PBY Catalina
| PBY Catalina | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| PBY-5 Catalina landing at NAS Jacksonville. | |
| Role | Flying boat patrol bomber |
| Manufacturer | Consolidated Aircraft |
| Designed by | Isaac M. Laddon |
| First flight | 28 March 1935 |
| Introduced | October 1936, USN |
| Retired | January 1957, USNR |
| Primary users | United States Navy United States Army Air Forces Royal Air Force Royal Canadian Air Force |
| Produced | 1936-1945 |
| Number built | 4,051 (est.) |
| Unit cost | $90,000 as of 1935 |
| Variants | Bird Innovator |
The Consolidated PBY Catalina was an American flying boat of the 1930s and 1940s produced by Consolidated Aircraft. It could be equipped with depth charges, bombs, torpedoes, and .50 Browning machineguns and was one of the most widely used multi-role aircraft of World War II. PBYs served with every branch of the US military and in the air forces and navies of many other nations. In the United States Army Air Forces and later in the USAF their designation was the OA-10, while Canadian-built PBYs were known as Cansos.
In World War II, PBYs were used as anti-submarine warfare aircraft, patrol bombers, convoy escorts, search and rescue aircraft, and transports. The PBY was the most successful aircraft of its kind, as no other flying boat was produced in greater numbers. The last active military PBYs were not retired from service until the 1980s. Even today, over seventy years after its first flight, the aircraft continues to fly as an airtanker in aerial firefighting operations all over the world.
In the acronym PBY, "PB" stands for "Patrol Bomber", and "Y" is the code for "Consolidated Aircraft", as designated in the 1922 United States Navy aircraft designation system.
Contents |
Development
Background
The PBY was originally designed to be a patrol bomber, an aircraft with a long operational range intended to locate and attack enemy transport ships at sea in order to compromise enemy supply lines. With a mind to a potential conflict in the Pacific Ocean, where troops would require resupply over great distances, the U.S. Navy in the 1930s invested millions of dollars in developing long-range flying boats for this purpose. Flying boats had the advantage of not requiring runways to take off and land, in effect having the entire ocean available as its runway. Several different flying boats were adopted by the Navy, but the PBY was the most widely used and produced.

Although slow and ungainly, PBYs distinguished themselves in World War II as exceptionally reliable. Allied armed forces used them successfully in a wide variety of roles that the aircraft was never intended for. They are remembered by many veterans of the war for their role in rescuing downed airmen, in which they saved the lives of thousands of aircrew shot down over the Pacific Ocean. PBY airmen called their aircraft the "cat" on combat missions and "Dumbo" in air-sea rescue service.[1]
Prototyping
As American dominance in the Pacific Ocean began to face competition from Japan in the 1930s, the U.S. Navy contracted Consolidated Aircraft and Douglas Aircraft Corporation in October 1933 to build competing prototypes for a patrol flying boat.[2] Naval doctrine of the 1930s and 1940s used flying boats in a wide variety of roles that today are handled by multiple special-purpose aircraft. The US Navy had adopted the Consolidated P2Y and Martin P3M models for this role in 1931, but both aircraft proved to be underpowered and hampered by short ranges and low maximum payloads.
Consolidated and Douglas both delivered single prototypes of their designs, the XP3Y-1 and XP3D-1, respectively. PB stood for Patrol Bomber, with Y being Consolidated Aircraft’s manufacturer identification. Consolidated's XP3Y-1 was an evolution of the XPY-1 design that had originally competed unsuccessfully for the P3M contract two years earlier and of the XP2Y design that the Navy had authorized for a limited production run. Although the Douglas aircraft was a good design, the Navy opted for Consolidated's prototype because the projected cost was only $90,000 per plane.

Consolidated's XP3Y-1 design (company Model 28) was revolutionary in many ways. The aircraft had a parasol wing with internal bracing that allowed the wing to be a virtual cantilever, except for two small streamlined struts on each side. Stabilizing floats, retractable to form streamlined wingtips in flight, were another aerodynamic innovation. The two-step hull design was similar to that of the P2Y, but the Model 28 had a cantilever cruciform tail unit instead of a strut-braced twin tail. Cleaner aerodynamics gave the Model 28 improved performance compared to earlier designs.
The powerplant for the prototype was two 825 hp (615 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1830-54 Twin Wasp engines mounted on the wing’s leading edges. Armament comprised four 0.30 in (7.62 mm) Browning machineguns and up to 2,000 lb (907 kg) of bombs.
The XP3Y-1 had its first flight on 28 March 1935 after which it was transferred to the US Navy for service trials. The XP3Y-1 soon proved to have significant performance improvements over current patrol flying boats. The Navy requested further development in order to bring the aircraft into the category of patrol bomber, and in October 1935 the prototype was returned to Consolidated for further work. The work included installation of 900 hp (671 kW) R-1830-64 engines. For the redesignated XPBY-1, Consolidated introduced redesigned vertical tail surfaces. The XPBY-1 had its maiden flight on 19 May 1936, during which a record non-stop distance flight of 3,443 miles (5,541 km) was achieved.
The XPBY-1 was delivered to VP-11F in October 1936. The second squadron to be equipped was VP-12, which received the first of its aircraft in early 1937. The second production order was placed on 25 July 1936. Over the next three years, the PBY design would be gradually improved and successive models introduced.
| Model | Production period & distinguishing features | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| PBY-1 | September 1936 - June 1937 Original production model. |
60 |
| PBY-2 | May 1937 - February 1938 Minor alterations to tail structure, hull reinforcements. |
50 |
| PBY-3 | November 1936 - August 1938 Higher power engines. |
66 |
| PBY-4 | May 1938 - June 1939 Higher power engines, propeller spinners, acrylic glass blisters over waist guns (some later units). |
32 |
| PBY-5 | September 1940 - July 1943 Higher power engines (using higher octane fuel), discontinued use of propeller spinners, standardized waist gun blisters. |
684 |
| PBY-5A | October 1941 - January 1945 Hydraulically-actuated, retractable tricycle landing gear for amphibious operation. Introduced tail gun position, replaced bow single gun position with bow "eyeball" turret equipped with twin .30 machine guns (some later units), improved armor, self-sealing fuel tanks.[3] |
802 |
| PBY-6A | January 1945 - May 1945 Incorporated changes from PBN-1,[4] including a taller vertical tail, increased wing strength for greater carrying capacity, new electrical system, standardized "eyeball" turret, and a radome over cockpit for radar. |
175 |
* An estimated 4,051 Catalinas, Cansos, and GSTs of all variants were produced between June 1937 and May 1945 for the US Navy, USAAF, United States Coast Guard, Allied nations, and civilian customers.

The Naval Aircraft Factory made significant modifications to the PBY design, many of which would have significantly interrupted deliveries had they been incorporated on the Consolidated production lines.[5] The new aircraft, officially known as the PBN-1 Nomad, had several differences from the basic PBY. The most visually apparent upgrades were to the bow, sharpened and extended two feet, and to the tail, which was enlarged and featured a new shape. Other improvements included larger fuel tanks, increasing range by 50%, and stronger wings permitting a 2,000 lb (908 kg) higher gross takeoff weight. An auxiliary power unit was installed, along with a modernized electrical system, and the weapons were upgraded with continuous-feed mechanisms.[5]
The majority (138) of the 156 PBN-1s produced served with the Soviet Navy. The remaining 18 aircraft were assigned to training units at NAS Whidbey Island and NAF Newport.[6] Later, improvements found in the PBN-1 – notably, the larger tail – were incorporated into the amphibious PBY-6A.
Operational history
Roles in World War II
The final construction figure is estimated at around 4,000 aircraft, and these were deployed in practically all of the operational theatres of World War II. The PBY served with distinction and played a prominent and invaluable role in the war against the Japanese. This was especially true during the first year of the War in the Pacific, because the PBY and the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress were the only two available aircraft with the range necessary. As a result they were used in almost every possible military role until a new generation of aircraft became available.
Anti-submarine warfare
PBYs were the most extensively used ASW aircraft in both the Atlantic and Pacific Theaters of the Second World War, and were also used in the Indian Ocean, flying from the Seychelles. One of their jobs was escorting convoys to Murmansk. By 1943, U-boats were well armed with anti-aircraft guns and two Victoria Crosses were won by Catalina pilots pressing home attacks on U-boats in the face of heavy fire: John Cruickshank RAF, in 1944 against U-347 and in the same year Flight Lt. David Hornell RCAF (posthumously) against U-1225. Catalinas destroyed 40 U-boats in total but suffered losses of their own. On December 7, 1941, Mitsubishi A6M fighters from Akagi attacked NAS Kaneohe Bay at Oahu, Hawaii, destroying or disabling all of the 33 PBYs stationed there.
Maritime patrol

In their role as patrol aircraft, Catalinas participated in some of the most notable engagements of World War II. The aircraft's parasol wing and large waist blisters allowed for a great deal of visibility; this, combined with its long range and endurance, made it well suited for the task.
- A Coastal Command Catalina with a USN commander among the British crew which located the German battleship Bismarck on May 26, 1941 while she tried to evade Royal Navy forces.[7]
- A flight of Catalinas spotted the Japanese fleet approaching Midway Island, beginning the Battle of Midway.[8]
- An RCAF Canso flown by Squadron Leader L.J. Birchall foiled Japanese plans to destroy the Royal Navy's Indian Ocean fleet on April 4, 1942 when it detected the Japanese carrier fleet approaching Ceylon (Sri Lanka).[9]
Several squadrons of PBY-5As and -6As in the Pacific theater were specially modified to operate as night convoy raiders. Outfitted with state-of-the-art magnetic anomaly detection gear and painted flat black, these "Black Cats" attacked Japanese supply convoys at night. Catalinas were surprisingly successful in this highly unorthodox role.[10] Between August 1943 and January 1944, Black Cat squadrons had sunk 112,700 tons of merchant shipping, damaged 47,000 tons, and damaged 10 Japanese warships. The Royal Australian Air Force also operated as night raiders, with RAAF four squadrons Nos 11,20,42 and 43 Catalinas mounting mine-laying operations using magnetic and acoustic mines from 23 April 1943 until July 1945 in the South West Pacific area deep into Japanese-held waters, that bottled up ports and shipping routes and kept ships in the deeper waters to become targets for the US Submarines, they increased their range and effectiveness by dispensing with armour and by removing the self sealing from the aircrafts fuel tanks this work was classified and regarded as top secret until many years after the cessation of hostilities over 230 RAAF airmen lost their lives in WW2; they tied up the major strategic ports such as Balikpapan that produced 80% of the Japanese oil supplies. In late 1944 their precison mining sometimes from as low as 200 feet in the hours of darkness in missions that sometimes exceeded 20 hours duration, one included the bottling up the Japanese fleet in Manila Bay planned to assist General MacArthur's landing at Mindoro in the Philippines. They also operating out of Jinamoc in Leyte Gulf, mined ports on the Chinese Coast from Hong Kong as far north as Wenchow. They were the only non American heavy bombers squadrons operating north of Morotai in 1945. The RAAF Catalinas regularly mounted nuisance night bombing raids on Japanese bases, they earned the motto of 'The first and the Furthest' as a testimony to their design and endurance. These raids included the major base at Rabaul. RAAF aircrews developed 'terror bombs', essentially empty beer bottles with razor blades inserted into the necks, these produced high pitched screams as they fell and kept Japanese soldiers awake and in fear of their life.{See Gaunt. 'Cats at War' and Cleworth 'The Fabulous Catalina' {date=December 2008}}
Search and rescue
PBYs were employed by every branch of the US military as rescue aircraft. A PBY piloted by Lt. Cmdr. Adrian Marks (USN) rescued 56 sailors from the USS Indianapolis after the ship was sunk during World War II. PBYs continued to function in this capacity for decades after the end of the war.
Early commercial use
PBYs were also used for commercial air travel. Still the longest commercial flights (in terms of time aloft) ever made in aviation history were the Qantas flights flown weekly from 29 June 1943 through July, 1945 over the Indian Ocean. To thumb their nose at the Japanese (who controlled the area), Qantas offered non-stop service between Perth and Colombo, a distance of 3,592 nm (5,652 km). As the PBY typically cruises at 110 knots, this took from 28-32 hours and was called the "flight of the double sunrise", since the passengers saw two sunrises during their non-stop journey. The flight was made with radio silence (because of the possibility of Japanese attack) and had a maximum payload of 1000 lbs or three passengers plus 65 kg of armed forces and diplomatic mail.[11]
Post-WWII employment

With the end of the war, flying boat versions were quickly retired from the U.S. Navy, but amphibians remained in service for many years. The last Catalina on active U.S. service was a PBY-6A operating with a Naval Reserve squadron, retired 3 January 1957.[2] It must be noted a PBY was being maintained at Clark Air Base, Republic of the Philippines, as late as 1968. The PBY subsequently equipped the world's smaller armed services, in fairly substantial numbers, into the late 1960s.
The USAF Strategic Air Command had PBYs (OA-10s) in service from 1946 through 1947.
The Brazilian Air Force flew Catalinas in naval air patrol missions against German submarines starting in 1943. The aircraft also performed air mail service. In 1948 a transport squadron was formed and equipped with PBY-5As converted to the role of amphibian transport. The 1st Air Transport Squadron (ETA-1) was based in the port city of Belem and flew Catalinas and C-47s in well-maintained condition until 1982. Catalinas were convenient for supplying military detachments scattered among the Amazon waterways. They reached places where only long range transport helicopters would dare go. ETA-1 insignia was a winged turtle with the motto "Though slowly, I always get there". Today, the last Brazilian Catalina (ex-RCAF) is displayed at the Airspace Museum (MUSAL), in Rio de Janeiro.[12]
Jacques-Yves Cousteau used a PBY-6A (N101CS) as part of his diving expeditions. His second son, Philippe, was killed while attempting a water landing in the Tagus river near Lisbon, Portugal, June 28 1979. His plane had just been repaired when he took it out for a flight. As he landed, one of the plane's propellers separated, cut through the cockpit and killed the younger Cousteau.
Of the few dozen remaining airworthy Catalinas, the majority are in use today as aerial firefighting planes.
China Airlines, the official airline of the Republic of China (Taiwan) was founded with two PBY amphibians.
Catalina affair
The Catalina Affair is the name given to a Cold War incident in which a Swedish military Catalina was shot down by Soviet aircraft over the Baltic Sea in June 1952 while investigating the earlier crash of a Swedish Douglas DC-3.
Variants
- XP3Y-1
- Prototype Model 28 flying boat later re-designated XBPY-1, one built (USN Bureau No. 9459). Later fitted with a 48-foot diameter ring to sweep magnetic mines. A 550-HP Ranger engine drove a generator to produce a magnetic field.[13]
- XBPY-1
- Prototype version of the Model 28 for the United States Navy, a re-engined XP3Y-1 with two 900hp R-1830-64 engines, one built.
- PBY-1 (Model 28-1)
- Initial production variant with two 900hp R-1830-64 engines, 60 built.
- PBY-2 (Model 28-2)
- Equipment changes and improved performance, 50 built.
- PBY-3 (Model 28-3)
- Powered by two 1000hp R-1830-66 engines, 66 built.
- PBY-4 (Model 28-4)
- Powered by two 1050hp R-1830-72 engines, 33 built (including one initial as a XBPY-4 which later became the XBPY-5A).
- PBY-5 (Model 28-5)
- Either two 1200hp R-1830-82 or -92 engines and provision for extra fuel tanks, 683 built (plus one built at New Orleans), some aircraft to the RAF as the Catalina IVA and one to the United States Coast Guard. The PBY-5 was also built in the Soviet Union as the GST.
- XPBY-5
- One PBY-4 converted into an amphibian and first flown in November 1939.
- PBY-5A (Model 28-5A)
- Amphibious version of the PBY-5 with two 1200hp R-1830-92 engines, first batch (of 124) had one 0.3in bow gun the remainder had two bow guns. 803 built including diversions to the United States Army Air Corps, the RAF (as the Catalina IIIA) and one to the United States Coast Guard.
- PBY-6A
- Amphibious version with two 1200hp R-1830-92 engines and a taller fin and rudder. Radar scanner fitted above cockpit and two 0.5 in nose guns. 175 built including 21 transferred to the Soviet Navy.
- PBY-6AG
- One PBY-6A used by the United States Coast Guard as a staff transport.
- PB2B-1
- Boeing Canada built version of the PBY-5, 165 built most supplied to the RAF and RNZAF as the Catalina IVB.
- PB2B-2
- Boeing Canada built version of the PBY-5 but having a taller fin of the PBN-1, 67 built most supplied to the RAF as the Catalina VI.
- PBN-1
- Naval Aircraft Factory built version of the PBY-5 with major modification including a 2ft bow extension, re-designed wingtip floats and tail surfaces and a revised electrical system. 155 built for delivery to the RAF as the Catalina V although 138 were loaned to the Soviet Navy.
- PBV-1A
- Canadian Vickers built version of the PBY-5A, 380 built including 150 to the Royal Canadian Air Force as the Canso-A and the rest to the USAAF as the OA-10A.
- OA-10
- PBY-5A transferred to the United States Army Air Corps, 58 aircraft survivors re-designated A-10 in 1948.
- OA-10A
- Canadian Vickers built version of the PBV-1, survivors re-designated A-10A in 1948. Three additional aircraft from Navy in 1949 as A-10As.
- OA-10B
- Former PBY-6As transferred to the USAAC, 75 aircraft re-designated A-10B in 1948.
- Catalina I
- Direct purchase aircraft for the Royal Air Force, same as the PBY-5 with six 0.303in guns (one in bow, four in beam blisters and one aft of the hull step) and powered by two 1200hp R-1830-S1C3-G engines, 109 built.
- Catalina IA
- Operated by the Royal Canadian Air Force as the Canso, 14 built.
- Catalina IB
- Lend-lease PBY-5Bs for the RAF, 225 aircraft built.
- Catalina II
- Equipment changes, six built.
- Catalina IIA
- Vickers-Canada built Catalina II for the RAF, 50 built.
- Catalina IIIA
- Former US Navy PBY-5As used by the RAF on the North Atlantic Ferry Service, 12 aircraft.
- Catalina IVA
- Lend-lease PBY-5s for the RAF, 93 aircraft.
- Catalina IVB
- Lend-lease PB2B-1s for the RAF, some to the Royal Australian Air Force.
- Catalina VI
- Lend-lease PB2B-2s for the RAF, some to the RAAF.
- GST
- Soviet built version of the PBY-5.
Operators

 Argentina
Argentina Australia
Australia Brazil
Brazil Canada
Canada Chile
Chile China
China Colombia
Colombia Denmark
Denmark Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador France
France Iceland
Iceland Indonesia
Indonesia Israel
Israel Mexico
Mexico Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Norway
Norway Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Philippines
Philippines South Africa
South Africa Sweden
Sweden Soviet Union
Soviet Union United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States Uruguay
Uruguay
Survivors
- See also: PBY Catalina survivors
Specifications (PBY-5A)
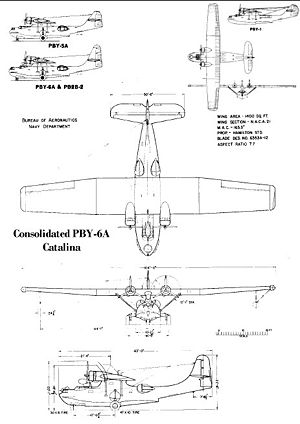
Data from Encyclopedia of World Air Power,[14] Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II,[4] Handbook of Erection and Maintenance Instructions for Navy Model PBY-5 and PBY-5A Airplanes[15] and Quest for Performance[16]
General characteristics
- Crew: 8 — pilot, co-pilot, bow turret gunner, flight mechanic, radioman, navigator and two waist gunners
- Length: 63 ft 10 7/16 in (19.46 m)
- Wingspan: 104 ft 0 in (31.70 m)
- Height: 21 ft 1 in (6.15 m)
- Wing area: 1,400 ft² (130 m²)
- Empty weight: 20,910 lb (9,485 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 35,420 lb (16,066 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Pratt & Whitney R-1830-92 Twin Wasp radial engines, 1,200 hp (895 kW each) each
- Zero-lift drag coefficient: 0.0309
- Drag area: 43.26 ft² (4.02 m²)
- Aspect ratio: 7.73
Performance
- Maximum speed: 196 mph (314 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 125 mph (201 km/h)
- Range: 2,520 mi (4,030 km)
- Service ceiling 15,800 ft (4,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,000 ft/min (5.1 m/s)
- Wing loading: 25.3 lb/ft² (123.6 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.034 hp/lb (0.056 kW/kg)
- Lift-to-drag ratio: 11.9
Armament
- 3× .30 cal (7.62 mm) machine guns (two in nose turret, one in ventral hatch at tail)
- 2× .50 cal (12.7 mm) machine guns (one in each waist blister)
- 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs or depth charges, torpedo racks were also available
See also
Related development
- PB2Y Coronado
Comparable aircraft
- Dornier Do 24
- Grumman Albatross
- Kawanishi H6K
- Short Sunderland
- Harbin PS-5
- Canadair CL-215
Related lists
- List of PBY Catalina operators
- List of flying boats
References
Notes
- ↑ Weathered, William W. "Comment and Discussion". United States Naval Institute Proceedings, October 1968.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cacutt, Len, ed. “PBY Catalina: Ocean Patroller.” Great Aircraft of the World. London: Marshall Cavendish, 1989. p. 187-194. ISBN 1-85435-250-4.
- ↑ Bridgeman, Leonard. “The Consolidated Vultee Model 28-5A Catalina Amphibian.” Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London: Studio, 1946. p. 218. ISBN 1 85170 493 0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bridgeman, Leonard. “The Consolidated Vultee Model 28 Catalina.” Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London: Studio, 1946. p. 218. ISBN 1 85170 493 0.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bridgeman, Leonard. “The Naval Aircraft Factory Catalina.” Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London: Studio, 1946. p. 247. ISBN 1 85170 493 0.
- ↑ "Naval Aircraft Factory PBN-1 Nomad". Aviation Enthusiast Corner. Retrieved on 2006-03-31.
- ↑ Smith, Leonard B. (1941). "Report of Scouting and Search of PBY-5 No. AH545 "Catalina" for Bismarck 26 May, 1941". Retrieved July 31, 2005.
---- "Bismarck: British/American Cooperation and the Destruction of the German Battleship." Retrieved August 2, 2005. - ↑ United States Naval Historical Center (1999). "Scouting and Early Attacks from Midway, 3-4 June 1942". Retrieved July 31, 2005.
- ↑ Brereton Greenhous et al. The Crucible of War 1939-1945: The Official History of the Royal Canadian Air Force, Vol. III. p. 386. ISBN 978-0802005748
- ↑ It was hazardous, however; before an attack, one crew messaged, "Please inform next of kin."
- ↑ Qantas history. The Catalinas
- ↑ MUSAL. Consolidated Vultee 28 (PBY-5A/C-10A) “Catalina”
- ↑ Hayward, John T., VADM USN "Comment and Discussion" United States Naval Institute Proceedings August 1978 p.24
- ↑ Gunston, Bill (ed.) (1981). Encyclopedia of World Air Power. London: Aerospace Publishing Ltd. ISBN 0-517-53754-0
- ↑ Handbook of Erection and Maintenance Instructions for Navy Model PBY-5 and PBY-5A Airplanes]
- ↑ Loftin, LK, Jr.. "Quest for performance: The evolution of modern aircraft. NASA SP-468". Retrieved on 2006-04-22.
Bibliography
- Creed, Roscoe. PBY: The Catalina Flying Boat. Annapolis, MD: US Naval Institute Press, 1986. ISBN 0-87021-526-4.
- Crocker, Mel. Black Cats and Dumbos: WW II's Fighting PBYs. Crocker Media Expressions, 2002. ISBN 0-97129-010-5.
- Dorney, Louis B. US Navy PBY Catalina Units of the Pacific War. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2007. ISBN 1-84176-911-8.
- Hendrie, Andrew. Flying Cats: The Catalina Aircraft in World War II. Annapolis, MD: US Naval Institute Press, 1988. ISBN 0-87021-213-3.
- Kinzey, Bert. PBY Catalina in Detail & Scale. Carrollton, TX: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 2000. ISBN 1-88897-419-2.
- Knott, Richard C. Black Cat Raiders of World War II. Annapolis, MD: US Naval Institute Press, 2000. ISBN 1-55750-471-7.
- Legg, David. Consolidated PBY Catalina: The Peacetime Record. Annapolis, MD: US Naval Institute Press, 2002. ISBN 1-55750-245-5.
- Ragnarsson, Ragnar. US Navy PBY Catalina Units of the Atlantic War. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2006. ISBN 1-84176-910-X.
- Scarborough, William E. PBY Catalina in Action (Aircraft number 62). Carrollton, TX: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1983. ISBN 0-89747-149-0.
- Scarborough, William E. PBY Catalina - Walk Around. Carrollton, TX: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1996. ISBN 0-89747-357-4.
- Wagner, Ray. The Story of the PBY Catalina (Aero Biographies Volume 1). San Diego, CA: Flight Classics, 1972.
External links
- Picture of PH-PBY, a Consolidated PBY-5A Catalina
- Photos of EC-FMC, a Consolidated PBY-5A Catalina located in Ocaña, Spain
- PBY Catalina Foundation
- PBY Catalina International Association
- PBY.com
- PBY Memorial Association
- Second Emergency Rescue Squadron Memorial Page
- Lt. Nathan Gordon, PBY pilot and Medal of Honor recipient
- Catalina Group of New Zealand
- Black Cats: U.S. Navy PBY Catalinas fighting in the Pacific during WWII
- (in French) Naissance d'un PBY 6A Catalina "Calypso" (Birth of a PBY 6A Catalina named Calypso
- The Catalina Society (Plane Sailing) UK
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||
