International Phonetic Alphabet
| International Phonetic Alphabet | |
| Type | Partially featural alphabet |
|---|---|
| Spoken languages | Used for phonetic and phonemic transcription of any language |
| Time period | since 1888 |
| Parent systems | Romic alphabet → Phonotypic alphabet → International Phonetic Alphabet |
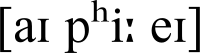 |
|
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | |
| International Phonetic Alphabet |
|---|
|
History |
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)[note 1] is a system of phonetic notation based on the Latin alphabet, devised by the International Phonetic Association as a standardized representation of the sounds of spoken language.[1] The IPA is used by linguists, speech pathologists and therapists, foreign language teachers and students, singers, actors, lexicographers, and translators.[2][3]
The IPA is designed to represent only those qualities of speech that are distinctive in spoken language: phonemes, intonation, and the separation of words and syllables.[1] To represent additional qualities of speech such as tooth-gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft palate, an extended set of symbols called the Extensions to the IPA is used.[2]
Occasionally symbols are added, removed, or modified by the International Phonetic Association. As of 2008, there are 107 distinct letters, 52 diacritics, and 4 prosody marks in the IPA proper.
History
In 1886, a group of French and British language teachers, led by the French linguist Paul Passy, formed what would come to be known (from 1897 onwards) as the International Phonetic Association (in French, l’Association phonétique internationale).[4] The original alphabet was based on a spelling reform for English known as the Romic alphabet, but in order to make it usable for other languages, the values of the symbols were allowed to vary from language to language.[5] For example, the sound [ʃ] (sh in shoe) was originally represented with the letter <c> in English, but with the letter <x> in French.[4] However, in 1888, the alphabet was revised so as to be uniform across languages, thus providing the base for all future revisions.[4][6]
Since its creation, the IPA has undergone a number of revisions. After major revisions and expansions in 1900 and 1932, the IPA remained unchanged until the IPA Kiel Convention in 1989. A minor revision took place in 1993, with the addition of four mid-central vowels[2] and the removal of symbols for voiceless implosives.[7] The alphabet was last revised in May 2005, with the addition of a symbol for the labiodental flap.[8] Apart from the addition and removal of symbols, changes to the IPA have consisted largely in renaming symbols and categories, and modifying typefaces.[2]
Extensions of the alphabet are relatively recent; "Extensions to the IPA" was created in 1990 and officially adopted by the International Clinical Phonetics and Linguistics Association in 1994.[9]
Description

The general principle of the IPA is to provide one symbol for each distinctive sound (or speech segment).[10] This means that it does not use letter combinations to represent single sounds,[note 2] or single letters to represent multiple sounds (the way <x> represents [ks] or [gz] in English). There are no letters that have context-dependent sound values (as <c> does in English and other European languages), and finally, the IPA does not usually have separate letters for two sounds if no known language makes a distinction between them (a property known as "selectiveness"[2]).[note 3]
Among the symbols of the IPA, 107 represent consonants and vowels, 31 are diacritics that are used to further specify these sounds, and 19 are used to indicate such qualities as length, tone, stress, and intonation.[note 4]
Letterforms
The symbols chosen for the IPA are meant to harmonize with the Latin alphabet.[note 5] For this reason, most symbols are either Latin or Greek letters, or modifications thereof. However, there are symbols that are neither: for example, the symbol denoting the glottal stop, <ʔ>, has the form of a "gelded" question mark, and was originally an apostrophe.[note 6] In fact, there are a few symbols, such as that of the voiced pharyngeal fricative, <ʕ>, which, though modified to blend with the Latin alphabet, were inspired by glyphs in other writing systems (in this case, the Arabic letter <ﻉ>, `ain).[7]
Despite its preference for letters that harmonize with the Latin alphabet, the International Phonetic Association has occasionally admitted symbols that do not have this property. For example, before 1989, the IPA symbols for click consonants were <ʘ>, <ʇ>, <ʗ>, and <ʖ>, all of which were derived either from existing symbols, or from Latin and Greek letters. However, except for <ʘ>, none of these symbols was widely used among Khoisanists or Bantuists, and as a result, they were replaced by the less Latin-like but more widespread symbols <ʘ>, <ǀ>, <ǃ>, <ǂ>, and <ǁ> at the IPA Kiel Convention in 1989.[11]
Symbols and sounds
The International Phonetic Alphabet is based on the Latin alphabet, using as few non-Latin forms as possible.[4] The Association created the IPA so that the sound values of most consonants taken from the Latin alphabet would correspond to “international usage”.[4] Hence, the letters <b>, <d>, <f>, (hard) <ɡ>, (non-silent) <h>, (unaspirated) <k>, <l>, <m>, <n>, (unaspirated) <p>, (voiceless) <s>, (unaspirated) <t>, <v>, <w>, and <z> have the values used in English; and the vowels from the Latin alphabet (<a>, <e>, <i>, <o>, <u>) correspond to the sound values of Latin: [i] is like the vowel in machine, [u] is as in rule, etc. Other letters may differ from English, but are used with these values in other European languages, such as <j>, <r>, and <y>.
This inventory was extended by using capital or cursive forms, diacritics, and rotation. There are also several derived or taken from the Greek alphabet, though the sound values may differ. For example, <ʋ> is a vowel in Greek, but an only indirectly related consonant in the IPA. Two of these (<θ> and <χ>) are used unmodified in form; for others (including <β>, <ɣ>, <ɛ>, <ɸ>, and <ʋ>) subtly different glyph shapes have been devised, which may be encoded in Unicode separately from their "parent" letters.
The sound values of modified Latin letters can often be derived from those of the original letters.[12] For example, letters with a rightward-facing hook at the bottom represent retroflex consonants; and small capital letters usually represent uvular consonants. Apart from the fact that certain kinds of modification to the shape of a letter generally correspond to certain kinds of modification to the sound represented, there is no way to deduce the sound represented by a symbol from the shape of the symbol (unlike, for example, in Visible Speech).
Beyond the letters themselves, there are a variety of secondary symbols which aid in transcription. Diacritic marks can be combined with IPA letters to transcribe modified phonetic values or secondary articulations. There are also special symbols for suprasegmental features such as stress and tone that are often employed.
Usage
- Further information: Phonetic transcription
Although the IPA offers over a hundred symbols for transcribing speech, it is not necessary to use all relevant symbols at the same time; it is possible to transcribe speech with various levels of precision. The most precise kind of phonetic transcription, in which sounds are described in as much detail as the system allows, without any regard for the linguistic significance of the distinctions thus made, is known as narrow transcription. Anything else is termed broad transcription, though "broad" is obviously a relative term. Both kinds of transcriptions are generally enclosed in brackets,[1] but broad transcriptions are sometimes enclosed in slashes instead of brackets.

Broad transcription only distinguishes sounds which are considered different by speakers of a language. Sounds that may be pronounced differently between styles and dialects or depending on neighbouring sounds can be considered the "same" sound in the sense that they are allophones of the same phoneme. When a word is written as phonemes, it is usually enclosed in slashes. For example, the pronunciation of the English word "little" may be transcribed broadly using the IPA as /lɪtl/, and this broad (imprecise) transcription is a correct (accurate) description of many, if not all, pronunciations. This broad transcription merely identifies the separate phonetically relevant components of the word, and it does not indicate the variety of corresponding sounds. On the other hand, the narrow transcription (placed between square brackets) specifies the way each sound is pronounced. A more narrow transcription of "little" would be different depending on the way it is said: [lɪɾɫ] (General American), [lɪʔɫ] (Cockney), or [lɪːɫ] are just a few possibilities.
Neither broad nor narrow transcription using the IPA provides an absolute description; rather, they provide relative descriptions of phonetic sounds. This is especially true with respect to the IPA vowels: there exists no hard and fast mapping between IPA symbols and formant frequency ranges, and in fact one set of formant frequencies may correspond to two different IPA symbols, depending on the phonology of the language in question.
Educational initiative
There is some interest in using native speakers to produce sound and video files of all the IPA speech sounds. Such a project would encompass a large subset of the world's languages. This would aid linguistic and anthropologic research, as well as help teach language learning. A standard reference IPA could preserve examples of speech sounds. For education, the IPA can help standardize resources which prepare students and children for language acquisition through familiarization and subsequent imitation of the breadth of human speech sounds.[13] Research by Flege, Mackay and Piske (2002) and Sebastián-Gallés, Echeverría and Bosch (2005) have shown that early exposure to extra phonetic sounds and uses improves later comprehension and pronunciation (accent).
Use
Linguists
Although IPA is popular for transcription by linguists, it is also common to use Americanist phonetic notation or IPA together with some nonstandard symbols, for reasons including reducing the error rate on reading handwritten transcriptions or (arguable) awkwardness of IPA in some situations. The exact practice may vary somewhat between languages and even individual researchers, so authors are generally encouraged to include a chart or other explanation of their choices.[14]
Dictionaries
Many British dictionaries, among which are learner's dictionaries such as the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary and the Cambridge Advanced Learner's Dictionary, now use the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent the pronunciation of words.[15] However, most American (and some British) volumes use their own conventions intended to be more intuitive for readers unfamiliar with the IPA. For example, the pronunciation-representation systems in many American dictionaries (such as Merriam-Webster) use "y" for IPA [j] and "sh" for IPA [ʃ], reflecting common representations of those sounds in written English.[16] (In IPA, [y] represents the sound of the French u (as in tu), and [sh] represents the pair of sounds in grass hut.)
One of the benefits of using an alternative to the IPA is the ability to use a single symbol for a sound pronounced differently in different dialects. For example, the American Heritage Dictionary uses ŏ for the vowel in cot (kŏt) but ô for the one in caught (kôt).[17] Some American speakers pronounce the vowels ŏ and ô the same way (for example, like IPA [ɒ] in the Boston dialect); for those speakers who maintain the distinction, depending on the accent, the vowel in cot may vary from [ɑ] to [a], while the vowel in caught may vary from [ɔ] to [ɑ], or may even be a diphthong. Using one symbol for the vowel in cot (instead of having different symbols for different pronunciations of the o) enables the dictionary to provide meaningful pronunciations for speakers of most dialects of English.
The IPA is also not universal among dictionaries in other countries and languages. Mass-market Czech multilingual dictionaries, for instance, tend to use the IPA only for sounds not found in the Czech language.[18]
Orthographies and capital variants
- See also: Latin characters in Unicode
IPA symbols have been incorporated into the standard orthographies of various languages, notably in Subsaharan Africa but in other regions as well. These include for example: Hausa; Fula; Akan; Gbe languages; and Manding languages.
An example of capital letter forms for IPA symbols is Kabiyé of northern Togo, which has Ɔ Ɛ Ɖ Ŋ Ɣ Ʃ Ʊ (or Ʋ) (capital ɔ ɛ ɖ ŋ ɣ ʃ ʊ (or ʋ)): MBƱ AJƐYA KIGBƐNDƱƱ ŊGBƐYƐ KEDIƔZAƔ SƆSƆƆ TƆM SE. Other IPA-paired capitals include Ɑ Ɓ Ƈ Ɗ Ə/Ǝ Ɠ Ħ Ɯ Ɱ Ɲ Ɵ Ʈ Ʒ Ɽ.
The abovementioned and other capital forms are supported by Unicode, but appear in Latin ranges other than the IPA extensions.
Opera
IPA has widespread use among opera singers for preparation, especially among English-speaking singers who rarely sing in their native language. Opera librettos are authoritatively transcribed in IPA, such as Nico Castel's volumes[19] and Timothy Cheek's book Singing in Czech.[20] Opera singers' ability to read IPA was recently used by the Visual Thesaurus, which employed several opera singers "to make recordings for the 150,000 words and phrases in VT's lexical database. ...for their vocal stamina, attention to the details of enunciation, and most of all, knowledge of IPA."[21]
Letters
The International Phonetic Alphabet divides its letter symbols into three categories: pulmonic consonants, non-pulmonic consonants, and vowels.[22][23] Each character is assigned a number, to prevent confusion between similar letters (such as ɵ and θ), for example in printing manuscripts. Different categories of sounds are assigned different ranges of numbers.
Pulmonic consonants
A pulmonic consonant is a consonant made by obstructing the glottis (the space between the vocal cords) or oral cavity (the mouth) and either simultaneously or subsequently letting out air from the lungs. Pulmonic consonants make up the majority of consonants in the IPA, as well as in human language. All consonants in the English language fall into this category.[24]
The pulmonic consonant table, which includes most consonants, is arranged in rows that designate manner of articulation, meaning how the consonant is produced, and columns that designate place of articulation, meaning where in the vocal tract the consonant is produced. The main chart includes only consonants with a single place of articulation.
| View this table as an image. | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place of articulation → | Labial | Coronal | Dorsal | Radical | Glottal | ||||||||||||
| Bilabial | Labiodental | Dental | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Epiglottal | |||||||
| Manner of articulation ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Nasal | m | ɱ | n | ɳ | ɲ | ŋ | ɴ | ||||||||||
| Plosive | p b | p̪ b̪ | t d | ʈ ɖ | c ɟ | k ɡ | q ɢ | ʡ | ʔ | ||||||||
| Fricative | ɸ β | f v | θ ð | s z | ʃ ʒ | ʂ ʐ | ç ʝ | x ɣ | χ | ʁ | ħ | ʕ | ʜ | ʢ | h ɦ | ||
| Approximant | β̞ | ʋ | ɹ | ɻ | j | ɰ | |||||||||||
| Trill | ʙ | r | ʀ | я* | |||||||||||||
| Tap or Flap | ⱱ̟† | ⱱ† | ɾ | ɽ | ɢ̆ | ʡ̯ | |||||||||||
| Lateral Fricative | ɬ ɮ | * | * | * | |||||||||||||
| Lateral Approximant | l | ɭ | ʎ | ʟ | |||||||||||||
| Lateral Flap | ɺ | * | ʎ̯ | ʟ̆ | |||||||||||||
- Notes
- Asterisks (*) next to symbols mark reported sounds that do not (yet) have official IPA symbols. See the respective articles for ad hoc symbols found in the literature.
- Daggers (†) mark IPA symbols that have recently been added to Unicode. As of Unicode 5.1.0, this is the case of the labiodental flap, symbolized by a right-hook v:
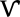 . These will display properly with a recent version of Charis SIL, Doulos SIL or DejaVu Sans fonts installed.
. These will display properly with a recent version of Charis SIL, Doulos SIL or DejaVu Sans fonts installed. - In rows where some symbols appear in pairs (the obstruents), the symbol to the right represents a voiced consonant (except breathy-voiced [ɦ]). However, [ʔ] cannot be voiced, and the voicing of [ʡ] is ambiguous.[25] In the other rows (the sonorants), the single symbol represents a voiced consonant.
- Although there is a single symbol for the coronal places of articulation for all consonants but fricatives, when dealing with a particular language, the symbols may be treated as specifically dental, alveolar, or post-alveolar, as appropriate for that language, without diacritics.
- Shaded areas indicate articulations judged to be impossible.
- The symbols [ʁ, ʕ, ʢ] represent either voiced fricatives or approximants.
- In many languages, such as English, [h] and [ɦ] are not actually glottal, fricatives, or approximants. Rather, they are bare phonation.[26]
- It is primarily the shape of the tongue rather than its position that distinguishes the fricatives [ʃ ʒ], [ɕ ʑ], and [ʂ ʐ].
Coarticulation
Coarticulated consonants are sounds that involve two simultaneous places of articulation (are pronounced using two parts of the vocal tract). In English, the [w] in "went" is a coarticulated consonant, because it is pronounced by rounding the lips and raising the back of the tongue. Other languages, such as French and Swedish, have different coarticulated consonants.
| View this table as an image | |
|---|---|
| ʍ | Voiceless labialized velar approximant |
| w | Voiced labialized velar approximant |
| ɥ | Voiced labialized palatal approximant |
| ɕ | Voiceless palatalized postalveolar (alveolo-palatal) fricative |
| ʑ | Voiced palatalized postalveolar (alveolo-palatal) fricative |
| ɧ | Voiceless "palatal-velar" fricative |
- Note
- [ɧ] is described as a "simultaneous [ʃ] and [x]".[27] However, this analysis is disputed. (See voiceless palatal-velar fricative for discussion.)
Affricates and double articulation
Affricates and doubly articulated stops are represented by two symbols joined by a tie bar, either above or below the symbols. The six most common affricates are optionally represented by ligatures, though this is no longer official IPA usage,[1] because a great number of ligatures would be required to represent all affricates this way. Alternatively, a superscript notation for a consonant release is sometimes used to transcribe affricates, for example tˢ for t͡s, paralleling kˣ ~ k͡x. The symbols for the palatal plosives, <c ɟ>, are often used as a convenience for [t͡ʃ d͡ʒ] or similar affricates, even in official IPA publications, so they must be interpreted with care.
| View this table as an image. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tie bar | Ligature | Description |
| t͡s | ʦ | voiceless alveolar affricate |
| d͡z | ʣ | voiced alveolar affricate |
| t͡ʃ | ʧ | voiceless postalveolar affricate |
| d͡ʒ | ʤ | voiced postalveolar affricate |
| t͡ɕ | ʨ | voiceless alveolo-palatal affricate |
| d͡ʑ | ʥ | voiced alveolo-palatal affricate |
| t͡ɬ | – | voiceless alveolar lateral affricate |
| k͡p | – | voiceless labial-velar plosive |
| ɡ͡b | – | voiced labial-velar plosive |
| ŋ͡m | – | labial-velar nasal stop |
- Note
- If your browser uses Arial Unicode MS to display IPA characters, the following incorrectly formed sequences may look better due to a bug in that font: ts͡, tʃ͡, tɕ͡, dz͡, dʒ͡, dʑ͡, tɬ͡, kp͡, ɡb͡, ŋm͡.
Non-pulmonic consonants
Non-pulmonic consonants are sounds whose airflow is not dependent on the lungs. These include clicks (found in the Khoisan languages of Africa) and implosives (found in languages such as Swahili).
| View this table as an image | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clicks | Implosives | Ejectives | |||
| ʘ | Bilabial | ɓ | Bilabial | ʼ | For example: |
| ǀ | Laminal alveolar ("dental") | ɗ | Alveolar | pʼ | Bilabial |
| ǃ | Apical (post-) alveolar ("retroflex") | ʄ | Palatal | tʼ | Alveolar |
| ǂ | Laminal postalveolar ("palatal") | ɠ | Velar | kʼ | Velar |
| ǁ | Lateral coronal ("lateral") | ʛ | Uvular | sʼ | Alveolar fricative |
- Notes
- Clicks are double articulated and have traditionally been described as having a forward 'release' and a rear 'accompaniment', with the click letters representing the release. Therefore all clicks would require two letters for proper notation: [k͡ǂ, ɡ͡ǂ, ŋ͡ǂ, q͡ǂ, ɢ͡ǂ, ɴ͡ǂ] etc., or [ǂ͡k, ǂ͡ɡ, ǂ͡ŋ, ǂ͡q, ǂ͡ɢ, ǂ͡ɴ]. When the dorsal articulation is omitted, a [k] may usually be assumed. However, recent research disputes the concept of 'accompaniment'.[28] In such approaches, the click letter represents both articulations, there is no velar-uvular distinction, and the accompanying letter represents the manner of the click: [ǂ, ɡǂ, ŋǂ] etc.
- Symbols for the voiceless implosives [ƥ, ƭ, ƈ, ƙ, ʠ] are no longer supported by the IPA, though they remain in Unicode. Instead, the IPA uses the voiced equivalent with a voiceless diacritic: [ɓ̥, ʛ̥], etc.
- Although not confirmed from any language, and therefore not explicitly recognized by the IPA, a retroflex implosive, [ᶑ], is supported in the Unicode Phonetic Extensions Supplement, added in version 4.1 of the Unicode Standard, or can be created as a composite [ɗ̡].
- The ejective symbol often stands in for a superscript glottal stop in glottalized but pulmonic sonorants, such as [mˀ], [lˀ], [wˀ], [aˀ]. These may also be transcribed as creaky [m̰], [l̰], [w̰], [a̰].
Vowels


The IPA defines a vowel as a sound which occurs at a syllable center.[29] Below is a chart depicting the vowels of the IPA. The IPA maps the vowels according to the position of the tongue.
The vertical axis of the chart is mapped by vowel height. Vowels pronounced with the tongue lowered are at the bottom, and vowels pronounced with the tongue raised are at the top. For example, [ɑ] (said as the "a" in "palm") is at the bottom because the tongue is lowered in this position. However, [i] (said as the vowel in "meet") is at the top because the sound is said with the tongue raised to the roof of the mouth.
In a similar fashion, the horizontal axis of the chart is determined by vowel backness. Vowels with the tongue moved towards the front of the mouth (such as [ɛ], the vowel in "met") are to the left in the chart, while those in which it is moved to the back (such as [ʌ], the vowel in "but") are placed to the right in the chart.
In places where vowels are paired, the right represents a rounded vowel (in which the lips are rounded) while the left is its unrounded counterpart.
- View the vowel chart as an image
| Front | Near- front | Central | Near- back | Back | ||
| Close |
|
|||||
| Near-close | ||||||
| Close-mid | ||||||
| Mid | ||||||
| Open-mid | ||||||
| Near-open | ||||||
| Open | ||||||
- Notes
- [a] officially represents a front vowel, but there is little distinction between front and central open vowels, and [a] is frequently used for an open central vowel. [14] However, if disambiguation is required, the retraction diacritic may be added to indicate an open central vowel ([a̱]).
Diacritics
Diacritics are small markings which are placed around the IPA letter in order to show a certain alteration or more specific description in the letter's pronunciation.[30] Sub-diacritics (markings normally placed below a letter or symbol) may be placed above a symbol having a descender (informally called a tail), e.g. ŋ̊.[30]
The dotless i, <ı>, is used when the dot would interfere with the diacritic. Other IPA symbols may appear as diacritics to represent phonetic detail: tˢ (fricative release), bʱ (breathy voice), ˀa (glottal onset), ᵊ (epenthetic schwa), oʊ (diphthongization). Additional diacritics were introduced in the Extensions to the IPA, which were designed principally for speech pathology.
| View the diacritic table as an image | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Syllabicity diacritics | |||
| ɹ̩ n̩ | Syllabic | e̯ ʊ̯ | Non-syllabic |
| Consonant-release diacritics | |||
| tʰ dʰ | Aspirated[a] | d̚ | No audible release |
| dⁿ | Nasal release | dˡ | Lateral release |
| Phonation diacritics | |||
| n̥ d̥ | Voiceless | s̬ t̬ | Voiced |
| b̤ a̤ | Breathy voiced[b] | b̰ a̰ | Creaky voiced |
| Articulation diacritics | |||
| t̪ d̪ | Dental | t̼ d̼ | Linguolabial |
| t̺ d̺ | Apical | t̻ d̻ | Laminal |
| u̟ t̟ | Advanced | i̠ t̠ | Retracted |
| ë ä | Centralized | e̽ ɯ̽ | Mid-centralized |
| e̝ ɹ̝ ˔ | Raised (ɹ̝ = voiced alveolar nonsibilant fricative) | ||
| e̞ β̞ ˕ | Lowered (β̞ = bilabial approximant) | ||
| Co-articulation diacritics | |||
| ɔ̹ x̹ | More rounded | ɔ̜ x̜ʷ | Less rounded |
| tʷ dʷ | Labialized or labio-velarized | tʲ dʲ | Palatalized |
| tˠ dˠ | Velarized | tˁ aˁ | Pharyngealized |
| ɫ z̴ | Velarized or pharyngealized | ||
| e̘ o̘ | Advanced tongue root | e̙ o̙ | Retracted tongue root |
| ẽ z̃ | Nasalized | ɚ ɝ | Rhotacized |
- Notes
- a^ With aspirated voiced consonants, the aspiration is also voiced. Many linguists prefer one of the diacritics dedicated to breathy voice.
- b^ Some linguists restrict this breathy-voice diacritic to sonorants, and transcribe obstruents as bʱ.
The state of the glottis can be finely transcribed with diacritics. A series of alveolar plosives ranging from an open to a closed glottis phonation are:
| [t] | voiceless | [d̤] | breathy voice, also called murmured |
| [d̥] | slack voice | [d] | modal voice |
| [d̬] | stiff voice | [d̰] | creaky voice |
| [ʔ͡t] | glottal closure |
Suprasegmentals
These symbols describe the features of a language above the level of individual consonants and vowels, such as prosody, tone, length, and stress, which often operate on syllables, words, or phrases: that is, elements such as the intensity, pitch, and gemination of the sounds of a language, as well as the rhythm and intonation of speech.[31] Although most of these symbols indicate distinctions that are phonemic at the word level, symbols also exist for intonation on a level greater than that of the word.[31]
| View this table as an image | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length, stress, and rhythm | ||||||
| ˈa | Primary stress (symbol goes before stressed syllable) |
ˌa | Secondary stress (symbol goes before stressed syllable) |
|||
| aː kː | Long (long vowel or geminate consonant) |
aˑ | Half-long | |||
| ə̆ | Extra-short | a.a | Syllable break | |||
| s‿a | Linking (absence of a break) | |||||
| Intonation | ||||||
| | | Minor (foot) break | ‖ | Major (intonation) break | |||
| ↗ | Global rise | ↘ | Global fall | |||
| Tone diacritics and tone letters | ||||||
| ŋ̋ e̋ | e˥ | Extra high / top | ꜛke | Upstep | ||
| ŋ́ é | e˦ | High | ŋ̌ ě | Rise | ||
| ŋ̄ ē | e˧ | Mid | ||||
| ŋ̀ è | e˨ | Low | ŋ̂ ê | Fall | ||
| ŋ̏ ȅ | e˩ | Extra low / bottom | ꜜke | Downstep | ||
Finer distinctions of tone may be indicated by combining the tone diacritics and letters shown here, though not many fonts support this. The primary examples are high (mid) rising ɔ᷄, ɔ˧˥; low rising ɔ᷅, ɔ˩˧; high falling ɔ᷇, ɔ˥˧; low (mid) falling ɔ᷆, ɔ˧˩; peaking ɔ᷈, ɔ˧˥˧; and dipping ɔ᷉, ɔ˧˩˧. A work-around for diacritics sometimes seen when a language has more than one rising or falling tone, and the author does not wish to completely abandon the IPA, is to restrict generic rising ɔ̌ and falling ɔ̂ for the higher-pitched of the rising and falling tones, ɔ˥˧ and ɔ˧˥, and to use the non-standard subscript diacritics ɔ̗ and ɔ̖ for the lower-pitched rising and falling tones, ɔ˩˧ and ɔ˧˩. When a language has four level tones, the two mid tones are sometimes transcribed as high-mid ɔ̍ (non-standard) and low-mid ɔ̄.
Obsolete symbols and nonstandard symbols
The IPA inherited alternate symbols from various traditions, but eventually settled on one for each sound. The other symbols are now considered obsolete. An example is ɷ which has been standardised to ʊ. Several symbols indicating secondary articulation have been dropped altogether, with the idea that such things should be indicated with diacritics: ƍ for zʷ is one. In addition, the rare voiceless implosive series ƥ ƭ ƈ ƙ ʠ has been dropped; they are now written ɓ̥ ɗ̥ ʄ̊ ɠ̊ ʛ̥ respectively.
There are also unsupported or ad hoc symbols from local traditions that find their way into publications that otherwise use the standard IPA. This is especially common with affricates such as ƛ for t͡ɬ (the "tl" in "Nahuatl").
IPA extensions
Extensions to the IPA, also often abbreviated as extIPA, is a group of symbols whose original purpose was to accurately transcribe disordered speech. At the IPA Kiel Convention in 1989, a group of linguists drew up the initial set of symbols for the Extended IPA.[32] Extensions to the IPA were first published in 1990, and modified over the next few years before its official publication in the Journal of the International Phonetic Association in 1994 allowed it to be officially adopted by the ICPLA.[33] While its original purpose was to transcribe disordered speech, linguists have used it to designate a number of unique sounds within standard communication, such as hushing, gnashing teeth, and smacking lips. The Extensions to the IPA have also been used to record certain peculiarities in an individual's voice, such as nasalized voicing.[2]
Aside from the extIPA, another set of symbols is used for voice quality (VoQS), such as whispering.
Segments that have no symbols
The remaining blank cells on the IPA chart can be filled without too much difficulty if the need arises. Some ad hoc symbols have appeared in the literature, for example for the retroflex lateral flap and the voiceless lateral fricative series, the epiglottal trill, and the labiodental plosives. (See the grey symbols in the PDF chart.) Diacritics can supply much of the remainder, which would indeed be appropriate if the sounds were allophones.[34]
Consonants without letters
Representations of consonant sounds outside of the core set are created by adding diacritics to symbols for similar sound values. The Spanish bilabial approximant is commonly written as a lowered fricative, [β̞]. Similarly, voiced lateral fricatives would be written as raised lateral approximants, [ɭ˔ ʎ̝ ʟ̝]. A few languages such as Banda have a bilabial flap as the preferred allophone of what is elsewhere a labiodental flap. It has been suggested that this be written with the labiodental flap symbol and the advanced diacritic, [ѵ̟].[35]
Similarly, a labiodental trill would be written [ʙ̪] (bilabial trill and the dental sign), and labiodental stops [p̪ b̪] rather than with the ad hoc symbols sometimes found in the literature. Other taps can be written as extra-short plosives or laterals, e.g. [ɟ̆ ɢ̆ ʟ̆], though in some cases the diacritic would need to be written below the letter. A retroflex trill can be written as a retracted [r̠], just as retroflex fricatives sometimes are. The remaining consonants, the uvular laterals (ʟ̠ etc.) and the palatal trill, while not strictly impossible, are very difficult to pronounce and are unlikely to occur even as allophones in the world's languages.
Vowels without letters
The vowels are similarly manageable by using diacritics for raising, lowering, fronting, backing, centering, and mid-centering.[36] For example, the unrounded equivalent of [ʊ] can be transcribed as mid-centered [ɯ̽], and the rounded equivalent of [æ] as raised [ɶ̝]. True mid vowels are lowered [e̞ ø̞ ɘ̞ ɵ̞ ɤ̞ o̞], while centered [ɪ̈ ʊ̈] and [ä] are near-close and open central vowels, respectively. The only known vowels that cannot be represented in this scheme are the compressed vowels, which would require a dedicated diacritic, such as [ʏ̫].
Symbol names
An IPA symbol is often distinguished from the sound it is intended to represent since there is not a one-to-one correspondence between symbol and sound in broad transcription. While the Handbook of the International Phonetic Association states that no official names exist for symbols, it admits the presence of one or two common names for each character that are commonly used.[37] The symbols also have nonce names in the Unicode standard. In some cases, the Unicode names and the IPA names do not agree. For example, IPA calls ɛ "epsilon", but Unicode calls it "small letter open E".
The traditional names of the Latin and Greek letters are usually used for unmodified symbols.[note 7] Letters which are not directly derived from these alphabets, such as [ʕ], may have a variety of names, sometimes based on the appearance of the symbol, and sometimes based on the sound that it represents. In Unicode, some of the symbols of Greek origin have Latin forms for use in IPA; the others use the symbols from the Greek section.
For diacritics, there are two methods of naming. For traditional diacritics, the IPA uses the name of the symbol from a certain language, for example, é is acute, based on the name of the symbol in English and French. In non-traditional diacritics, the IPA often names a symbol according to an object it resembles, as d̪ is called bridge.
ASCII transliterations, IPA influence on other phonetic alphabets
- See also: Unicode and HTML
Since the IPA uses symbols that are outside the ASCII character set, several systems have been developed that map the IPA symbols to ASCII characters. Notable systems include Kirshenbaum, SAMPA, and X-SAMPA. The usage of mapping systems in on-line text has to some extent been adopted in the context input methods, allowing convenient keying of IPA characters that would be otherwise unavailable on standard keyboard layouts.
See also
- Articulatory phonetics
- IAST
- IPA chart for English
- List of phonetics topics
- Phonetic transcription
- SAMPA, X-SAMPA and Kirshenbaum are other methods of mapping IPA designations into ASCII.
- Semyon Novgorodov - the inventor of IPA-based Yakut alphabet.
- TIPA provides IPA support for LaTeX.
- Unicode Phonetic Symbols
Notes
- ↑ "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself (from the phrase 'International Phonetic Alphabet') that resistance seems pedantic. Context usually serves to disambiguate the two usages." (Laver 1994:561)
- ↑ In contrast, English sometimes uses combinations of two letters to represent single sounds, such as the digraphs sh and th for the sounds [ʃ] and [θ]/[ð], respectively.
- ↑ For instance, flaps and taps are two different kinds of articulation, but since no language has (yet) been found to make a distinction between, say, an alveolar flap and an alveolar tap, the IPA does not provide such sounds with dedicated symbols. Instead, it provides a single symbol (in this case, [ɾ]) for both sounds. Strictly speaking, this makes the IPA a phonemic alphabet, not a phonetic one.
- ↑ There are five basic tone marks, which are combined for contour tones; six of these combinations are in common use.
- ↑ "The non-roman letters of the International Phonetic Alphabet have been designed as far as possible to harmonize well with the roman letters. The Association does not recognise makeshift letters; It recognises only letters which have been carefully cut so as to be in harmony with the other letters." (IPA 1949)
- ↑ Technically, the symbol [ʔ] could be considered Latin-derived, since the question mark may have originated as "Qo", an abbreviation of the Latin word quæstio, "question".
- ↑ For example, [p] is called "Lower-case P" and [χ] is "Chi." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 171)
Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 International Phonetic Association (IPA), Handbook.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 MacMahon, Michael K. C. (1996). "Phonetic Notation". in P. T. Daniels and W. Bright (eds.). The World's Writing Systems. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 821–846. ISBN 0-19-507993-0.
- ↑ Wall, Joan (1989). International Phonetic Alphabet for Singers: A Manual for English and Foreign Language Diction. Pst. ISBN 1877761508. http://www.amazon.com/International-Phonetic-Alphabet-Singers-Language/dp/1877761508.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 International Phonetic Association, Handbook, pp 194–196
- ↑ "Originally, the aim was to make available a set of phonetic symbols which would be given different articulatory values, if necessary, in different languages." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, pp 195–196)
- ↑ Passy, Paul (1888). "Our revised alphabet". The Phonetic Teacher: 57–60.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Pullum and Ladusaw, Phonetic Symbol Guide, pp 152 & 209
- ↑ Nicolaidis, Katerina (September 2005). "Approval of New IPA Sound: The Labiodental Flap". International Phonetic Association. Retrieved on 2006-09-17.
- ↑ International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 186
- ↑ “From its earliest days…the International Phonetic Association has aimed to provide ‘a separate sign for each distinctive sound; that is, for each sound which, being used instead of another, in the same language, can change the meaning of a word’.” (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 27)
- ↑ Laver, Principles of Phonetics,pp 174–175
- ↑ "The new letters should be suggestive of the sounds they represent, by their resemblance to the old ones." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 196)
- ↑ "Information Development News", Information Development (December 2004), pp. 233-238.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Sally Thomason (January 2, 2008). "Why I Don't Love the International Phonetic Alphabet". Language Log.
- ↑ "Phonetics". Cambridge Dictionaries Online (2002). Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- ↑ "Merriam-Webster Online Pronunciation Symbols". Retrieved on 2007-06-04.
Agnes, Michael (1999). Webster's New World College Dictionary. New York, NY: Macmillan USA. xxiii. ISBN 0-02-863119-6.
Pronunciation respelling for English has detailed comparisons. - ↑ "Pronunciation Key". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. Bartleby.com (2000). Retrieved on 2006-09-19.
- ↑ (Czech) Fronek, J. (2006) (in Czech). Velký anglicko-český slovník. Praha: Leda. ISBN 80-7335-022-X. "In accordance with long-established Czech lexicographical tradition, a modified version of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is adopted in which letters of the Czech alphabet are employed.".
- ↑ "Nico Castel's Complete Libretti Series". Castel Opera Arts. Retrieved on 2008-09-29.
- ↑ Cheek, Timothy (2001). Singing in Czech. The Scarecrow Press. pp. 392. ISBN 0-8108-4003-0 ISBN-13: 978-0-8108-4003-4. http://scarecrowpress.com/Catalog/SingleBook.shtml?command=Search&db=%5EDB/CATALOG.db&eqSKUdata=0810840030.
- ↑ Zimmer, Benjamin (2008-05-14). "Operatic IPA and the Visual Thesaurus". Language Log. University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved on 2009-09-29.
- ↑ "Segments can usefully be divided into two major categories, consonants and vowels." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 3)
- ↑ International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 6.
- ↑ Fromkin, Victoria; Rodman, Robert (1998) [1974]. An Introduction to Language (6th edition ed.). Fort Worth, TX: Harcourt Brace College Publishers. ISBN 0-03-018682-X.
- ↑ Ladefoged and Maddieson, 1996, Sounds of the World's Languages, §2.1.
- ↑ Ladefoged and Maddieson, 1996, Sounds of the World's Languages, §9.3.
- ↑ Ladefoged, Peter; Ian Maddieson (1996). The sounds of the world's languages. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 329–330. ISBN 0-631-19815-6.
- ↑ Amanda L. Miller et al., "Differences in airstream and posterior place of articulation among Nǀuu lingual stops". Submitted to the Journal of the International Phonetic Association. Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- ↑ International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 10.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 14-15.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 13.
- ↑ "At the 1989 Kiel Convention of the IPA, a sub-group was established to draw up recommendations for the transcription of disordered speech." ("Extensions to the IPA: An ExtIPA Chart" in International Phonetic Association, Handbook, pp 186.)
- ↑ "Extensions to the IPA: An ExtIPA Chart" in International Phonetic Association, Handbook, pp 186-187.
- ↑ "Diacritics may also be employed to create symbols for phonemes, thus reducing the need to create new letter shapes." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 27)
- ↑ Olson, Kenneth S.; & Hajek, John. (1999). The phonetic status of the labial flap. Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 29 (2), 101-114.
- ↑ "The diacrtics...can be used to modify the lip or tongue position implied by a vowel symbol." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 16)
- ↑ "...the International Phonetic Association has never officially approved a set of names..." (International Phonetic Association, Handbook, p. 31)
References
- Ball, Martin J.; John H. Esling & B. Craig. Dickson (1995). "The VoQS system for the transcription of voice quality". Journal of the International Phonetic Alphabet 25 (2): 71–80.
- Duckworth, M.; G. Allen, M.J. Ball (December 1990). "Extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet for the transcription of atypical speech". Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics 4 (4): 273–280.
- Hill, Kenneth C. (March 1988). "Review of Phonetic symbol guide by G. K. Pullum & W. Ladusaw". Language 64 (1): 143–144. doi:.
- International Phonetic Association (1989). "Report on the 1989 Kiel convention". Journal of the International Phonetic Alphabet 19 (2): 67–80.
- International Phonetic Association (1999). Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-65236-7 (hb); ISBN 0-521-63751-1 (pb).
- Jones, Daniel (1988). English pronouncing dictionary (revised 14th edition ed.). London: Dent. OCLC 18415701.
- Ladefoged, Peter (September 1990). "The revised International Phonetic Alphabet". Language 66 (3): 550–552. doi:.
- Ladefoged, Peter; Morris Hale (September 1988). "Some major features of the International Phonetic Alphabet". Language 64 (3): 577–582. doi:.
- Laver, John (1994). Principles of Phonetics. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-45031-4 (hb); ISBN 0-521-45655-X (pb).
- Pullum, Geoffrey K.; William A. Laduslaw (1986). Phonetic symbol guide. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-68532-2.
- Skinner, Edith; Timothy Monich, and Lilene Mansell (1990). Speak with Distinction. New York, NY: Applause Theatre Book Publishers.
External links
General
- A little encyclopedia of phonetics, Peter Roach, Professor of Phonetics, University of Reading, UK. (pdf)
- The International Phonetic Association web site
- The International Phonetic Alphabet (revised to 2005) Symbols for all languages are shown on this one-page chart.
- IPA copy & paste charts, keyboards, etc by IPA.Webstuff.org
- Learning the IPA for English, (Standard American English)
- Information on IPA by Omniglot
- IPA Chart in Unicode and XHTML/CSS
- Using IPA fonts with Mac OS X: The Comprehensive Guide, an article explaining how to install and use freeware fonts and keyboard layouts to type in the International Phonetic Alphabet on OS X.
Free IPA font downloads
- Charis SIL, a very complete international font (Latin, Greek, Cyrillic) in roman, italic, and bold typefaces that includes tone letters and pre-composed tone diacritics on IPA vowels, the new labiodental flap, and many non-standard phonetic symbols. Based on Bitstream Charter, this font suffers from extremely bad hinting when rendered by Freetype on Linux.
- Doulos SIL, a Times/Times New Roman style font. It contains the same characters as Charis SIL, but only in a single face, roman.
- TIPA, a font and system for entering IPA phonetic transcriptions in LaTeX documents.
- DejaVu fonts [1] have full Unicode IPA support.[2]
- Gentium, a professionally designed international font (Latin, Greek, Cyrillic) in roman and italic typefaces that includes the IPA, but not yet tone letters or the new labiodental flap. For bold typefaces but only the most basic IPA letters, Gentium Basic may be used.
Keyboard input
- Complete Guide: Beginners’ guide to using IPA on Windows, Mac OS and Linux, covering many office applications and browsers
- Online keyboard
- IPA Character Picker Web-based input method
- Online keyboard with MP3 sound files for IPA symbols
- Downloadable IPA-SIL keyboard layout for Mac OS X for Unicode IPA input
- Downloadable IPA keyboard layout for Microsoft Windows for Unicode IPA input
- IPACharMap is an on-screen keyboard for point and click character entry, which can then be copied and pasted into a unicode-aware word processor. Based on IPA Palette.
- IPA Palette is the Mac OS X version of IPACharMap.
- IPATotal keyboard
- Microsoft Template - Creates a Toolbar for Microsoft Word. (This uses macros)
Sound files
- Paul Meier Dialect Services — IPA Charts, including English diphthongs
- Peter Ladefoged's Course in Phonetics (with sound files)
- IPA chart with AIFF sound files for IPA symbols
- An introduction to the sounds of languages
- IPA chart with MP3 sound files for all IPA symbols on the chart (limited version is available to anyone)
- Flash version of IPA charts, with sound samples
- Another set of IPA sound samples
- Complete IPA chart with sound samples, including English diphthongs
Unicode charts
- Unicode chart for main IPA lettersPDF (127 KB)
- Unicode chart for IPA modifier lettersPDF (97.9 KB)
- Unicode chart including IPA diacriticsPDF (112 KB)
- International Phonetic Alphabet in Unicode
- Unicode-HTML codes for IPA symbols: Tables of symbol names, character entity references and/or numeric character references at PennState.
- MySQL Unicode collation chart for IPA and other phonetic blocks
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||