South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
|
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
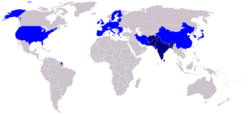 Members • Observers
|
||||
| Headquarters | Kathmandu, Nepal | |||
| Membership | 8 member states 6 observers |
|||
| Leaders | ||||
| - | Chairman | Mahinda Rajapaksa | ||
| - | Secretary General | Sheel Kant Sharma | ||
| Establishment | December 8 1985 | |||
| Area | ||||
| - | Total | 5,130,746 km2 (7th1) 1,980,992 sq mi |
||
| Population | ||||
| - | 2004 estimate | 1,467,255,669 (1st1) | ||
| - | Density | 285.9/km2 740.5/sq mi |
||
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate | |||
| - | Total | US$ 4,074,031 million (3rd1) | ||
| - | Per capita | US$ 2,777 | ||
| Currency | see footnote 2 | |||
| Time zone | (UTC+4½ to +6) | |||
| Website http://www.saarc-sec.org/ |
||||
| 1 | If considered as a single entity. | |||
| 2 | A unified currency has been proposed. Present currencies (ISO 4217 codes bracketed): Afghan afghani (AFG) • Bangladeshi taka (BDT) • Bhutanese ngultrum (BTN) • Indian rupee (INR) • Maldivian rufiyaa (MVR) • Nepalese rupee (NPR) • Pakistani rupee (PKR) • Sri Lankan rupee (LKR) |
|||
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an economic and political organization of eight countries in Southern Asia. In terms of population, its sphere of influence is the largest of any regional organization: almost 1.5 billion people, the combined population of its member states. It was established on December 8, 1985 by India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Maldives and Bhutan. In April 2007, at the Association's 14th summit, Afghanistan became its eighth member.
Contents[hide] |
History
In the late 1970s, Bangladeshi president Ziaur Rahman proposed the creation of a trade bloc consisting of South Asian countries. The idea of regional cooperation in South Asia was again mooted in May 1980. The foreign secretaries of the seven countries met for the first time in Colombo in April 1981. The Committee of the Whole, which met in Colombo in August 1981, identified five broad areas for regional cooperation. New areas of cooperation were added in the following years. Brief on SAARC." South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. The objectives of the Association as defined in the Charter are
- to promote the welfare of the peoples of South Asia and to improve their quality of life;
- to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region and to provide all individuals the opportunity to live in dignity and to realize their full potential;
- to promote and strengthen collective self-reliance among the countries of South Asia;
- to contribute to mutual trust, understanding and appreciation of one another's problems;
- to promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in the economic, social, cultural, technical and scientific fields;
- to strengthen cooperation with other developing countries;
- to strengthen cooperation among themselves in international forums on matters of common interest; and
- to cooperate with international and regional organisations with similar aims and purposes.
The Declaration on South Asian Regional Cooperation was adopted by the Foreign Ministers in 1983 in New Delhi. During the meeting, the Ministers also launched the Integrated Programme of Action (IPA) in nine agreed areas, namely, Agriculture; Rural Development; Telecommunications; Meteorology; Health and Population Activities; Transport; Postal Services; Science and Technology; and Sports, Arts and Culture. The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) was established when its Charter was formally adopted on 8 December 1985 by the Heads of State or Government of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan was added to the regional grouping at the behest of India on November 13, 2005, With the addition of Afghanistan, the total number of member states were raised to eight (8). In April 2006, the United States of America and South Korea made formal requests to be granted observer status. The European Union has also indicated interest in being given observer status, and made a formal request for the same to the SAARC Council of Ministers meeting in July 2006 the foreign ministers of the SAARC countries agreed in principle to grant observer status to the US, South Korea and the European Union.
Secretariat
The SAARC Secretariat was established in Kathmandu on 16 January 1987 and was inaugurated by Late King Birendra Bir Bikram Shah of Nepal.
It is headed by a Secretary General appointed by the Council of Ministers from Member Countries in alphabetical order for a three-year term. He is assisted by the Professional and the General Services Staff, and also an appropriate number of functional units called Divisions assigned to Directors on deputation from Member States. "Memorandum of Understanding on the Establishment of the Secretariat." South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. November 17, 1986. The Secretariat coordinates and monitors implementation of activities, prepares for and services meetings, and serves as a channel of communication between the Association and its Member States as well as other regional organizations. The Memorandum of Understanding on the establishment of the Secretariatwhich was signed by Foreign Ministers of member countries on 17 November 1986 at Bangalore, India contains various clauses concerning the role, structure and administration of the SAARC Secretariat as well as the powers of the Secretary-General. In several recent meetings the heads of state or government of member states of SAARC have taken some important decisions and bold initiatives to strengthen the organisation and to widen and deepen regional co-operation. The SAARC Secretariat and Member States observe 8 December as the SAARC Charter Day.
Ineffectiveness
SAARC's inability to play a crucial role in integrating South Asia is often credited to the political and military rivalry between India and Pakistan. It is due to these economic, political, and territorial disputes that South Asian nations have not been able to harness the benefits of a unified economy. Over the years, SAARC's role in South Asia has been greatly diminished and is now used as a mere platform for annual talks and meetings between its members.
Political issues
SAARC has intentionally laid more stress on "core issues" mentioned above rather than more decisive political issues like the Kashmir dispute and the Sri Lankan civil war. However, political dialogue is often conducted on the margins of SAARC meetings. SAARC has also refrained itself from interfering in the internal matters of its member states. During the 12th and 13th SAARC summits, extreme emphasis was laid upon greater cooperation between the SAARC members to fight terrorism.
Free trade agreement
Over the years, the SAARC members have expressed their unwillingness on signing a free trade agreement. Though India has several trade pacts with Maldives, Nepal, Bhutan and Sri Lanka, similar trade agreements with Pakistan and Bangladesh have been stalled due to political and economic concerns on both sides. India has been constructing a barrier across its borders with Bangladesh and Pakistan. In 1993, SAARC countries signed an agreement to gradually lower tariffs within the region, in Dhaka. Eleven years later, at the 12th SAARC Summit at Islamabad, SAARC countries devised the South Asia Free Trade Agreement which created a framework for the establishment of a free trade area covering 1.4 billion people. This agreement went into force on January 1, 2006. Under this agreement, SAARC members will bring their duties down to 20 per cent by 2007.
Dhaka 2005 Summit
The summit accorded observer status to People's Republic of China, Japan, South Korea and United States of America. The nations also agreed to organize development funds under a single financial institution with a permanent secretariat, that would cover all SAARC programs ranging from social, to infrastructure, to economic ones.
Membership
Current members
Observers
 Australia[1]
Australia[1] China
China European Union[2]
European Union[2] Iran[3]
Iran[3] Japan[2]
Japan[2] Mauritius [4]
Mauritius [4] Myanmar (Burma) [1]
Myanmar (Burma) [1] South Korea
South Korea United States
United States
Secretaries General
| January 16, 1987 to 15 October, 1989 | |
| October 17, 1989 to December 31, 1991 | |
| January 1 1992 to December 31, 1993 | |
| January 1, 1994 to December 31, 1995 | |
| January 1, 1996 to December 31, 1998 | |
| January 1, 1999 to January 10, 2002 | |
| January 11, 2002 to February 28, 2005 | |
| March 1, 2005 to February 29, 2008 | |
| March 1, 2008 to present |
List of SAARC summits
|
|
Future membership
 The People's Republic of China has shown its interest in joining SAARC.[5] While Pakistan and Bangladesh support China's candidature, India is more reluctant about the prospect of Chinese membership, while Bhutan does not even have diplomatic relations with China.[6] However, during the 2005 Dhaka summit, India agreed on granting observer status to the PRC along with
The People's Republic of China has shown its interest in joining SAARC.[5] While Pakistan and Bangladesh support China's candidature, India is more reluctant about the prospect of Chinese membership, while Bhutan does not even have diplomatic relations with China.[6] However, during the 2005 Dhaka summit, India agreed on granting observer status to the PRC along with  Japan. During the 14th summit, Nepal along with Pakistan and Bangladesh, announced their support for the membership of China.[7][8][9] China seeks greater involvement in SAARC, however, finds it too early to apply for full membership. [10]
Japan. During the 14th summit, Nepal along with Pakistan and Bangladesh, announced their support for the membership of China.[7][8][9] China seeks greater involvement in SAARC, however, finds it too early to apply for full membership. [10]
 The Islamic Republic of Iran, a state with borders to two SAARC members, has traditionally enjoyed strong cultural, economic and political relationships with Afghanistan, Pakistan, India and Bangladesh and has expressed its desire to become a member of the South Asian organization. On 22 February 2005, the Foreign Minister of Iran, Kamal Kharrazi, indicated Iran's interest in joining SAARC by saying that his country could provide the region with "East-West connectivity".[11] On 3 March 2007, Iran asked to join the SAARC as an observer. SAARC Secretary-General Lyonpo Chenkyab Dorji responded by saying that Iran's request for observer status would be taken up during a meeting of ministers of foreign affairs of SAARC member countries in the 3 April summit in New Delhi.[12][9]
The Islamic Republic of Iran, a state with borders to two SAARC members, has traditionally enjoyed strong cultural, economic and political relationships with Afghanistan, Pakistan, India and Bangladesh and has expressed its desire to become a member of the South Asian organization. On 22 February 2005, the Foreign Minister of Iran, Kamal Kharrazi, indicated Iran's interest in joining SAARC by saying that his country could provide the region with "East-West connectivity".[11] On 3 March 2007, Iran asked to join the SAARC as an observer. SAARC Secretary-General Lyonpo Chenkyab Dorji responded by saying that Iran's request for observer status would be taken up during a meeting of ministers of foreign affairs of SAARC member countries in the 3 April summit in New Delhi.[12][9]
 The Russian Federation intends to become an observer as well, and is supported by India.[13][14]
The Russian Federation intends to become an observer as well, and is supported by India.[13][14]
 Union of Myanmar has expressed an interest in joining as a full member. If done so, Myanmar will become the ninth member in the group. India is currently backing Myanmar.[15][16]
Union of Myanmar has expressed an interest in joining as a full member. If done so, Myanmar will become the ninth member in the group. India is currently backing Myanmar.[15][16]
 The Republic of South Africa has participated in meetings.[17]
The Republic of South Africa has participated in meetings.[17]
Comparison with other regional blocs
| Regional bloc1 | Area | Population | GDP ($US) | Member states1 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km² | sq mi | in millions (PPP) | in millions (nominal) | per capita (PPP) | per capita (nominal) | |||
| AU | 29,797,500 | 11,504,879 | 897,548,804 | 1,515,000 | 1,131,850 | 1,896 | 1,261 | 53 |
| ASEAN (2007 est.) | 4,497,493 | 1,736,000 | 566,500,000 | 3,115,480 | 1,173,000 | 5,541 | 2,041 | 10 |
| CACM | 422,614 | 163,172 | 37,816,598 | 159,536 | 84,792 | 4,219 | 2,242 | 5 |
| CARICOM | 462,344 | 178,512 | 14,565,083 | 64,219 | 24,020 | 4,409 | 1,649 | (14+1)3 |
| CCASG / GCC | 2,285,844 | 882,569 | 35,869,438 | 536,223 | 717,800 | 14,949 | 20,011 | 6 |
| CEFTA | 298,148 | 115,116 | 28,929,682 | 222,041 | 122,001 | 7,675 | 4,217 | (7+1)3 |
| EU (2007 est.) | 4,324,782 | 1,669,808 | 497,000,000 | 14,953,000 | 16,574,000 | 28,213 | 33,482 | 27 |
| EurAsEC | 20,789,100 | 8,026,720 | 208,067,618 | 1,689,137 | 1,125,528 | 8,118 | 5,409 | 6 |
| EFTA (2007 est.) | 529,600 | 204,480 | 12,660,623 | 567,500 | 743,300 | 44,828 | 60,000 | 4 |
| GAFTA | 9,421,946 | 3,637,834 | 280,727,416 | 1,341,298 | N/A | 4,778 | N/A | (16+1)3 |
| GUAM | 810,506 | 312,938 | 63,764,600 | 456,173 | 106,469 | 7,154 | 1,670 | 4 |
| NAFTA (2007 est.) | 21,783,850 | 8,410,792 | 445,000,000 | 15,857,000 | 15,723,000 | 35,491 | 35,564 | 3 |
| PARTA | 528,151 | 203,920 | 34,137,339 | 858,970 | N/A | 2,954 | N/A | (12+2)3 |
| SAARC | 5,136,740 | 1,983,306 | 1,467,255,669 | 4,074,031 | N/A | 2,777 | N/A | 8 |
| Unasur / Unasul | 17,339,153 | 6,694,684 | 370,158,470 | 2,868,430 | N/A | 7,749 | N/A | 12 |
| UN and countries for reference2 |
Area | Population | GDP ($US) | Units4 | ||||
| km² | sq mi | in millions (PPP) | in millions (nominal) | per capita (PPP) | per capita (nominal) | |||
| UN | 133,178,011 | 51,420,318 | 6,411,682,270 | 55,167,630 | 48,245,198 | 8,604 | 7,524 | 192 |
| Brazil (2007 est.) | 8,514,877 | 3,287,612 | 183,888,841 | 1,804,000 | 1,067,706 | 10,073 | 6,842 | 27 |
| Canada (2007 est.) | 9,984,670 | 3,855,103 | 33,000,000 | 1,274,000 | 1,406,000 | 38,200 | 42,738 | 13 |
| India (2007 est.) | 3,287,590 | 1,269,346 | 1,120,000,000 | 4,726,000 | 1,089,000 | 4,182 | 1,004 | 35 |
| Japan (2007 est.) | 377,873 | 145,898 | 127,433,494 | 4,346,000 | 4,346,000 | 33,800 | 38,341 | 47 |
| PR China5 (2007 est.) | 9,596,960 | 3,705,407 | 1,321,851,888 | 7,043,000 | 3,420,000 | 5,300 | 2,800 | 33 |
| Russia (2007 est.) | 17,075,200 | 6,592,772 | 142,500,000 | 2,076,000 | 1,286,000 | 14,600 | 9,056 | 83 |
| USA (2007 est.) | 9,826,630 | 3,794,083 | 302,000,000 | 13,543,000 | 13,794,700 | 43,500 | 45,594 | 50 |
|
smallest value among the blocs compared largest value among the blocs compared
Footnotes |
||||||||
See also
- South Asia Free Trade Agreement
- SAARC Consortium on Open and Distance Learning
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation
- BIMSTEC
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- South Asian Economic Union
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 colombopage.com
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 thehimalayantimes.com
- ↑ tehrantimes.com
- ↑ island.lk
- ↑ Afghan and further Chinese membership prospects
- ↑ China's membership prospects
- ↑ chennaionline.com
- ↑ telegraphnepal.com
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 irna.ir
- ↑ China seeks bigger role in Saarc- Hindustan Times
- ↑ Iran's membership prospects
- ↑ upi.com
- ↑ english.people.com.cn
- ↑ monstersandcritics.com
- ↑ Sri Lanka News | Online edition of Daily News - Lakehouse Newspapers
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ » SAARC nations call for transparency in social sector - Thaindian News
South Asia Free Trade Agreement SAARC Consortium on Open and Distance Learning Mekong-Ganga Cooperation BIMSTEC Asia Cooperation Dialogue South Asian Economic Union SAARC Countries Transportation System
External links
|
|||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
