Iğdır Province
 |
|
| Location of Iğdır Province in Turkey | |
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Region: | Eastern Anatolia Region, Turkey |
| Area: | 3,587 (km²) |
| Total Population | 179,839 TUIK 2007 (est) |
| Licence plate code: | 76 |
| Area code: | 0476 |
| Governor Website | http://www.igdir.gov.tr |
| Weather forecast | turkeyforecast.com/weather/igdir |
Iğdır (Turkish: Iğdır, Kurdish: Îdir, Armenian: Իգդիր, Azerbaijani: İğdır, Russian: Игдир, Persian: ایگدیر) is a province in eastern Turkey, located along the border with Armenia, Azerbaijan (the area of Nakhchivan), and Iran. Its adjacent provinces are Kars to the northwest and Ağrı to the west and south. It occupies an area of 3,587 km²[1] and population of 179,839 (2006 est.), it was 168,634 in 2000 (up from 142,601 in 1990).
Turkey's highest mountain, the Biblical Mount Ararat (Ağrı Dağı) is in Iğdır, but much of the land is a wide plain far below the mountain. The climate is the warmest in this part of Turkey, cotton can be grown in Iğdır. Iğdır is where Noah is said to have thrived following the flood. The Armenian border is marked by the Aras River.
The provincial capital is the city of Iğdır.
Contents |
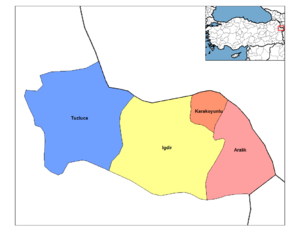
Districts
Iğdır province is divided into 4 districts (capital district in bold):
- Aralık
- Iğdır
- Karakoyunlu
- Tuzluca
Etymology
The area is named after a western Turkish clan Iğdıroğlu belonging to a branch of the Oghuz Turks.[2] They spread throughout Anatolia and there are towns and villages named Iğdır in Malatya and other parts of Turkey today.[3]
History

Archaeological research has uncovered Hurrian settlements in the Iğdır region going back to 4000 BC. The area was part of the Urartu kingdom circa 800 BC. There is an Urartu statuary in the area. It remained under Urartian control until its transition to the Orontid Dynasty of the Kingdom of Armenia. Seleucid and Sassanid forces were prominent from the 4th century BC, followed by the Arab armies of Islam in 646. Turks and Mongols fought through here for 400 years from 1064 onwards until the area was settled by Kara Koyunlu and then Ak Koyunlu Turkish tribes in the early 15th century.

A warfare ensued between Ottoman Empire and the Persian Empire from 1534 until 1746. In 1746, most of the land within the province of Iğdır today was ceded to Persia and became part of the Erivan khanate, a Muslim principality in Persia. The northern part of the province remained in Persian hands until after the Russo-Persian War, 1826-1828 when it became part of the Russian Empire under the Treaty of Turkmenchay. Under Russian administration, the area became the Surmalu uyezd (with its capital at the city of Iğdır) of the Armenian Oblast and later the Erivan Governorate. The southern half of the province remained in Ottoman hands through most of the 19th century but was also brought within the Russian Empire by Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78.
By the end of World War I, the whole area was under Russian control and Iğdır came under the administration of the Democratic Republic of Armenia as part of the Ararat province but upon the arrival of the newly founded Turkish army, Iğdır was ceded to Turkey by the Soviet Union in the Treaty of Kars. A substantial Armenian population remained in the area throughout this history of struggle between great powers. Armenians formed the ethnic majority in the city of Iğdır itself until 1919-1920 when most either died or fled due to starvation and ethnic cleansing.[4]
Region was saved and rescued by the Turkish Army under command of General Kazım Karabekir on 14 November 1920 and then, it gained status of administrative township in 1924, county status in 1934 and province status in 1992 respectively.[5]
Demographics

Today, Iğdır has a mixed population of Turks, and Azerbaijani Turks (who form the majority.[6] Kurds.[7]) The spring festival nevruz which is native to Iran is widely celebrated in Iğdır. The rural areas of Iğdır province have a higher population density (30 inhabitants/km²) than those of neighbouring provinces.
|
|
|
|
Places of interest

- The caravanserai of Zor, believed to have been built by an Armenian architect in the 13th or 14th century, is located 35km south-west of the city of Iğdır, and is named after the nearby village of Zor. It is one of halting places between Batumi-Tabriz High-way. Carvans used to stay over-here before passing over Çilli pass restoration works have been started for this subject ork of art which has been put under protection in 1988.[8] The ruins of an Armenian church was once located in the same area, but today nothing remains of it.[9]
- Sürmeli castle, 25 km west of the city of Iğdır and on the road to Tuzluca, is the site of a medieval Armenian town. However, it is currently inaccessible due to border restrictions.
- Statues with Ram Heads, Cementer stones with ram heads existing almost in all old cementers in Iğdır Plain are remnants from Kara Koyunlu period. These cementers of brave, heroic persons and young persons who had died in youth age.[10]
External links
- (Turkish) Official website of the Iğdır Province
- (Turkish) Official website of the Iğdır Municipality
- Armenian History and Presence in Iğdır
References
- ↑ GeoHive: Country Data: Turkey
- ↑ :: Iğdir Belediyesi ::
- ↑ igdir köyü
- ↑ VirtualAni - An account of Igdir from National Geographic, 1919
- ↑ "Introduction of Iğdır", Iğdır Municipality Publishing, 2003
- ↑ (Turkish) Hürriyet
- ↑ Distribution of Kurdish People — GlobalSecurity.org
- ↑ "Her Yönüyle Iğdır", Ziya Zakir Acar, 2004
- ↑ VirtualAni - The Caravanserai of Zor
- ↑ "Introduction of Iğdır", Iğdır Municipality Publishing, 2003
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||