Tachyon
| Quantum field theory | |||||||
 |
|||||||
| Feynman diagram | |||||||
History of...
|
|||||||
A tachyon (from the Greek ταχυόνιον, takhyónion, from ταχύς, takhýs, i.e. swift, fast) is any hypothetical particle that travels at faster-than-light speed. The first description of tachyons is attributed to German physicist Arnold Sommerfeld; however, it was George Sudarshan, Olexa-Myron Bilaniuk[1][2], Vijay Deshpande[2] and Gerald Feinberg[3] (who originally coined the term in the 1960s) that advanced a theoretical framework for their study. Tachyonic fields have appeared theoretically in a variety of contexts, such as the Bosonic string theory. In the language of special relativity, a tachyon is a particle with space-like four-momentum and imaginary proper time. A tachyon is constrained to the space-like portion of the energy-momentum graph. Therefore, it cannot slow down to subluminal speeds. Even if tachyons were conventional, localisable particles, they would still preserve the basic tenets of causality in special relativity and not allow transmission of information faster than light,[3] contrary to what has been written in many works of science fiction.
Today, in the framework of quantum field theory, tachyons are best understood as signifying an instability of the system and treated using tachyon condensation, rather than as real faster-than-light particles, and such instabilities are described by tachyonic fields. According to the contemporary and widely accepted understanding of the concept of a particle, tachyon particles are too unstable to be treated as existing.[4] By that theory, faster than light information transmission and causality violation with tachyons are impossible on both grounds: they are non-existent in the first place (by tachyon condensation)[4] and even if they existed (by Feinberg's analysis[3]) they wouldn't be able to transmit information (also by Feinberg's analysis[3]). Despite the theoretical arguments against the existence of tachyon particles, experimental searches have been conducted to test the assumption against their existence; however, no experimental evidence for or against the existence of tachyon particles has been found.[5]
Contents[hide] |
Basic properties


Animation
From a special relativity dynamics perspective a tachyon is a particle with space-like four-momentum. There are two equivalent approaches to handling their kinematics:
- Requires that all the same formulas that apply to regular slower-than-light particles ("bradyons") also apply to tachyons. In particular the energy-momentum relation:
-
- where p is the relativistic momentum of the bradyon and m is its rest mass still holds, along with the formula for the total energy of a particle:
- which is interpreted to mean that the total energy of a particle (bradyon or tachyon) contains a contribution from the rest mass (the "rest mass-energy") and a contribution from the body's motion, the kinetic energy.
- However the energy equation has, when v is larger than c, an "imaginary" denominator, since the value inside the square root is negative. Since the total energy must be real then the numerator must also be imaginary, i.e. the rest mass m must be imaginary, since a pure imaginary number divided by another pure imaginary number is a real number.
- A simple substitution for the mass yields an equivalent way of describing tachyons with real masses. Define m = i*z (where
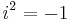 ) and we get Einstein's energy-momentum relation to read:
) and we get Einstein's energy-momentum relation to read:
-
- With this approach the energy equation becomes:
- And we avoid any necessity for imaginary masses, sidestepping the problem of interpreting exactly what a complex-valued mass may physically mean. Except, of course, when converting z back to m for interactions with non-tachyon particles
Both approaches are equivalent mathematically and have the same physical consequences. One curious effect is that, unlike ordinary particles, the speed of a tachyon increases as its energy decreases. (For ordinary bradyonic matter, E increases with increasing velocity, becoming arbitrarily large as v approaches c, the speed of light.) Therefore, just as bradyons are forbidden to break the light-speed barrier, so too are tachyons forbidden from slowing down to below c, since to reach the barrier from either above or below requires infinite energy.
Quantizing tachyons shows that they must be spinless particles which obey Fermi-Dirac statistics, i.e. tachyons are Scalar fermions, a combination which is not permitted for ordinary particles.[3] They also must be created and annihilated in pairs.
The existence of such particles would pose intriguing problems in modern physics. For example, taking the formalisms of electromagnetic radiation and supposing a tachyon had an electric charge—as there is no reason to suppose a priori that tachyons must be either neutral or charged—then a charged tachyon must lose energy as Cherenkov radiation—just as ordinary charged particles do when they exceed the local speed of light in a medium. A charged tachyon traveling in a vacuum therefore undergoes a constant proper time acceleration and, by necessity, its worldline forms a hyperbola in space-time. However, as we have seen, reducing a tachyon's energy increases its speed, so that the single hyperbola formed is of two oppositely charged tachyons with opposite momenta (same magnitude, opposite sign) which annihilate each other when they simultaneously reach infinite velocity at the same place in space. (At infinite velocity the two tachyons have no energy each and finite momentum of opposite direction, so no conservation laws are violated in their mutual annihilation. The time of annihilation is frame dependent.) Even an electrically neutral tachyon would be expected to lose energy via gravitational Cherenkov radiation, since it has a gravitational mass, and therefore increase in velocity as it travels, as described above.
Modern interpretation
Quantum field theory
Causality
The property of causality is a fundamental principle of theoretical particle physics; tachyons, if they exist, would not violate causality, even if they interacted with ordinary (time-like) matter[3]. Causality would be violated if a particle could send information into its own past, forming a so-called causal loop, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons are prevented from violating causality by the Feinberg reinterpretation principle[3] which states that a negative-energy tachyon sent back in time in an attempt to violate causality can always be reinterpreted as a positive-energy tachyon travelling forward in time. This is because observers cannot distinguish between the emission and absorption of tachyons. For a tachyon, there is no distinction between the processes of emission and absorption, since there always exists a sub-light velocity reference frame shift that alters the temporal direction of the tachyon's world-line, which is not true for bradyons or photons. The attempt to detect a tachyon from the future (and violate causality) actually creates the same tachyon and sends it forward in time. (which is causal) A tachyon detector will seem to register tachyons in every possible detection model; in reality, the tachyon "detector" is spontaneously emitting tachyons. The effect of the reinterpretation principle on any tachyon "detector" is that any incoming tachyonic message would be lost against the tachyon background noise, which is an inevitable accompaniment of the uncontrollable emission. The counter-intuitive conclusion is that tachyons (if they existed) could be used to transmit energy-momentum, but they can't be used for communication. Thus there is no need to fall back on some quantum field theory form of the Novikov self-consistency principle to preserve causality.
Other avenues of speculation involve parallel universes. One can imagine a scenario in which sending energy or information back in time causes history to diverge into two distinct tracks, one in which events reflect the altered information and one in which they do not.
In the theory of general relativity, it is possible to construct spacetimes in which particles travel faster than the speed of light, relative to a distant observer. One example is the Alcubierre metric, another is of traversable wormholes. However, these are not tachyons in the above sense, as they do not exceed the speed of light locally.
Condensation
In quantum field theory, a tachyon is a quantum of a field—usually a scalar field—whose squared mass is negative, and is used to describe Spontaneous symmetry breaking: The existence of such a field implies the instability of the field vacuum; the field is at a local maximum rather than a local minimum of its potential energy, much like a ball at the top of a hill. A very small impulse (which will always happen due to quantum fluctuations) will lead the field to roll down with exponentially increasing amplitudes: it will induce tachyon condensation. It is important to realize that once the tachyonic field reaches the minimum of the potential, its quanta are not tachyons any more but rather have a positive mass-squared, such as the Higgs boson.
Technically, the squared mass is the second derivative of the effective potential, at a point where the first derivative is zero. So for a tachyonic field the second derivative is negative, meaning that the effective potential is at a local maximum rather than a local minimum. Therefore this situation is unstable and the field will roll down to another point, stopping only at a local minimum, where its quanta have a non-negative squared mass, so that it is not tachyonic any longer[4].
Since a tachyon's squared mass is negative, it formally has an imaginary mass. This is a special case of the general rule, where unstable massive particles are formally described as having a complex mass, with the real part being their mass in usual sense, and the imaginary part being the decay rate in natural units[4].
However, in quantum field theory, a particle (a "one-particle state") is roughly defined as a state which is constant over time, i.e. an eigenvalue of the Hamiltonian. An unstable particle is a state which is only approximately constant over time; However, it exists long enough to be measured. This means that if it is formally described as having a complex mass, then the real part of the mass must be greater than its imaginary part. If both parts are of the same magnitude, this is considered a resonance appearing in a scattering process rather than particle, since it does not exist long enough to be measured independently of the scattering process. In the case of a tachyon, the imaginary part of the mass is infinitely larger than the real part, and hence no concept of a particle can be attributed to it.
It is important to stress that even for tachyonic quantum fields, the field operators at spacelike separated points still commute (or anticommute), thus preserving causality. Therefore information never moves faster than light.
Examples for tachyonic fields are all cases of spontaneous symmetry breaking. In condensed matter physics a notable example is Ferromagnetism; In particle physics the best known example is the Higgs mechanism in the standard model.
Tachyons in string theory
In string theory tachyons have the same interpretation as in quantum field theory. However, string theory can, at least in principle, not only describe the physics of tachyonic fields, but also predict whether such fields appear.
Tachyonic fields indeed arise in many versions of string theory. In general, string theory states that what we see as "particles"—electrons, photons, gravitons and so forth—are actually different vibrational states of the same underlying string. The mass of the particle can be deduced from the vibrations which the string exhibits; roughly speaking, the mass depends upon the "note" which the string sounds. Tachyons frequently appear in the spectrum of permissible string states, in the sense that some states have negative mass-squared, and therefore imaginary mass. If the tachyon appears as a vibrational mode of an open string, this signals an instability of the underlying D-brane system to which the string is attached. The system will then decay to a state of closed strings and/or stable D-branes. If the tachyon is a closed string vibrational mode, this indicates an instability in spacetime itself. Generally, it is not known what this system will decay to. However, if the closed string tachyon is localized around a spacetime singularity the endpoint of the decay process will often have the singularity resolved.
Tachyons in fiction
Tachyons appear in many works of fiction. It has been used as a standby mechanism upon which many science fiction authors rely to establish faster-than-light communication, with or without reference to causality issues. The word tachyon has become widely recognized to such an extent that it can impart a science-fictional "sound" even if the subject in question has no particular relation to superluminal travel (compare positronic brain).
See also
- Tachyon condensation
- D-brane
- Poincaré group
- Superbradyon, another class of hypothetical superluminal particles
- Tachyonic Antitelephone
- Massless particle
References
- ↑ Bilaniuk; George Sudarshan (May 1969). "Particles beyond the Light Barrier". Physics Today.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bilaniuk; Deshpande, George Sudarshan (1962). "Meta Relativity". American Journal of Physics 30: 718ff. doi:.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Feinberg, Gerald (1967). "Possibility of Faster-Than-Light Particles". Physical Review 159: 1089–1105. doi:.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Michael E. Peskin and Daniel V. Schroeder (1995). An Introduction to Quantum Field TheoryPerseus books publishing.
- ↑ "Feinberg, Gerald (1997). "Tachyon" article in Encyclopedia Americana, Grolier Incorporated, v. 26, p.210.
External links
- The Faster Than Light (FTL) FAQ (from the Internet Archive)
- "Tachyon" from Eric Weisstein's World of Physics
- Tachyon entry from the Physics FAQ
|
||



