Oceania
For the Superstate in George Orwell's novel, see Nations of Nineteen Eighty-Four.
Oceania
| Area | 9,008,458 km² (3,478,185.1 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 32,000,000 (6th) |
| Countries | |
| Dependencies | |
| Languages |
25 Official
|
| Time Zones | UTC+8 (Australian Western Standard Time) to UTC-6 (Easter Island) (West to East) |
Oceania (sometimes Oceanica[1]) is a geographical, often geopolitical, region consisting of numerous lands—mostly islands in the Pacific Ocean and vicinity. The term "Oceania" was coined in 1831 by French explorer Dumont d'Urville. The term is used today in many languages to define one of the continents[2][3][4] and is one of eight terrestrial ecozones.
Ethnologically, the islands that are included in Oceania are divided into the subregions of Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.[5]
The boundaries of Oceania are defined in a number of ways. Most definitions recognize parts of Australasia such as Australia, New Zealand and New Guinea, and all or part of the Malay Archipelago as belonging to Oceania.[6][7][8]
Contents |
Extent
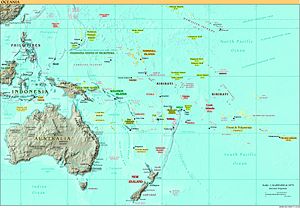
Oceania is traditionally understood as being composed of three regions: Micronesia, Melanesia and Polynesia. As with any region, however, interpretations vary; increasingly, geographers and scientists divide Oceania into Near Oceania and Remote Oceania.[9]
Most of Oceania consists of island nations comprising thousands of coral atolls and volcanic islands, with small human populations. Australia is the only continental country but Indonesia has land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and Malaysia. If the Australia-New Guinea continent is included then the highest point is Puncak Jaya in Papua at 4,884 m (16,024 ft) and the lowest point is Lake Eyre, Australia at 16 m (52 ft) below sea level.
Regions

Descriptions of the regions and constituents of Oceania vary according to source. The table below shows the subregions and countries of Oceania as broadly categorised according to the scheme for geographic subregions used by the United Nations.[10] The information shown follows sources in cross-referenced articles; where sources differ, provisos have been clearly indicated. These territories and regions are subject to various additional categorisations, of course, depending on the source and purpose of each description.
| Name of region, followed by countries and their flags[11] |
Area (km²) |
Population (1 July 2002 estimate) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australasia[12] | ||||
| 7,686,850 | 21,050,000 | 2.7 | Canberra | |
| 268,680 | 4,108,037 | 14.5 | Wellington | |
| Dependencies territories of Australia: | ||||
| 135 | 1,493 | 3.5 | Flying Fish Cove | |
| 14 | 632 | 45.1 | West Island | |
| 35 | 1,866 | 53.3 | Kingston | |
| Melanesia[15] | ||||
| 18,270 | 856,346 | 46.9 | Suva | |
| 499,852 | 4,211,532 | 8.4 | Jakarta | |
| 19,060 | 207,858 | 10.9 | Nouméa | |
| 462,840 | 5,172,033 | 11.2 | Port Moresby | |
| 28,450 | 494,786 | 17.4 | Honiara | |
| 12,200 | 196,178 | 16.1 | Port Vila | |
| Micronesia | ||||
| 702 | 135,869 | 193.5 | Palikir | |
| 549 | 160,796 | 292.9 | Hagåtña | |
| 811 | 96,335 | 118.8 | South Tarawa | |
| 181 | 73,630 | 406.8 | Majuro | |
| 21 | 12,329 | 587.1 | Yaren (de facto) | |
| 477 | 77,311 | 162.1 | Saipan | |
| 458 | 19,409 | 42.4 | Melekeok[18] | |
| 2 | Wake Island | |||
| Polynesia[19] | ||||
| 199 | 68,688 | 345.2 | Pago Pago, Fagatogo[20] | |
| 966 | 609 | 3.2 | Waitangi | |
| 240 | 20,811 | 86.7 | Avarua | |
| 163.6 | 3,791 | 23.1 | Hanga Roa | |
| 3,961 | 257,847 | 61.9 | Papeete | |
| 28,311 | 1,283,388 | 188.6 | Honolulu | |
| 1,981 | 22,080 | 11.14 | Wé | |
| 260 | 2,134 | 8.2 | Alofi | |
| 5 | 47 | 10 | Adamstown | |
| 2,944 | 214,265 | 60.7 | Apia | |
| 10 | 1,431 | 143.1 | —[21] | |
| 748 | 106,137 | 141.9 | Nukuʻalofa | |
| 26 | 11,146 | 428.7 | Funafuti | |
| 274 | 15,585 | 56.9 | Mata-Utu | |
| Total | 9,008,458 | 35,834,670 | 4.0 | |
| Total minus mainland Australia | 1,338,988 | 14,784,670 | 11.2 | |
See Also: List of Oceanian countries by population

Interpretative details and controversies
- New Zealand is the western corner of the Polynesian Triangle. Its indigenous Māori constitute one of the major cultures of Polynesia. It is also, however, considered part of Australasia.[8]
- Hawaii is the northern corner of the Polynesian Triangle and is generally included in Oceania, though politically it is part of the United States. The Hawaiian language is a Polynesian member of the Oceanic language family, and Hawaiian culture is one of the major cultures of Polynesia.
- The U.S. territories in the North Pacific are generally considered part of Oceania.
- Rapa Nui, or Easter Island, is the eastern corner of the Polynesian triangle. A Polynesian island in the eastern Pacific Ocean and part of the territory of Chile, it is generally included in Oceania, in which case the most easterly place in Polynesia and Oceania is its dependency Isla Salas y Gómez 415 km to the East.
- The line in Indonesia dividing Oceania from Asia varies in location and is sometimes considered to be the Wallace Line. See the transcontinental country article.
- East Timor is often reckoned as a part of Oceania due to its location to the east of the Wallace Line and its cultural ties to Pacific peoples. See transcontinental country; [1] Biogeographically, East Timor lies within Wallacea, an ecological transition zone between Asia and Australasia. This transition is less known and less favoured these days as a continental boundary.
- Australia is sometimes not included in Oceania. Terms such as Pacific Islands or South Sea Islands might be used to describe Oceania without Australia (and New Zealand). The term "Australasia" invariably includes Australia, and usually includes New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, and some other parts of Oceania. This term is sometimes controversial, though, as it may may be interpreted as implying an association with Asia — a separate continent — or too great an association with Australia. The term is actually derived from the word "Austral", meaning "of, relating to, or coming from the south". This word represents the common root of both names: Australia and Australasia.
- Although Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands belong to the Commonwealth of Australia, they are west of Sumatra and are commonly associated with Asia, and not with Oceania.
- In its widest sense, the term may embrace the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, thereby including other islands in the Pacific Rim such as the Ryukyu, Kuril and Aleutian islands, the Japanese Archipelago and Taiwan.[2]
Ecogeography
Oceania is one of eight terrestrial ecozones, which constitute the major ecological regions of the planet. The Oceania ecozone includes all of Micronesia, Fiji, and all of Polynesia except New Zealand. New Zealand, New Guinea and nearby islands, Australia, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and New Caledonia constitute the separate Australasia ecozone.
Sport
Pacific Games
The Pacific Games (formerly known as the South Pacific Games) is a multi-sport event, much like the Olympics, (albeit on a much smaller scale), with participation exclusively from countries around the Pacific. It is held every four years and began in 1963.
Football
The Oceania Football Confederation (OFC) is one of six association football confederations[22] under the auspices of FIFA, the international governing body of the sport. The OFC is the only confederation without an automatic qualification to the World Cup Finals. Currently the winner of the OFC qualification tournament must play off against an Asian confederation side to qualify for the World Cup[23],[24].
Oceania has only been represented at three World Cup Finals — Australia in 1974 and 2006 and New Zealand in 1982. However, Australia is now no longer a member of the Oceania Football Confederation, having joined the Asian Football Confederation in 2006.
See also
- Art of Oceania
- Economy of Oceania
- Europeans in Oceania
- Festival of Pacific Arts
- Flags of Oceania
- Geography of Oceania
- History of Oceania
- Military history of Oceania
- Oceania (journal)
- Pacific Games
- Pacific Islands Forum
- Secretariat of the Pacific Community
- United Nations geoscheme for Oceania
Notes
- ↑ "Oceanica" in WordWeb Online dictionary and thesaurus. http://www.wordwebonline.com/en/OCEANICA
- ↑ The Atlas of Canada - The World - Continents
- ↑ List of IOC members (122) by continent. International Olympic Committee: 112th session, Moscow 2001
- ↑ Encarta Mexico "Oceanía"
- ↑ "Oceania". 2005. The Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed. Columbia University Press.
- ↑ Merriam Webster's Online Dictionary (based on Collegiate vol., 11th ed.) 2006. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster, Inc.
- ↑ See, e.g., The Atlas of Canada - The World - Continents
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 United Nations Statistics Division - Countries of Oceania
- ↑ Ben Finney, The Other One-Third of the Globe, Journal of World History, Vol. 5, No. 2, Fall, 1994
- ↑ United Nations Statistics Division - Countries of Oceania
- ↑ Regions and constituents as per UN categorisations/map except notes 2-3, 6. Depending on definitions, various territories cited below (notes 3, 5-7, 9) may be in one or both of Oceania and Asia or North America.
- ↑ The use and scope of this term varies. The UN designation for this subregion is "Australia and New Zealand."
- ↑ New Zealand is often considered part of Polynesia rather than Australasia.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Christmas Island and Cocos (Keeling) Islands are Australian external territories in the Indian Ocean southwest of Indonesia.
- ↑ Excludes parts of Indonesia, island territories in Southeast Asia (UN region) frequently reckoned in this region.
- ↑ Indonesia is generally considered a territory of Southeastern Asia (UN region); wholly or partially, it is also frequently included in Australasia or Melanesia. Figures include Indonesian portion of New Guinea (Irian Jaya) and Maluku Islands.
- ↑ Papua New Guinea is often considered part of Australasia as well as Melanesia.
- ↑ On 7 October 2006, government officials moved their offices in the former capital of Koror to Melekeok, located 20 km northeast of Koror on Babelthuap Island.
- ↑ Excludes the US state of Hawaii, which is distant from the North American landmass in the Pacific Ocean, and Easter Island, a territory of Chile in South America.
- ↑ Fagatogo is the seat of government of American Samoa.
- ↑ Tokelau, a domain of New Zealand, has no capital: each atoll has its own administrative centre.
- ↑ FIFA confederations
- ↑ FIFA world cup 2010 - Oceania preliminary competition
- ↑ FIFA world cup 2010 - qualifying rounds and places available by confederation
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||