Council, after discussing the issue over several days, a draft resolution demanding the immediate withdrawal of United States forces from Panama[30] was vetoed on 23 December by three of the permanent members of the Security Council,[31] France, United Kingdom, and the United States who cited its right of self-defense of 35,000 Americans present on the Panama Canal.[32]
It is claimed that the Panamanian people overwhelmingly supported the invasion.[33] According to one poll, 92% of Panamanian adults supported the U.S. incursion, and 76% wished that U.S. forces had invaded in October during the coup.[33] 74% of Americans polled approved the action.[33] Panama's legislature declared Dec. 20, 2007, the anniversary of the 1989 U.S. invasion, as a day of national mourning. [34]
Peru recalled its ambassador in protest of the invasion.
The Washington Post disclosed several rulings of the Office of Legal Counsel, issued shortly before the invasion, in regards to the U.S. armed forces being charged with making an arrest abroad. One ruling Interpreted the Executive Order against Assassination of Foreign Leaders, which prohibits the intentional killing of foreign leaders as suggesting that accidental killings would be acceptable foreign policy. Another ruling concludes that the Posse Comitatus Act of 1878, which prohibits the armed forces from making arrests without Congressional authorization, is effective only within the boundaries of the US, such that the military could be used as a police force abroad — for example, in Panama, to enforce a federal court warrant against Noriega.[35]
Aftermath
Guillermo Endara, in hiding in the Panama Canal Zone, was sworn in as president by a judge on the night preceding the invasion. In later years, he staged a hunger strike, calling attention to the poverty and homelessness left in the wake of both the Noriega years and destruction caused by the U.S. invasion[36] For nearly two weeks after the invasion, there was widespread looting and lawlessness, a contingency which the United States military indicated it had not anticipated. This looting inflicted catastrophic losses on many Panamanian businesses, some of which took several years to recover. On July 19, 1990, a group of 60 companies based in Panama filed a lawsuit against the United States Government in Federal District Court in New York City alleging that the U.S. action against Panama was "done in a tortious, careless and negligent manner with disregard for the property of innocent Panamanian residents". Most of the businesses had insurance, but the insurers either went bankrupt or refused to pay, claiming acts of war are not covered.[37]
About 20,000 people lost their homes and became refugees from the invasion. About 2,700 families that were displaced by the Chorrillo fire were each given $6,500 by the United States to build a new house or apartment in selected areas in or near the city. However, numerous problems were reported with the new constructions just two years after the invasion.[38]
The government of Guillermo Endara designated the first anniversary of the U.S. invasion a "national day of reflection". On that day hundreds of Panamanians marked the day with a "black march" through the streets of this capital to denounce the U.S. invasion and Endara's economic policies. Protesters echoed claims that 3,000 people were killed as a result of U.S. military action.Since Noriega's ouster, Panama has had three presidential elections, with candidates from opposing parties succeeding each other in the Palacio de las Garzas. Panama's press, however, is still subject to numerous restrictions.[39] On February 10, 1990, the Endara government abolished Panama's military and reformed the security apparatus by creating the Panamanian Public Forces. In 1994, a constitutional amendment permanently abolished the military of Panama. Concurrent with a severe recession in Latin America throughout the 1990s, Panama's GDP recovered by 1993, but very high unemployment remained a serious problem.
Noriega was brought to the US to await trial. One of the charges brought against him was dropped when what had been widely reported as 50 kilograms of cocaine, was revealed to be tamales. [40]
Timeline
Information in this section[13]
September 1987
- Senate passes resolution urging Panama to reestablish a civilian government. Panama protests alleged U.S. violations of the Canal Treaty.
November 1987
- Senate resolution cuts military and economic aid to Panama. Panamanians adopt resolution restricting U.S. military presence.
February 1988
- Noriega indicted on drug-related charges. U.S. forces begin planning contingency operations in Panama (OPLAN BLUE SPOON).

March 1988
- 14th March: First of four deployments of U.S. forces begins providing additional security to U.S. installations.
- 16th March: PDF officers attempt a coup against Noriega.
April 1988
- 5th April: Additional U.S. forces deployed to provide security.
- 9th April: Joint Task Force Panama activated.
May 1989
- 7th May: Civilian elections are held; opposition alliance tally shows their candidate, Guillermo Endara, beating Noriega's candidate, Carlos Duque, by a 3 to 1 margin. The election is declared invalid two days later by Noriega.
- 11th May: President Bush orders 1,900 additional combat troops to Panama (Operation NIMROD DANCER).
- 22nd May: Convoys conducted to assert U.S. freedom of movement. Additional transport units travelled from bases in the territorial US to bases in Panama, and back, for this express purpose.
Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep 89
- U.S. begins conducting joint training/freedom of movement exercises (SAND FLEAS and PURPLE STORMS). Additional transport units continued from this date to travel repeatedly from bases in the territorial US to bases in Panama, and back, for this express purpose.
Oct 89
- 3rd Oct: Noriega defeats second coup attempt.
Dec 89
- 15th Dec: Noriega refers to himself as leader of Panama and mentions a state of war with the U.S.
- 16th Dec: Marine lieutenant shot and killed by PDF. Navy lieutenant and wife detained and assaulted by PDF.
- 17th Dec: NCA directs execution of Operation JUST CAUSE.
- 18th Dec: Army lieutenant shoots PDF sergeant. Joint Task Force South (JTFSO) advance party deploys. JCS designates D-Day/H-Hour as 200100R Dec 89.
- 19th Dec: U.S. forces alerted, marshaled and launched.
D-Day 20 Dec 89
- The United States Invasion of Panama begins. The operation was conducted as a campaign with limited military objectives. JTFSO objectives in PLAN 90-2 were to: Protect U.S. lives and key sites and facilities, capture and deliver Noriega to competent authority, neutralize PDF forces, neutralize PDF command and control, support establishment of a U.S.-recognized government in Panama, and restructure the PDF. Major operations detailed elsewhere continued to the 24th of Dec.
D-Day + 14, 3 Jan 90
- Noriega surrenders to U.S. forces.
D-Day + 23, 12 Jan 90
- Operation JUST CAUSE ends and PROMOTE LIBERTY begins.
Major operations and U.S. units involved
Operations
All 27 objectives related to the Panamanian Defense Force were completed on D-Day: December 20, 1989; as initial forces moved to new objectives, follow-on forces from 7th Inf Div (L) moved into the western areas of Panama and into Panama City.
D-Day -1 19th Dec 89-
- 2d Bde, 7th Inf Div (L), Alerted for deployment. DRF 1 (3/27th Inf) and DRF 2 Initial Reaction Company (C/2/27th INF) Deploys.
D-Day 20 Dec 89 -
- Remaninder of the 2d Bde, 7th Inf Div (L), Deploys and closes in Panama.
D-Day + 1, 21 Dec 89 -
- JCS directs execution of PLAN BLIND LOGIC.
- Panama Canal reopened for daylight operations.
- Refugee situation becomes critical.
- TF Bayonet begins CMO in Panama City.
- Marriott Hotel secured and hostages evacuated.
D-Day + 2, 22 Dec 89 -
- FPP established.
- CMO and stability operations become primary focus.
- 2d Bde, 7th Inf Div (L), deploys to Rio Hato.
- 1st Bde (9th Regiment), 7th Inf Div (L), alerted for deployment.
D-Day + 3, 23 Dec 89 -
- International airport reopened.
- 2d Bde, 7th Inf Div (L) and SF elements begin ops in west.
- 96th CA Bn assumes responsibility for DC Camp from USARSO.
- 1st Bde (9th Regiment) 7th Inf Div (L) closes in Panama.
D-Day + 4, 24 Dec 89 -
- Noriega enters Papal Nunciatura.
- Money for Weapons program initiated.
- Combined U.S./FPP patrols begin.
D-Day + 5, 25 Dec 89 -
- Rangers secure David.
- Operations in western Panama continue successfully.
D-Day + 14, 3 Jan 90 - Noriega surrenders to U.S. forces. D-Day + 23, 12 Jan 90 - Operation JUST CAUSE ends and PROMOTE LIBERTY begins.
Above information[13]
Units involved in Operation Just Cause
- 5th Infantry Division (Mechanized)
-
- 4th Battalion, 6th Infantry Regiment
- 7th Infantry Division (Light)
-
- 27th Infantry Regiment
- 2nd Battalion, 27th Infantry Regiment (DRF 2)
- 3rd Battalion, 27th Infantry Regiment (DRF 1)
- 4th Battalion, 21st Infantry Regiment
- 5th Battalion, 21st Infantry Regiment
- 3rd Battalion, 17th Infantry Regiment
- 4th Battalion, 17th Infantry Regiment
- 6th Battalion, 8th Field Artillery Regiment
- B Battery, 7th Battalion, 15th Field Artillery Regiment
- B Battery, 2-62d ADA
- 1st Battalion, 123rd Aviation Regiment
- 9th Infantry Regiment
- XVIII Airborne Corps
- 82nd Airborne Division
- 1st and 2nd Battalions, 504th Parachute Infantry Regiment
- A Company, 3rd Battalion (Airborne), 505th Parachute Infantry Regiment
- 4th Battalion, 325th Parachute Infantry Regiment
- 1st Battalion, 82nd Aviation Regiment (AH-64 Apache Helicopter force)
- C Company, 3rd Battalion, 73rd Armor Regiment (Airborne)
- 82nd Airborne Division
- United States Marine Corps
- Marine Security Forces Battalion Panama
- 3rd Battalion, 6th Marine Regiment
- India Company
- Kilo Company
- Weapons Company (det)
- FAST Platoon
- Delta Company, 2nd Light Armored Infantry Battlion
- Det (G), 2nd BSSG, 2nd FSSG
- United States Navy
- United States Naval Small Craft and Technical Training School (NAVSCIATTS)
- USS Vreeland (FF-1068)
- Military Police
- 511th MP Company (Fort Drum, New York)
- 988th MP Company (Fort Benning, Georgia)
- 555th MP Company (Fort Lee, Virginia)
- 437th MP Company (Fort Belvoir,Virginia)
- 534th MP Company (Fort Clayton, Panama)
- HHD, 92nd MP Battalion (Fort Clayton, Panama)
- 549th MP Company (Fort Davis, Panama)
- 401st MP Company (Fort Hood, Texas)
- 16th MP Brigade (Fort Bragg, North Carolina)
- 1138th MP Company, Det. 1, Missouri Army National Guard, Doniphan, Missouri
- 1st Special Operations Command
- 5th Special Forces Group Fort Campbell, KY.
- 7th Special Forces Group (A)
- 160th SOAR (A) Night Stalkers
- SEAL Team 4
- SEAL Team 6
- 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment-DELTA
- 75th Ranger Regiment
- 4th Psychological Operations Group
- 3rd Battalion, 9th Infantry Regiment, 7th Infantry Division (Light)
- United States Air Force
- 40th Tactical Airlift Squadron (317th Tactical Airlift Wing)
- 50th Tactical Airlift Squadron (314th Tactical Airlift Wing)
- 63d Military Airlift Wing
- 437th Military Airlift Wing
- 512th Military Airlift Wing
- 172d Military Airlift Wing
- 107th Military Intelligence BN
- 3d Mobile Aerial Port Squadron (3d MAPS)
- 37th Tactical Fighter Wing
- U.S. Southern Command
- U.S. Army South (USARSO)
- 193rd Infantry Brigade
- 59th Engineer Company (Sapper)
- 536 Engineer Battalion
- 154th Signal Battalion
- 1st Battalion, 228th Aviation Regiment
- MEDDAC
- DENTAC
- 324th Support Group
- 470th Military Intelligence Brigade
- Armed Forces Radio and Television Services (AFRTS)
Related operations
- Operation Acid Gambit – operation undertaken by 1st SFOD-D and the 160th SOAR to rescue Kurt Muse, a US citizen involved in the broadcast of anti-Noriega material, during Operation Just Cause.
- Operation Blade Jewel
- Operation Nifty Package – operation undertaken by SEALs to destroy Manuel Noriega's two escape routes, destroying his private jet at Paitilla Airfield and his gunship, which was docked in a canal. Noriega surrendered to US troops on 3 January 1990.
- Operation Nimrod Dancer – 7th ID(light) wargames at Ft. Sherman.
- Operation Prayer Book
- Operation Promote Liberty – operation to rebuild the Panamanian military and civilian infrastructure.
- Operation Purple Storm – operation to assert, display and exercise U.S. freedom of movement rights with convoys traveling in and out of Panama for that express purpose.
- Operation Sand Flea – operation to exercise, display and assert U.S. freedom of movement rights with convoys traveling in and out of Panama for that express purpose.
See also
- The Panama Deception (1992) winner of the 1992 Academy Award for Documentary Feature.
Notes and references
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Jones, Howard. Crucible of Power: A History of U.S. Foreign Relations Since 1897. 2001, page 494.
- ↑ Frederick Kempe, Divorcing the Dictator (New York, Putnam, 1990), ppg 26-30, 162
- ↑ a report by the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights concluded that numerous human rights violations occurred in Panama during Noriega's government [[Report on the situation of human rights in Panama. November 9, 1989]].
- ↑ "THE WIMP FACTOR" American Heritage Magazine, November 1989.
- ↑ "The Noriega Challenge to George Bush’s Credibility and the 1989 Invasion of Panama". 2000.
- ↑ United Nations Security Council Verbatim Report meeting 2899 page 24, Mr Pickering United States of America on December 20, 1989 (retrieved 2008-08-28)
- ↑ Facts On File World News Digest, December 22, 1989, "U.S. Forces Invade Panama, Seize Wide Control; Noriega Eludes Capture." FACTS.com [1].
- ↑ Los Angeles Times, 'December 22, 1990, "Some Blame Rogue Band of Marines for Picking Fight, Spurring Panama Invasion", Kenneth Freed.
- ↑ Washington Post in The Panama Deception article, accessed 29th September 2008.
- ↑ www.globalsecurity.org, Joint History Office, Office of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Operation Just Cause, p 2, Retrieved on 10 February 2007
- ↑ New York Times, December 21, 1989, "A Transcript of President Bush's Address on the Decision to Use Force".
- ↑ Noriega, Manuel and Eisner, Peter. America's Prisoner — The Memoirs of Manuel Noriega. Random House, 1997.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Operation Just Cause Historical Summary at GlobalSecurity.Org
- ↑ Estados Unidos invade Panamá Crónica de una invasión anunciada, Patricia Pizzurno and Celestino Andrés Araúz. According to this piece, the PDF had 46,000 troops of which all were trained for combat. "Para entonces las Fuerzas de Defensa poseían 16.000 efectivos, de los cuales apenas 3.000 estaban entrenados para el combate."
- ↑ "Fires and Helicopters Transforming Panama City", The New York Times (1989-12-21). "Residents said that many of the wooden houses near the headquarters had been hit by gunfire and artillery fire"
- ↑ See the documentary "The Panama Deception"
- ↑ Cole, Ronald H. United States. Office of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Operation Just Cause: the planning and execution of joint operations in Panama, February 1988-1990. Washington, DC: Joint History Office, Government Printing Office, 1995. P40
- ↑ Los Angeles Times, December 21, 1989, "Combat in Panama, Operation Just Cause".
- ↑ Baker, Russell (January 3, 1990). "OBSERVER; Is This Justice Necessary?", The New York Times, The New York Times Company. Retrieved on 2007-11-09.
- ↑ http://www.dtic.mil/doctrine/jel/history/justcaus.pdf
- ↑ USA Panama Invasion 1989
- ↑ About PHR
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20040807044444/http://www.phrusa.org/research/health_effects/humojc.html
- ↑ John Lindsay-Poland (2003). Emperors in the Jungle: The Hidden History of the U.S. in Panama. Duke University Press. ISBN 0-8223-3098-9, p. 118.
- ↑ Page 167, American Patriotism in a Global Society by Betty Jean Craige (1996) [http://books.google.com/books?id=H2eo_h2OE2wC&pg=PA\ 167&dq=%22American+Patriotism+in+a+Global+Society%22++deaths+OR+casualties&ei=Y\ uccSbDzBoGCywSdiNmcCQ]
- ↑ [http://www.answers.com/topic/united-states-in\ vasion-of-panama#wp-_note-14]
- ↑ [2] April 7, 1991 Human Rights in Post-Invasion Panama: Justice Delayed is Justice Denied
- ↑ International Development Research Centre, "The Responsibility to Protect", December 2001, http://www.idrc.ca/openebooks/963-1/
- ↑ New York Times, December 21, 1989, "U.S. Denounced by Nations Touchy About Intervention", James Brooke.
- ↑ United Nations Security Council Draft Resolution S-21048 on 22 December 1989 (retrieved 2007-09-13)
- ↑ United Nations Security Council Verbatim Report meeting 2902 page 15 on December 23, 1989 (retrieved 2007-09-13)
- ↑ United Nations Security Council Verbatim Report meeting 2902 page 10 on December 22, 1989 (retrieved 2007-09-13)
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Pastor, Robert A. Exiting the Whirlpool: U.S. Foreign Policy Toward Latin America and the Caribbean. 2001, page 96.
- ↑ Panama makes anniversary of U.S. invasion day of national mourning - People's Daily Online
- ↑ Henkin, Louis. Right V. Might: International Law and the Use of Force. 1991, page 161-2.
- ↑ Brittanica
- ↑ New York Times, July 21, 1990, "Panama Companies Sue U.S. for Damages".
- ↑ Christian Science Monitor, December 20, 1991, "El Chorrillo Two years after the U.S. invaded Panama, those displaced by the war have new homes."
- ↑ Attacks on the Press 2001: Panama - Committee to Protect Journalists
- ↑ 50 kilos of Cocaine was tamales Washington Post 1/23/1990 Retrieved September 29 2008.
Bibliography
- New York Times, December 21, 1989, "For a Panamanian, Hope and Tragedy", Roberto Eisenmann. (Opinion piece)
- Hagemeister, Stacy & Solon, Jenny. Operation Just Cause: Lessons Learned – Volume I, II & III (Bulletin No. 90-9). Fort Leavenworth, Kansas: Center for Army Lessons Learned – U.S. Army Combined Arms Command. October, 1990.
- Stephen J. Ducat. 2004. The Wimp Factor. Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 0-8070-4344-3. p. 101-102.
- Mellander, Gustavo A.; Nelly Maldonado Mellander (1999). Charles Edward Magoon: The Panama Years. Río Piedras, Puerto Rico: Editorial Plaza Mayor. ISBN 1563281554. OCLC 42970390.
- Mellander, Gustavo A. (1971). The United States in Panamanian Politics: The Intriguing Formative Years. Danville, Ill.: Interstate Publishers. OCLC 138568.
- Murillo, Luis E. (1995). The Noriega Mess: The Drugs, the Canal, and Why America Invaded. 1096 pages, illustrated. Berkeley: Video Books. ISBN 0-923444-02-5.
External links
- Confessions Of An Economic Hit Man
- GlobalSecurity.org: Marines In Panama:1988 - 1990
- BBC News Archive: 1989: U.S. forces oust General Noriega
- 1989 Report on the Situation of Human Rights in Panama by the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights describes human rights violations by the Noriega regime before Operation Just Cause.
- How Television Sold the Panama Invasion – Extra!, January 1990; a publication of the media watch group, FAIR.
- Panama: Background of U.S. Invasion of 1989 – historical timeline.
- Operation Just Cause – an excerpt from Deterring Democracy, by Noam Chomsky.
- Photographs from the XVIII Airborne Corps History Office.
- More photographs.
- Tactical map of Operation Just Cause.
- Effects of the military intervention by the United States of America in Panama on the situation in Central America - UN General Assembly Meeting 29 December 1989
|
|||||||||||