Humerus
| Bone: Humerus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
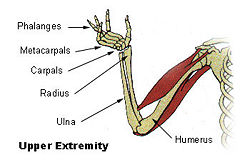
| Upper extremity | |
 |
|
| Gray's | subject #51 209 |
| MeSH | Humerus |
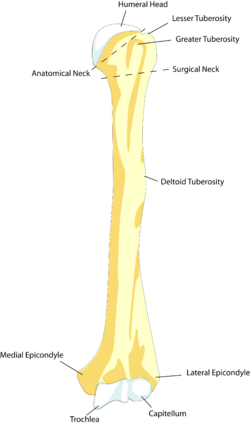
The humerus is a long bone in the arm or forelimb that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. Anatomically, it connects the scapula and the ulna, and consists of the following three sections:
- Upper extremity of humerus
- Body of humerus
- Lower extremity of humerus
Contents |
Humerus
- The deltoid originates on the lateral third of the clavicle, acromion and the spine of the scapula, it is inserted on the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus and has several actions including abduction, extension, and rotation.
- Pectoralis major, teres major and latissimus dorsi, insert at the intertubercular groove of the humerus. They work to adduct and medially rotate the humerus.
- Biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis, and brachioradialis (which attaches distally) act to flex the elbow. The biceps, however, does not attach to the humerus.
- Triceps brachii and anconeus extend the elbow, and attach to the posterior side of the humerus.
The axillary nerve
The most common type of shoulder dislocation is an anterior or inferior dislocation of the humerus of the glenohumeral joint. This dislocation has the potential to injure the axillary nerve or axillary artery. Signs and symptoms of this dislocation include a loss of the normal shoulder contour and a palpable depression under the acromion.
The Ulnar Nerve
The ulnar nerve at the distal end of the humerus near the elbow is sometimes referred to in popular culture as 'the funny bone'. Striking this nerve can cause a tingling sensation ("funny" feeling), and sometimes a significant amount of pain.
Additional images
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
|
|||||||||||||||||