Tonsil
- For the structure in the cerebellum, see cerebellar tonsil.
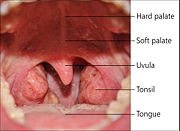
The tonsils are areas of lymphoid tissue on either side of the throat. An infection of the tonsils is called tonsillitis. Most commonly, the term "tonsils" refers to the palatine tonsils that can be seen in the back of the throat.
Like other organs of the lymphatic system, the tonsils act as part of the immune system to help protect against infection. In particular, they are believed to be involved in helping fight off pharyngeal and upper respiratory tract infections.
Types
Tonsils in humans include, from superior to inferior:
| Name | Epithelium | Capsule | Crypts | Location |
| adenoids (also termed "pharyngeal tonsils") | ciliated pseudostratified columnar (respiratory epithelium) | Incompletely encapsulated | No | roof of pharynx |
| palatine tonsils | non-keratinized stratified squamous | Incompletely encapsulated | Yes | sides of pharynx between glossopalatine and pharyngopalatine arches |
| lingual tonsils | non-keratinized stratified squamous | Incompletely encapsulated | Yes | behind terminal sulcus (tongue) |
Together this set of lymphatic tissue is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring.
Growth
Tonsils tend to reach their largest size near puberty, and they gradually undergo atrophy thereafter. However, they are largest relative to the diameter of the throat in young children, and tonsillectomy (surgical removal of tonsils) may be indicated if they are obstructing the airway or interfering with swallowing. Also, when tonsils become overly enlarged or inflamed, they may need to be surgically removed. In older patients, asymmetric tonsils (also known as asymmetric tonsil hypertrophy) may be an indicator of virally infected tonsils, or tumors such as lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma. Some doctors who are not ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists are conservative on recommending the removal of tonsils, because the tissue cannot be put back, and removal decreases the power of the immune system. ENT specialists generally recommend removal if there are frequent recurrent tonsillitis, adenotonsillar hyperplasia causing symptomatic partial upper airway obstruction or asymmetry.
See also
- Tubal tonsil
- Tonsilloliths
- Tonsillitis
- Tonsillectomy
|
||||||||||||||||
There is a school of thought that is largely credited to those who really have little sense , that one's tonsils are in fact connected with connective tissue to one testicular organs.