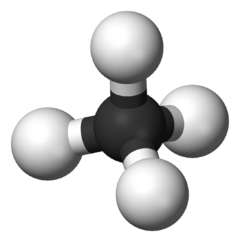
Methane
| Methane | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
| Other names | Marsh gas, firedamp |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 74-82-8 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | CH4 |
| Molar mass | 16.0425 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Density | 0.717 kg/m3, gas |
| Melting point |
-182.5 °C, 91 K, -297 °F |
| Boiling point |
-161.6 °C, 112 K, -259 °F |
| Solubility in water | 3.5 mg/100 mL (17 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly flammable (F+) |
| NFPA 704 |
 4
1
0
|
| R-phrases | R12 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S9, S16, S33 |
| Flash point | -188 °C |
| Related compounds | |
| Related Alkanes | Ethane, propane |
| Related compounds | Methanol, chloromethane, formic acid, formaldehyde, silane |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references |
|
Methane is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH4. It is the simplest alkane, and the principal component of natural gas. Methane's bond angles are 109.5 degrees. Burning methane in the presence of oxygen produces carbon dioxide and water. The relative abundance of methane and its clean burning process makes it a very attractive fuel. However, because it is a gas at normal temperature and pressure, methane is difficult to transport from its source. In its natural gas form, it is generally transported in bulk by pipeline or LNG carriers; few countries still transport it by truck.
Methane is a relatively potent greenhouse gas with a high global warming potential of 72 (averaged over 20 years) or 25 (averaged over 100 years).[1] Methane in the atmosphere is eventually oxidized, producing carbon dioxide and water. As a result, methane in the atmosphere has a half life of seven years (if no methane were added, then every seven years, the amount of methane would halve).
The abundance of methane in the Earth's atmosphere in 1998 was 1745 parts per billion, up from 700 ppb in 1750. In the same time period, CO2 increased from 278 to 365 parts per million. The radiative forcing effect due to this increase in methane abundance is about one-third of that of the CO2 increase.[2] In addition, there is a large, but unknown, amount of methane in methane clathrates in the ocean floors. The Earth's crust contains huge amounts of methane. Large amounts of methane are produced anaerobically by methanogenesis. Other sources include mud volcanoes which are connected with deep geological faults.
Contents[hide] |
Properties
Methane is the major component of natural gas, about 87% by volume. At room temperature and standard pressure, methane is a colorless, odorless gas; the smell characteristic of natural gas is an artificial safety measure caused by the addition of an odorant, often methanethiol or ethanethiol. Methane has a boiling point of −161 °C at a pressure of one atmosphere. As a gas it is flammable only over a narrow range of concentrations (5–15%) in air. Liquid methane does not burn unless subjected to high pressure (normally 4–5 atmospheres).
Potential health effects
Methane is not toxic; however, it is highly flammable and may form explosive mixtures with air. Methane is violently reactive with oxidizers, halogens, and some halogen-containing compounds. Methane is also an asphyxiant and may displace oxygen in an enclosed space. Asphyxia may result if the oxygen concentration is reduced to below 19.5% by displacement . The concentrations at which flammable or explosive mixtures form are much lower than the concentration at which asphyxiation risk is significant. When structures are built on or near landfills, methane off-gas can penetrate the buildings' interiors and expose occupants to significant levels of methane. Some buildings have specially engineered recovery systems below their basements to actively capture such fugitive off-gas and vent it away from the building. An example of this type of system is in the Dakin Building, Brisbane, California.
Reactions of methane
Main reactions with methane are: combustion, steam reforming to syngas, and halogenation. In general, methane reactions are hard to control. Partial oxidation to methanol, for example, is difficult to achieve; the reaction typically progresses all the way to carbon dioxide and water.
Combustion
In the combustion of methane, several steps are involved:
Methane is believed to form a formaldehyde (HCHO or H2CO). The formaldehyde gives a formyl radical (HCO), which then forms carbon monoxide (CO). The process is called oxidative pyrolysis:
CH4 + O2 → CO + H2 + H2O
Following oxidative pyrolysis, the H2 oxidizes, forming H2O, replenishing the active species, and releasing heat. This occurs very quickly, usually in significantly less than a millisecond.
2H2 + O2 →2H2O
Finally, the CO oxidizes, forming CO2 and releasing more heat. This process is generally slower than the other chemical steps, and typically requires a few to several milliseconds to occur.
2CO + O2 →2CO2
The result of the above is the following total equation:
where bracketed "g" stands for gaseous form and bracketed "l" stands for liquid form.
Hydrogen activation
The strength of the carbon-hydrogen covalent bond in methane is among the strongest in all hydrocarbons, and thus its use as a chemical feedstock is limited. Despite the high activation barrier for breaking the C–H bond, CH4 is still the principal starting material for manufacture of hydrogen in steam reforming. The search for catalysts which can facilitate C–H bond activation in methane and other low alkanes is an area of research with considerable industrial significance.
Reactions with halogens
Methane reacts with all halogens given appropriate conditions, as follows:
CH4 + X2 → CH3X + HX
where X is a halogen: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), or iodine (I). This mechanism for this process is called free radical halogenation. When X is Cl, this mechanism has the following form:
- If used isomolecular (equal molecule analogy) quantities in CH2X2, CHX3, even CX4 also produses. Using a large overquantitity of CH4 reduces the production of CH2X2, CHX3, X4 and more clean CH3X produces.
1. Radical generation:
![Cl_2 \xrightarrow[\triangle]{UV} 2Cl^. - 239 kJ](/2009-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.7_2009-05/I/fc7a8ad8af57852d0e67226ad13a48fa.png)
- The needed energy comes from UV radiation or heating,
2. Radical exchanges:
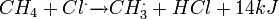
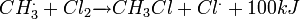
3. Radiacal extermination:
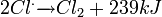
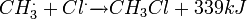
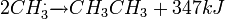
Uses
Fuel
- For more on the use of methane as a fuel, see: natural gas
Methane is important for electrical generation by burning it as a fuel in a gas turbine or steam boiler. Compared to other hydrocarbon fuels, burning methane produces less carbon dioxide for each unit of heat released. At about 891 kJ/mol, methane's combustion heat is lower than any other hydrocarbon; but a ratio with the molecular mass (16.0 g/mol) divided by the heat of combustion (891 kJ/mol) shows that methane, being the simplest hydrocarbon, produces more heat per mass unit than other complex hydrocarbons. In many cities, methane is piped into homes for domestic heating and cooking purposes. In this context it is usually known as natural gas, and is considered to have an energy content of 39 megajoules per cubic meter, or 1,000 BTU per standard cubic foot.
Methane in the form of compressed natural gas is used as a vehicle fuel, and is claimed to be more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels such as gasoline/petrol and diesel.
Research is being conducted by NASA on methane's potential as a rocket fuel. One advantage of methane is that it is abundant in many parts of the solar system and it could potentially be harvested in situ, providing fuel for a return journey. [4]
Industrial uses
Methane is used in industrial chemical processes and may be transported as a refrigerated liquid (liquefied natural gas, or LNG). While leaks from a refrigerated liquid container are initially heavier than air due to the increased density of the cold gas, the gas at ambient temperature is lighter than air. Gas pipelines distribute large amounts of natural gas, of which methane is the principal component.
In the chemical industry, methane is the feedstock of choice for the production of hydrogen, methanol, acetic acid, and acetic anhydride. When used to produce any of these chemicals, methane is first converted to synthesis gas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, by steam reforming. In this process, methane and steam react on a nickel catalyst at high temperatures (700–1100 °C).
![CH_4 + H_2O \xrightarrow[700-1100^oC]{Ni} CO + 3H_2](/2009-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.7_2009-05/I/cd8f5a0d855b7ea1e51de43ce679c28c.png)
The ratio of carbon monoxide to hydrogen in synthesis gas can then be adjusted via the water gas shift reaction to the appropriate value for the intended purpose.
CO + H2O → CO2 + H2
Less significant methane-derived chemicals include acetylene, prepared by passing methane through an electric arc, and the chloromethanes (chloromethane, dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride), produced by reacting methane with chlorine gas. However, the use of these chemicals is declining, acetylene as it is replaced by less costly substitutes, and the chloromethanes due to health and environmental concerns.
Sources of methane
Natural gas fields
The major source of methane is extraction from geological deposits known as natural gas fields. It is associated with other hydrocarbon fuels and sometimes accompanied by helium and nitrogen. The gas at shallow levels (low pressure) is formed by anaerobic decay of organic matter and reworked methane from deep under the Earth's surface. In general, sediments buried deeper and at higher temperatures than those which give oil generate natural gas. Methane is also produced in considerable quantities from the decaying organic wastes of solid waste landfills.
Alternative sources
Apart from gas fields an alternative method of obtaining methane is via biogas generated by the fermentation of organic matter including manure, wastewater sludge, municipal solid waste (including landfills), or any other biodegradable feedstock, under anaerobic conditions. Methane hydrates/clathrates (icelike combinations of methane and water on the sea floor, found in vast quantities) are a potential future source of methane. Cattle belch methane accounts for 16% of the world's annual methane emissions to the atmosphere. [5] The livestock sector in general (primarily cattle, chickens, and pigs) produces 37% of all human-induced methane".[6] However animals "that put their energies into making gas are less efficient at producing milk and meat". Early research has found a number of medical treatments and dietary adjustments that help limit the production of methane in ruminants.[7] [8] [9]
Industrially, methane can be created from common atmospheric gases and hydrogen (produced, for example, by electrolysis) through chemical reactions such as the Sabatier process, Fischer-Tropsch process. Coal bed methane extraction is a method for extracting methane from a coal deposit, while enhanced coal bed methane recovery is a method of recovering methane from an unminable coal seam.
A recent scientific experiment has also yielded results pointing to one species of plant[10] producing trace methane.[11].
Methane in Earth's atmosphere


Early in the Earth's history—about 3.5 billion years ago—there was 1,000 times as much methane in the atmosphere as there is now. The earliest methane was released into the atmosphere by volcanic activity. During this time, Earth's earliest life appeared. These first, ancient bacteria added to the methane concentration by converting hydrogen and carbon dioxide into methane and water. Oxygen did not become a major part of the atmosphere until photosynthetic organisms evolved later in Earth's history. With no oxygen, methane stayed in the atmosphere longer and at higher concentrations than it does today.
In present times, due to the increase in oxygen, the amount of methane has decreased. The average mole concentration of methane at the Earth's surface in 1998 was 1,745 ppb.[12] Its concentration is higher in the northern hemisphere as most sources (both natural and human) are larger. The concentrations vary seasonally with a minimum in the late summer mainly due to removal by the hydroxyl radical.
Methane is created near the surface, and it is carried into the stratosphere by rising air in the tropics. Uncontrolled build-up of methane in Earth's atmosphere is naturally checked—although human influence can upset this natural regulation—by methane's reaction with hydroxyl radicals formed from singlet oxygen atoms and with water vapor.
Methane as a greenhouse gas
Methane in the Earth's atmosphere is an important greenhouse gas with a global warming potential of 25 over a 100-year period. This means that a methane emission will have 25 times the impact on temperature of a carbon dioxide emission of the same mass over the following 100 years. Methane has a large effect for a brief period (a net lifetime of 8.4 years in the atmosphere), whereas carbon dioxide has a small effect for a long period (over 100 years). Because of this difference in effect and time period, the global warming potential of methane over a 20 year time period is 72. The Earth's methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases.[13] Usally, excess methane from landfills and other natural producers of methane are burned so CO2 is released into the atmosphere instead of methane because methane is such a more effective greenhouse gas.
Emissions of methane
Houweling et al. (1999) give the following values for methane emissions (Tg/a=teragrams per year):[12]

| Origin | CH4 Emission | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (Tg/a) | Type (%/a) | Total (%/a) | |
| Natural Emissions | |||
| Wetlands (incl. Rice agriculture) | 225 | 83 | 37 |
| Termites | 20 | 7 | 3 |
| Ocean | 15 | 6 | 3 |
| Hydrates | 10 | 4 | 2 |
| Natural Total | 270 | 100 | 45 |
| Anthropogenic Emissions | |||
| Energy | 110 | 33 | 18 |
| Landfills | 40 | 12 | 7 |
| Ruminants (Livestock) | 115 | 35 | 19 |
| Waste treatment | 25 | 8 | 4 |
| Biomass burning | 40 | 12 | 7 |
| Anthropogenic Total | 330 | 100 | 55 |
| Sinks | |||
| Soils | -30 | -5 | -5 |
| Tropospheric OH | -510 | -88 | -85 |
| Stratospheric loss | -40 | -7 | -7 |
| Sink Total | -580 | -100 | -97 |
| Emissions + Sinks | |||
| Imbalance (trend) | +20 | ~2.78 Tg/ppb | +7.19 ppb/a |
Slightly over half of the total emission is due to human activity.[13]
Living plants (e.g. forests) have recently been identified as a potentially important source of methane. A 2006 paper calculated emissions of 62–236 Tg a-1, and "this newly identified source may have important implications".[14][15] However the authors stress "our findings are preliminary with regard to the methane emission strength".[16] These findings have been called into question in a 2007 paper which found "there is no evidence for substantial aerobic methane emission by terrestrial plants, maximally 0.3% of the previously published values".[17]
Long term atmospheric measurements of methane by NOAA show that the build up of methane has slowed dramatically over the last decade, after nearly tripling since pre-industrial times [18]. It is thought that this reduction is due to reduced industrial emissions and drought in wetland areas.
Very recent data now suggests that methane concentrations may be rising again [19].
Removal processes
The major removal mechanism of methane from the atmosphere involves radical chemistry ; it reacts with the hydroxyl radical (·OH), initially formed from water vapor broken down by oxygen atoms that come from the cleavage of ozone by ultraviolet radiation:
- CH4 + ·OH → ·CH3 + H2O
This reaction in the troposphere gives a methane lifetime of 9.6 years. Two more minor sinks are soil sinks (160 year lifetime) and stratospheric loss by reaction with ·OH, ·Cl and ·O1D in the stratosphere (120 year lifetime), giving a net lifetime of 8.4 years.[12] Oxidation of methane is the main source of water vapor in the upper stratosphere (beginning at pressure levels around 10 kPa).
The methyl radical formed in the above reaction will, during normal daytime conditions in the troposphere, usually react with another hydroxyl radical to form formaldehyde. Note that this is not strictly oxidative pyrolysis as described previously. Formaldehyde can react again with a hydroxyl radical to form carbon dioxide and more water vapor. Note that sidechains in these reatcions may interact with nitrogen compounds that will likely produce ozone, thus supplanting radicals required in the initial reaction. [20]
Sudden release from methane clathrates
At high pressures, such as are found on the bottom of the ocean, methane forms a solid clathrate with water, known as methane hydrate. An unknown, but possibly very large quantity of methane is trapped in this form in ocean sediments. The sudden release of large volumes of methane from such sediments into the atmosphere has been suggested as a possible cause for rapid global warming events in the Earth's distant past, such as the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum of 55 million years ago.
Theories suggest that should global warming cause them to heat up sufficiently, all of this methane could again be suddenly released into the atmosphere. Since methane is twenty-five times stronger (for a given weight, averaged over 100 years) than CO2 as a greenhouse gas; this would immensely magnify the greenhouse effect, heating Earth to unprecedented levels (see Clathrate gun hypothesis).
Release of methane from bogs
Although less dramatic than release from clathrates, but already happening, is an increase in the release of methane from bogs as permafrost melts. Although records of permafrost are limited, recent years (1999 to 2007) have seen record thawing of permafrost in Alaska and Siberia.
Recent measurements in Siberia show that the methane released is five times greater than previously estimated [21].
Extraterrestrial methane
Methane has been detected or is believed to exist in several locations of the solar system. It is believed to have been created by abiotic processes, with the possible exception of Mars.
- Moon - traces are present in the thin atmosphere[22]
- Mars - the atmosphere contains 10 ppb methane
- Jupiter - the atmosphere contains about 0.3% methane
- Saturn - the atmosphere contains about 0.4% methane
- Uranus - the atmosphere contains 2.3% methane
- Ariel - methane is believed to be a constituent of Ariel's surface ice
- Miranda
- Oberon - about 20% of Oberon's surface ice is composed of methane-related carbon/nitrogen compounds
- Titania - about 20% of Titania's surface ice is composed of methane-related organic compounds
- Umbriel - methane is a constituent of Umbriel's surface ice
- Neptune - the atmosphere contains 1.6% methane
- Pluto - spectroscopic analysis of Pluto's surface reveals it to contain traces of methane[27][28]
- Eris - infrared light from the object revealed the presence of methane ice
- Comet Halley
- Comet Hyakutake - terrestrial observations found ethane and methane in the comet[30]
- Extrasolar planet HD 189733b - This is the first detection of an organic compound on planets outside the solar system. It is unknown how it originated, when the high temperature (700°C) favors the formation of carbon monoxide instead. [31]
- Interstellar clouds[32]
See also
- 2007 Zasyadko mine disaster
- Abiogenic petroleum origin
- Anaerobic digestion
- Anaerobic respiration
- Biogas
- Greenhouse gas
- Halomethane, halogenated methane derivatives.
- List of alkanes
- Methanation
- Methane clathrate, form of water ice which contains methane.
- Methanogen, archaea that produce methane as a metabolic by-product.
- Methanogenesis, the formation of methane by microbes.
- Methanotroph, bacteria that are able to grow using methane as their only source of carbon and energy.
- Methyl group, a functional group similar to methane.
- Organic gas
- Thomas Gold
References
- ↑ IPCC Fourth Assessment Report
- ↑ "Radiative Forces of Climate Change". Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. IPCC. Retrieved on 2008-05-26.
- ↑ SCHAUM'S OUTLINE SERIES, ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- ↑ http://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2007/04may_methaneblast.htm?list123532
- ↑ Miller, G. Tyler. Sustaining the Earth: An Integrated Approach. U.S.A.: Thomson Advantage Books, 2007. 160.
- ↑ "Livestock’s Long Shadow–Environmental Issues and Options". Retrieved on 2007-01-04.
- ↑ California Cows Fail Latest Emissions Test
- ↑ New Zealand Tries to Cap Gaseous Sheep Burps
- ↑ Research on use of bacteria from the stomach lining of kangaroos (who don't emit methane) to reduce methane in cattle
- ↑ Plants do emit methane after all - earth - 02 December 2007 - New Scientist Environment
- ↑ Methane emissions from terrestrial plants under aerobic conditions Nature, January 12, 2006
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "Trace Gases: Current Observations, Trends, and Budgets". Climate Change 2001. United Nations Environment Programme.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Technical summary". Climate Change 2001. United Nations Environment Programme.
- ↑ "Methane emissions from terrestrial plants under aerobic conditions". Nature (2006-01-12). Retrieved on 2006-09-07.
- ↑ "Plants revealed as methane source". BBC (2006-01-11). Retrieved on 2006-09-07.
- ↑ "Global warming - the blame is not with the plants". eurekalert.org (2006-01-18). Retrieved on 2006-09-06.
- ↑ Duek, Tom A.; Ries de Visser, Hendrik Poorter, Stefan Persijn, Antonie Gorissen, Willem de Visser, Ad Schapendonk, Jan Verhagen, Jan Snel, Frans J. M. Harren, Anthony K. Y. Ngai, Francel Verstappen, Harro Bouwmeester, Laurentius A. C. J. Voesenek, Adrie van der Werf (2007-03-30). "No evidence for substantial aerobic methane emission by terrestrial plants: a 13C-labelling approach.". New Phytologist (Blackwell) 175: 29. doi:. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02103.x. Retrieved on 2007-04-23.
- ↑ "SCIENTISTS PINPOINT CAUSE OF SLOWING METHANE EMISSIONS". NOAA news Online. Retrieved on 2007-05-23.
- ↑ "Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) Indicates Sharp Rise in Carbon Dioxide and Methane in 2007=NOAA news Online". Retrieved on 2008-06-16.
- ↑ "Methane and Carbon Monoxide in the Troposphere". Retrieved on 2008-07-18.
- ↑ "Methane bubbles climate trouble". BBC (2006-09-07). Retrieved on 2006-09-07.
- ↑ Stern, S.A. (1999). "The Lunar atmosphere: History, status, current problems, and context". Rev. Geophys. 37: 453–491. doi:.
- ↑ H. B. Niemann, et al. (2005). "The abundances of constituents of Titan’s atmosphere from the GCMS instrument on the Huygens probe". Nature 438: 779–784. doi:.
- ↑ Waite, J. H.; et al.; (2006); Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer: Enceladus Plume Composition and Structure, Science, Vol. 311, No. 5766, pp. 1419–1422
- ↑ A L Broadfoot, S K Bertaux, J E Dessler et al. (December 15 1989). "Ultraviolet Spectrometer Observations of Neptune and Triton". Science 246: 1459–1466. doi:. PMID 17756000. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1989Sci...246.1459B. Retrieved on 2008-01-15.
- ↑ Ron Miller; William K. Hartmann (May 2005). The Grand Tour: A Traveler's Guide to the Solar System (3rd ed.). Thailand: Workman Publishing. pp. 172–73. ISBN 0-7611-3547-2.
- ↑ Tobias C. Owen, Ted L. Roush et al. (6 August 1993). "Surface Ices and the Atmospheric Composition of Pluto". Science 261 (5122): 745–748. doi:. PMID 17757212. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/261/5122/745. Retrieved on 2007-03-29.
- ↑ "Pluto". SolStation (2006). Retrieved on 2007-03-28.
- ↑ B. Sicardy et al (2006). "Charon’s size and an upper limit on its atmosphere from a stellar occultation". Nature 439: 52. doi:. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v439/n7072/abs/nature04351.html.
- ↑ Mumma, M.J.; Disanti, M.A., dello Russo, N., Fomenkova, M., Magee-Sauer, K., Kaminski, C.D., and D.X. Xie (1996). "Detection of Abundant Ethane and Methane, Along with Carbon Monoxide and Water, in Comet C/1996 B2 Hyakutake: Evidence for Interstellar Origin". Science 272: 1310. doi:. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-bib_query?bibcode=1996Sci...272.1310M.
- ↑ Stephen Battersby (2008-02-11). "Organic molecules found on alien world for first time". Retrieved on 2008-02-12.
- ↑ J. H. Lacy, J. S. Carr, N. J. Evans, II, F. Baas, J. M. Achtermann, J. F. Arens (1991). "Discovery of interstellar methane - Observations of gaseous and solid CH4 absorption toward young stars in molecular clouds". Astrophysical Journal 376: 556–560. doi:. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1991ApJ...376..556L.
External links
- Gavin Schmidt, Methane: A Scientific Journey from Obscurity to Climate Super-Stardom, NASA Goddard, September 2004
- Methane thermodynamics
- Methane in tundra and oceans to be released in atmosphere
- Inorganic Methane
- International Chemical Safety Card 0291
- Methane Hydrates
- Computational Chemistry Wiki
- Safety data for methane
- Dynamic Viscosity of Methane
- Thermal Conductivity of Methane
- METHANE-EATING BUG HOLDS PROMISE FOR CUTTING GREENHOUSE GAS. Media Release, GNS Science, New Zealand]
- Catalytic conversion of methane to more useful chemicals and fuels
|
||||||||