Occipital bone
| Bone: Occipital bone | |
|---|---|
 |
|
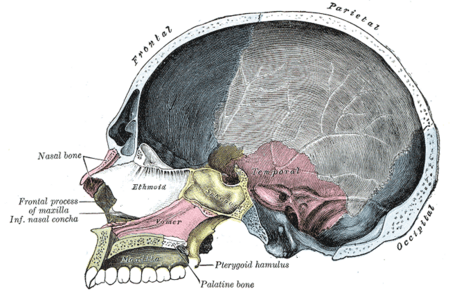
| Sagittal section of skull. (Occipital bone is at right, in blue.) | |
 |
|
| Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Occipital bone is at bottom, in blue.) | |
| Gray's | subject #31 129 |
| Articulations | the two parietals, the two temporals, the sphenoid, and the atlas |
The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoid in shape and curved on itself. It is pierced by a large oval aperture, the foramen magnum, through which the cranial cavity communicates with the vertebral canal.
- The curved, expanded plate behind the foramen magnum is named the squama occipitalis.
- The thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen is called the basilar part of occipital bone.
- On either side of the foramen are the lateral parts of occipital bone.
Contents |
Foramen magnum
- See also Foramen magnum
The foramen magnum is a large oval aperture with its long diameter antero-posterior; it is wider behind than in front where it is encroached upon by the condyles.
It transmits the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the accessory nerves, the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, and the membrana tectoria and alar ligaments.
Angles
The superior angle of the occipital bone articulates with the occipital angles of the parietal bones and, in the fetal skull, corresponds in position with the posterior fontanelle.
The inferior angle is fused with the body of the sphenoid. The lateral angles are situated at the extremities of the grooves for the transverse sinuses: each is received into the interval between the mastoid angle of the parietal and the mastoid part of the temporal.
Borders
The superior borders extend from the superior to the lateral angles: they are deeply serrated for articulation with the occipital borders of the parietals, and form by this union the lambdoidal suture.
The inferior borders extend from the lateral angles to the inferior angle; the upper half of each articulates with the mastoid portion of the corresponding temporal, the lower half with the petrous part of the same bone.
These two portions of the inferior border are separated from one another by the jugular process, the notch on the anterior surface of which forms the posterior part of the jugular foramen.
Structure
The occipital, like the other cranial the outer and inner tables, between which is the cancellous tissue or diploë; the bone is especially thick at the ridges, protuberances, condyles, and anterior part of the basilar part; in the inferior fossæ it is thin, semitransparent, and destitute of diploë.
Additional images
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
See also
- Bone terminology
- Comparative anatomy
- Neanderthal
- Occipital bun
- Terms for anatomical location
- Ossification of occipital bone
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||