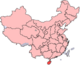
Haikou
| Haikou | |
| — Prefecture-level city — | |
| Chinese transcription(s) | |
| - Chinese | 海口 |
|---|---|
| - Pinyin | Hǎikǒu |
 |
|
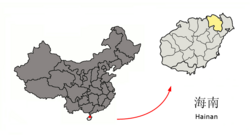 |
|
 Haikou
|
|
| Coordinates: | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Hainan |
| Area | |
| - Total | 2,304.84 km² (889.9 sq mi) |
| Population (2006) | |
| - Total | 830,192 |
| - Density | 360.2/km² (932.9/sq mi) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | 570000 |
| Area code(s) | 898 |
| Website: http://www.haikou.gov.cn/ | |
Haikou (Chinese: 海口; pinyin: Hǎikǒu), situated at the north of Hainan island, is the capital of Hainan Province of the People's Republic of China and has an estimated population of 830,192 (2006), therefore by far the largest city on the island.
Contents |
History
Haikou originally served as the port for Qiongshan, the ancient administrative capital of Hainan island, located 5 km inland.
In the 13th century it was fortified and became a military post under the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). The port is located west of the mouth of the Nandu, Hainan's principal river.
When Qiongshan was opened to foreign trade under the Treaty of Tianjin (1858), Haikou started to rival the old administrative city.
In 1926, Haikou overtook Qiongshan in population in the 1930s after it was declared a separate administrative county.
Haikou was developed as a port during the Sino-Japanese War (1937–45) when the Japanese invaded and occupied Hainan Island from early 1939 to 1945.
Since 1949, Haikou has maintained its position as Hainan's main port, handling more than half of the island's total trade. It has replaced Qiongshan as the island's administrative capital.
In 1988, Haikou was made a prefecture-level city as well as the capital of the newly-created Hainan Province.
Geography
Haikou has an area of 2,304.84 square kilometers.[1] It is situated on the north coast of Hainan Island, facing the Leizhou Peninsula, across the Hainan Strait (15 km wide); in an area that reaches from Zengmu Ansha in the south to the Qiongzhou Strait in the north; bordering the sea areas of the South China Sea and facing Vietnam in the west across Beibu Bay.
Climate
The city of Haikou is on the northern edge of the torrid zone, and is part of the monsoon tropical zone. April to October is the active period for tropical storms and typhoons; most occur between August and September. May to October is the rainy season with most rainfall coming in September.[2]
Average temperature (°C):
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.5 | 18.5 | 21.4 | 24.8 | 27.4 | 28.3 | 28.5 | 27.9 | 27.1 | 25.0 | 22.1 | 19.0 | 23.0 |
Average rainfall (mm):
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22.8 | 32.2 | 46.2 | 96.9 | 177.3 | 209.8 | 200.5 | 211.6 | 278.4 | 178.1 | 90.2 | 41.8 | 1591.5 |
Environment
A UN environmental organization listed Haikou as having the 5th best air quality out of 160 surveyed cities.[3] The air quality in Haikou rates, on average, 28 on the air quality index, ranking the city number one in China among medium and large sized cities.[4]
The groundwater is of international standard, and is classified as mineral water.
In 1995, the Haikou city government began an initiative to improve the quality of life for its residents. With the approval of the World Health Organization, and China's Ministry of Health, a ten-point plan was undertaken to address such issues as:
- Community health care
- Vaccinations for children
- Waste recycling
- Greenbelts and urban trees
- Environmentally friendly construction
- Public toilets
- Sewage treatment
- Communications
- Noise pollution
By 2004, the city had established 43 new community health service centers reaching 85 percent of the population. The initiative has increased the size of Haikou's green spaces to 2,000 hectares, with trees lining 40 percent of its roads. Noise pollution has dropped from 61.1db to 58.2db. 300 public toilets have been built. All industrial effluents, industrial waste water and solid waste, and all live sewage, is now processed through centralized treatment centers, and is disposed of without environmental impact. These improvements and others have increased life expectancy in Haikou to 78.26 years.[5]
Haikou city has also built 163 model ecological villages. Now, over 200,000 villagers in 933 villages have tap water in their homes.
Economy
The GDP per capita was $3,049 USD in 2007, ranked number 43 among 659 Chinese cities.
Haikou exports great quantities of agricultural produce and livestock. There is a small amount of industry, including canning, textiles, rice hulling, and light engineering.
Tourism
Haikou received 4.11 million tourists in 2002, up 7.99 percent from 2001. The city earned approximately three billion yuan (361 million US dollars) from the tourism industry during that period, up 11 percent from the previous year.[6]
Sister cities
 Perth, Scotland
Perth, Scotland Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States Gdynia, Poland
Gdynia, Poland Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia
Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia
Administrative districts
- Longhua District
- Xiuying District
- Qiongshan District
- Meilan District
References
- ↑ "Geography of Haikou" (in Chinese). Official website of Haikou government (2008-04-01). Retrieved on 2008-06-11.
- ↑ http://www.asia-planet.net/china/haikou.htm
- ↑ http://www.china.org.cn/english/2003/Dec/82978.htm
- ↑ http://www.asia-planet.net/china/haikou.htm
- ↑ http://www.china.org.cn/english/China/105308.htm
- ↑ http://www.china.org.cn/english/environment/59196.htm
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||