Machine gun




- For other uses of the phrase, see Machine Gun (disambiguation).
A machine gun is a fully-automatic mounted or portable firearm, usually designed to fire rifle cartridges in quick succession from an ammunition belt or large-capacity magazine, typically at a rate of several hundred rounds per minute. The first machine guns were manually operated, for example, by turning a hand crank.
In United States law, machine gun is a term of art for any fully-automatic firearm, and also for any component or part that will modify an existing firearm into a fully-automatic firearm.[1]
Contents |
Caliber overview
Machine guns are generally categorized as submachine guns, machine guns, or autocannons. The distinction between submachine guns and machine guns is subtle, hinging upon whether the ammunition used is intended for use in side arms (chiefly semi-automatic pistols) or rifles; the difference between machine guns and autocannons is based on caliber, with autocannons using calibers larger than 15 mm.[2]
Another factor is whether the gun fires conventional rounds or explosive rounds. Guns firing large-caliber explosive rounds are generally considered either autocannons or automatic grenade launchers ("grenade machine guns"). By contrast to the other two categories (submachine guns and autocannons), machine guns (like rifles) tend to share a very high ratio of barrel length to caliber (a long barrel for a small caliber); indeed, a true machine gun is essentially a fully-automatic rifle, and the boundaries between the two are often blurred. Often, the criterion for a machine gun as opposed to an automatic rifle is considered to be the presence of a quick change barrel or other cooling system (see below).
Overview of modern automatic machine guns

Unlike semi-automatic firearms, which require one trigger pull per bullet fired, a machine gun is designed to fire bullets as long as the trigger is held down and ammunition is fed into the weapon. Although the term "machine gun" is often used by civilians to describe all fully automatic weapons, in military usage the term is restricted to relatively heavy weapons fired from some sort of support rather than hand-held, able to provide continuous or frequent bursts of automatic fire for as long as ammunition lasts. Machine guns are normally used against unprotected or lightly-protected personnel, or to provide suppressive fire.
Some machine guns have in practice maintained suppressive fire almost continuously for hours; other automatic weapons overheat after less than a minute of use. Because they become very hot, practically all machine guns fire from an open bolt, to permit air cooling from the breech between bursts. They also have either a barrel cooling system, or removable barrels which allow a hot barrel to be replaced.
Although subdivided into "light", "medium", "heavy" or "general purpose", even the lightest machine guns tend to be substantially larger and heavier than other automatic weapons. Squad automatic weapons (SAWs) are a variation of light machine gun and only require one operator (sometimes with an assistant to carry ammunition). Medium and heavy machine guns are either mounted on a tripod or on a vehicle; when carried on foot, the machine gun and associated equipment (tripod, ammunition, spare barrels) require additional crew members.
The majority of machine guns are belt-fed, although some light machine guns are fed from drum or box magazines, and some vehicle-mounted machine guns are hopper-fed.
Other automatic weapons are subdivided into several categories based on the size of the bullet used, and whether the cartridge is fired from a positively locked closed bolt, or a non-positively locked open bolt. Fully automatic firearms using pistol-caliber ammunition are called machine pistols or submachine guns largely on the basis of size. Selective fire rifles firing a full-power rifle cartridge from a closed bolt are called automatic rifles, while those of lighter weight and that are more easily carried are called assault rifles. The difference in construction was driven by the difference in intended deployment. Automatic rifles (such as the Browning Automatic Rifle were designed to be a high duty cycle arm for support of other troops, and were often made and deployed with quick change barrel assemblies to allow quick replacement of over heated barrels to allow for continued fire, and may have been operated by both the person actually firing the weapon as well as an additional crewman to assist in providing and caring for ammunition and the barrels, similar to a reduced version of a squad weapon (above). The assault rifle generally was made for a more intermittent duty cycle, and was designed to be easily carried and used by a single person.
Assault rifles are a compromise between the size and weight of pistol-caliber submachine gun and a full size traditional automatic rifle by firing intermediate sized cartridges and allowing semi-automatic, burst and full-automatic fire options (selective fire). The modern legal definition of "assault rifle" is of significance in states like California, where according to state law, certain weapons that resemble true assault rifles, but are only capable of semi-automatic (or autoloading), are categorized as "assault weapons" and are illegal to purchase or own by civilian residents of the state, even after a less restrictive ban by the federal government was allowed to lapse after having no impact on these weapons use in crime. Therefore, supporters of gun rights generally consider the use of the phrase "assault weapon" to be pejorative when used to describe these civilian firearms, and this term is seldom used outside of the United States in this context.
The machine gun's primary role in modern ground combat is to provide suppressive fire on an opposing force's position, forcing the enemy to take cover and reducing the effectiveness of his fire . This either halts an enemy attack or allows friendly forces to attack enemy positions with less risk.
Light machine guns usually have simple iron sights. A common aiming system is to alternate solid ("ball") rounds and tracer ammunition rounds (usually one tracer round for every four ball rounds), so shooters can see the trajectory and "walk" the fire into the target, and direct the fire of other soldiers.
Many heavy machine guns, such as the Browning M2 .50 caliber machine gun, are accurate enough to engage targets at great distances. During the Vietnam War, Carlos Hathcock set the record for a long-distance shot at 7382 ft (2250 m) with a .50 caliber heavy machine gun he had equipped with a telescopic sight.[3] This led to the introduction of .50 caliber anti-materiel sniper rifles, such as the Barrett M82.
Operation

All machine guns follow a cycle:
- Pulling manually or electrically the bolt assembly/bolt carrier rearward by way of the cocking lever to the point bolt carrier engages a sear and stays at rear position until trigger is activated making bolt carrier move forward
- Loading fresh round into chamber and locking bolt
- Firing round by way of a firing pin or striker(except for aircraft medium caliber using electric ignition primers) hitting the primer that ignites the powder when bolt reaches locked position.
- Unlocking and removing the spent case from the chamber and ejecting it out of the weapon as bolt is moving rearward
- Loading the next round into the firing chamber. Usually the recoil spring aka main spring tension pushes bolt back into battery and a cam strips the new round from a feeding device, belt or box.
Cycle is repeated as long as trigger is activated by operator Releasing the trigger resets the trigger mechanism by engaging a sear so the weapon stops firing with bolt carrier fully at the rear.
The operation is basically the same for all semi automatic or automatic weapons, regardless of the means of activating these mechanisms. Some examples:
- Machine pistols and submachine guns (like the World War II "grease gun," MAC-10 or the Uzi) are usually blowback operated.
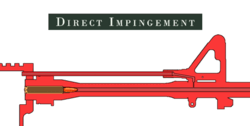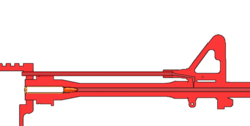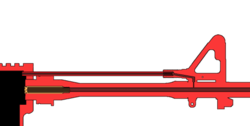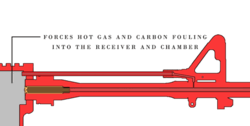

- Most assault rifles and squad automatic weapons are gas operated. Some weapons, such as the AR-15/M16, do not have piston, the gasses operating the bolt carrier by way of the gasses acting directly on it, it's called direct impingement. Others, such as the SA80, AR-18 and AK patterns, have a bolt carrier that unlocks and operates the bolt by way of the gasses acting on a piston .
- A recoil actuated machine gun uses the recoil to first unlock and then operate the action. Heavy machine guns, such as the M2 .50 and Browning .50, are of this type. A cam, lever or actuator demultiplicates the energy of the recoil to operate the bolt.
- An externally actuated machine gun uses an external power source, such as an electric motor or even a hand crank to move its mechanism through the firing sequence. Most modern weapons of this type are called chain guns in reference to their driving mechanism. Gatling guns and revolver cannon have several barrels or chambers on a rotating carrousel and a system of cams that load, cock, and fire each mechanism progressively as it rotates through the sequence. The continuous nature of the rotary action allows for an incredibly high cyclic rate of fire, often several thousand rounds per minute. Not all chain guns use multiple barrels or chambers, though. Chain guns are less prone to jamming than a gun operated by gas or recoil, as the external power source will eject misfired rounds with no further trouble. This is not possible if the force needed to eject the round comes from the round itself. Chain guns are generally used with large shells, 20 mm in diameter or more They offer benefits of reliability and firepower, though the weight and size of the power source and driving mechanism makes them impractical for use outside of a vehicle or aircraft mount.
Heavy machine guns were often water cooled but air cooled MG have interchangeable barrels, which must be changed periodically to avoid overheating. The higher the rate of fire, the more often barrels must be changed and allowed to cool. To minimize this, most air-cooled guns are fired only in short bursts or at a reduced rate of fire.

In weapons where the round seats and fires at the same time, mechanical timing is essential for operator safety, to prevent the round from firing before it is seated properly. Machine guns are controlled by one or more mechanical sears. When a sear is in place, it effectively stops the bolt at some point in its range of motion. Some sears stop the bolt when it is locked to the rear. Other sears stop the firing pin from going forward after the round is locked into the chamber.
Almost all weapons have a "safety" sear, which simply keeps the trigger from engaging.
History
The Chinese had much success with creating a repeating crossbow; the most common model, the Zhuge Nu, better known in the West as the Chu-ko-nu, is typically attributed to 2nd and 3rd century strategist Zhuge Liang,[4] who developed it for the Kingdom of Shu during the Three Kingdoms period. However, a buried library in the ancient state of Chu indicates that some sort of repeating crossbow had at the very least been designed in the 3rd century BC. Other multi-shot weapons have a long development, going back to the 1st century in the West, with some claiming there were plans for a multi-shot arrow by Hero of Alexandria. Leonardo Da Vinci devised plans for one in the 15th century.
Some of the earliest firearms and attempts at higher rates of fire and some machine-gun-like traits existed as early as the 16th century, when Fathullah Shirazi (c. 1582), a Persian-Indian engineer and polymath who worked for Akbar the Great in the Mughal Empire, invented a multi-barrel gun, which had multiple gun barrels that fired hand cannons loaded with gunpowder. He also invented a primitive autocannon.[5]
However, it would not be until the mid-19th century that successful machine-gun designs came into existence. The key characteristic of modern machine guns, their relatively high rate of fire and more importantly machine (automatic) loading, came with the Model 1862 Gatling gun, which was adopted by the United States Navy. These weapons were still powered by hand; however, this changed with Hiram Maxim's idea of harnessing recoil energy to power reloading in his Maxim machine gun. Dr. Gatling also experimented with electric-motor-powered models; this externally powered machine reloading has seen use in modern weapons as well. The Vandenburg and Miltrailleuse volley (organ) gun concepts have been revived partially in the early 21st century in the form of electronically controlled, multibarreled volley guns. It is important to note that what exactly constitutes a machine gun, and whether volley guns are a type of machine gun, and to what extent some earlier types of devices are considered to be like machine guns, is a matter of debate in many cases and can vary depending which language and exact definition is used.
Early rapid-firing weapons
Among first known ancestor of multi-shot weapons was created by James Puckle, a London lawyer, who patented what he called "The Puckle Gun" on May 15, 1718. It was a design for a 1 in. (25.4 mm) caliber, flintlock revolver cannon able to fire 9 rounds before reloading, intended for use on ships.[6] According to Puckle, it was able to fire round bullets at Christians and square bullets at Turks.[6] While ahead of its time, foreshadowing the designs of revolvers, it was not adopted or produced.
In 1777, Philadelphia gunsmith Joseph Belton offered the Continental Congress a "new improved gun", which was capable of firing up to twenty shots in five seconds, automatically, and was capable of being loaded by a cartridge. Congress requested that Belton modify 100 flintlock muskets to fire eight shots in this manner, but rescinded the order when Belton's price proved too high.[7][8]
In the early and mid-19th century, a number of rapid-firing weapons appeared which offered multi-shot fire, and a number of semi-automatic weapons as well as volley guns. Volley guns (such as the Mitrailleuse) and double barreled pistols relied on duplicating all parts of the gun. Pepperbox pistols did away with needing multiple hammers but used multiple barrels. Revolvers further reduced this to only needing a pre-prepared magazine using the same barrel and ignitions. However, like the Puckle gun, they were still only semiautomatic.
The coffee-mill gun of the Civil War featured both automatic loading and single barrel, only separated functionally from the modern machine gun by being hand-powered rather than using cartridges.
The Gatling gun, patented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling, was the first to offer controlled, sequential automatic fire with automatic loading. The design's key features were machine loading of prepared cartridges and a hand-operated crank for sequential high-speed firing. It first saw very limited action in the American Civil War and was subsequently improved. Many were sold to other armies in the late 1800s and continued to be used into the early 1900s, until they were gradually supplanted by Maxim guns. Early multi-barrel guns were approximately the size and weight of contemporary artillery pieces, and were often perceived as a replacement for cannon firing grapeshot or cannister shot.[9] The large wheels required to move these guns around required a high firing position which increased the vulnerability of their crews.[9] Sustained firing of gunpowder cartridges generated a cloud of smoke making concealment impossible until smokeless powder became available in the late 19th century.[10] Gatling guns were targeted by artillery they could not reach and their crews were targeted by snipers they could not see.[9] The Gatling gun was used most successfully to expand European colonial empires by killing warriors of non-industrialized societies.[9]
The Gatlings were the first widely used rapid-fire guns and, due to their multiple barrels, could offer more sustained fire than the first generation of air-cooled, recoil-operated machine guns. The weight, complexity, and resulting cost of the multibarrel design meant recoil-operated weapons, which could be made lighter and cheaper, would supplant them. Recoil operated machine guns were light enough to be moved by one man, were easier to move through rough terrain, and could be fired from a lower, protected position. It would be another 50 years before the concept was again used to allow extremely high rates of fire, such as in miniguns, and automatic aircraft cannons.
Maxim gun

The first machine gun was invented in 1881 by Sir Hiram Maxim. The "Maxim gun" used the recoil power of the previously fired bullet to reload rather than being hand-powered, enabling a much higher rate of fire than was possible using earlier designs such as the Nordenfelt and Gatling weapons. Maxim's other great innovation was the use of water cooling (via a water jacket around the barrel) to reduce overheating. Maxim's gun was widely adopted and derivative designs were used on all sides during the First World War, most famously - during stalemate at The Battle of the Somme. The design required fewer crew, was lighter, and more usable than earlier Nordenfelt guns and Gatling guns.
Heavy guns based on the Maxim such as the Vickers machine gun were joined by many other machine weapons, which mostly had their start in the early 20th century such as the Hotchkiss machine gun. Submachine guns (e.g., the German MP18) as well as lighter machine guns (the Chauchat, for example) saw their first major use in World War I, along with heavy use of large-caliber machine guns. The biggest single cause of casualties in World War I was actually artillery, but combined with wire entanglements, machine guns earned a fearsome reputation. The automatic mechanisms of machine guns were applied to handguns, giving rise to automatic pistols (and eventually machine pistols) such as the Borchardt (1890s) and later submachine guns (such as the Beretta 1918). Machine guns were mounted in aircraft for the first time in World War I. Firing through a moving propeller was solved in a variety of ways, including the interrupter gear, metal reinforcement of the propeller, or simply avoiding the problem with wing-mounted guns or having a pusher propeller.
Interwar era and World War II
During the interwar years, many new designs were developed, such as the Browning M2 .50 caliber (12.7 mm) in 1933, which, along with others, were used in World War II. The trend toward automatic rifles, lighter machine guns, and more powerful submachine guns resulted in a wide variety of firearms that combined characteristics of ordinary rifles and machine guns. The Cei-Rigotti (1900s), Fedorov Avtomat (1910s), AVS-36 Simonov (1930s), MP44, M2 Carbine, AK-47, and AR-15 have come to be known as assault rifles (after the German term sturmgewehr). Many aircraft were equipped with machine cannons, and similar cannon (nicknamed "Pom-pom guns") were used as antiaircraft weapons. The designs of Bofors of Sweden were widely used by both sides and have greatly influenced similar weapons developed since then.
Germany developed during the interwar years the first widely-used and successful general-purpose machine gun, the Maschinengewehr 34, which inspired many modern machine gun developments. The later Maschinengewehr 42 was feared during WWII by Allied forces as it was capable of firing at a rate of 1200-1800 rpm with pauses of only a few seconds to replace the quick-change barrel when operated by experienced soldiers . The successor of the MG42, the MG3, is still today in use in the German army. Many modern machine guns are derived from the MG42.
Modern era
The Cold War era saw mostly a refinement of weapon types in the form of lower weight and higher reliability. The semi-automatic rifles of World War II vintage were almost totally replaced by lighter assault rifles such as the M16 and Soviet AK-47. Infantry adopted general-purpose machine guns like the American M60 for squad use, using air cooling for lighter weight. Heavy machine guns were retained for ground vehicles and fortifications. For aircraft use, even heavy machine guns proved to lack killing power in the air-to-air role, and by the late 1950s fighter aircraft armament had almost totally switched to automatic cannons. Machine guns, with lower recoil, remained popular for helicopters and for ground attack aircraft, supplemented by new Gatling-style, electric multibarrel weapons like the American Minigun. In police, special operations, and other paramilitary roles, smaller automatic weapons, including light submachine guns and machine pistols, proliferated, many relying on ubiquitous pistol rounds.
The last major use of a manual machine gun, was a manual grenade machine gun during the 1970s used on river boats in the Vietnam Conflict. The manual type, the Mk 18 Mod 0 was replaced by fully automatic ones such as the Mk 19 grenade launcher.
Future

Conventional machine-gun development has been slowed by the fact that existing machine-gun designs are adequate for most purposes, although significant developments are taking place with regard to antiarmor and antimissile weapons.
Electronically controlled machine guns with ultrahigh rates of fire, like Metal Storm's weapons may see use in some applications, although current small-caliber weapons of this type have found little use: they are too light for anti-vehicle use, but too heavy (especially with the need to carry a tactically useful amount of ammunition) for individual soldiers. The trend towards higher reliability and lower mass for a given power will likely continue. Another example is the six barreled, 4000 round per minute, XM214 minigun "six pack" developed by General Electric. It has a complex power train and weighs 85 pounds, factors which may, in some circumstances, mitigate against its deployment.
Human interface
The most common interface on machine guns is a pistol grip and trigger. On earlier manual machine guns, the most common type was a hand crank. On externally powered machine guns, such as miniguns, an electronic button or trigger on a joystick is commonly used. Light machine guns often have a butt stock attached, while vehicle and tripod mounted machine guns usually have spade grips. In the late 20th century, scopes and other complex optics became more common as opposed to the more basic iron sights.
Loading systems in early manual machine guns were often from a hopper of loose (un-linked) cartridges. Manual-operated volley guns usually had to be reloaded manually all at once (each barrel reloaded by hand). With hoppers, the rounds could often be added while the weapon was firing. This gradually changed to belt-fed types. Belts were either held in the open by the person, or in a bag or box. Some modern vehicle machine guns used linkless feed systems however.

Modern machine guns are usually mounted in one of four ways. The first is a bipod - often these are integrated with the weapon. This is common on light machine guns and also medium machine guns. Another major way is with a larger tripod, where the person holding it does not form a 'leg' of support. Medium and heavy machine guns usually use tripods. On ships and aircraft machine guns are usually mounted on a pintle mount - basically a steel post that is connected to the frame. Tripod and pintle mounts are usually used with spade grips. The last major mounting type is one that is disconnected from humans, as part of an armament system, such as a tank coaxial or part of aircraft's armament. These are usually electrically-fired and have complex sighting systems. (For examples see US Helicopter Armament Subsystems).
Notes
- ↑ In United States law, a Machine Gun is defined (in part) by The National Firearms Act of 1934, as “... any weapon which shoots ... automatically more than one shot, without manual reloading, by a single function of the trigger.”
- ↑ Marchant-Smith, C.J., & Haslam, P.R., Small Arms & Cannons, Brassey's Battlefield Weapons Systems & Technology, Volume V, Brassey's Publishers, London, 1982, p.169,
- ↑ Henderson, Charles. Marine Sniper Berkley Caliber. (2005) ISBN 0-425-10355-2.
- ↑ CHU-KO-NU - The Chinese Repeating Crossbow
- ↑ A. K. Bag (2005), "Fathullah Shirazi: Cannon, Multi-barrel Gun and Yarghu", Indian Journal of History of Science 40 (3), pp. 431-436.
- ↑ Harold L. Peterson (2000). Arms and Armor in Colonial America, 1526-1783. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 217 - 218. ISBN 048641244X.
- ↑ United States Continental Congress (1907). Journals of the Continental Congress. USGPO., pages 324, 361
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Emmott, N.W. "The Devil's Watering Pot" United States Naval Institute Proceedings September 1972 p.70
- ↑ Emmott, N.W. "The Devil's Watering Pot" United States Naval Institute Proceedings September 1972 pp.72
See also
- Light machine gun
- Medium machine gun
- Heavy machine gun
- Firearm action
- Metal Storm
- Squad automatic weapon
- Breda (machine gun)
- Weapon
- General-purpose machine gun
- List of firearms
- Mitrailleuse - The French word for machine gun, but also a type of manual volley gun.
- Submachine gun
- Autocannon
External links
- Articles about Guns and Weapons in War
- subguns.com - US site with discussion on the topic and controlling US laws, and many machine guns for sale under US regulations
- MachineGun.com - Machine guns available for law enforcement and military sales.
- How Stuff Works - Article on the operation of Machine Guns, animated diagrams are included.
- Gun history
- U.S. Patent 15,315 -- A patent for an early automatic cannon
- Vickers Machine gun site
- The REME Museum of Technology - machine guns
