Regions of the Philippines
| Philippines | ||||||||
 This article is part of the series: |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Government | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Political history · Constitution
|
||||||||
| Executive | ||||||||
| President (list) Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo 2001 – 2010 Vice President (list) Executive Departments |
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Judiciary | ||||||||
| Supreme Court
Chief Justice Reynato Puno |
||||||||
| Elections | ||||||||
| Commission on Elections Chairman: Jose Melo Elections: 2010 | 2004 | 1998 | 1992 | 1986 | All Referenda: 1987 | 1984 | 1981 |
||||||||
|
||||||||
Foreign relations |
||||||||
|
Other countries · Atlas |
||||||||
In the Philippines, regions (Filpino:rehiyon, ISO 3166-2:PH) are administrative division that serve primarily to organize the 81 provinces (lalawigan) for administrative convenience. Most government offices establish regional offices instead of individual provincial offices, usually (but not necessarily always) in the city designated as the regional center.
The regions themselves do not possess a separate local government, with the exception of the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, which has an elected regional assembly and governor. The Cordillera Administrative Region was originally intended to be autonomous (Cordillera Autonomous Region), but the failure of two plebiscites for its establishment reduced it to a regular administrative region.
Contents |
History
Regions first came to existence in on September 24, 1972 when the provinces of the Philippines were organized into 11 regions by Presidential Decree No. 1 as part of the Integrated Reorganization Plan of President Ferdinand Marcos.
Since that time, other regions have been created and some provinces have been transferred from one region to another.
- July 7, 1975: Region XII created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- August 21, 1975: Region IX divided into Sub-Region IX-A' and Sub-Region IX-B. Minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- November 7, 1975: National Capital Region created.
- August 1, 1989: Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao created by Ompet Palogan.
- October 23, 1989: Cordillera Administrative Region created.
- October 12, 1990: Executive Order issued to reorganize the Mindanao regions but the reorganization never happened (possibly due to lack of government funds).
- February 23, 1995: Region XIII (Caraga) created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- 1997: Minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- September 19, 2001: Most Mindanao regions reorganized and some renamed.
- May 17, 2002: Region IV-A (CALABARZON) and Region IV-B (MIMAROPA) created from the former Region IV (Southern Tagalog) region.
- May 23, 2005: Palawan transferred from MIMAROPA to Western Visayas; MIMAROPA renamed to MIMARO.
- August 19, 2005: The E.O. 429 of May 23, 2005 transferring Palawan from MIMAROPA to Western Visayas was later held in abeyance by Administrative Order #129.
List of regions
The Philippines consists of 17 regions. The regions are geographically combined into the three island groups of Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. Following is a list of the regions in their island groupings. To get overviews of the regions, see the respective articles on the island groups. The regions CALABARZON, MIMAROPA, and SOCCSKSARGEN are capitalized because they are acronyms that stand for their component provinces or cities.[1]
Luzon
| Map | Region (short name) |
Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
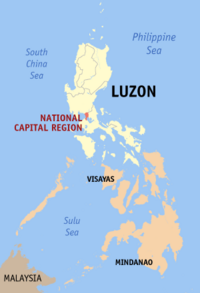 |
National Capital Region (NCR; Metro Manila) |
Manila |
|
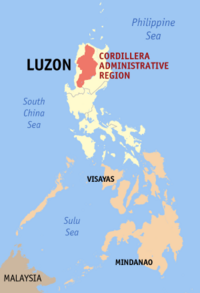 |
Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) |
Baguio City | |
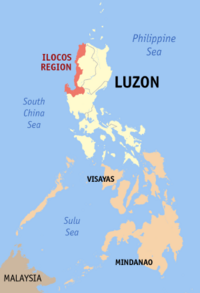 |
Ilocos Region (Region I) |
San Fernando City, La Union |
|
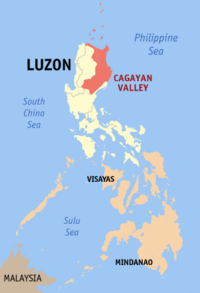 |
Cagayan Valley (Region II) |
Tuguegarao City |
|
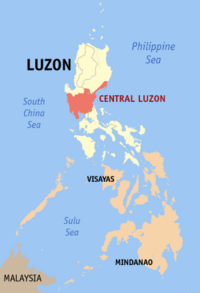 |
Central Luzon (Region III) |
San Fernando City, Pampanga |
|
 |
CALABARZON (Region IV-A) |
Calamba City | |
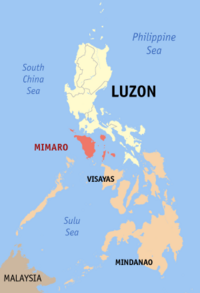 |
MIMAROPA (Region IV-B) |
Calapan City | |
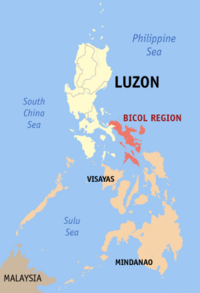 |
Bicol Region (Region V) |
Legazpi City |
|
Visayas
| Map | Region (short name) |
Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
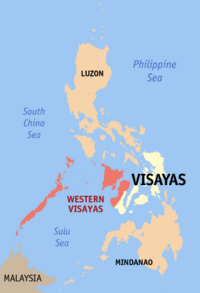 |
Western Visayas (Region VI) |
Iloilo City |
|
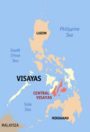 |
Central Visayas (Region VII) |
Cebu City |
|
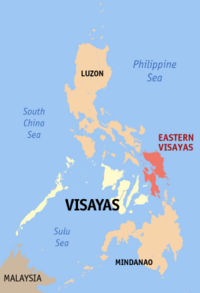 |
Eastern Visayas (Region VIII) |
Tacloban City |
|
Mindanao
| Map | Region (short name) |
Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
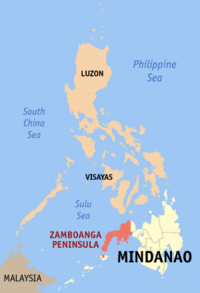 |
Zamboanga Peninsula (Region IX) |
Pagadian City | |
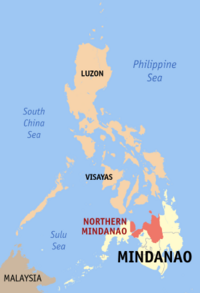 |
Northern Mindanao (Region X) |
Cagayan de Oro |
|
 |
Davao Region (Region XI) |
Davao City |
|
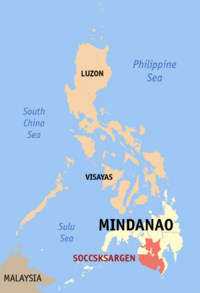 |
SOCCSKSARGEN (Region XII) |
Koronadal City |
|
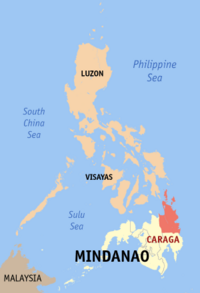 |
Caraga (Region XIII) |
Butuan City |
|
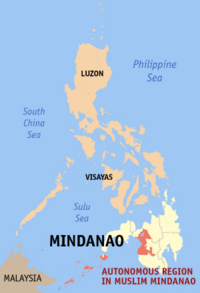 |
Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) |
Cotabato City |
|
Defunct regions
The following are regions that do not exist, explanations about their current status follow each region's name.
- Southern Tagalog (divided into CALABARZON or Region IV-a and MIMAROPA or Region IV-B)
- Western Mindanao (now Zamboanga Peninsula, still designated as Region IX)
- Central Mindanao (now SOCCSKSARGEN, still designated as Region XII)
- Southern Mindanao (now Davao, still designated as Region XI)
Notes
- ↑ Some regions use acroyms in their names, examples include CALABARZON, which is derived from CAvite, LAguna, BAtangas, Rizal, and QueZON; MIMARO, which is derived from MIndoro (for Mindoro Occidental and Mindoro Oriental), MArinduque, ROmblon, and PA'lawan; and SOCCSKSARGEN, which is derived from SOuth Cotabato, Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, SARangani, and GENeral Santos City.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 A highly urbanized city, independent from any province.
- ↑ An independent municipality, not governed by any province.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 An independent component city, not under the jurisdiction of any provincial government.
- ↑ A component city, part of the province of Basilan, but whose regional services are provided by the offices of Region IX.
See also
- Super regions of the Philippines
References
- National Statistical Coordination Board
- Philippines-Archipelago (Political Map)
- National Statistics Office
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||