Laparoscopic surgery

Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS), bandaid surgery, keyhole surgery, or pinhole surgery is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5-1.5cm) as compared to larger incisions needed in traditional surgical procedures. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery performed on the thoracic or chest cavity is called thoracoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic and thoracoscopic surgery belong to the broader field of endoscopy.
The key element in laparoscopic surgery is the use of a laparoscope. There are two types: a telescopic rod lens system, that is usually connected to a video camera (single chip or three chip) or a digital laparoscope where the charge-coupled device is placed at the end of the laparoscope, eliminateing the rod lens system. Also attached is a fiber optic cable system connected to a 'cold' light source (halogen or xenon), to illuminate the operative field, inserted through a 5 mm or 10 mm cannula or trocar to view the operative field. The abdomen is usually insufflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a working and viewing space. The abdomen is essentially blown up like a balloon (insufflated), elevating the abdominal wall above the internal organs like a dome. The gas used is CO2, which is common to the human body and can be absorbed by tissue and removed by the respiratory system. It is also non-flammable, which is important because electrosurgical devices are commonly used in laparoscopic procedures.
Contents |
History
It is difficult to credit one individual with the pioneering of laparoscopic approach. In 1902 Georg Kelling, of Dresden, Saxony, performed the first laparoscopic procedure in dogs and in 1910 Hans Christian Jacobaeus of Sweden reported the first laparoscopic operation in humans. In the ensuing several decades, numerous individuals refined and popularized the approach further for laparoscopy. The introduction of computer chip television camera was a seminal event in the field of laparoscopy. This innovation in technology provided the means to project a magnified view of the operative field onto a monitor, and at the same time freed both the operating surgeon's hands, thereby facilitating performance of complex laparoscopic procedures. Prior to its conception, laparoscopy was a surgical approach with very limited application and used mainly for purposes of diagnosis and performance of simple procedures in gynecologic applications.
The introduction in 1990 of a laparoscopic clip applier with twenty automatically advancing clips (rather than a single load clip applier that would have to be taken out, reloaded and reintroduced for each clip application) made surgeons more comfortable with making the leap to laparoscopic cholecystectomies (gall bladder removal). On the other hand, some surgeons continue to use the single clip appliers as they save as much as $200 per case for the patient, detract nothing from the quality of the clip ligation, and add only seconds to case length.
Procedures
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most common laparoscopic procedure performed. In this procedure, 5-10mm diameter instruments (graspers, scissors, clip applier) can be introduced by the surgeon into the abdomen through trocars (hollow tubes with a seal to keep the CO2 from leaking). Rather than a minimum 20cm incision as in traditional cholecystectomy, four incisions of 0.5-1.0cm will be sufficient to perform a laparoscopic removal of a gallbladder. Since the gall bladder is similar to a small balloon that stores and releases bile, it can usually be removed from the abdomen by suctioning out the bile and then removing the deflated gallbladder through the 1cm incision at the patient's navel. The length of postoperative stay in the hospital is minimal, and same-day discharges are possible in cases of early morning procedures.
In certain advanced laparoscopic procedures where the size of the specimen being removed would be too large to pull out through a trocar site, as would be done with a gallbladder, an incision larger than 10mm must be made. The most common of these procedures are removal of all or part of the colon (colectomy), or removal of the kidney (nephrectomy). Some surgeons perform these procedures completely laparoscopically, making the larger incision toward the end of the procedure for specimen removal, or, in the case of a colectomy, to also prepare the remaining healthy bowel to be reconnected (create an anastomosis). Many other surgeons feel that since they will have to make a larger incision for specimen removal anyway, they might as well use this incision to have their hand in the operative field during the procedure to aid as a retractor, dissector, and to be able to feel differing tissue densities (palpate), as they would in open surgery. This technique is called hand-assist laparoscopy. Since they will still be working with scopes and other laparoscopic instruments, CO2 will have to be maintained in the patient's abdomen, so a device known as a hand access port (a sleeve with a seal that allows passage of the hand) must be used. Surgeons that choose this hand-assist technique feel it reduces operative time significantly vs. the straight laparoscopic approach, as well as providing them more options in dealing with unexpected adverse events (i.e. uncontrolled bleeding) that may otherwise require creating a much larger incision and converting to a fully open surgical procedure.
Conceptually, the laparoscopic approach is intended to minimise post-operative pain and speed up recovery times, while maintaining an enhanced visual field for surgeons. Due to improved patient outcomes, in the last two decades, laparoscopic surgery has been adopted by various surgical sub-specialties including gastrointestinal surgery (including bariatric procedures for morbid obesity), gynecologic surgery and urology. Based on numerous prospective randomized controlled trials, the approach has proven to be beneficial in reducing post-operative morbidities such as wound infections and incisional hernias (especially in morbidly obese patients), and is now deemed safe when applied to surgery for cancers such as cancer of colon.
The restricted vision, the difficulty in handling of the instruments (new hand-eye coordination skills are needed), the lack of tactile perception and the limited working area are factors which add to the technical complexity of this surgical approach. For these reasons, minimally invasive surgery has emerged as a highly competitive new sub-specialty within various fields of surgery. Surgical residents who wish to focus on this area of surgery gain additional training during one or two years of fellowship after completing their basic surgical residency.
The first transatlantic surgery (Lindbergh Operation) ever performed was a laparoscopic gallbladder removal.
Advantages
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an open procedure. These include:
- reduced blood loss, which reduces the chance of needing a blood transfusion.
- smaller incision, which reduces pain and shortens recovery time.
- less pain, leading to less pain medication needed.
- Although procedure times are usually slightly longer, hospital stay is less, and often with a same day discharge which leads to a faster return to everyday living.
- reduced exposure of internal organs to possible external contaminants thereby reduced risk of acquiring infections.
- can be used in Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) surgery to put the eggs back into the fallopian tubes
Risks
Some of the risks are briefly described below:
- The most significant risks are from trocar injuries to either blood vessels or small or large bowel. The risk of such injuries is increased in patients who are obese or have a history of prior abdominal surgery. The initial trocar is typically inserted blindly. While these injuries are rare, significant complications can occur. Vascular injuries can result in hemorrhage that may be life threatening. Injuries to the bowel can cause a delayed peritonitis. It is very important that these injuries be recognized as early as possible. There is an excellent review of trocar injuries by the FDA at: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/medicaldevicesafety/stamp/trocar.html
- Some patients have sustained electrical burns unseen by surgeons who are working with electrodes that leak current into surrounding tissue. The resulting injuries can result in perforated organs and lead to peritonitis.
- Many patients with existing pulmonary disorders may not tolerate pneumoperitoneum (gas in the abdominal cavity), resulting in a need for conversion to open surgery after the initial attempt at laparoscopic approach.
- Not all of the CO2 introduced into the abdominal cavity is removed through the incisions during surgery. Gas tends to rise, and when a pocket of CO2 rises in the abdomen, it pushes against the diaphragm (the muscle that separates the abdominal from the thoracic cavities and facilitates breathing), and can exert pressure on the phrenic nerve. This produces a sensation of pain that may extend to the patient's shoulders. For an appendectomy, the right shoulder can be particularly painful. In some cases this can also cause considerable pain when breathing. In all cases, however, the pain is transient, as the body tissues will absorb the CO2 and eliminate it through respiration. [1]
- Coagulation disorders and dense adhesions (scar tissue) from previous abdominal surgery may pose added risk for laparoscopic surgery and are considered relative contra-indications for this approach.
- Patients can often have trouble walking after surgery for a few days
Robotics and technology
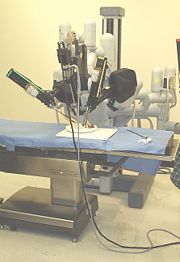
The process of minimally invasive surgery has been augmented by specialized tools for decades. However, in recent years, electronic tools have been developed to aid surgeons. Some of the features include:
- Visual magnification - use of a large viewing screen improves visibility
- Stabilization - Electromechanical damping of vibrations, due to machinery or shaky human hands
- Simulators - use of specialized virtual reality training tools to improve physicians' proficiency in surgery
- Reduced number of incisions
Robotic surgery has been touted as a solution to underdeveloped nations, whereby a single central hospital can operate several remote machines at distant locations. The potential for robotic surgery has had strong military interest as well, with the intention of providing mobile medical care while keeping trained doctors safe from battle.
Non robotic hand guided assistance systems
There are also user-friendly non robotic assistance systems that are single hand guided devices with a high potential to save time and money. These assistance devices are not bound by the restrictions of common medical robotic systems. The systems enhance the manual possibilities of the surgeon and his team, regarding the need of replacing static holding force during the intervention.
Some of the features are:
- Stabilisation of the camera picture because the whole static workload is conveyed by the assistance system.
- Some systems enable a fast repositioning and very short time for fixation of less than 0.02 seconds at the desired position. Some systems are lightweight constructions (18kg) and can withstand a force of 20 N in any position and direction.
- The benefit – a physically relaxed intervention team can work concentrated on the main goals during the intervention.
- The potentials of these systems enhance the possibilities of the mobile medical care with those lightweight assistance systems. These assistance systems meet the demands of true solo surgery assistance systems and are robust, versatile and easy to use.
See also
- Arthroscopy
- Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery
- Single port access surgery, also known as single incision laparoscopic surgery
Notes
References
- Surgical Device Poses a Rare but Serious Peril from the New York Times (Registration required)
- "Laparoscopy in Urology". Journal of Minimal Access Surgery 1 (4). 2005. http://www.journalofmas.com/showBackIssue.asp?issn=0972-9941;year=2005;volume=1;issue=4;month=October-December.
- Laparoscopic surgeries
- Mastery of Endoscopic and Laparoscopic Surgery W. Stephen, M.D. Eubanks; Steve Eubanks (Editor); Lee L., M.D. Swanstrom (Editor); Nathaniel J. Soper (Editor) Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2nd Edition 2004