Pulmonary vein
| Vein: Pulmonary vein | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Anterior (frontal) view of the opened heart. White arrows indicate normal blood flow. | |
 |
|
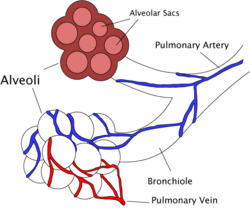
| Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
| Latin | venae pulmonales |
| Gray's | subject #165 642 |
| Drains from | lungs |
| Drains to | left atrium |
| Artery | pulmonary artery |
| Precursor | truncus arteriosus |
| MeSH | Pulmonary+Veins |
The four pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. They are the only veins in the post-fetal human body that carry oxygenated (red) blood.
Contents |
Types
They are four in number, two from each lung, and are destitute of valves. They are
- right inferior
- right superior
- left inferior
- left superior
Path
They commence in a capillary net-work upon the walls of the air sacs, where they are continuous with the capillary ramifications of the pulmonary artery, and, joining together, form one vessel for each lobule.
These vessels uniting successively, form a single trunk for each lobe, three for the right, and two for the left lung.
The vein from the middle lobe of the right lung generally unites with that from the upper lobe, so that ultimately two trunks from each lung are formed; they perforate the fibrous layer of the pericardium and open separately into the upper and back part of the left atrium.
Occasionally the three veins on the right side remain separate, and not infrequently the two left pulmonary veins end by a common opening into the left atrium. Following from this, it's true that the number of pulmonary veins opening into the left atrium can vary between three and five in the healthy population.
At the root of the lung, the superior pulmonary vein lies in front of and a little below the pulmonary artery; the inferior is situated at the lowest part of the hilus of the lung and on a plane posterior to the upper vein. Behind the pulmonary artery is the bronchus.
Within the pericardium, their anterior surfaces are invested by the serous layer of this membrane.
The right pulmonary veins pass behind the right atrium and superior vena cava; the left in front of the descending thoracic aorta.
Additional images
External links
- SUNY Figs 19:05-08
- Illustration at infomat.net
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||