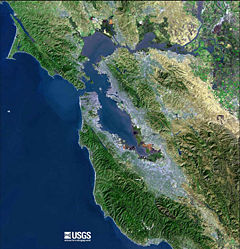
Napa County, California
| Napa County, California | |
| Map | |
 Location in the state of California |
|
 California's location in the U.S. |
|
| Statistics | |
| Founded | 1850 |
|---|---|
| Seat | Napa |
| Area - Total - Land - Water |
788 sq mi (2,041 km²) 754 sq mi (1,953 km²) 35 sq mi (91 km²), 4.38% |
| Population - (2000) - Density |
124,279 166/sq mi (64/km²) |
| Website: www.co.napa.ca.us | |
Napa County is a county located north of the San Francisco Bay Area in the U.S. state of California. It is part of the Napa, California, Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of 2000 the population is 124,279. The county seat is Napa. Napa County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. Parts of the county's territory were given to Lake County in 1861. The word napa is of Native American derivation and has been variously translated as "grizzly bear", "house", "motherland", "fish". Of the many explanations of the name's origin, the most plausible seems to be that it is derived from the Patwin word napo meaning house, although local residents will often cite an urban legend that gives the translation as "you will always return".
Napa County, once the producer of many different crops, is known today for its wine industry, rising in the 1960s to the first rank of wine regions with France and Italy.
Contents |
Demographics
As of the census[1] of 2000, there were 124,279 people, 45,402 households, and 30,691 families residing in the county. The population density was 165 people per square mile (64/km²). There were 48,554 housing units at an average density of 64 per square mile (25/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 79.98% White, 1.32% Black or African American, 0.84% Native American, 2.97% Asian, 0.23% Pacific Islander, 10.95% from other races, and 3.71% from two or more races. 23.67% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 11.9% were of German, 9.7% English, 8.6% Irish, 6.7% Italian and 5.3% American ancestry according to Census 2000. 75.3% spoke English, 19.5% Spanish and 1.1% Tagalog as their first language.
There were 45,402 households out of which 31.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 53.2% were married couples living together, 9.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.4% were non-families. 25.8% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.62 and the average family size was 3.16.
In the county the population was spread out with 24.1% under the age of 18, 8.5% from 18 to 24, 27.7% from 25 to 44, 24.3% from 45 to 64, and 15.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 99.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.4 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $51,738, and the median income for a family was $61,410. Males had a median income of $42,137 versus $31,781 for females. The per capita income for the county was $26,395. About 5.6% of families and 8.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.6% of those under age 18 and 5.6% of those age 65 or over.
Geography and environment

According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 788 square miles (2,042 km²), of which, 754 square miles (1,952 km²) of it is land and 35 square miles (89 km²) of it (4.38%) is water.
Napa is warmer in the summer than Sonoma County to the west or Santa Barbara County, a wine-producing county in southern California. Thus, the Napa wineries favor varietals such as Cabernet Sauvignon, while Pinot Noir and Chardonnay are more the specialty of Sonoma wineries and Santa Barbara wineries. At the north end of Napa County, in the Mayacamas Mountains, lies Mount Saint Helena, the Bay Area's second tallest peak at 4,344 feet (1,323 m) and home to Robert Louis Stevenson State Park. At the west side of the Napa Valley is Hood Mountain, elevation 2,750 feet (838 m).
Napa County is home to a variety of flora and fauna including numerous rare and endangered species such as Tiburon Indian paintbrush and Contra Costa goldfields.
History
In prehistoric times the valley was inhabited by the Patwin Native Americans, with possible habitation by Wappo tribes in the northwestern foothills. Most villages are thought to have been constructed near the floodplains of watercourses that drain the valley. These people were called Diggers and their food consisted wild roots, acorns, small animals, earthworms, grasshoppers, and bread made from crushed California buckeye kernels. In winter they would construct huts made of tree branches. In summer they camped near rivers and streams. In winter months, they were half clad in wild animal skins and at other times they wore no clothing. The maximum prehistoric population is thought not to have exceeded 5000 persons.[2]
In 1776 a fort was erected by the Spanish Governor, Felipe de Neve a short distance northwest of Napa, on an elevated plateau. Russians from Sonoma County's Fort Ross grazed cattle and sheep in the Napa Valley in the early 1800s and in 1841 a survey party from the fort placed a plaque on the summit of Mount Saint Helena.
During the era between 1821 and 1846 when California was a province of independent Mexico, Napa County was divided into the following 12 ranchos:
|
|
|
Don Francis Castro and Father Jose Altimura were the first Europeans to explore the Napa Valley in 1823. When the first white settlers arrived in the early 1830s, there were six tribes in the valley speaking different dialects and they were often at war with each other. The Mayacomos tribe lived in the area where Calistoga was founded. The Callajomans were in the area near where the town of St. Helena now stands. Further south, the Kymus dwelt in the middle part of the valley. The Napa and Ulcus tribes occupied part of the area where the City of Napa now exists while the Soscol tribe occupied the portion that now makes up the southern end of the valley. Many of the native peoples died during a small-pox epidemic in 1838. Settlers also killed several over claims of cattle theft.
George Calvert Yount was a noteworthy early settler in Napa County and is believed to be the first Anglo-saxon resident in the county. When Yount first arrived there in 1831, he made his living hunting and trapping. In 1836 Yount obtained a grant from the Mexican government for the Caymus rancho where he built what is said to be the first log house in California. Soon afterward, he built a sawmill and grain mill and was the first person to plant a vineyard in the county. Following Yount's death in 1865 at age 71, the town of Yountville was named in his honor.
Colonel Joseph B. Chiles a guide for one of the earliest immigrant trains to California, was granted Rancho Catacula in 1844. The Town of Napa was founded by Nathan Coombs in 1847.
Following the event of the Mexican–American War, Bear Flag Revolt in 1846 and the Mexican Cession in 1848, settlers were granted deeds from the original ranchos during the 1850s through 1870s. To this day, a number of streets and landmarks around the valley reflect the names of these districts and original grantees.

Napa County was formed and became one of the original California counties when the state became part of the United States in 1849.
The county's population began to swell in mid century as pioneers, prospectors and entrepreneurs moved in and set up residence. During this period, settlers primarily raised cattle, farmed grain and fruit crops. Mineral mining also played a role in the economics of the county. While gold was being prospected in other areas of the state in the 1850s, Napa County became a center for silver and quick silver mining.
Two entrepreneurs who made their mark on Napa County during the mid 1800s were Edward Turner Bale and Samuel Brannan. Following his marriage to General Vallejo’s niece Maria Guadalupe Soberanes, Bale became a citizen of Mexico and was granted the 17,000-acre (69 km2) Carne Humana Rancho in the northern end of the valley. Bale completed building the Bale Grist Mill a few miles north of St. Helena in 1846. Brannan purchased land in the northern end of the valley at the foot of Mount Saint Helena and founded Calistoga. He began developing it as a resort town taking advantage of or the area’s numerous mineral hot springs. He also founded the Napa Valley Railroad Company in 1864 to bring tourists to Calistoga from San Francisco ferry boats that docked in Vallejo. Brannan’s railroad venture failed and was sold at a foreclosure sale in 1869. The railroad eventually came under ownership of Southern Pacific Railroad late in the 19th century.
Descendents of George Yount and Edward Bale played key roles in the early development of Napa County's wine industry. Bale's daughter Caroline married winemaker Charles Krug in 1860. Bale provided a dowry that included 20 acres (80,937 m²) of land north of St. Helena, California. Krug planted a vineyard and established the valley's first commercial winery on this land. Yount's daughter Elizabeth married Thomas Rutherford in 1864. The couple received 1040 acres (4.209 km²) of land as a wedding present from Elizabeth's father in the area of the valley now known as Rutherford. Rutherford established himself as a serious grower and producer of fine wines in the following years.
In 1866 John Lawley established a toll road from Calistoga over Mount Saint Helena to Lake County.
Robert Louis Stevenson's book The Silverado Squatters provides a snapshot of life and insight into some of the characters that lived around the valley during the later part of the 19th century. Stevenson, accompanied by his new bride Fanny Vandegrift and her 12 year old son from a previous marriage, Lloyd Osbourne, spent the late spring and early summer of 1880 honeymooning in an abandoned bunk house at a played out mine near the summit of Mount St. Helena. In the book, Stevenson's descriptive writing style documented his ventures in the area and profiled several of the early pioneers who played a role in shaping the region's commerce and society.
The Veterans Home was established in Yountville in 1884 by the San Francisco chapter of the Grand Army of the Republic. The State of California assumed administration of the Home in 1897.
Stevenson's book also brought attention to the various spas and hot springs in the county. From Calistoga to Æetna Springs in Pope Valley to Soda Springs Resort a few miles east of Napa, tourists of the late 1800s and early 1900s made the county their destination much the same as modern day tourists. The resorts became very popular with San Franciscans anxious to escape the infamously cold and foggy weather that often plagues the city to enjoy the warmer climate that Napa County offered.
By the end of the 20th century's first decade farmers had planted over 500,000 fruit and nut trees in the county. This helped to soften the blows to the agricultural economy caused by the phylloxera infestation in the county's vineyards and upcoming prohibition that crippled the wine industry.
Wine in Napa Valley

Napa Valley is widely considered one of the top AVAs in California, and all of the United States, with a history dating back to the early nineteenth century. By the end of the nineteenth century there were more than one hundred and forty wineries in the area. Of those original wineries several still exist in the valley today including Charles Krug Winery, Shramsburg, Chateau Montelena and Beringer. Viticulture in Napa suffered a setback when prohibition was enacted across the country in 1920. Furthering the damage was an infestation of the phylloxera root louse which killed many of the vines through the valley. These two events caused many wineries to shut down and stalled the growth of the wine industry in Napa County for years. Following the Second World War, the wine industry in Napa began to thrive again.

In 1965, Napa Valley icon Robert Mondavi broke away from his family's Charles Krug estate to found his own. This was the first new large scale winery to be established in the valley since before prohibition. Following the establishment of the Mondavi estate, the number of wineries in the valley continued to grow, as did the region's reputation.

In addition to large scale wineries, Napa Valley's boutique wineries produce some of the world's best wines. The producers of these wines include but are not limited to: Araujo, Bryant Family, Colgin Cellars, Dalla Valle Maya, Diamond Creek, Dominus Estate, Duckhorn Vineyards, Dunn Howell Mountain, Grace Family, Harlan, Husic, Kistler, Jericho Canyon Vineyards, Marcassin, Screaming Eagle, Shafer Hillside Select, Sine Qua Non, Spencer-Roloson Winery and Vineyard 29.
Today Napa Valley features more than three hundred wineries and grows many different grape varieties including Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, Merlot, Zinfandel, and other popular varietals. Napa Valley is visited by as many as five million people each year.
Growth, rural and agricultural preservation
Napa County has maintained a rural agricultural environment in a large portion of the valley floor while neighboring Sonoma, Solano and Yolo counties have allowed large tracts of former farmland to be rezoned for commercial and residential development. In 1968 vintners and civic leaders in the county seized an opportunity to preserve farmland by taking advantage of the Williamson Act [3] enacted by the California Legislature to give landowners property tax relief for designating their land for agricultural purposes. This agricultural preserve [4] on the floor of the valley in unincorporated areas between Napa and Calistoga was the first of its kind in the state. Initially, the preserve encompassed 23,000 acres (93.078 km²), since founding it has grown to more than 30,000 acres (121.41 km²).
The county has resisted encroachment on the preserve since it was created with voters reaffirming their desire keep it intact on several occasions. In 1990 voters passed Measure J [5] adopting an initiative freezing all county zoning changes until the year 2020 unless there is a ⅔ majority vote to adopt such changes. Measure J was reaffirmed by a 5-2 vote of the California Supreme Court in 1995 in the case of Devita v. County of Napa [6].
The Land Trust of Napa County [7] was founded in 1976 by a group of local citizens with a mission to protect the natural diversity, scenic open space and agricultural vitality of the county. The trust acquires conservation easements, facilitates land transfers to local, state and federal agencies along with accepting outright donations of land within and outside the boundary of the agricultural preserve. The trust now covers over 50,000 acres (202.34 km²) [8].
While establishment of the agricultural preserve and the land trust has slowed residential development in much of the county, residential growth within the incorporated cities has continued at a moderate pace. Several substantial homes have been built on the hills surrounding the valley in areas not covered by the preserve or the land trust. A large portion of the land south of the City of Napa remained undeveloped for many decades until the 1980s. Several wine bottling facilities and wine storage warehouses now stand on what was once vacant land. A number of light industries have also sprung up in this region as new business parks have been built. The growth of American Canyon,[9] Napa County’s southernmost and newest city; incorporated in 1992 has prompted the establishment of several new retail outlets in the southern end of the county in recent years. American Canyon has also established a green belt preserve of over 1000 acres (4.047 km²) on the western and eastern sides of the city.
Politics
| Year | DEM | GOP | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 65.2% 28,212 | 32.9% 14,251 | 1.9% 810 |
| 2004 | 59.5% 33,666 | 39.0% 22,059 | 1.5% 874 |
| 2000 | 54.3% 28,097 | 39.9% 20,633 | 5.8% 2,994 |
| 1996 | 50.9% 24,588 | 36.1% 17,439 | 13.0% 6,292 |
| 1992 | 45.3% 24,215 | 29.3% 15,662 | 25.4% 13,578 |
| 1988 | 48.1% 22,283 | 50.2% 23,235 | 1.7% 772 |
| 1984 | 40.8% 18,599 | 57.8% 26,322 | 1.4% 640 |
| 1980 | 33.8% 14,898 | 53.7% 23,632 | 12.5% 550 |
| 1976 | 44.9% 18,048 | 51.8% 20,839 | 3.3% 1,318 |
| 1972 | 37.0% 14,529 | 59.6% 23,403 | 3.4% 1,329 |
| 1968 | 45.3% 14,762 | 43.8% 14,270 | 11.0% 3,580 |
| 1964 | 62.7% 19,580 | 37.1% 11,567 | 0.2% 63 |
| 1960 | 46.9% 13,499 | 52.6% 15,125 | 0.5% 154 |
Napa is a strongly Democratic county in Presidential and congressional elections. The last Republican to win a majority in the county was George H.W. Bush in 1988.
Napa is part of California's 1st congressional district, which is held by Democrat Mike Thompson. In the state legislature Napa is in the 7th Assembly district, which is held by Democrat Noreen M. Evans, and the 2nd Senate district, which is held by Democrat Pat Wiggins.
On Nov. 4, 2008 Napa County voted 55.9 % against Proposition 8 which amended the California Constitution to ban same-sex marriages.
Cities and towns
- American Canyon
- Calistoga
- Napa
- St. Helena
- Yountville
| Unincorporated Communities A-L | Unincorporated Communities M-Z |
|---|---|
|
|
Adjacent counties
- Solano County, California - south, southeast
- Sonoma County, California - west
- Lake County, California - north
- Yolo County, California - east
National protected area
- San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge (part)
Rivers and creeks
- Napa River
- Milliken Creek
- Putah Creek
Lakes, marshes and reservoirs
- East Napa Reservoir
- East Side Reservoir
- Fiege Reservoir
- Lake Berryessa
- Lake Hennessey
- Lake Marie
- Lake Orville
- Lake Whitehead
- Milliken Reservoir
- Napa Sonoma Marsh
- Rector Reservoir
- West Napa Reservoir
Transportation infrastructure
Major highways
 Interstate 80 (1 mile in the southeastern corner)
Interstate 80 (1 mile in the southeastern corner) State Route 12
State Route 12 State Route 29
State Route 29 State Route 121
State Route 121 State Route 128
State Route 128
Public transportation
Napa Valley VINE operates local bus service in Napa, along with an intercity route along State Route 29 between Vallejo (Solano County) and Calistoga. Limited service runs from Calistoga to Santa Rosa (Sonoma County).
Airports
Napa County Airport is a general aviation airport located just south of the City of Napa.
Rail
Napa Valley Railroad (AAR reporting marks NVRR) is mostly used by the Napa Valley Wine Train, a dining/excursion service.
Media
- Napa Valley Register
- Napa SentinelGTF
- KVON AM
- KVYN FM
Trivia

- The default wallpaper for the Windows XP operating system is Bliss, a Bitmap photograph of a landscape in the Napa Valley, [10] with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds. The photograph inspired Windows XP's 200-million USD advertising campaign Yes you can.
- In the television series Good Times, the characters would always refer to wine or champagne coming from Napa Valley as "imported". An example from the episode "Too Old Blues" when James was surprised that Florida bought champagne to celebrate his new job, she exclaimed "You told me to. We bought that imported stuff, all the way from Napa Valley, California."
- On November 19, 2005 Grammy Award winning singer Christina Aguilera married music executive Jordan Bratman in Napa Valley.
References
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ↑ Environmental Assessment for the Napa Valley Wine Train, Napa County and the California Public Utilities Commission, Earth Metrics Inc. report 10072, January, 1990
- ↑ [1] explanation of Williamson Act
- ↑ [2] Napa Chamber of Commerce info on Napa County Agricultural Preserve
- ↑ http://www.napalaw.com/forms/measurej.html] article about Measure J
- ↑ http://www.ceres.ca.gov/ceqa/cases/1995/devita_030695.html] Devita v County of Napa
- ↑ Napa Valley Vintners/About/Land Trust of Napa County
- ↑ [3] Land Trust of Napa County website
- ↑ [4] City of American Canyon website
- ↑ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). "No view of Palouse from Windows". The Slice. Retrieved on 01/09/2007.
See also
- Eriophyllum latilobum
- Lasthenia conjugens
- List of school districts in Napa County, California
- Napa County Airport
- Napa City-County Library
External links
- Napa County official website
- Now history
- Summary of Napa County History from 1891
- Napa County History
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|