Ovary
- "Ovaria" redirects here. This is also a proposed section and a synonym of Solanum.
An ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ found in female organisms. It is often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in females are homologous to testes in males. The term gonads refers to the ovaries in females and testes in males.
Human anatomy
Ovaries are oval shaped and, in the human, measure approximately 3 cm x 1.5 cm x 1.5 cm. The ovary (for a given side) is located in the lateral wall of the pelvis in a region called the ovarian fossa. The fossa usually lies beneath the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery.
Each ovary is then attached to the Fimbre of the Fallopian Tube. Usually each ovary takes turns releasing eggs every month; however, if there was a case where one ovary was absent or dysfunctional then the other ovary would continue providing eggs to be released.
Ligaments
In the human the paired ovaries lie within the pelvic cavity, on either side of the uterus, to which they are attached via a fibrous cord called the ovarian ligament. The ovaries are uncovered in the peritoneal cavity but are tethered to the body wall via the suspensory ligament of the ovary. The part of the broad ligament of the uterus that covers the ovary is known as the mesovarium.
Extremities
There are two extremities to the ovary:
- The end to which the uterine tube attach is called the tubal extremity.
- The other extremity is called the uterine extremity. It points downward, and it is attached to the uterus via the ovarian ligament.
Histology
Cell Types
- Follicular Cells - flat epithelial cells that originate from surface epithelium covering the ovary
- granulosa cells - surrounding follicular cells have change from flat to cuboidal and proliferated to produce a stratified epithelium
- Gametes[1]
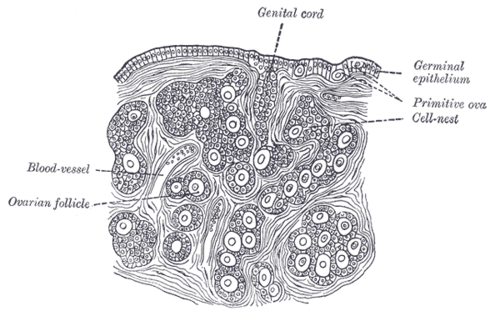
Section of the ovary of a newly born child. Germinal epithelium is seen at top. Primitive ova are seen in their cell-nests. The Genital cord or genital ridge is still discernible in this young child. A blood vessel and an ovarian follicle is also seen
- The outermost layer is called the germinal epithelium.
- The tunica albuginea covers the cortex.
- The ovarian cortex consists of ovarian follicles and stroma in between them. Included in the follicles are the cumulus oophorus, membrana granulosa (and the granulosa cells inside it), corona radiata, zona pellucida, and primary oocyte. The zona pellucida, theca of follicle, antrum and liquor folliculi are also contained in the follicle. Also in the cortex is the corpus luteum derived from the follicles.
- The innermost layer is the ovarian medulla. It can be hard to distinguish between the cortex and medulla, but follicles are usually not found in the medulla.
Quotes
- "It's an ovary!" ~The Magic School Bus
See also
Additional images
References
- ↑ Langman's Medical Embryology, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 10th ed, 2006
External links
- [1] From the American Medical Association
- [2] Merck Online Medical Library: Female Reproductive System
See also
|
Female reproductive system |
|
| Adnexa |
|
Follicles/Folliculogenesis
|
corpus (hemorrhagicum, luteum, albicans) • Theca folliculi (externa, interna) • Follicular antrum (Follicular fluid) • Corona radiata • Zona pellucida • Membrana granulosa (Granulosa cells)
|
|
|
Ovaries/Oogenesis
|
Germinal epithelium • Tunica albuginea • cortex (Cumulus oophorus, Stroma) • Medulla
|
|
|
|
Isthmus • Ampulla • Infundibulum • Fimbria
|
|
|
|
Broad (components: Mesovarium, Mesosalpinx, Mesometrium contents: Round of uterus, Proper of ovary) • Suspensory of ovary • Cardinal
|
|
|
| Uterus |
corpus/body (Cavity of the body, Fundus)
cervix/neck (External orifice, Canal of the cervix, Internal orifice)
layers (Endometrium, Myometrium, Perimetrium) • Uterine horns
|
|
| Vulva/mons pubis |
|
|
vestibular glands/ducts (Bartholin's glands/Bartholin's ducts, Skene's glands/Skene's ducts) • Fossa of vestibule of vagina • Vaginal fornix • Hymen • Orifice
|
|
|
|
commissures (Anterior • Posterior) • Frenulum labiorum pudendi • Labia majora • Cleft of venus • Labia minora • Vulval vestibule • interlabial sulci
|
|
|
|
Vestibular bulbs • Clitoral crura • Corpus cavernosa • Clitoral glans (Frenulum, Hood)
|
|
|
| Breast |
Mammary glands • Nipple • Areola • Lactiferous duct • Cooper's ligaments
|
|
| Vestiges |
Wolffian (Gartner's duct, Epoophoron, Paroöphoron) • Canal of Nuck
|
|
| Other |
G-spot • Urethral sponge • Perineal sponge
|
|

