Demographics of India
| Demographics of the Republic of India | |
|---|---|
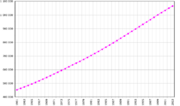 Population of India, 1961-2003 |
|
| Size: | 1,129,866,154 (2007 est) |
| Growth: | 1.38% (2007 est) |
| Birth: | 22.69 births/1,000 population (2007 est) |
| Death: | 6.58 deaths/1,000 population (2007 est) |
| Life expectancy: | 68.59 years (2007 est) |
| Life expectancy(m): | 66.28 years (2007 est) |
| Life expectancy(f): | 71.17 years (2007 est) |
| Fertility: | 2.7 children born/woman (NFHS-3, 2007) |
| Age Structure: | |
| 0-14 years: | 31.5% (male 189,238,487/female 172,168,306)(2008 est) |
| 15-64 years: | 63.3% (male 374,157,581/female 352,868,003) (2008 est) |
| 65-0ver years: | 5.2% (male 28,285,796/female 31,277,725) (2008 est) |
| Sex Ratio: | |
| At birth: | 1.12 male(s)/female (2008) |
| Under 15 years: | 1.10 male(s)/female (2008) |
| 15-64 years: | 1.06 male(s)/female (2008) |
| Nationality: | |
| nationality: | noun: Indian adjective: Indic |
| Major ethnic: | See Ethnic Groups of India |
| Language: | |
| Official: | See Official languages of India |
| Spoken: | See List of Indian languages by number of native speakers |
The Demographics of India are overall remarkably diverse. India's population of approximately 1.13 billion people (estimate for March 10, 2008) comprises approximately one-sixth of the world's population. India has more than two thousand ethnic groups, and every major religion is represented, as are four major families of languages (Indo-European, Dravidian, Austro-Asiatic and Tibeto-Burman languages) as well as a language isolate (the Nihali language[1] spoken in parts of Maharashtra). Further complexity is lent by the great variation that occurs across this population on social parameters such as income and education. Only the continent of Africa exceeds the linguistic, genetic and cultural diversity of the nation of India.[2]
Contents |
Salient features
India occupies 2.4% of the world's land area and supports over 17.5% of the world's population. India has more arable land area than any country except the United States[3], and more water area than any country except Canada and the United States. Indian life, therefore revolves mostly around agriculture and allied activities in small villages, where the overwhelming majority of Indians live. As per the 2001 census, 72.2% of the population[4] lives in about 638 thousand villages[5] and the remaining 27.8%[6] lives in over 5,100 towns and over 380 urban agglomerations.[7]
Census
The most recent census of India was performed in 2001 for enumeration as of March 1 of that year.[8] It was the 14th census in an unbroken series, and the 6th after independence in 1947 (with the exception that census could not be held for Assam in the 1981 and Jammu & Kashmir in 1991). Eight censuses were performed under the British Raj, the first one was carried out throughout the 1860s and completed in 1872(The first incomplete census). After this, there has been one census every decade starting in 1881(First complete census).
The total population calculated for 1 March 2001 was 1,027,015,247, making the 2001 census the first to count more than a billion Indians.[9] The population had risen by 21.34% compared to the 1991 total. The female population had increased by 0.3 percentage points to 48.4%.[9]
Religious demographics
80.5% of the Indians are Hindus, with 13.4% of the population Muslim, making India home to the third-largest Muslim population in the world after Indonesia and Pakistan. India also contains the majority of the world's Zoroastrians, Sikhs, Jains and Bahá'í. Other religious groups include Christians (2.3%), Buddhists (0.8%), Jains (0.4%), and Jews.
Religious majorities vary greatly by state. Jammu and Kashmir is the sole majority Muslim state; Nagaland is majority Christian; Punjab is mostly Sikh; Manipur is of Sanamahism.
The table below summarizes the findings of the 2001 census with regards to religion in India:
- All figures in %.
- Gender Ratio*: no of females/1000 males
- Others including Bahá'ís, Jews, and Parsis.
- Tribal Animists (and non religious) are grouped under Others after 1926 (1931 census onwards)
| Composition | Hindus[10] | Muslims[11] | Christians[12] | Sikhs[13] | Buddhist[14] | Jains[15] | Others[16] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % total of population 2005 | 80.4% | 13.4% | 2.3% | 1.9% | 1.1% | 0.4% | 0.5% |
| 10-Yr Growth % (est '91–'01)[17][β] | 20.3% | 29.5% | 22.6% | 18.2% | 24.5% | 26.0% | 103.1% |
| Sex ratio* (avg. 944) | 935 | 940 | 1009 | 895 | 955 | 940 | 100 |
| Literacy rate (avg. 79.9) | 75.5 | 60.0 | 90.3 | 70.4 | 73.0 | 95.0 | 50.0 |
| Work Participation Rate | 40.4 | 31.3 | 39.7 | 37.7 | 40.6 | 32.9 | 48.4 |
| Rural sex ratio[17] | 944 | 953 | 1001 | 895 | 958 | 937 | 995 |
| Urban sex ratio[17] | 922 | 907 | 1026 | 886 | 944 | 941 | 966 |
| Child sex ratio (0–6 yrs) | 925 | 950 | 964 | 786 | 942 | 870 | 976 |
α. ^ The data excludes Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati District of Manipur
β. ^ The data is "unadjusted" (without excluding Assam and Jammu and Kashmir); 1981 census was not conducted in Assam and 1991 census was not conducted in Jammu and Kashmir
Linguistic demographics
40% of the Hindus speak Hindi while the rest speak Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Gujarati,Kannada and other languages. Almost 70% of the Muslims speak Urdu while the rest speak Kashmiri, Bengali, Malayalam, Tamil, Gujarati and other languages. About one-third of the Christians speak Malayalam, one-sixth speak Tamil while the rest speak a variety of languages. In total, there are 1,652 languages and dialects spoken in India.[18]
| Rank | Language | 2001 census[1] (total population 1,004.59 million) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | ||
| 1 | Hindi dialects[19] | 422,048,642 | 41.03% |
| 2 | Bengali | 83,369,769 | 8.11% |
| 3 | Telugu | 74,002,856 | 7.37% |
| 4 | Marathi | 71,936,894 | 6.99% |
| 5 | Tamil | 60,793,814 | 5.91% |
| 6 | Urdu | 51,536,111 | 5.01% |
| 7 | Gujarati | 46,091,617 | 4.48% |
| 8 | Kannada | 37,924,011 | 3.69% |
| 9 | Malayalam | 33,066,392 | 3.21% |
| 10 | Oriya | 33,017,446 | 3.21% |
| 11 | Punjabi | 29,102,477 | 2.83% |
| 12 | Assamese | 13,168,484 | 1.28% |
| 13 | Maithili | 12,179,122 | 1.18% |
| 14 | Santali | 6,469,600 | 0.63% |
| 15 | Kashmiri | 5,527,698 | 0.54% |
| 16 | Nepali | 2,871,749 | 0.28% |
| 17 | Sindhi | 2,535,485 | 0.25% |
| 18 | Konkani | 2,489,015 | 0.24% |
| 19 | Dongri | 2,282,589 | 0.22% |
| 20 | Meitei (Manipuri) | 1,466,705* | 0.14% |
| 21 | Bodo | 1,350,478 | 0.13% |
| 22 | Sanskrit | 14,135 | N |
* Excludes figures of Paomata, Mao-Maram and Purul sub-divisions of Senapati district of Manipur for 2001.
** The percentage of speakers of each language for 2001 has been worked out on the total population of India excluding the population of Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati district of Manipur due to cancellation of census results.
N - Stands for negligible.
Demographic statistics

Total Population: 1,147.996 million (July 2008 est. CIA)[21] 1,028.7 million (2001 Census final figures, March 1 enumeration and estimated 124,000 in areas of Manipur that could not be covered in the enumeration)

Rural Population: 72.2%, male: 381,668,992, female: 360,948,755 (2001 Census)
Urban Population:
Age structure:
0–14 years: 30.8%, male: 188,208,196, female: 171,356,024
15–64 years: 64.3%, male: 386,432,921, female: 364,215,759
65+ years: 4.9%, male: 27,258,259, female: 30,031,289 (2007 est.) The median age of Indians is 25.1 years.
Population growth rate: 1.38% (2007 est.)
Birth rate: 22.69 births/1,000 population (2007 est.)
Death rate: 6.58 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)

Literacy rate: 79.9%
Percent of the population under the poverty line: 22% (2006 est.)
Unemployment Rate: 7.8%
Net migration rate: − -0.05 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2007 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.098 male(s)/female
15–64 years: 1.061 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.908 male(s)/female
total population: 1.064 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
Infant mortality rate: total: 34.61 deaths/1,000 live births (2007 est.) female: 29.23 deaths/1,000 live births male: 39.42 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 68.59 years
male: 66.28 years
female: 71.17 years (2007 est.)
Total fertility rate: 2.81 children born/woman (2007 est.) The TFR (Total number of children born per women ) according to Religion in 2001 was :
Hindus - 2.0, Muslims - 2.4, Sikhs - 1.6, Christians - 2.1, Buddhists - 2.1, Jains - 1.4 , Animists and Others - 2.99, Tribals - 3.16, Scheduled Castes - 2.89.
Nationality:
noun: Indian(s)
adjective: Indian
Religions: Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.8%, Buddhists 0.8%, Jains 0.4%, others 0.7%, unspecified 0.1% (2001 Census) [22][23] [24][25].
Scheduled Castes and Tribes: Scheduled Castes: 16.2% (2001 Census) Scheduled Tribes: 8.2% (2001 Census)
Languages: See Languages of India and List of Indian languages by total speakers. There are 216 languages with more than 10,000 native speakers in India. The largest of these is Hindi with some 337 million (the second largest being Bengali with some 207 million). 22 languages are recognized as official languages. In India, there are 1,652 languages and dialects in total.[18][26]
2025 Estimate
Table 2: Population Projections (in millions)
| Year | Under 15 | 15-64 | 65+ | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 361 | 604 | 45 | 1010 |
| 2005 | 368 | 673 | 51 | 1093 |
| 2010 | 370 | 747 | 58 | 1175 |
| 2015 | 372 | 819 | 65 | 1256 |
| 2020 | 373 | 882 | 76 | 1331 |
Source: Based on P.N. Mari Bhat, "Indian Demographic Scenario 2025", Institute of Economic Growth, New Delhi, Discussion Paper No. 27/2001.
Ethnic groups
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unlike the United States of America, United Kingdom, and Australian Censuses, the national Census of India does not recognize racial or ethnic groups within India,[27] but recognizes many of the tribal groups as Scheduled Castes and Tribes (see list of Scheduled Tribes in India).
It should be noted that Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman and Austro-Asiatic are mainly linguistic terms and denote speakers of these linguistic groups.
For a list of ethnic groups in the Republic of India (as well as neighboring countries) see ethnic groups of the Indian subcontinent or the tree diagram above.
Further reading
- International Institute for Population Sciences and Macro International (2007-09-09). "Summary of Findings" (PDF). Third National Family Health Survey. International Institute for Population Sciences.
See also
- Ethnic groups of India
- Indian diaspora
- Geography of India
- Racial groups of India
External links
- Census of India; Govt. site with detailed data from 2001 census
- Census of India map generator; generates maps based on 2001 census figures
- Census-2001 Religion wise data
- Demographic data for India; provides sources of demographic data for India
- Peopling of India
- Kokrajhar District Information Gateway - Census 2001
- Population Explosion in West Bengal: A Survey A Study by South Asia Research Society, Calcutta
- indianchild.com - Population of India
- District Level Estimates of Fertility from India’s 2001 Census
References
- ↑ SIL International. "Ethnologue report for Language Isolate". Retrieved on 2007-10-11.
- ↑ India, a Country Study United States Library of Congress, Note on Ethnic groups
- ↑ GM Crops Around the World – an accurate picture GM Freeze, Table 3
- ↑ Rural-Urban distribution Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Rural-Urban Distribution. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ Number of Villages Census of India: Number of Villages Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ Rural-Urban distribution Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Rural-Urban Distribution. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ Urban Agglomerations and Towns Census of India: Urban Agglomerations and Towns. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ Census of India, Govt. of India - Ministry of Home Affairs, Official web-site | We also count people in India
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Indian Census
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Hindus". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Muslims". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Christians". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Sikhs". Census of India 2001: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Buddhists". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Jains". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Other religions". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "Census of India.". Census of India. Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Mother Tongues of India According to the 1961 Census
- ↑ includes Western Hindi, Eastern Hindi, Bihari languages, Rajasthani languages and Pahari languages.
- ↑ National Population Policy of India
- ↑ CIA World Factbook - India
- ↑ Religious Composition Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ↑ International Religious Freedom Report 2007-India International Religious Freedom Report 2007. U.S. Department of State.
- ↑ CIA's The World Factbook - India
- ↑ Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs - Background Note: India
- ↑ Rupert Goodwins. Smashing India's language barriers. ZDNet UK.
- ↑ Kumar, Jayant. Census of India. 2001. September 4, 2006. Indian Census
|
|||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||