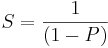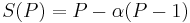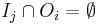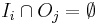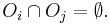Parallel computing

Parallel computing is a form of computation in which many calculations are carried out simultaneously,[1] operating on the principle that large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which are then solved concurrently ("in parallel"). There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level-, instruction-level-, data-, and task parallelism. Parallelism has been employed for many years, mainly in high-performance computing, but interest in it has grown lately due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.[2] As power consumption by computers has become a concern in recent years,[3] parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multicore processors.[4]
Parallel computers can be roughly classified according to the level at which the hardware supports parallelism—with multi-core and multi-processor computers having multiple processing elements within a single machine, while clusters, MPPs, and grids use multiple computers to work on the same task. Specialized parallel computer architectures are sometimes used alongside traditional processors, for accelerating specific tasks.
Parallel computer programs are more difficult to write than sequential ones,[5] because concurrency introduces several new classes of potential software bugs, of which race conditions are the most common. Communication and synchronization between the different subtasks is typically one of the greatest barriers to getting good parallel program performance. The speed-up of a program as a result of parallelization is given by Amdahl's law.
Contents |
Background
Traditionally, computer software has been written for serial computation. To solve a problem, an algorithm is constructed and implemented as a serial stream of instructions. These instructions are executed on a central processing unit on one computer. Only one instruction may execute at a time—after that instruction is finished, the next is executed.[6]
Parallel computing, on the other hand, uses multiple processing elements simultaneously to solve a problem. This is accomplished by breaking the problem into independent parts so that each processing element can execute its part of the algorithm simultaneously with the others. The processing elements can be diverse and include resources such as a single computer with multiple processors, several networked computers, specialized hardware, or any combination of the above.[6]
Frequency scaling was the dominant reason for improvements in computer performance from the mid-1980s until 2004. The runtime of a program is equal to the number of instructions multiplied by the average time per instruction. Maintaining everything else constant, increasing the clock frequency decreases the average time it takes to execute an instruction. An increase in frequency thus decreases runtime for all computation-bounded programs.[7]
However, power consumption by a chip is given by the equation P = C × V2 × F, where P is power, C is the capacitance being switched per clock cycle (proportional to the number of transistors whose inputs change), V is voltage, and F is the processor frequency (cycles per second).[8] Increases in frequency increase the amount of power used in a processor. Increasing processor power consumption led ultimately to Intel's May 2004 cancellation of its Tejas and Jayhawk processors, which is generally cited as the end of frequency scaling as the dominant computer architecture paradigm.[9]
Moore's Law is the empirical observation that transistor density in a microprocessor doubles every 18 to 24 months.[10] Despite power consumption issues, and repeated predictions of its end, Moore's law is still in effect. With the end of frequency scaling, these additional transistors (which are no longer used for frequency scaling) can be used to add extra hardware for parallel computing.
Amdahl's law and Gustafson's law

Theoretically, the speed-up from parallelization should be linear—doubling the number of processing elements should halve the runtime, and doubling it a second time should again halve the runtime. However, very few parallel algorithms achieve optimal speed-up. Most of them have a near-linear speed-up for small numbers of processing elements, which flattens out into a constant value for large numbers of processing elements.
The potential speed-up of an algorithm on a parallel computing platform is given by Amdahl's law, originally formulated by Gene Amdahl in the 1960s.[11] It states that a small portion of the program which cannot be parallelized will limit the overall speed-up available from parallelization. Any large mathematical or engineering problem will typically consist of several parallelizable parts and several non-parallelizable (sequential) parts. This relationship is given by the equation:
where S is the speed-up of the program (as a factor of its original sequential runtime), and P is the fraction that is parallelizable. If the sequential portion of a program is 10% of the runtime, we can get no more than a 10x speed-up, regardless of how many processors are added. This puts an upper limit on the usefulness of adding more parallel execution units. "When a task cannot be partitioned because of sequential constraints, the application of more effort has no effect on the schedule. The bearing of a child takes nine months, no matter how many women are assigned."[12]
Gustafson's law is another law in computer engineering, closely related to Amdahl's law. It can be formulated as:

where P is the number of processors, S is the speed-up, and  the non-parallelizable part of the process.[13] Amdahl's law assumes a fixed-problem size and that the size of the sequential section is independent of the number of processors, whereas Gustafson's law does not make these assumptions.
the non-parallelizable part of the process.[13] Amdahl's law assumes a fixed-problem size and that the size of the sequential section is independent of the number of processors, whereas Gustafson's law does not make these assumptions.
Dependencies
Understanding data dependencies is fundamental in implementing parallel algorithms. No program can run more quickly than the longest chain of dependent calculations (known as the critical path), since calculations that depend upon prior calculations in the chain must be executed in order. However, most algorithms do not consist of just a long chain of dependent calculations; there are usually opportunities to execute independent calculations in parallel.
Let Pi and Pj be two program fragments. Bernstein's conditions[14] describe when the two are independent and can be executed in parallel. For Pi, let Ii be all of the input variables and Oi the output variables, and likewise for Pj. P i and Pj are independent if they satisfy
Violation of the first condition introduces a flow dependency, corresponding to the first statement producing a result used by the second statement. The second condition represents an anti-dependency, when the first statement overwrites a variable needed by the second expression. The third and final condition, q, is an output dependency. When two variables write to the same location, the final output must have arisen from the second statement.[15]
Consider the following functions, which demonstrate several kinds of dependencies:
1: function Dep(a, b) 2: c := a·b 3: d := 2·c 4: end function
Operation 3 in Dep(a, b) cannot be executed before (or even in parallel with) operation 2, because operation 3 uses a result from operation 2. It violates condition 1, and thus introduces a flow dependency.
1: function NoDep(a, b) 2: c := a·b 3: d := 2·b 4: e := a+b 5: end function
In this example, there are no dependencies between the instructions, so they can all be run in parallel.
Bernstein’s conditions do not allow memory to be shared between different processes. For that, some means of enforcing an ordering between accesses is necessary, such as semaphores, barriers or some other synchronization method.
Race conditions, mutual exclusion, synchronization, and parallel slowdown
Subtasks in a parallel program are often called threads. Some parallel computer architectures use smaller, lightweight versions of threads known as fibers, while others use bigger versions known as processes. However, "threads" is generally accepted as a generic term for subtasks. Threads will often need to update some variable that is shared between them. The instructions between the two programs may be interleaved in any order. For example, consider the following program:
| Thread A | Thread B |
| 1A: Read variable V | 1B: Read variable V |
| 2A: Add 1 to variable V | 2B: Add 1 to variable V |
| 3A Write back to variable V | 3B: Write back to variable V |
If instruction 1B is executed between 1A and 3A, or if instruction 1A is executed between 1B and 3B, the program will produce incorrect data. This is known as a race condition. The programmer must use a lock to provide mutual exclusion. A lock is a programming language construct that allows one thread to take control of a variable and prevent other threads from reading or writing it, until that variable is unlocked. The thread holding the lock is free to execute its critical section (the section of a program that requires exclusive access to some variable), and to unlock the data when it is finished. Therefore, to guarantee correct program execution, the above program can be rewritten to use locks:
| Thread A | Thread B |
| 1A: Lock variable V | 1B: Lock variable V |
| 2A: Read variable V | 2B: Read variable V |
| 3A: Add 1 to variable V | 3B: Add 1 to variable V |
| 4A Write back to variable V | 4B: Write back to variable V |
| 5A: Unlock variable V | 5B: Unlock variable V |
One thread will successfully lock variable V, while the other thread will be locked out—unable to proceed until V is unlocked again. This guarantees correct execution of the program. Locks, while necessary to ensure correct program execution, can greatly slow a program.
Locking multiple variables using non-atomic locks introduces the possibility of program deadlock. An atomic lock locks multiple variables all at once. If it cannot lock all of them, it does not lock any of them. If two threads each need to lock the same two variables using non-atomic locks, it is possible that one thread will lock one of them and the second thread will lock the second variable. In such a case, neither thread can complete, and deadlock results.
Many parallel programs require that their subtasks act in synchrony. This requires the use of a barrier. Barriers are typically implemented using a software lock. One class of algorithms, known as lock-free and wait-free algorithms, altogether avoids the use of locks and barriers. However, this approach is generally difficult to implement and requires correctly designed data structures.
Not all parallelization results in speed-up. Generally, as a task is split up into more and more threads, those threads spend an ever-increasing portion of their time communicating with each other. Eventually, the overhead from communication dominates the time spent solving the problem, and further parallelization (that is, splitting the workload over even more threads) increases rather than decreases the amount of time required to finish. This is known as parallel slowdown.
Fine-grained, coarse-grained, and embarrassing parallelism
Applications are often classified according to how often their subtasks need to synchronize or communicate with each other. An application exhibits fine-grained parallelism if its subtasks must communicate many times per second; it exhibits coarse-grained parallelism if they do not communicate many times per second, and it is embarrassingly parallel if they rarely or never have to communicate. Embarrassingly parallel applications are considered the easiest to parallelize.
Consistency models

Parallel programming languages and parallel computers must have a consistency model (also known as a memory model). The consistency model defines rules for how operations on computer memory occur and how results are produced.
One of the first consistency models was Leslie Lamport's sequential consistency model. Sequential consistency is the property of a parallel program that its parallel execution produces the same results as a sequential program. Specifically, a program is sequentially consistent if "... the results of any execution is the same as if the operations of all the processors were executed in some sequential order, and the operations of each individual processor appear in this sequence in the order specified by its program".[16]
Software transactional memory is a common type of consistency model. Software transactional memory borrows from database theory the concept of atomic transactions and applies them to memory accesses.
Mathematically, these models can be represented in several ways. Petri nets, which were introduced in Carl Adam Petri's 1962 doctoral thesis, were an early attempt to codify the rules of consistency models. Dataflow theory later built upon these, and Dataflow architectures were created to physically implement the ideas of dataflow theory. Beginning in the late 1970s, process calculi such as calculus of communicating systems and communicating sequential processes were developed to permit algebraic reasoning about systems composed of interacting components. More recent additions to the process calculus family, such as the π-calculus, have added the capability for reasoning about dynamic topologies. Logics such as Lamport's TLA+, and mathematical models such as traces and Actor event diagrams, have also been developed to describe the behavior of concurrent systems.
Flynn's taxonomy
Michael J. Flynn created one of the earliest classification systems for parallel (and sequential) computers and programs, now known as Flynn's taxonomy. Flynn classified programs and computers by whether they were operating using a single set or multiple sets of instructions, whether or not those instructions were using a single or multiple sets of data.
| Single Instruction |
Multiple Instruction |
|
|---|---|---|
| Single Data |
SISD | MISD |
| Multiple Data |
SIMD | MIMD |
The single-instruction-single-data (SISD) classification is equivalent to an entirely sequential program. The single-instruction-multiple-data (SIMD) classification is analogous to doing the same operation repeatedly over a large data set. This is commonly done in signal processing applications. Multiple-instruction-single-data (MISD) is a rarely used classification. While computer architectures to deal with this were devised (such as systolic arrays), few applications that fit this class materialized. Multiple-instruction-multiple-data (MIMD) programs are by far the most common type of parallel programs.
According to David A. Patterson and John L. Hennessy, "Some machines are hybrids of these categories, of course, but this classic model has survived because it is simple, easy to understand, and gives a good first approximation. It is also—perhaps because of its understandability—the most widely used scheme."[17]
Types of parallelism
Bit-level parallelism
From the advent of very-large-scale integration (VLSI) computer-chip fabrication technology in the 1970s until about 1986, speed-up in computer architecture was driven by doubling computer word size—the amount of information the processor can execute per cycle.[18] Increasing the word size reduces the number of instructions the processor must execute to perform an operation on variables whose sizes are greater than the length of the word. For example, where an 8-bit processor must add two 16-bit integers, the processor must first add the 8 lower-order bits from each integer using the standard addition instruction, then add the 8 higher-order bits using an add-with-carry instruction and the carry bit from the lower order addition; thus, an 8-bit processor requires two instructions to complete a single operation, where a 16-bit processor would be able to complete the operation with a single instruction.
Historically, 4-bit microprocessors were replaced with 8-bit, then 16-bit, then 32-bit microprocessors. This trend generally came to an end with the introduction of 32-bit processors, which has been a standard in general-purpose computing for two decades. Not until recently (c. 2003–2004), with the advent of x86-64 architectures, have 64-bit processors become commonplace.
Instruction-level parallelism
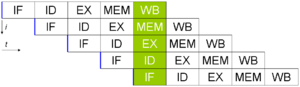
A computer program is, in essence, a stream of instructions executed by a processor. These instructions can be re-ordered and combined into groups which are then executed in parallel without changing the result of the program. This is known as instruction-level parallelism. Advances in instruction-level parallelism dominated computer architecture from the mid-1980s until the mid-1990s.[19]
Modern processors have multi-stage instruction pipelines. Each stage in the pipeline corresponds to a different action the processor performs on that instruction in that stage; a processor with an N-stage pipeline can have up to N different instructions at different stages of completion. The canonical example of a pipelined processor is a RISC processor, with five stages: instruction fetch, decode, execute, memory access, and write back. The Pentium 4 processor had a 35-stage pipeline.[20]

In addition to instruction-level parallelism from pipelining, some processors can issue more than one instruction at a time. These are known as superscalar processors. Instructions can be grouped together only if there is no data dependency between them. Scoreboarding and the Tomasulo algorithm (which is similar to scoreboarding but makes use of register renaming) are two of the most common techniques for implementing out-of-order execution and instruction-level parallelism.
Data parallelism
Data parallelism is parallelism inherent in program loops, which focuses on distributing the data across different computing nodes to be processed in parallel. "Parallelizing loops often leads to similar (not necessarily identical) operation sequences or functions being performed on elements of a large data structure."[21] Many scientific and engineering applications exhibit data parallelism.
A loop-carried dependency is the dependence of a loop iteration on the output of one or more previous iterations. Loop-carried dependencies prevent the parallelization of loops. For example, consider the following pseudocode that computes the first few Fibonacci numbers:
1: PREV2 := 0 2: PREV1 := 1 3: CUR := 1 4: do: 5: CUR := PREV1 + PREV2 6: PREV2 := PREV1 7: PREV1 := CUR 8: while (CUR < 10)
This loop cannot be parallelized because CUR depends on itself (PREV1) and PREV2, which are computed in each loop iteration. Since each iteration depends on the result of the previous one, they cannot be performed in parallel. As the size of a problem gets bigger, the amount of data-parallelism available usually does as well.[22]
Task parallelism
Task parallelism is the characteristic of a parallel program that "entirely different calculations can be performed on either the same or different sets of data".[21] This contrasts with data parallelism, where the same calculation is performed on the same or different sets of data. Task parallelism does not usually scale with the size of a problem.[22]
Hardware
Memory and communication
Main memory in a parallel computer is either shared memory (shared between all processing elements in a single address space), or distributed memory (in which each processing element has its own local address space).[23] Distributed memory refers to the fact that the memory is logically distributed, but often implies that it is physically distributed as well. Distributed shared memory is a combination of the two approaches, where the processing element has its own local memory and access to the memory on non-local processors. Accesses to local memory are typically faster than accesses to non-local memory.

Computer architectures in which each element of main memory can be accessed with equal latency and bandwidth are known as Uniform Memory Access (UMA) systems. Typically, that can be achieved only by a shared memory system, in which the memory is not physically distributed. A system that does not have this property is known as a Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture. Distributed memory systems have non-uniform memory access.
Computer systems make use of caches—small, fast memories located close to the processor which store temporary copies of memory values (nearby in both the physical and logical sense). Parallel computer systems have difficulties with caches that may store the same value in more than one location, with the possibility of incorrect program execution. These computers require a cache coherency system, which keeps track of cached values and strategically purges them, thus ensuring correct program execution. Bus snooping is one of the most common methods for keeping track of which values are being accessed (and thus should be purged). Designing large, high-performance cache coherence systems is a very difficult problem in computer architecture. As a result, shared-memory computer architectures do not scale as well as distributed memory systems do.[23]
Processor–processor and processor–memory communication can be implemented in hardware in several ways, including via shared (either multiported or multiplexed) memory, a crossbar switch, a shared bus or an interconnect network of a myriad of topologies including star, ring, tree, hypercube, fat hypercube (a hypercube with more than one processor at a node), or n-dimensional mesh.
Parallel computers based on interconnect networks need to have some kind of routing to enable the passing of messages between nodes that are not directly connected. The medium used for communication between the processors is likely to be hierarchical in large multiprocessor machines.
Classes of parallel computers
Parallel computers can be roughly classified according to the level at which the hardware supports parallelism. This classification is broadly analogous to the distance between basic computing nodes. These are not mutually exclusive; for example, clusters of symmetric multiprocessors are relatively common.
Multicore computing
A multicore processor is a processor that includes multiple execution units ("cores"). These processors differ from superscalar processors, which can issue multiple instructions per cycle from one instruction stream (thread); by contrast, a multicore processor can issue multiple instructions per cycle from multiple instruction streams. Each core in a multicore processor can potentially be superscalar as well—that is, on every cycle, each core can issue multiple instructions from one instruction stream.
Simultaneous multithreading (of which Intel's HyperThreading is the best known) was an early form of pseudo-multicoreism. A processor capable of simultaneous multithreading has only one execution unit ("core"), but when that execution unit is idling (such as during a cache miss), it uses that execution unit to process a second thread. Intel's Core and Core 2 processor families are Intel's first true multicore architectures. IBM's Cell microprocessor, designed for use in the Sony Playstation 3, is another prominent multicore processor.
Symmetric multiprocessing
A symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) is a computer system with multiple identical processors that share memory and connect via a bus.[24] Bus contention prevents bus architectures from scaling. As a result, SMPs generally do not comprise more than 32 processors.[25] "Because of the small size of the processors and the significant reduction in the requirements for bus bandwidth achieved by large caches, such symmetric multiprocessors are extremely cost-effective, provided that a sufficient amount of memory bandwidth exists."[24]
Distributed computing
A distributed computer (also known as a distributed memory multiprocessor) is a distributed memory computer system in which the processing elements are connected by a network. Distributed computers are highly scalable.
Cluster computing

A cluster is a group of loosely coupled computers that work together closely, so that in some respects they can be regarded as a single computer.[26] Clusters are composed of multiple standalone machines connected by a network. While machines in a cluster do not have to be symmetric, load balancing is more difficult if they are not. The most common type of cluster is the Beowulf cluster, which is a cluster implemented on multiple identical commercial off-the-shelf computers connected with a TCP/IP Ethernet local area network.[27] Beowulf technology was originally developed by Thomas Sterling and Donald Becker. The vast majority of the TOP500 supercomputers are clusters.[28]
Massive parallel processing
A massively parallel processor (MPP) is a single computer with many networked processors. MPPs have many of the same characteristics as clusters, but MPPs have specialized interconnect networks (whereas clusters use commodity hardware for networking). MPPs also tend to be larger than clusters, typically having "far more" than 100 processors.[29] In an MPP, "each CPU contains its own memory and copy of the operating system and application. Each subsystem communicates with the others via a high-speed interconnect."[30]

Blue Gene/L, the fourth fastest supercomputer in the world according to the November 2008 TOP500 ranking, is an MPP.
Grid computing
Grid computing is the most distributed form of parallel computing. It makes use of computers communicating over the Internet to work on a given problem. Because of the low bandwidth and extremely high latency available on the Internet, grid computing typically deals only with embarrassingly parallel problems. Many grid computing applications have been created, of which SETI@home and Folding@Home are the best-known examples.[31]
Most grid computing applications use middleware, software that sits between the operating system and the application to manage network resources and standardize the software interface. The most common grid computing middleware is the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC). Often, grid computing software makes use of "spare cycles", performing computations at times when a computer is idling.
Specialized parallel computers
Within parallel computing, there are specialized parallel devices that remain niche areas of interest. While not domain-specific, they tend to be applicable to only a few classes of parallel problems.
- Reconfigurable computing with field-programmable gate arrays
Reconfigurable computing is the use of a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) as a co-processor to a general-purpose computer. An FPGA is, in essence, a computer chip that can rewire itself for a given task.
FPGAs can be programmed with hardware description languages such as VHDL or Verilog. However, programming in these languages can be tedious. Several vendors have created C to HDL languages that attempt to emulate the syntax and/or semantics of the C programming language, with which most programmers are familiar. The best known C to HDL languages are Mitrion-C, Impulse C, DIME-C, and Handel-C.
AMD's decision to open its HyperTransport technology to third-party vendors has become the enabling technology for high-performance reconfigurable computing.[32] According to Michael R. D'Amour, CEO of DRC Computer Corporation, "when we first walked into AMD, they called us 'the socket stealers.' Now they call us their partners."[32]
- GPGPU with graphics processing units

General-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU) is a fairly recent trend in computer engineering research. GPUs are co-processors that have been heavily optimized for computer graphics processing.[33] Computer graphics processing is a field dominated by data parallel operations—particularly linear algebra matrix operations.
In the early days, GPGPU programs used the normal graphics APIs for executing programs. However, recently several new programming languages and platforms have been built to do general purpose computation on GPUs with both Nvidia and AMD releasing programming environments with CUDA and CTM respectively. Other GPU programming languages are BrookGPU, PeakStream, and RapidMind. Nvidia has also released specific products for computation in their Tesla series.
- Application-specific integrated circuits
Several Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) approaches have been devised for dealing with parallel applications.[34][35][36]
Because an ASIC is (by definition) specific to a given application, it can be fully optimized for that application. As a result, for a given application, an ASIC tends to outperform a general-purpose computer. However, ASICs are created by X-ray lithography. This process requires a mask, which can be extremely expensive. A single mask can cost over a million US dollars.[37] (The smaller the transistors required for the chip, the more expensive the mask will be.) Meanwhile, performance increases in general-purpose computing over time (as described by Moore's Law) tend to wipe out these gains in only one or two chip generations.[32] High initial cost, and the tendency to be overtaken by Moore's-law-driven general-purpose computing, has rendered ASICs unfeasible for most parallel computing applications. However, some have been built. One example is the peta-flop RIKEN MDGRAPE-3 machine which uses custom ASICs for molecular dynamics simulation.
- Vector processors

A vector processor is a CPU or computer system that can execute the same instruction on large sets of data. "Vector processors have high-level operations that work on linear arrays of numbers or vectors. An example vector operation is A = B × C, where A, B, and C are each 64-element vectors of 64-bit floating-point numbers."[38] They are closely related to Flynn's SIMD classification.[38]
Cray computers became famous for their vector-processing computers in the 1970s and 1980s. However, vector processors—both as CPUs and as full computer systems—have generally disappeared. Modern processor instruction sets do include some vector processing instructions, such as with AltiVec and Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE).
Software
Parallel programming languages
Concurrent programming languages, libraries, APIs, and parallel programming models have been created for programming parallel computers. These can generally be divided into classes based on the assumptions they make about the underlying memory architecture—shared memory, distributed memory, or shared distributed memory. Shared memory programming languages communicate by manipulating shared memory variables. Distributed memory uses message passing. POSIX Threads and OpenMP are two of most widely used shared memory APIs, whereas Message Passing Interface (MPI) is the most widely used message-passing system API. One concept used in programming parallel programs is the future concept, where one part of a program promises to deliver a required datum to another part of a program at some future time.
Automatic parallelization
Automatic parallelization of a sequential program by a compiler is the "holy grail" of parallel computing. Despite decades of work by compiler researchers, automatic parallelization has had only limited success.[39]
Mainstream parallel programming languages remain either explicitly parallel or (at best) partially implicit, in which a programmer gives the compiler directives for parallelization. A few fully implicit parallel programming languages exist—SISAL, Parallel Haskell, and (for FPGAs) Mitrion-C—but these are niche languages that are not widely used.
Application checkpointing
The larger and more complex a computer, the more that can go wrong and the shorter the mean time between failures. Application checkpointing is a technique whereby the computer system takes a "snapshot" of the application—a record of all current resource allocations and variable states, akin to a core dump; this information can be used to restore the program if the computer should fail. Application checkpointing means that the program has to restart from only its last checkpoint rather than the beginning. For an application that may run for months, that is critical. Application checkpointing may be used to facilitate process migration.
Applications
As parallel computers become larger and faster, it becomes feasible to solve problems that previously took too long to run. Parallel computing is used in a wide range of fields, from bioinformatics (to do protein folding) to economics (to do simulation in mathematical finance). Common types of problems found in parallel computing applications are:[40]
- Dense linear algebra
- Sparse linear algebra
- Spectral methods (such as Cooley-Tukey Fast Fourier transform)
- N-body problems (such as Barnes-Hut simulation)
- Structured grid problems (such as Lattice Boltzmann methods),
- Unstructured grid problems (such as found in finite element analysis)
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Combinational logic (such as brute-force cryptographic techniques)
- Graph traversal (such as Sorting algorithms)
- Dynamic programming
- Branch and bound methods
- Graphical models (such as detecting Hidden Markov models and constructing Bayesian networks)
- Finite State Machine simulation
History

The origins of true (MIMD) parallelism go back to Federico Luigi, Conte Menabrea and his "Sketch of the Analytic Engine Invented by Charles Babbage".[41][42] IBM introduced the 704 in 1954, through a project in which Gene Amdahl was one of the principal architects. It became the first commercially available computer to use fully automatic floating point arithmetic commands.[43] In 1958, IBM researchers John Cocke and Daniel Slotnick discussed the use of parallelism in numerical calculations for the first time.[44] Burroughs Corporation introduced the D825 in 1962, a four-processor computer that accessed up to 16 memory modules through a crossbar switch.[45] In 1967, Amdahl and Slotnick published a debate about the feasibility of parallel processing at American Federation of Information Processing Societies Conference.[44] It was during this debate that Amdahl's Law was coined to define the limit of speed-up due to parallelism.
In 1969, US company Honeywell introduced its first Multics system, a symmetric multiprocessor system capable of running up to eight processors in parallel.[44] C.mmp, a 1970s multi-processor project at Carnegie Mellon University, was "among the first multiprocessors with more than a few processors".[42] "The first bus-connected multi-processor with snooping caches was the Synapse N+1 in 1984."[42]
SIMD parallel computers can be traced back to the 1970s. The motivation behind early SIMD computers was to amortize the gate delay of the processor's control unit over multiple instructions.[46] In 1964, Slotnick had proposed building a massively parallel computer for the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.[44] His design was funded by the US Air Force, which was the earliest SIMD parallel-computing effort, ILLIAC IV.[44] The key to its design was a fairly high parallelism, with up to 256 processors, which allowed the machine to work on large datasets in what would later be known as vector processing. However, ILLIAC IV was called "the most infamous of Supercomputers", because the project was only one fourth completed, but took 11 years and cost almost four times the original estimate.[47] When it was finally ready to run its first real application in 1976, it was outperformed by existing commercial supercomputers such as the Cray-1.
References
- ↑ Almasi, G.S. and A. Gottlieb (1989). Highly Parallel Computing. Benjamin-Cummings publishers, Redwood City, CA.
- ↑ S.V. Adve et al. (November 2008). "Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits – increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures – are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance increases must largely come from increasing the number of processors (or cores) on a die, rather than making a single core go faster."
- ↑ Asanovic et al. Old [conventional wisdom]: Power is free, but transistors are expensive. New [conventional wisdom] is [that] power is expensive, but transistors are "free".
- ↑ Asanovic, Krste et al. (December 18, 2006). "The Landscape of Parallel Computing Research: A View from Berkeley" (PDF). University of California, Berkeley. Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2006-183. "Old [conventional wisdom]: Increasing clock frequency is the primary method of improving processor performance. New [conventional wisdom]: Increasing parallelism is the primary method of improving processor performance ... Even representatives from Intel, a company generally associated with the 'higher clock-speed is better' position, warned that traditional approaches to maximizing performance through maximizing clock speed have been pushed to their limit."
- ↑ Patterson, David A. and John L. Hennessy (1998). Computer Organization and Design, Second Edition, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, p. 715. ISBN 1558604286.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Barney, Blaise. "Introduction to Parallel Computing". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Retrieved on 2007-11-09.
- ↑ Hennessy, John L. and David A. Patterson (2002). Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach. 3rd edition, Morgan Kaufmann, p. 43. ISBN 1558607242.
- ↑ Rabaey, J. M. (1996). Digital Integrated Circuits. Prentice Hall, p. 235. ISBN 0131786091.
- ↑ Flynn, Laurie J. "Intel Halts Development of 2 New Microprocessors". The New York Times, May 8, 2004. Retrieved on April 22, 2008.
- ↑ Moore, Gordon E. (1965). "Cramming more components onto integrated circuits" (PDF). Electronics Magazine 4. Retrieved on 2006-11-11.
- ↑ Amdahl, G. (April 1967) "The validity of the single processor approach to achieving large-scale computing capabilities". In Proceedings of AFIPS Spring Joint Computer Conference, Atlantic City, N.J., AFIPS Press, pp. 483–85.
- ↑ Brooks, Frederick P. Jr. The Mythical Man-Month: Essays on Software Engineering. Chapter 2 – The Mythical Man Month. ISBN 0201835959
- ↑ Reevaluating Amdahl's Law (1988). Communications of the ACM 31(5), pp. 532–33.
- ↑ Bernstein, A. J. (October 1966). "Program Analysis for Parallel Processing,' IEEE Trans. on Electronic Computers". EC-15, pp. 757–62.
- ↑ Roosta, Seyed H. (2000). "Parallel processing and parallel algorithms: theory and computation". Springer, p. 114. ISBN 0387987169.
- ↑ Lamport, Leslie (September 1979). "How to Make a Multiprocessor Computer That Correctly Executes Multiprocess Programs", IEEE Transactions on Computers, C-28,9, pp. 690–91.
- ↑ Patterson and Hennessy, p. 748.
- ↑ Culler, David E.; Jaswinder Pal Singh and Anoop Gupta (1999). Parallel Computer Architecture - A Hardware/Software Approach. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, p. 15. ISBN 1558603433.
- ↑ Culler et al. p. 15.
- ↑ Patt, Yale (April 2004). "The Microprocessor Ten Years From Now: What Are The Challenges, How Do We Meet Them? (wmv). Distinguished Lecturer talk at Carnegie Mellon University. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Culler et al. p. 124.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Culler et al. p. 125.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Patterson and Hennessy, p. 713.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Hennessy and Patterson, p. 549.
- ↑ Patterson and Hennessy, p. 714.
- ↑ What is clustering? Webopedia computer dictionary. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ Beowulf definition. PC Magazine. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ Architecture share for 06/2007. TOP500 Supercomputing Sites. Clusters make up 74.60% of the machines on the list. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ Hennessy and Patterson, p. 537.
- ↑ MPP Definition. PC Magazine. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ Kirkpatrick, Scott (January 31, 2003). "Computer Science: Rough Times Ahead". Science, Vol. 299. No. 5607, pp. 668 - 669. DOI: 10.1126/science.1081623
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 D'Amour, Michael R., CEO DRC Computer Corporation. "Standard Reconfigurable Computing". Invited speaker at the University of Delaware, February 28, 2007.
- ↑ Boggan, Sha'Kia and Daniel M. Pressel (August 2007). GPUs: An Emerging Platform for General-Purpose Computation (PDF). ARL-SR-154, U.S. Army Research Lab. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ Maslennikov, Oleg (2002). "Systematic Generation of Executing Programs for Processor Elements in Parallel ASIC or FPGA-Based Systems and Their Transformation into VHDL-Descriptions of Processor Element Control Units". Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2328/2002: p. 272.
- ↑ Shimokawa, Y.; Y. Fuwa and N. Aramaki (18–21 November 1991). A parallel ASIC VLSI neurocomputer for a large number of neurons and billion connections per second speed. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. 3: pp. 2162–67.
- ↑ Acken, K.P.; M.J. Irwin, R.M. Owens (July 1998). "A Parallel ASIC Architecture for Efficient Fractal Image Coding". The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, 19(2):97–113(17)
- ↑ Kahng, Andrew B. (June 21, 2004) "Scoping the Problem of DFM in the Semiconductor Industry." University of California, San Diego. "Future design for manufacturing (DFM) technology must reduce design [non-recoverable expenditure] cost and directly address manufacturing [non-recoverable expenditures] – the cost of a mask set and probe card – which is well over $1 million at the 90 nm technology node and creates a significant damper on semiconductor-based innovation."
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Patterson and Hennessy, p. 751.
- ↑ Shen, John Paul and Mikko H. Lipasti (2005). Modern Processor Design: Fundamentals of Superscalar Processors. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 561. ISBN 0070570647. "However, the holy grail of such research - automated parallelization of serial programs - has yet to materialize. While automated parallelization of certain classes of algorithms has been demonstrated, such success has largely been limited to scientific and numeric applications with predictable flow control (e.g., nested loop structures with statically determined iteration counts) and statically analyzable memory access patterns. (e.g., walks over large multidimensional arrays of float-point data)."
- ↑ Asanovic, Krste, et al. (December 18, 2006). The Landscape of Parallel Computing Research: A View from Berkeley (PDF). University of California, Berkeley. Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2006-183. See table on pages 17-19.
- ↑ Menabrea, L. F. (1842). Sketch of the Analytic Engine Invented by Charles Babbage. Bibliothèque Universelle de Genève. Retrieved on November 7, 2007.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Patterson and Hennessy, p. 753.
- ↑ da Cruz, Frank (2003). "Columbia University Computing History: The IBM 704". Columbia University. Retrieved on 2008-01-08.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 44.4 Wilson, Gregory V (1994). "The History of the Development of Parallel Computing". Virginia Tech/Norfolk State University, Interactive Learning with a Digital Library in Computer Science. Retrieved on 2008-01-08.
- ↑ Anthes, Gry (November 19, 2001). "The Power of Parallelism". Computerworld. Retrieved on 2008-01-08.
- ↑ Patterson and Hennessy, p. 749.
- ↑ Patterson and Hennessy, pp. 749–50: "Although successful in pushing several technologies useful in later projects, the ILLIAC IV failed as a computer. Costs escalated from the $8 million estimated in 1966 to $31 million by 1972, despite the construction of only a quarter of the planned machine ... It was perhaps the most infamous of supercomputers. The project started in 1965 and ran its first real application in 1976."
External links
- Parallel computing at the Open Directory Project
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Introduction to Parallel Computing
- Designing and Building Parallel Programs, by Ian Foster
- Internet Parallel Computing Archive
- Parallel processing topic area at IEEE Distributed Computing Online
- Parallel Computing Works Free On-line Book
- Frontiers of Supercomputing Free On-line Book Covering topics like algorithms and industrial applications
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||