Miami International Airport
| Miami International Airport | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| IATA: MIA – ICAO: KMIA – FAA: MIA | |||
| Summary | |||
| Airport type | Public | ||
| Owner | Miami-Dade County | ||
| Operator | Miami-Dade Aviation Department (MDAD) | ||
| Serves | Miami, Florida | ||
| Elevation AMSL | 8 ft / 2 m | ||
| Website | |||
| Runways | |||
| Direction | Length | Surface | |
| ft | m | ||
| 8L/26R | 8,600 | 2,621 | Asphalt |
| 8R/26L | 10,506 | 3,202 | Asphalt |
| 9/27 | 13,000 | 3,962 | Asphalt |
| 12/30 | 9,354 | 2,851 | Asphalt |
| Statistics (2006) | |||
| Aircraft operations | 384,537 | ||
| Based aircraft | 345 | ||
| Passengers (2007) | 33,740,416 | ||
Source: Federal Aviation Administration[1]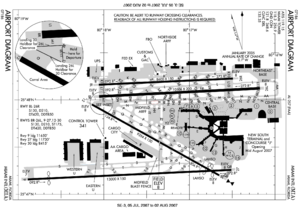 |
|||
Miami International Airport (IATA: MIA, ICAO: KMIA, FAA LID: MIA) is a public airport located eight miles (13 km) northwest of the central business district of Miami, in unincorporated Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States.[1] It is between the cities of Miami, Hialeah, Doral, and Miami Springs, the village of Virginia Gardens, and the unincorporated community of Fountainbleau. In September 2008, the airport regained it's title as the busiest in Florida.[2]
The airport is a hub for passenger airlines American Airlines, American Eagle, Gulfstream International Airlines under the Continental Connection name, and Executive Air under the American Eagle name; cargo airlines Arrow Air, Fine Air, UPS Airlines and FedEx Express; and charter airline Miami Air. Miami International Airport handles flights to cities throughout the Americas and Europe, as well as cargo flights to Asia, and is South Florida's main airport for long-haul international flights, although most domestic and low-cost carriers use Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International Airport and Palm Beach International Airport, which charge significantly lower fees to tenant airlines.
Miami is a major gateway between the United States and Latin America, and, along with Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson Airport, Miami is one of the largest aerial gateways into the American South, owing to its proximity to tourist attractions, local economic growth, large local Latin American and European populations, and strategic location to handle connecting traffic between North America, Latin America, and Europe. As of 2008, MIA is the twenty-third largest airport in the world in terms of passenger traffic. In the past, it has been a hub for Braniff International, Eastern Air Lines, Air Florida, the original National Airlines, the original Pan Am, United Airlines, and Iberia. As an international gateway to the United States it ranks third, behind New York-JFK in New York City and LAX in Los Angeles. Miami is also the proposed hub of two new start-up airlines, one which hopes to use the Eastern Airlines name.[3]
In 2007, 33,740,416 passengers traveled through the airport.[4]
In the first 10 months of 2007 more international passengers boarded U.S. carriers at Miami International than at any other U.S. airport.[5]
Contents
|
History


The airport was opened to flights in 1928 as Pan American Field, the operating base of Pan American Airways Corporation, on the north side of the modern airport property. After Pan Am acquired the New York, Rio, and Buenos Aires Line, it shifted most of its operations to the Dinner Key seaplane base, leaving Pan Am Field largely unused until Eastern Air Lines began flying there in 1934, followed by National Airlines in 1937.
In 1945, the City of Miami established a Port Authority and raised bond revenue to purchase the airport, which had meanwhile been renamed 36th Street Airport, from Pan Am. It was merged with an adjoining Army airfield in 1949 and expanded further in 1951. The old terminal on 36th Street was closed in 1959 when the modern passenger terminal (since greatly expanded) opened for service.
Air Force Reserve troop carier and rescue squadrons also operated from Miami International from 1949 through 1959, when the last such unit relocated to nearby Homestead Air Force Base, now Homestead Air Reserve Base.
Pan Am and Eastern remained Miami International Airport's main tenants until 1991, when both carriers went bankrupt. Their hubs at MIA were taken over by United Airlines and American Airlines. United slowly trimmed down its Miami operation through the 1990s, and eventually shut down its crew base and other operations facilities in Miami. At the same time, American expanded its presence at the airport, winning new routes to Latin America and transferring employees and equipment from its failed domestic hubs at Nashville and Raleigh-Durham. Today, Miami is American's largest air freight hub, and forms the main connecting point in the airline's north-south oriented international route network.
For many years, the airport was a common connecting point for passengers traveling from Europe to Latin America. However, stricter visa requirements for aliens in transit (a result, in part, of the September 11, 2001 attacks) have lessened MIA's role as an intercontinental connecting hub. In 2004, Iberia Airlines ended its hub operation in Miami, opting instead to run more direct flights from Spain to Central America. However, Air France still has flights to Port-au-Prince using smaller Airbus A320 and Embraer ERJ-145 aircraft.
Gulfstream International Airlines, Sky King Airlines, American Eagle and American Airlines all operate regular flights between MIA and several airports in Cuba, the one of the few direct airlink between the two nations. However, these flights must be booked through agents with special authorization from the Office of Foreign Assets Control, and are only generally available to government officials, journalists, researchers, professionals attending conferences, or expatriates visiting Cuban family.
Facilities and aircraft
Miami International Airport covers an area of 3,300 acres (1,335 ha) which contains four runways:[1]
- Runway 8L/26R: 8,600 x 150 ft (2,621 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 8R/26L: 10,506 x 200 ft (3,202 x 61 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 9/27: 13,000 x 150 ft (3,962 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 12/30: 9,354 x 150 ft (2,851 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
For the 12-month period ending December 31, 2006, the airport had 384,537 aircraft operations, an average of 1,053 per day: 77% scheduled commercial, 17% air taxi, 6% general aviation and <1% military. There are 345 aircraft based at this airport: 7% single-engine, 35% multi-engine and 58% jet..[1]
Terminal, airlines, and destinations


The main terminal at MIA is semicircular and has eight pier-shaped concourses, lettered A through J (B was demolished in 2005) in a counter-clockwise direction. Ticketing and departures are located on the upper level and baggage carousels are located on the lower level, the airport contains three customs arrival levels, on the third floor at both Concourse J and the now demolished Concourse B (though B customs are currently closed for renovations), and at the lower level of Concourse E; the largest of the three. Gates located in Concourses A-F and J, and some gates at Concourse H, can route arriving passengers to the main level (for domestic arrivals) or to the immigration halls (for international arrivals), however, gates at Concourse G and some at Concourse H are designed only for domestic arrivals. Two parking garages, the Dolphin and Flamingo Garages, are located inside the terminal's curvature, and are connected to the terminal by overhead walkways, it is expected that a third garage will be constructed to serve expansion for Concourse J; there is a heliport located atop a connecting point between the two garages.
At present, the terminal is being dramatically altered. Concourses A, B, C, and D, which primarily house American Airlines and its Oneworld partner's flights, are being merged into a single linear concourse to be called the "North Terminal". Portions of the new concourse have already been built as extensions of concourses A and D; to make space for completing the new terminal, the former concourse B has been already been demolished and concourse C will soon follow to accommodate new gates and lounges.[6] Although this construction was originally slated for completion by 2005, it has been delayed several times due to cost overruns: the current deadline for completion is summer of 2011.[7]
The remaining "South" (Concourses H and J) and "Central" (Concourses E, F, and G) Terminals have also been renovated and expanded with Concourse J, the newest addition to the airport, opening on August 29, 2007, (photo) being constructed with the support of fifteen Star Alliance and SkyTeam carriers: it is seven stories tall and has 15 gates, with a total floor area of 1.3 million square feet (120,000 m2) including two airline lounges and several offices. Currently, the new concourse is still in opening stages with the movement of most airlines located at Concourse A moving to the new area beginning on September 24, 2007, this was done to allow for renovations to be done at Concourse A, and includes American Airlines taking over gates at Concourse E to replace the gates it will lose at Concourse A. Currently, LAN Airlines, LAN Argentina, LAN Ecuador, LAN Peru, LACSA, TACA, COPA, US Airways, Avianca, United/Ted, TAM, Aerolíneas Argentinas, airberlin, Caribbean Airlines, Lufthansa, Swiss International, Air Canada, and El Al moved into the new concourse. Delta/Comair, Air France, and Alitalia, and COPA Airlines have also begun operating ticket counters at the new Concourse whilst using gate space at Concourse H, soon to be followed by AeroMexico (date unconfirmed). Continental has begun using gates on Concourse H with the ticket counters remaining between G and H concourses. British Airways, previously housed at concourse A, has moved its ticket counters to Concourse E and will use gates at Concourse F for the duration of the A concourse renovations.
After Concourse A is renovated, it is expected that Alaska Airlines, British Airways, LAN Airlines, LAN Argentina, LAN Ecuador, and LAN Peru will return to Concourse A, along with American Airlines; Iberia will also move its flights to the concourse for the first time. Aerolineas Argentinas, Caribbean Airlines, and LTU will then return to Concourse E once their gates have been vacated by American Airlines. Fire protection at the airport is provided by Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department[8] Station 12.[9]
Concourse A
Gates A1-A18
Concourse A was a recent addition to the airport and will eventually form part of American Airlines' North Terminal. It housed many American domestic and international flights, although all check-in counters for American are located adjacent to concourses C and D. Both American and British Airways had lounge facilities in Concourse A. On May 17, 2006, American Airlines opened their second Admirals Club lounge at Miami International in Terminal A; it is located on the mezzanine level. On November 9, 2007, Concourse A was temporarily closed as part of the North Terminal Renovation Project.
Concourse B

Concourse B was a former concourse operated by American Airlines. It was closed and demolished as part of the North Terminal Renovation project. The former Concourse B area of the airport contained a customs arrival facility serving International Arrivals from Concourses A, C, and D. Concourse B, together with C and D historically served as the base of operations for Eastern Airlines prior to its shut down.
Concourse C
The airside Concourse C consists of four gates accommodating small-to-medium jet aircraft such as the Boeing 737 or Boeing 757, as well as the Airbus A-300. American uses these gates for domestic flights and some departures to Central America and the Caribbean. The Concourse C check-in area is for American's international flights. During the course of the American Airlines/North Terminal project, Concourse C will be demolished, allowing for the creation of new gates where the concourse was located.
Concourse C Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses C and D
- American Airlines – Caribbean and First Class check-in
Concourse C Gate Usage
Gates C3, C5, C7, C9
- American Airlines (See Concourse D)
Concourse D
Although Concourse D was one of the original concourses in the MIA terminal, the original portion has been mostly closed, and the concourse now consists of a new extension which will eventually form part of American Airlines' North Terminal. American uses the concourse for domestic and international flights; the Concourse D check-in area is for domestic and Caribbean flights. American operates an Admirals Club on Concourse D.
Concourse D Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses D and E
- American Airlines - Latin American/Europe and Domestic Check-in, Self Check-in
- American Eagle
- Martinair
- Virgin Atlantic
Concourse D Gate Usage
Gates D31-34, D35A-D, D36-D40, D42-D51
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| American Airlines | Antigua, Aruba, Atlanta, Barbados, Baltimore/Washington, Belize City, Belo Horizonte, Bermuda, Bogotá, Boston, Buenos Aires-Ezeiza, Cali, Cancún, Caracas, Chicago-O'Hare, Dallas/Fort Worth, Denver, Detroit, Eagle/Vail [seasonal], Georgetown, Grand Cayman, Grenada, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Hartford/Springfield, Houston-Intercontinental, Kingston, La Paz (Bolivia), La Romana, Las Vegas, Liberia (CR), Lima, London-Heathrow, Los Angeles, Madrid, Managua, Maracaibo, Medellín-Córdova, Mexico City, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montego Bay, Montevideo, Montréal, Nashville, New Orleans, New York-JFK, New York-LaGuardia, Newark, Orlando, Panama City, Paris-Charles de Gaulle, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Port-au-Prince, Port of Spain, Providenciales, Puerto Plata, Punta Cana, Quito, Raleigh/Durham, Recife, Rio de Janeiro-Galeão, Salvador, San Salvador, Santa Cruz de la Sierra (Bolivia), São Paulo-Guarulhos, Santiago de Chile, St. Croix, St. Kitts, St. Louis, St. Lucia, St. Maarten, St. Thomas, San Francisco, San José (CR), San Juan, San Pedro Sula, Santiago (DR), Santo Domingo, Tampa, Tegucigalpa, Toronto-Pearson, Washington-Dulles, Washington-Reagan, Willemstad |
| AmericanConnection operated by Trans States Airlines | Charlotte, Indianapolis, Norfolk, Pittsburgh, Richmond |
| American Eagle | Charlotte, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky, Cleveland, Columbus (OH), Greensboro, Jacksonville (FL), Louisville, Memphis, Tallahassee |
| American Eagle operated by Executive Air | Cozumel, Fort Myers, Freeport, Jacksonville (FL), Key West, Marsh Harbour, Nassau, Sarasota/Bradenton, Savannah |
Concourse E

Concourse E is divided into two sections: a pier concourse, called "low E", and a satellite terminal, called "high E", connected by an airport people mover. Low E is mostly used by American Airlines; high E is used by various other carriers. The Admirals Club operated by American has temporarily reopened inside security after a renovation to the checkpoint. Concourse E contains Customs Arrival facilities for International Arrivals at Concourse D, E, and F. Concourse E, together with Concourse F historically served as the main operations area for Pan American Airways until its shut down in 1991.
Concourse E Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses E and F
- Aeroméxico
- Air Jamaica
- Alaska Airlines
- British Airways
- Cayman Airways
- Mexicana
Concourse E Gate Usage
Low E
Gates E1-E11
- Special Authority Cuban Charters operate from Low E
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| American Airlines | See Concourse D |
| American Airlines | Havana |
| American Eagle | Camagüey, Cienfuegos, Havana, Holguin, Santiago de Cuba |
High E
Gates E20-25, E30-E33
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| American Airlines | See Concourse D |
Concourse F
Concourse F Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses F and G
- Aerosur
- Avior Airlines
- Gulfstream International Airlines (Cuba Charters)
- Iberia Airlines
- Northwest Airlines
- Santa Barbara Airlines
- Sky King
- Sun Country
Concourse F Gate Usage
Gates F1-F23
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aeromexico | Mérida, Mexico City |
| Aerosur | Santa Cruz de la Sierra |
| Air Jamaica | Kingston, Montego Bay |
| Alaska Airlines | Seattle/Tacoma |
| Avior Airlines | Barcelona (Ven.) |
| British Airways | London-Heathrow |
| Cayman Airways | Cayman Brac, Grand Cayman |
| Iberia Airlines | Madrid |
| Insel Air | Curaçao |
| Martinair | Amsterdam, San José (CR) |
| Mexicana | Cancún, Mexico City |
| Santa Barbara Airlines | Caracas, Maracaibo, Valencia |
| Sun Country Airlines | Minneapolis/St. Paul [seasonal] |
| Surinam Airways | Aruba, Paramaribo |
| Travelspan Operated by North American Airlines | Georgetown, Port of Spain |
| Virgin Atlantic | London-Heathrow |
Concourse G

Concourse G Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses G and H
- AirTran Airways
- Continental Airlines
- Continental Connection operated by Gulfstream International Airlines
- Miami Air International
Concourse G Gate Usage
Gates G1-G16
- Note: Concourse G is the only domestic only concourse at the airport, all international arrivals for the concourse are handled at Concourse F
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirTran Airways | Atlanta, Baltimore/Washington |
| Bahamasair | Freeport, Nassau |
| Continental Airlines | Havana [scheduled charter] |
| Continental Connection operated by Gulfstream International Airlines | Havana [scheduled charter], Key West, Marsh Harbour, North Eleuthera, Orlando, Tampa |
| Northwest Airlines | Detroit, Memphis, Minneapolis/St. Paul |
| Sky King | Camagüey, Cienfuegos, Havana, Holguin, Santiago de Cuba) - scheduled charters |
Concourse H
Concourse H Ticket Counters
Located between Concourses G and H
- Bahamasair
- Continental Airlines
Concourse H Gate Usage
Gates H3-H17
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Air France | Cayenne, Fort-de-France, Paris-Charles de Gaulle, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince |
| Alitalia | Rome-Fiumicino |
| Continental Airlines | Cleveland [seasonal], Houston-Intercontinental, Newark |
| Continental Express operated by ExpressJet Airlines | Cleveland |
| Copa Airlines | Panama City |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky [seasonal], New York-JFK |
| Delta Connection operated by Comair | Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky |
Concourse J
Concourse J is a new concourse that opened on August 29, 2007 under Miami International Airport's South Terminal Renovation Project.[10] The Concourse was designed by Carlos Zapata of Studio Carlos Zapata in New York, with M.G.E., one of the largest Hispanic owned architecture firms in Florida, as the architect of record; the Concourse holds Star Alliance and SkyTeam Members, though due to renovation closures at concourse A, it currently holds several oneWorld alliance and non-affiliated airlines. Together with Concourse H, this area has been deemed the "South Terminal". It will be the only pier at the airport able to accept the new Airbus A380 (currently the only airline to commit an A380 to MIA is Lufthansa, for the MIA-FRA route) and has introduced a third customs and immigration facility at the airport, supplementing the ones at Concourses B and E; with international SkyTeam and Star Alliance members moving to this new terminal, the new facilities have eased the overcrowding problems that have plagued the concourse E immigration facilities since new US entry laws came into effect in late 2003. Once the North and South Terminals are both completed, all airlines not affiliated with either the Star Alliance, SkyTeam (South Terminal) alliances, or oneWorld alliance (North Terminal) will be housed at the remaining Concourses E, F and G.
Concourse J Ticket Counters

Located between Concourses H and J
- Aerolíneas Argentinas
- airberlin operated by LTU
- Air Canada
- Air France
- Alitalia
- Avianca
- Caribbean Airlines
- Copa Airlines
- Delta Air Lines
- LAN Airlines
- Lufthansa
- Lynx Air International
- Swiss International Air Lines
- TACA
- TAM Airlines
- United Airlines
- US Airways
Concourse J Gate Usage
Gates J2-J18
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aerolíneas Argentinas | Buenos Aires-Ezeiza |
| airberlin operated by LTU | Düsseldorf, Munich [seasonal] |
| Air Canada | Montréal, Toronto-Pearson |
| Avianca | Barranquilla, Bogotá, Cali, Cartagena, Medellín-Córdova, Pereira |
| Caribbean Airlines | Port of Spain |
| LAN Airlines | Bogotá, Caracas, Punta Cana, Santiago de Chile |
| LAN Argentina | Buenos Aires-Ezeiza, Punta Cana |
| LAN Ecuador | Guayaquil, Quito |
| LAN Perú | Lima |
| Lufthansa | Düsseldorf [seasonal], Frankfurt |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Zürich |
| TACA | Guatemala City, Managua, Roatán, San Pedro Sula, San José (CR), San Salvador, Tegucigalpa |
| LACSA | Bogotá, San José (CR) |
| TAM Airlines | Manaus, Rio de Janeiro-Galeão, Salvador, São Paulo-Guarulhos |
| United Airlines | Chicago-O'Hare, Denver, Washington-Dulles [begins January 6] |
| Ted operated by United Airlines | Chicago-O'Hare, Denver, Washington-Dulles [ends January 6] |
| United Express operated by Shuttle America | Chicago-O'Hare |
| US Airways | Charlotte, Philadelphia |
Charter Carriers
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirTransat | |
| Allegiant Air | |
| Aserca Airlines | |
| European Air | |
| ExpressJet Airlines | Samana-El Catey [seasonal] |
| Miami Air International | |
| North American Airlines | |
| Planet Airways | |
| Ryan International Airlines | |
| Skyservice (Toronto-Pearson) | |
| Sun Country | |
| Thomsonfly | |
| Travelspan operated by North American Airlines | Georgetown, Port of Spain |
- World Airways
Most charter airlines have counters at concourse F, and use concourse F or G for gates.
Ground transportation
Miami International Airport has direct public transport links to Miami-Dade Transit's Metrobus network, being served by routes 7, 37, 42, 57, 133, 236, 238, and the J; free shuttles are also provided to and from the Miami Airport and Hialeah Market Stations on the Tri-Rail commuter rail line, which operates trains once every two hours on weekends and more frequently on weekdays. The stations are close, within 5 minutes drive from the main terminal. MDT is currently planning to link the airport by people mover to the upcoming Miami Intermodal Center, which will provide access to Miami-Dade Metrorail as well as the future BayLink light rail to South Beach. Taxis and rental cars are available as well, as is the case in most airports.
Approximate time and cost to city center:
- Super Shuttle: fare US$9, time depends on stops.
- Metro Bus: $1.50 ($.75 reduced fare), approx. 35-40 mins via route 7 (East) or route J.
- Taxi fare $15.50, approx. 20 mins.
Cargo
The airport is one of the largest in terms of cargo in the United States,[11] and is the main connecting point for cargo between Latin America and the world. It is first in International freight and fourth in total freight for 2007. In 2000, LAN Cargo opened up a major operations base at the airport and currently operates the second largest cargo facility at the airport second to UPS. Most major passenger airlines, such as American Airlines use the airport to carry belly cargo on passenger flights though most cargo is operated through cargo only airlines. UPS Airlines, FedEx Express, and DHL, all operate their major Latin American operations through MIA.
Cargo Airlines
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| ABSA | |
| ABX Air | |
| Aerounion | |
| Air Tahoma | |
| Alitalia | |
| Amerijet International | |
| Arrow Air | |
| Astar Air Cargo | |
| Atlas Air | |
| Avialeasing | |
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | |
| Capital Cargo International Airlines | |
| Cargolux | |
| Centurion Air Cargo | |
| China Airlines Cargo | |
| Cielos del Peru | |
| DHL | |
| Estafeta Cargo | |
| Falcon Express Cargo | |
| FedEx Express | |
| Fine Air | |
| Florida West Cargo | |
| Focus Air Cargo | |
| Gemini Air Cargo | |
| IBC Airways | |
| Kitty Hawk Cargo | |
| Korean Air Cargo | |
| LAN Cargo | |
| Masair | |
| Martinair | |
| Mountain Air Cargo | |
| Polar Air Cargo | |
| Skyway Enterprises | |
| TAMPA Cargo | |
| Tradewinds Airlines | |
| UPS Airlines |
New Services
- Aerogal plans to begin service between Guayauil, Ecuador and Miami on December 7, 2008
- AeroRepública intends to begin flights to Bogotá and Medellin in 2009.[12]
- Air Europa will begin weekly service to the Canary Islands in March 2009.[13]
- American Airlines has applied to begin daily non-stop service to Valencia, Venezuela, pending Venezuelan government approval.
- Avior plans to begin non-stop service to Puerto Ordaz, Venezuela in 2008.[14]
- Avior has applied to begin three weekly flights to Valencia, Venezuela, pending US government approval.
- CSA Czech will begin weekly service to Prague in March 2009.
- Transaero will begin non-stop service between Miami and Moscow in 2008. [15]
- United Airlines will resume services to Miami in 2009 replacing Ted Airlines.
Incidents and accidents
Airline crashes involving MIA include:
- On April 25, 1951 Cubana de Aviación Flight 493, a Douglas DC-4 en route from Miami, Florida to Havana, Cuba, collides in mid-air with a United States Navy Beech SNB-1 Kansan off Key West. All 43 aboard both aircraft are killed.
- On February 1, 1957, Miami-bound Northeast Airlines Flight 823 crashed on take-off from New York's LaGuardia Airport.
- On January 6, 1960, National Airlines Flight 2511, a Douglas DC-6B bound from New York to Miami, crashes near Bolivia, North Carolina, when a bomb planted on board explodes in mid-air. All 34 people on board are killed.
- On February 12, 1963, Northwest Orient Airlines Flight 705 crashed into the Everglades while en route from Miami to Portland, Oregon via Chicago O'Hare, Spokane, and Seattle.
- On December 29, 1972, Eastern Air Lines Flight 401, a Lockheed L-1011, crashed into the Everglades (the subject of Hollywood movie, The Ghost Of Flight 401).
- On January 13, 1982, Air Florida Flight 90, a Boeing 737, crashed in Washington, D.C.. The aircraft had flown up from Miami on a flight earlier that day.
- On January 1, 1985 Eastern Air Lines Flight 980, a Boeing 727, crashed into the mountains in Bolivia. The plane originated in Asunción and was bound to Miami via La Paz, Bolivia and Guayaquil.
- On December 20, 1995, American Airlines Flight 965 crashed into a mountain while en route from Miami to Cali.
- On May 12, 1996, ValuJet Flight 592 crashed into the Everglades after take-off form Miami en route to Atlanta.
- On October 2, 1996, Aeroperú Flight 603 crashed after takeoff from Lima, Peru. The flight, which originated in Miami, was continuing to Santiago, Chile.
- On August 7, 1997, Fine Air 101, a Douglas DC-8 cargo plane, crashed onto NW 72nd Avenue less than a mile (1.6 km) from the airport.
- On February 2, 1998, two Skyway Enterprises Shorts 330-200 aircraft (N2630A and N2629Y) were damaged beyond repair by a tornado at Miami International Airport. Both aircraft had to be written off. No one was injured.[16]
- On December 22, 2001, American Airlines Flight 63, en route from Paris to Miami, was the target of "shoe bomber" Richard Reid.
- On December 7, 2005, forty-four year old Rigoberto Alpizar, a passenger aboard American Airlines Flight 924, claimed to have a bomb in his carry-on luggage while boarding the flight's second leg to Orlando, Florida after arriving on a flight from Quito, Ecuador; the flight had just arrived from Medellín, Colombia. Federal air marshals reportedly shot and killed the man as he attempted to escape the plane after being confronted onboard, marking the first time an air marshal has fired a weapon on or near an airplane.
- On August 31, 2006, US Airways Flight 431 from Charlotte caught fire on the runway. All 118 passengers and crew on board were evacuated safely and there were no injuries. The fire occurred in the left wheel well of the 737 after the tires blew upon landing, and was extinguished with foam by firefighters. Passengers have stated that the plane was shaking violently as it landed.[17]
In Popular Culture
Miami International Airport has been used for scenes in many movies and TV shows, including:
- The 1980s television show Miami Vice had many airport scenes filmed on location at MIA.
- The 2002 film Big Trouble has a final chase scene that was filmed at MIA's Concourse C.
- The 2002 film Catch Me if You Can has Leonardo DiCaprio's character spending a little time in the terminal. However, Catch Me If You Can was actually filmed at the old terminal for Ontario International Airport in Ontario, California.
- The fall 2002 and 2007 installments of The Amazing Race (season 3 and season 11, respectively) began in Miami and had shots at MIA while teams booked and boarded flights (to Mexico City in season 3, and to Ecuador in season 11).
- The 2005 film Red Eye has a scene including the Miami International Airport. The scene takes place as Lisa is running from the police after her plane lands.
- The 2006 film Casino Royale has a major action sequence set at Miami International Airport, where James Bond foils a terrorist attempt to destroy a prototype airplane. The scenes, however, were filmed at Ruzyně International Airport near Prague, Czech Republic. Other exterior scenes (and the fire sprinklers going off) were filmed on the backlot of Pinewood Studios and Dunsfold Park, England.
- CSI: Miami mentions Miami International Airport occasionally in episodes and a few scenes have been filmed there.
See also
- Busiest airports in the United States by international passenger traffic
- Florida World War II Army Airfields
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 FAA Airport Master Record for MIA (Form 5010 PDF), effective 2007-10-25
- ↑ http://www.orlandosentinel.com/business/custom/tourism/orl-airport2508oct25,0,525777.story
- ↑ New airline could have famous name - Mass High Tech: The Journal of New England Technology:
- ↑ 2007 Traffic Report
- ↑ BTS | October 2007 Airline Traffic Data: 10-Month 2007 System Traffic Up 3.6 Percent From 2006
- ↑ http://acb-architects.com/airtrans-miami.htm
- ↑ http://www.miamitodaynews.com/news/070524/story1.shtml
- ↑ "Airport Fire Rescue Division". Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department. Miami-Dade County. Retrieved on August 30, 2006.
- ↑ "Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Stations". Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department. Miami-Dade County. Retrieved on August 30, 2006.
- ↑ http://www.miamiherald.com/103/story/50030.html
- ↑ http://www.airports.org/cda/aci_common/display/main/aci_content07_c.jsp?zn=aci&cp=1-5-54-4819_666_2__
- ↑ Perú 21 / Economía
- ↑ http://www.miamiherald.com/business/breaking-news/story/771615.html
- ↑ El Diario de Guayana
- ↑ Transaero Gets a Piece of American Pie
- ↑ Aviation Safety Network retrieved 26 November 2006
- ↑ "Jetliner evacuated after fire in wheel well", CNN
External links
- Miami International Airport (official site)
- Miami International AirportPDF (501 KiB) brochure from CFASPP (September 2007)
- FAA Airport Diagram(PDF), effective 20 November 2008
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KMIA
- ASN accident history for MIA
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KMIA
- FAA current MIA delay information
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|