New Horizons
 |
|
| Organization | NASA |
|---|---|
| Major contractors | JHU APL, SwRI |
| Mission type | Flyby |
| Flyby of | Jupiter, Pluto, and Charon |
| Flyby date | July 14, 2015 |
| Launch date | January 19, 2006 |
| Launch vehicle | Atlas V-551 |
| Mission duration | Flyby of Pluto (>10 yr) |
| NSSDC ID | 2006-001A |
| Home page | New Horizons Home |
| Mass | 478 kg |
| Orbital elements | |
| Inclination | Currently negligible (As of 2006[update]) |

New Horizons is a robotic spacecraft mission by NASA currently underway. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study the dwarf planet Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, and Hydra. NASA may also approve flybys of one or more other Kuiper Belt Objects.
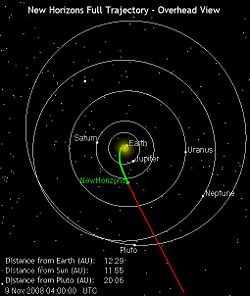
New Horizons was launched on 19 January 2006 directly into an Earth-and-solar-escape trajectory. It had an Earth-relative velocity of about 10.1 miles per second or 36,360 miles per hour (16.26 km/s or 58,536 km/h) after its last engine shut down, making it the fastest spacecraft and man-made object launched/created, to date. It flew by Jupiter on 28 February 2007 at 5:43:40 UTC and Saturn's orbit on 8 June 2008 at 10:00:00 UTC. It will arrive at Pluto on 14 July 2015 then continue into the Kuiper belt.
Contents |
Background
New Horizons is the first mission in NASA's New Frontiers mission category, larger and more expensive than Discovery missions but smaller than "flagship" programs. The cost of the mission (including spacecraft and instrument development, launch vehicle, mission operations, data analysis, and education/public outreach) is approximately $650 million over 15 years (from 2001 to 2016). An earlier proposed Pluto mission – Pluto Kuiper Express – was cancelled by NASA in 2000 for budgetary reasons.
The New Horizons craft was built primarily by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL). The mission's principal investigator is Dr. S. Alan Stern (NASA Associate Administrator, formerly of the Southwest Research Institute).
Overall control, after separation from the launch vehicle, is performed at Mission Operations Center (MOC) at the Applied Physics Laboratory. The science instruments are operated at the Clyde Tombaugh Science Operations Center (T-SOC) in Boulder, Colorado. Navigation, which is not realtime, is performed at various contractor facilities; KinetX is the lead on the New Horizons navigation team and is responsible for planning trajectory adjustments as the spacecraft speeds toward the outer solar system.
New Horizons was originally planned as a voyage to what was then the only unexplored planet in the Solar System. When the spacecraft was launched, Pluto was still classified as a planet, later to be reclassified as a dwarf planet by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). However, some members of the New Horizons team, including Alan Stern, disagree with the IAU definition and therefore still describe Pluto as the ninth planet.[1] Pluto's newly-discovered satellites, Nix and Hydra, also have a connection with the spacecraft: The first letters of their names, N and H, are the initials of "New Horizons". The moons' discoverers chose these names for this reason, in addition to Nix and Hydra's relationship to the mythological Pluto.[2]
In addition to the scientific equipment, there are several cultural artifacts travelling with the spacecraft. These include a collection of 430,000 names stored on a compact disc,[3] a piece of Scaled Composites SpaceShipOne,[4] and an American flag, along with other mementos.[5] One of the trim weights on the spacecraft is a Florida state quarter, and principal investigator Alan Stern has also confirmed that some of the ashes of Pluto discoverer Clyde Tombaugh are aboard the spacecraft.[6]
Mission profile
Launch


The launch of New Horizons was originally scheduled for January 11, 2006, but was initially delayed until January 17 to allow for borescope inspections of the Atlas rocket's kerosene tank. Further delays related to low cloud ceiling conditions downrange, high winds and technical difficulties unrelated to the rocket itself prevented launch for a further two days. The probe finally lifted off from Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, directly south of Space Shuttle Launch Complex 39, at 14:00 EST on January 19, 2006.
The Centaur second stage reignited at 14:30 EST (19:30 UTC), successfully sending the probe out of Earth orbit. New Horizons took only nine hours to reach the Moon's orbit, passing lunar orbit before midnight EST that day.
Although there were backup launch opportunities in February 2006 and February 2007, only the first 23 days of the 2006 window permitted the Jupiter flyby. Any launch outside that period would have forced the spacecraft to fly a slower trajectory directly to Pluto, delaying its encounter by 2–4 years.
The craft was launched by a Lockheed Martin Atlas V 551 rocket, with a Boeing Star 48B third stage added to increase the heliocentric (escape) speed. This was the first launch of the 551 configuration of the Atlas V. Previous flights had used none, two, or three solid boosters, but never five. This puts the Atlas V 551 takeoff thrust, at well over 2 million lbf (9 MN), past the Delta IV-Heavy, of under 2 million lbf. The major part of this thrust is supplied by two Russian RD-180 engines, 4.152 MN each. The Delta IVH remains the larger vehicle, at over 1,600,000 lb (725 Mg) versus AV-010's 1,260,000 lb (570 Mg). The Atlas V rocket had earlier been slightly damaged when Hurricane Wilma swept across Florida on October 24, 2005. One of the solid rocket boosters was hit by a door. The booster was replaced with an identical unit, rather than inspecting and requalifying the original.[7]
The Star 48B third stage is also on a hyperbolic solar system escape orbit, and beat the New Horizons spacecraft to Jupiter. So did two small despin masses, the "yo-yo masses," released from the stage. However, since they are not in controlled flight, they did not receive the correct gravity assist, and will only pass within 200 million miles (320 million km) of Pluto.[8]
New Horizons holds the record as the fastest spacecraft ever launched, having achieved the highest Earth-relative velocity and thus leaving Earth faster than any other spacecraft to date. It is also the first spacecraft launched directly into a solar escape trajectory, which requires an approximate velocity of 16.5 km/s, plus losses, all to be provided by the launcher. However, it will not be the fastest spacecraft to leave the solar system. This record is held by Voyager 1, currently travelling at 17.145 km/s (38,350 mph) relative to the Sun. Voyager 1 attained greater hyperbolic excess velocity from Jupiter and Saturn gravitational slingshots than New Horizons. Other spacecraft, such as Helios 1 & 2, can also be measured as the "fastest" objects, due to their orbital velocity relative to the Sun at perihelion. However, because they remain in solar orbit, their orbital energy relative to the Sun is lower than the five probes (and three other third stages on hyperbolic trajectories), including New Horizons, that achieved solar escape velocity. (The Sun has a far more massive gravity well than Earth.)
Trajectory corrections and instrument testing
On January 28 and January 30, 2006, mission controllers guided the probe through its first trajectory correction maneuver (TCM), which was divided into two parts called TCM-1A and TCM-1B. The total velocity change of these two corrections was about 18 meters per second. TCM-1 was accurate enough to permit the cancellation of TCM-2, the second of three originally scheduled corrections.[9]
During the week of February 20, controllers conducted initial in-flight tests of three onboard scientific instruments, the Alice ultraviolet imaging spectrometer, the PEPSSI plasma-sensor, and the LORRI long-range visible-spectrum camera. No scientific measurements or images were taken, but instrument electronics (and in the case of Alice, some electromechanical systems) were shown to be functioning correctly.[10]
On March 9 at 1700 UTC, controllers performed TCM-3, the last of three scheduled course corrections. The engines burned for 76 seconds, adjusting the spacecraft's velocity by about 1.16 meters per second.[11]
Passing Mars orbit and asteroid flyby
On April 7, 2006 at 10:00 UTC, the spacecraft passed the orbit of Mars, moving at roughly 21 km/s away from the Sun at a solar distance of 243 million kilometers.[12]
New Horizons made a distant flyby of the small asteroid 132524 APL (previously known by its provisional designation, 2002 JF56), at a distance of 101,867 km at 04:05 UTC on June 13, 2006. The best current estimate of the asteroid's diameter is approximately 2.3 kilometers, and the spectra obtained by New Horizons showed that APL is an S-type asteroid.
The spacecraft successfully tracked the asteroid over June 10 – June 12, 2006. This allowed the mission team to test the spacecraft's ability to track rapidly moving objects. Images were obtained through the Ralph telescope.[13]
Jupiter gravity assist

New Horizons' Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) took its first photographs of Jupiter on September 4, 2006. The spacecraft began further study of the Jovian system in December 2006.[14]
New Horizons received a Jupiter gravity assist with a closest approach at 5:43:40 UTC (12:43:40am EST) on February 28, 2007. It passed through the Jupiter system at 21 km/s (46,975 mph) relative to Jupiter (23 km/s (51,449 mph) relative to the Sun). The flyby increased New Horizons' speed away from the Sun by nearly 4 km/s (8,947 mph), putting the spacecraft on a faster trajectory to Pluto, about 2.5 degrees out of the plane of the Earth's orbit (the "ecliptic"). As of 2008, the gravitational attraction of the Sun has subsequently slowed down the spacecraft to about 12 miles per second (19.31 km/s).[15] New Horizons was the first probe launched directly towards Jupiter since the Ulysses probe in 1990.
While at Jupiter, New Horizons' instruments made refined measurements of the orbits of Jupiter's inner moons, particularly Amalthea. The probe's cameras measured volcanoes on Io and studied all four Galilean moons in detail, as well as long distance studies of the outer moons Himalia and Elara. Imaging of the Jovian system began on September 4, 2006.[16] The craft also studied Jupiter's Little Red Spot and the planet's magnetosphere and tenuous ring system.[17]
Pluto approach

The first images of Pluto from New Horizons were created between September 21–24, 2006, during a test of the LORRI. They were released on November 28.[18] The images, taken from a distance of approximately 4.2 billion kilometers (2.6 billion miles), confirmed the spacecraft's ability to track distant targets, critical for maneuvering toward Pluto and other Kuiper Belt objects.
It is planned for New Horizons to fly within 10,000 km (6,200 mi) of Pluto. New Horizons will have a relative velocity of 13.78 km/s at closest approach, and will come as close as 27,000 km (16,800 mi) to Charon, although these parameters may be changed during flight.
Kuiper Belt mission
After passing by Pluto, New Horizons will continue further into the Kuiper Belt. Mission planners are now searching for one or more additional Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs) on the order of 50–100 km (30–60 mi) in diameter for flybys similar to the spacecraft's Plutonian encounter. As maneuvering capability is limited, this phase of the mission is contingent on finding suitable KBOs close to New Horizons flight path, ruling out any possibility for a planned flyby of Eris, a trans-Neptunian object larger than Pluto.[19] The available region, being fairly close to the plane of the Milky Way and thus difficult to survey for dim objects, is one that has not been well-covered by previous KBO search efforts.
Summary of key mission dates
Already accomplished
- June 8, 2001 — New Horizons picked by NASA over a competing design, POSSE (Pluto and Outer Solar System Explorer).
- June 13, 2005 — Spacecraft departed APL for final testing at Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).
- September 24, 2005 — Spacecraft shipped to Cape Canaveral, through Andrews Air Force Base, aboard a C-17 Globemaster III cargo aircraft.
- December 17, 2005 — Transported from Hazardous Servicing Facility to Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41.
- January 11, 2006 — Primary launch window opened. Launch delayed for further testing.
- January 16, 2006 — Atlas V rocket launcher, serial number AV-010, rolled out onto pad.
- January 17, 2006 — First day launch attempts scrubbed because of unacceptable weather conditions (high winds).
- January 18, 2006 — Second launch attempt scrubbed because of morning power outage at the Applied Physics Laboratory.
- January 19, 2006 — Successful launch at 14:00 EST (19:00 UTC) after brief delay due to cloud cover.
- April 7, 2006 — The probe passed Mars' orbit.
- Early May, 2006 — The probe entered the asteroid belt.
- June 13, 2006 — The probe passed closest to the asteroid 132524 APL in the Belt at about 101,867 km at 04:05 UTC. Pictures were taken.
- Late October, 2006 — The probe left the asteroid belt.
- November 28, 2006 — First faint image of Pluto taken from a distance released.
- January 8, 2007 — Start of Jupiter encounter.
- January 10, 2007 — Long distance observations of outer moon Callirrhoe as a navigation exercise.
- February 28, 2007 — Jupiter flyby. Closest approach occurred at 05:43:40 UTC at 2.305 million km, 21.219 km/s.
- March 5, 2007 — End of Jupiter encounter phase.
- June 8, 2008 — The probe passed Saturn's orbit.
Planned
- March 18, 2011 — The probe will pass Uranus' orbit.
- August 1, 2014 — The probe will pass Neptune's orbit.
- July 14, 2015 — Flyby of Pluto around 11:47 UTC at 13695 km, 13.78 km/s.
- July 14, 2015 — Flyby of Charon around 12:01 UTC at 29473 km, 13.87 km/s.
- 2016-2020 — Possible flyby of one or more Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs).
- 2029 — The probe leaves the solar system.
Spacecraft subsystems
Structural overview
The spacecraft is comparable in size and general shape to a grand piano and has been compared to a "piano glued to a sports-car-sized satellite dish". As a point of departure, the team took inspiration from the Ulysses spacecraft,[20] which also carried an RTG and dish on a box-in-box structure through the outer Solar System. Many subsystems and components have flight heritage from APL's CONTOUR spacecraft, which in turn had heritage from APL's TIMED spacecraft.
Structural
The spacecraft's body forms a triangle, almost 2.5 feet (0.75 m) thick. (The Pioneers had hexagonal bodies, while the Voyagers, Galileo, and Cassini-Huygens had decagonal, hollow bodies.) A 7075 (alloy) aluminum tube forms the main structural column, between the launch vehicle adapter ring at the "rear," and the 2.1 m radio dish antenna affixed to the "front" flat side. The titanium fuel tank is in this tube. The radioisotope thermoelectric generator, or RTG attaches with a 4-sided titanium mount resembling a grey pyramid or stepstool. Titanium provides strength and thermal isolation. The rest of the triangle is primarily sandwich panels of thin aluminum facesheet (less than 1/64" or 0.4 mm) bonded to aluminum honeycomb core.

The structure is larger than strictly necessary, with empty space inside. The structure is designed to act as shielding, reducing electronics errors caused by radiation from the RTG. Also, the mass distribution required for a spinning spacecraft demands a wider triangle.
Propulsion and attitude control
New Horizons has both spin-stabilized (cruise) and three-axis stabilized (science) modes, controlled entirely with hydrazine monopropellant. Seventy-seven kilograms of hydrazine provides a delta-v capability of over 290 m/s after launch. Helium is used as a pressurant, with an elastomeric diaphragm assisting expulsion. The spacecraft's on-orbit mass including fuel will be over 470 kg for a Jupiter flyby trajectory, but would have been only 445 kg for a direct flight to Pluto. This would have meant less fuel for later Kuiper Belt operations and is caused by the launch vehicle performance limitations for a direct-to-Pluto flight.
There are 16 thrusters on New Horizons: four 1 lbf (4.4 N) and twelve 0.2 lbf (0.9 N) plumbed into redundant branches. The larger thrusters are used primarily for trajectory corrections, and the small ones (previously used on Cassini and the Voyager spacecraft) are used primarily for attitude control and spinup/spindown maneuvers. Two star cameras (from Galileo Avionica) are used for fine attitude control. They are mounted on the face of the spacecraft and provide attitude information while in spinning or in 3-axis mode. Between star camera readings, knowledge is provided by dual redundant Miniature Inertial Measurement Unit (MIMU) from Honeywell. Each unit contains three solid-state gyroscopes and three accelerometers. Two Adcole Sun sensors provide coarse attitude control. One detects angle to the Sun, while the other measures spin rate and clocking.
Power
A cylindrical radioisotope thermoelectric generator, or RTG, protrudes from one vertex in the plane of the triangle. The RTG will provide about 240 W, 30 V DC at launch, decaying to 200 W at encounter in 2015. The RTG, model "GPHS-RTG," was originally a spare from the Cassini mission. The RTG contains 11 kg (24 pounds) of plutonium-238 oxide pellets. Each pellet is clad in iridium, then encased in a graphite shell.
It was developed by the U.S. Department of Energy[21][22] at the Materials and Fuels Complex (formerly Argonne West), a part of the Idaho National Laboratory in Butte County, Arco, Idaho.[23] The plutonium was produced at Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico . Less than the original design goal was produced, due to delays at the United States Department of Energy, including security activities, which held up production. The mission parameters and observation sequence had to be modified for the reduced wattage; still, not all instruments can operate simultaneously. The Department of Energy transferred the space battery program from Ohio to Argonne in 2002 because of security concerns.
There are no onboard batteries. RTG output is relatively predictable; load transients are handled by a capacitor bank and fast circuit breakers.
Thermal
Internally, the structure is painted black. This equalizes temperature by radiative heat transfer.
Overall, the spacecraft is thoroughly blanketed to retain heat. Unlike the Pioneers and Voyagers, the radio dish is also enclosed in blankets which extend to the body. The heat from the RTG also adds warmth to the spacecraft in the outer solar system. In the inner solar system, the spacecraft must prevent overheating. Electronic activity is limited, power is diverted to shunts with attached radiators, and louvers are opened to radiate excess heat. Then, when the spacecraft is cruising inactively in the cold outer solar system, the louvers are closed, and the shunt regulator reroutes power to electric heaters.
Telecommunications

Communication with the spacecraft is via X band, at a rate of approximately 1000 bit/s from Pluto's distance (38 kbit/s at Jupiter) to a 70 m Deep Space Network (DSN) dish. The spacecraft uses dual redundant transmitters and receivers, and either right- or left-hand circular polarization. The downlink signal is amplified by dual redundant 12-watt TWTAs (traveling-wave tube amplifiers) mounted on the body under the dish. The receivers are new, low-power designs. The system can be controlled to power both TWTAs at the same time, and transmit a dual-polarized downlink signal to the DSN that could almost double the downlink rate. Initial tests with the DSN in this dual-polarized mode have been successful, and an effort to make the DSN polarization-combining technique operational is underway.
In addition to the high-gain antenna, there are two low-gain antennas and a medium-gain dish. The high-gain dish has a Cassegrain layout, composite construction, and a 2.1 meter diameter (providing well over 40 dB of gain, and a half-power beam width of about a degree). The prime-focus, medium-gain antenna, with a 0.3 meter aperture and 10-degree half-power beamwidth, is mounted to the back of the high-gain antenna's secondary reflector. The forward low-gain antenna is stacked atop the feed of the medium-gain antenna. The aft low-gain antenna is mounted within the launch adapter at the rear of the spacecraft. This antenna was only used for early mission phases near Earth, just after launch and for emergencies if the spacecraft had lost attitude control.
To save mission costs, the spacecraft will be in "hibernation" between Jupiter and Pluto. It will awaken once per year, for 50 days, for equipment checkout and trajectory tracking. The rest of the time, the spacecraft will be in a slow spin, sending a beacon tone once per week. Depending on frequency, the beacon indicates normal operation, or one of seven fault modes. New Horizons is the first mission to use the DSN's beacon tone system operationally, the system having been flight-tested by the DS1 mission.
Data handling
New Horizons will record scientific instrument data to its solid-state buffer at each encounter, then transmit the data to Earth. Data storage is done on two low-power solid-state recorders (one primary, one backup) holding up to 8 gigabytes (64 gigabits) each. Because of the extreme distance from Pluto and the Kuiper Belt, only one buffer load at those encounters can be saved. This is because New Horizons will have left the vicinity of Pluto (or future target object) by the time it takes to transmit the buffer load back to Earth.
Part of the reason for the delay between the gathering and transmission of data is because all of the New Horizons instrumentation is body-mounted. In order for the cameras to record data, the entire probe must turn, and the one-degree-wide beam of the high-gain antenna will almost certainly not be pointing toward Earth. Previous spacecraft, such as the Voyager program probes, had a rotatable instrumentation platform (a "scan platform") that could take measurements from virtually any angle without losing radio contact with Earth. New Horizons' elimination of excess mechanisms was implemented to save weight, shorten the schedule, and improve reliability to achieve a 15+-year lifetime.
(The Voyager 2 spacecraft experienced platform jamming at Saturn; the demands of long time exposures at Uranus led to modifications of the probe to rotate the entire probe instead to achieve the time exposure photos at Uranus and Neptune, similar to how New Horizons will rotate.)
Flight computer
The spacecraft carries two computer systems, the Command and Data Handling system and the Guidance and Control processor. Each of the two systems is duplicated for redundancy, giving a total of four computers. The processor used is the Mongoose-V, a 12 MHz radiation-hardened version of the MIPS R3000 CPU. Multiple clocks and timing routines are implemented in hardware and software to help prevent faults and downtime.
To conserve heat and mass, spacecraft and instrument electronics are housed together in IEMs (Integrated Electronics Modules). There are two redundant IEMs. Including other functions such as instrument and radio electronics, each IEM contains 9 boards.
Mission science
Instrument suite
The spacecraft carries seven scientific instruments. Total mass is 31 kg; rated power is 21 watts (though not all instruments operate simultaneously).[24]
- Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI)
- a visible-light, high-resolution CCD imager with a 208.3 mm (8.2 inch) aperture and 1024×1024 monochromatic CCD. Resolution is 5 microradians (approximately one arcsecond). The CCD is chilled far below freezing by a passive radiator on the antisolar face of the spacecraft. This temperature differential requires insulation, and isolation from the rest of the structure. The Ritchey-Chretien mirrors and metering structure are made of silicon carbide, to boost stiffness, reduce weight, and prevent warping at low temperatures. The optical elements sit in a composite light shield, and mount with titanium and fibreglass for thermal isolation. Overall mass is 8.6 kg, with the OTA weighing about 5.6 kg,[25] for one of the largest silicon-carbide telescopes yet flown.
- Pluto Exploration Remote Sensing Investigation (PERSI)
- This consists of two instruments: The Ralph telescope, 6 centimetres in aperture, with two separate channels: a visible-light CCD imager (MVIC- Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera) with broadband and color channels, and a near-infrared imaging spectrometer, LEISA (Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array). LEISA is derived from a similar instrument on the EO-1 mission. The second instrument is an ultraviolet imaging spectrometer, Alice. Alice resolves 1,024 wavelength bands in the far and extreme ultraviolet (from 180 to 50 nanometres), over 32 view fields. This Alice is derived from an Alice on the Rosetta mission. Ralph, designed afterwards, was named after Alice's husband on The Honeymooners. Ralph and Alice are names, not acronyms.
- Plasma and high energy particle spectrometer suite (PAM)
- Two instruments, consisting of SWAP (Solar Wind Analyser around Pluto), a toroidal electrostatic analyzer and retarding potential analyser, and PEPSSI (Pluto Energetic Particle Spectrometer Science Investigation), a time of flight ion and electron sensor. SWAP measures particles of up to 6.5 keV, PEPSSI goes up to 1 MeV. Because of the tenuous solar wind at Pluto's distance, the SWAP instrument has the largest aperture of any such instrument ever flown.
- Radio Science Experiment (REX)
- REX will use an ultrastable crystal oscillator (essentially a calibrated crystal in a miniature oven) and some additional electronics to conduct radio science investigations using the communications channels. These are small enough to fit on a single card. Since there are two redundant communications subsystems, there are two, identical REX circuit boards.
- Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter (VBSDC)
- Built by students at the University of Colorado at Boulder, the Student Dust Counter will operate continuously through the trajectory to make dust measurements. It consists of a detector panel, about 18 inches × 12 inches (460 mm by 300 mm), mounted on the antisolar face of the spacecraft (the ram direction), and an electronics box within the spacecraft. The detector contains fourteen PVDF panels, twelve science and two reference, which generate voltage when impacted. Effective collecting area is 0.125 m². No dust counter has operated past the orbit of Uranus; models of dust in the outer solar system, especially the Kuiper Belt, are speculative. The dust counter is named for Venetia Burney, who first suggested the name "Pluto" at the age of 11.
Science objectives and observation plan

Jupiter observations
The flyby came within about 32 Jovian radii (3 Gm) of Jupiter and was the center of a 4-month intensive observation campaign. Jupiter is an interesting, ever-changing target, observed intermittently since the end of the Galileo mission. New Horizons also has instruments built using the latest technology, especially in the area of cameras. They are much improved over Galileo's cameras, which were evolved versions of Voyager cameras which, in turn, were evolved Mariner cameras. The Jupiter encounter also served as a shakedown and dress rehearsal for the Pluto encounter. Because of the much shorter distance from Jupiter to Earth, the communications link can transmit multiple loadings of the memory buffer. The mission will actually return more data from Jupiter than Pluto. Imaging of Jupiter began on September 4, 2006, after which several images were taken.[26]
Jupiter

The primary encounter goals included Jovian cloud dynamics, which were greatly reduced from the Galileo observation program, and particle readings from the magnetotail of the Jovian magnetosphere. The spacecraft trajectory coincidentally flew down the magnetotail for months. New Horizons also examined the Jovian nightside for aurorae and lightning.
New Horizons also provided the first close-up examination of Oval BA, a storm feature that has informally become known as the "Little Red Spot", since the storm turned red. It was still a white spot when Cassini flew by.

Jovian moons
The major (Galilean) moons were in poor position. The aim point of the gravity-assist maneuver meant the spacecraft passed millions of kilometers from any of the Galilean moons. Still, the New Horizons instruments were intended for small, dim targets, so they were scientifically useful on large, distant moons. LORRI searched for volcanoes and plumes on Io. The infrared capabilities of LEISA searched for chemical compositions (including Europa ice dopants), and nightside temperatures (including hotspots on Io). The ultraviolet resolution of Alice searched for aurorae and atmospheres, including the Io torus.
Minor moons such as Amalthea had their orbit solutions refined. The cameras determined their position, acting as "reverse optical navigation".
Pluto flyby
Observations of Pluto, with LORRI plus Ralph, will begin about 6 months prior to closest approach. The targets will be only a few pixels across. This should detect any rings or any additional moons (eventually down to 2 kilometers diameter), for avoidance and targeting maneuvers, and observation scheduling. 70 days out, resolution will exceed the Hubble Space Telescope's resolution, lasting another two weeks after the flyby. Long-range imaging will include 40 km (25 mi) mapping of Pluto and Charon 3.2 days out. This is half the rotation period of Pluto-Charon and will allow imaging of the side of both bodies that will be facing away from the spacecraft at closest approach. Coverage will repeat twice per day, to search for changes due to snows or cryovolcanism. Still, due to Pluto's tilt and rotation, a portion of the northern hemisphere will be in shadow at all times.
During the flyby, LORRI should be able to obtain select images with resolution as high as 50 m/px (if closest distance is around 10,000 km), and MVIC should obtain 4-color global dayside maps at 1.6 km resolution. LORRI and MVIC will attempt to overlap their respective coverage areas to form stereo pairs. LEISA will obtain hyperspectral near-infrared maps at 7 km/px globally and 0.6 km/pixel for selected areas. Meanwhile, Alice will characterize the atmosphere, both by emissions of atmospheric molecules (airglow), and by dimming of background stars as they pass behind Pluto (occultation).
During and after closest approach, SWAP and PEPSSI will sample the high atmosphere and its effects on the solar wind. VBSDC will search for dust, inferring meteoroid collision rates and any invisible rings. REX will perform active and passive radio science. Ground stations on Earth will transmit a powerful radio signal as New Horizons passes behind Pluto's disk, then emerges on the other side. The communications dish will measure the disappearance and reappearance of the signal. The results will resolve Pluto's diameter (by their timing) and atmospheric density and composition (by their weakening and strengthening pattern). (Alice can perform similar occultations, using sunlight instead of radio beacons.) Previous missions had the spacecraft transmit through the atmosphere, to Earth ("downlink"). Low power and extreme distance means New Horizons will be the first such "uplink" mission. Pluto's mass and mass distribution will be evaluated by their tug on the spacecraft. As the spacecraft speeds up and slows down, the radio signal will experience a Doppler shift. The Doppler shift will be measured by comparison with the ultrastable oscillator in the communications electronics.
Reflected sunlight from Charon will allow some imaging observations of the nightside. Backlighting by the Sun will highlight any rings or atmospheric hazes. REX will perform radiometry of the nightside.
Initial, highly-compressed images will be transmitted within days. The science team will select the best images for public release. Uncompressed images will take about nine months to transmit, depending on Deep Space Network traffic. It may turn out, however, that fewer months will be needed. The spacecraft link is proving stronger than expected, and it is possible that both downlink channels may be ganged together to boost performance even further.
- Primary objectives (required)
- Characterize the global geology and morphology of Pluto and Charon
- Map chemical compositions of Pluto and Charon surfaces
- Characterize the neutral (non-ionized) atmosphere of Pluto and its escape rate
Loss of any of these objectives will constitute a failure of the mission.
- Secondary objectives (expected)
- Characterize the time variability of Pluto's surface and atmosphere
- Image select Pluto and Charon areas in stereo
- Map the terminators (day/night border) of Pluto and Charon with high resolution
- Map the chemical compositions of select Pluto and Charon areas with high resolution
- Characterize Pluto's ionosphere, and its interaction with the solar wind
- Search for neutral species such as H2, HCN, hydrocarbons, and other nitriles in the atmosphere
- Search for any Charon atmosphere
- Determine bolometric bond albedos for Pluto and Charon
- Map surface temperatures of Pluto and Charon
It is expected, but not demanded, that most of these objectives will be met.
- Tertiary objectives (desired)
- Characterize the energetic particle environment at Pluto and Charon
- Refine bulk parameters (radii, masses) and orbits of Pluto and Charon
- Search for additional moons, and any rings
These objectives may be attempted, though they may be skipped in favor of the above objectives. An objective to measure any magnetic field of Pluto was dropped. A magnetometer instrument could not be implemented within a reasonable mass budget and schedule, and SWAP and PEPSSI could do an indirect job detecting some magnetic field around Pluto.
Asteroid belt

Because of the need to conserve fuel for possible encounters with Kuiper-belt objects subsequent to the Pluto flyby, intentional encounters with objects in the asteroid belt were not planned. Subsequent to launch, the New Horizons team scanned the spacecraft's trajectory to determine if any asteroids would, by chance, be close enough for observation. In May 2006 it was discovered that New Horizons would pass close to the tiny asteroid 132524 APL on June 13, 2006. Closest approach occurred at 4:05 UTC at a distance of 101,867 kilometers. The asteroid was imaged by Ralph (use of LORRI at that time was not possible due to proximity to sun), which gave the team a chance to exercise Ralph's capabilities, and make observations of the asteroid's composition as well as light and phase curves. The asteroid's size was estimated to be 2.5 kilometers in diameter.[27][28][29]
Neptune Trojans
New Horizons' trajectory to Pluto passes near Neptune's trailing Lagrange point ("L5"). A number of "Trojan asteroids" have been discovered in these regions recently, although it is not yet known if New Horizons will pass close to any. If any asteroids are found to be close enough to be studied, observations will be planned.[30] Unfortunately, the Lagrange point comes shortly before the Pluto encounter. Depending on where the asteroid is along the spacecraft trajectory, New Horizons may not have significant downlink bandwidth, and thus free memory, for Trojan data.
Kuiper-Belt objects
New Horizons is designed to fly past one or more Kuiper-belt objects after passing Pluto. Because the flight path is determined by the Pluto flyby, with only minimal hydrazine remaining, objects must be found within a cone, extending from Pluto, of less than a degree's width, within 55 AU. Past 55 AU, the communications link becomes too weak, and the RTG wattage will have decayed significantly enough to hinder observations. Desirable KBOs will be well over 50 km in diameter, neutral in color (to compare with the reddish Pluto), and, if possible, possess a moon. Because the population of KBOs appears quite large, multiple objects may qualify. Large ground telescopes will find suitable objects up until the Pluto flyby; the Pluto aim point, plus some thruster firing, will then determine the subsequent trajectory. KBO flyby observations will be similar to those at Pluto, but reduced due to lower light, power, and bandwidth.
References
- ↑ "Unabashedly Onward to the Ninth Planet". New Horizons website. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2008-10-25.
- ↑ "Pluto’s Two Small Moons Christened Nix and Hydra". New Horizons website. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2008-10-25.
- ↑ "Home". New Horizons website. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
- ↑ "Pluto Mission to Carry Piece of SpaceShipOne", Space.com (December 20, 2005).
- ↑ "To Pluto, With Postage", collectSPACE (October 28, 2008).
- ↑ title=www.space.com/astronotes/astronotes.html New Horizons launches on voyage to Pluto and beyond (January 19, 2006, from 'spaceflightnow.com'. Retrieved 2007-10-23.)
- ↑ "Damage prompts booster replacement for Pluto probe". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved on 2007-07-31.
- ↑ "Derelict Booster to Beat Pluto Probe to Jupiter". Space.com. Retrieved on September 22, 2006.
- ↑ Stern, Alan (January 31 2006). "Our Aim Is True" (HTML). The PI's Perspective. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
- ↑ Stern, Alan (February 27 2006). "Boulder and Baltimore" (HTML). The PI's Perspective. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ "Outbound for the Frontier, New Horizons Crosses the Orbit of Mars", Johns Hopkins APL (April 7, 2006).
- ↑ "New Horizons Tracks an Asteroid", Johns Hopkins APL (June 15, 2006).
- ↑ "New Horizons Web Site". Pluto.jhuapl.edu. Retrieved on 2008-10-27.
- ↑ The episode of the History Channel program The Universe devoted to Pluto and Neptune mentions this, as in its August 26, 2008 broadcast.
- ↑ Alexander, Amir (September 27, 2006). "New Horizons Snaps First Picture of Jupiter". The Planetary Society. Retrieved on 2006-12-19.
- ↑ "Fantastic Flyby", NASA, May 1, 2007
- ↑ "New Horizons, Not Quite to Jupiter, Makes First Pluto Sighting".
- ↑ NASA (2006-04-11). "Hubble Finds 'Tenth Planet' is Slightly Larger than Pluto". Press release. Retrieved on 2006-06-10.
- ↑ http://www.boulder.swri.edu/pkb/ssr/ssr-fountain.pdf
- ↑ The use of a plutonium RTG battery resulted in minor demonstrations some days before launch by about 30 anti-nuclear protesters. The amount of radioactive plutonium in the RTG is 10.9 kg, about one-third the amount on-board the Cassini-Huygens probe when it launched in 1997. That launch was protested by over 300 people. The United States Department of Energy estimated the chances of a launch accident that would release radiation into the atmosphere at 1 in 350 and monitored the launch as it always does when RTGs are involved. It was believed that a worst-case scenario of total dispersal of on-board plutonium would spread the equivalent radiation of 80% the average annual dosage in North America from background radiation over an area with a radius of 65 miles (~110 km), with cleanup costing anywhere from $241 million – $1.2 billion USD per square mile.
- ↑ Pluto Probe Launch Scrubbed for Tuesday January 18, 2006
- ↑ Friederich, Steven (December 16, 2003). "Argonne Lab is developing battery for NASA missions", Idaho State Journal.
- ↑ Y. Guo, R. W. Farquhar (2006). "Baseline design of New Horizons mission to Pluto and the Kuiper belt". Acta Astronautica 58 (10): 550–559. doi:.
- ↑ A. F. Cheng et al.. "Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager on New Horizons".
- ↑ Pluto probe gets an eyeful in Jupiter flyby February 28, 2007
- ↑ Stern, Alan (June 1 2006). "A Summer's Crossing of the Asteroid Belt" (HTML). The PI's Perspective. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
- ↑ "JF56 Ecounter, Encounter Date 13 June 2006 UT". Pluto New Horizons Mission, Supporting Observations for 2002. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
- ↑ "New Horizons Tracks an Asteroid" (HTML). Headlines: New Horizons Web site. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-15.
- ↑ Stern, Alan (May 1 2006). "Where Is the Centaur Rocket?" (HTML). The PI's Perspective. Johns Hopkins APL. Retrieved on 2006-06-11.
See also
- Timeline of solar system exploration
- Outer solar system
- List of spaceflights (2006)
Media
A paper model of the New Horizons spacecraft can be built from the sheets below:
- Paper cutouts (requires Adobe Acrobat Reader)
- Instructions
A paper model of Pluto, and a dynamic model of the Pluto-Charon system, can be built by visiting: New Horizons Models
External links
- Official New Horizons mission website
- New Horizons (PKB) Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- New Horizons animation of visit through Jupiter's magnetic field
- Deep Space Network @ Home a proposal that could increase the data return at Pluto-Charon.
- New Horizons APOD
- The New Horizons spacecraft – Spaceflight Now, January 8, 2006 (from the NASA mission press kit)
- How the mission got its name
- NSSDC page
- Johns Hopkins Magazine - Mission: Pluto
- New Horizons Set To Launch With Minimum Amount of Plutonium
- NASA's New Horizons mission also a new horizon for INL
- Unofficial "Where is New Horizons Now?"
- Keep tracking New Horizons on your Dashboard (Mac OS X Tiger)
- Student-Built Dust Detector Renamed Venetia, Honoring Girl Who Named Ninth Planet
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
