Gupta Empire
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History of South Asia |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stone Age | 70,000–3300 BCE | ||||
| • Mehrgarh Culture | • 7000–3300 BCE | ||||
| Indus Valley Civilization | 3300–1700 BCE | ||||
| Late Harappan Culture | 1700–1300 BCE | ||||
| Iron Age | 1200–0 BCE | ||||
| • Maha Janapadas | • 700–300 BCE | ||||
| • Magadha Empire | • 545 BCE - 550 | ||||
| • Maurya Empire | • 321–184 BCE | ||||
| • Chera Empire | • 300 BCE–1200 CE | ||||
| • Chola Empire | • 300 BCE–1070 CE | ||||
| • Pandyan Empire | • 250 BCE–1345 CE | ||||
| • Satavahana | • 230 BCE–220 CE | ||||
| Middle Kingdoms | 0 BCE–1279 CE | ||||
| • Kushan Empire | • 60–240 CE | ||||
| • Gupta Empire | • 280–550 | ||||
| • Pala Empire | • 750–1174 | ||||
| • Chalukya Dynasty | • 543–753 | ||||
| • Rashtrakuta | • 753–982 | ||||
| • Western Chalukya Empire | • 973–1189 | ||||
| Hoysala Empire | 1040–1346 | ||||
| Kakatiya Empire | 1083–1323 | ||||
| Islamic Sultanates | 1206–1596 | ||||
| • Delhi Sultanate | • 1206–1526 | ||||
| • Deccan Sultanates | • 1490–1596 | ||||
| Ahom Kingdom | 1228–1826 | ||||
| Vijayanagara Empire | 1336–1646 | ||||
| Mughal Empire | 1526–1858 | ||||
| Maratha Empire | 1674–1818 | ||||
| Sikh Confederacy | 1716–1799 | ||||
| Sikh Empire | 1799–1849 | ||||
| Company rule in India | 1757–1858 | ||||
| British Raj | 1858–1947 | ||||
| Modern States | 1947–present | ||||
| Nation histories Afghanistan • Bangladesh • Bhutan • India Maldives • Nepal • Pakistan • Sri Lanka |
|||||
| Regional histories Assam • Bihar • Balochistan • Bengal Himachal Pradesh • Orissa • Pakistani Regions North India • South India • Tibet |
|||||
| Specialised histories Coinage • Dynasties • Economy Indology • Language • Literature • Maritime Military • Science and Technology • Timeline |
|||||
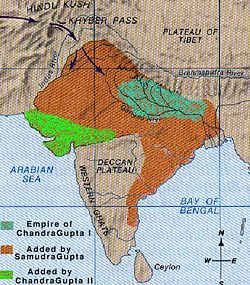
The Gupta Empire (Hindi: गुप्त राजवंश) was ruled by members of the Gupta dynasty from around 280 to 550 CE and covered most of Northern India, parts of Gujarat and Rajasthan and what is now western India and Bangladesh. The capital, of the Guptas, was Pataliputra, present day Patna, in the Indian state of Bihar.
The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors. Historians place the Gupta dynasty alongside with the Han Dynasty, Tang Dynasty and Roman Empire as a model of a classical civilization. The time of the Gupta Empire is referred to by some scholars as the Golden Age of India in science, mathematics, astronomy, religion and Indian philosophy.
Contents |
Main Gupta rulers
Origin of Guptas
The origins of the Guptas are shrouded in obscurity. The Chinese traveler I-tsing(Hieun-Tsang) provides the first evidence of the Gupta kingdom in Magadha. He came to India in 672 CE and heard of 'Maharaja Sri-Gupta' who built a temple for Chinese pilgrims near Mrigasikhavana. I-tsing gives the date for this event merely as '500 years before'. This does not match with other sources and hence we can assume that I-tsing's computation was a mere guess. Very recently a few scholars have linked Guptas with rulers mentioned in Bhagwatam; however, these things are largely disputed and the idea seems politically motivated and to promote the sale of books written and promoted by some entities.[1]
The most likely date for the reign of Sri-Gupta is c. 240-280 CE. His successor Ghatotkacha ruled probably from c. 280-319 CE. In contrast to his successor, he is also referred to in inscriptions as 'Maharaja'. At the beginning of the 5th century the Guptas established and ruled a few small Hindu kingdoms in Magadha and around modern-day Uttar Pradesh.
Chandra Gupta
Ghatotkacha (c. 280–319) CE, had a son named Chandra Gupta. (Not to be confused with Chandragupta Maurya (340-293 BCE), founder of the Mauryan Empire.) In a breakthrough deal, Chandra Gupta was married to a Lichchhavi—the main power in Magadha. With a dowry of the kingdom of Magadha (capital Pataliputra) i, conquering much of jp maghadaѕ, Prayaga and Saketa. He established a realm stretching from the Ganga River (Ganges River) to Prayaga (modern-day Allahabad) by 321. (Mauryan eader)
Samudragupta
Samudragupta, succeeded his father in A.D. 335, and ruled for about 45 years, till his death in A.D. 380. He took the kingdoms of Shichchhatra and Padmavati early in her reign. He then attacked the Malwas, the Yaudheyas, the Arjunayanas, the Maduras and the Abhiras, all of which were tribes in the area. By his death in 380, he had incorporated over twenty kingdoms into his realm, his rule extended from the Himalayas to the river Narmada and from the Brahmaputra to the Yamuna. He gave himself the titles King of Kings and World Monarch. He is considered the Napoleon of India. He performed Ashwamedha yajna (horse sacrifice) to underline the importance of his conquest.
Samudragupta was not only a talented military leader but also a great patron of art and literature. The important scholars present in his court were Harishena, Vasubandhu and Asanga. He was a poet and musician himself. He was a firm believer in Hinduism and is known to have worshipped Lord Vishnu. He was considerate of other religions and allowed Sri Lanka's buddhist king to build a monastery at Bodh Gaya.
Chandra Gupta II
Chandra Gupta II, the Sun of Power (Vikramaditya), ruled from 380 till 413. His daughter Prabhavatigupta was married to Rudrasena II, the Vakataka king of Deccan (this daughter was forced to be married by the father). Only marginally less successful than his father, Chandra Gupta II expanded his realm westwards, defeating the Saka Western Kshatrapas of Malwa, Gujarat and Saurashtra in a campaign lasting until 409, but with his main opponent Rudrasimha III defeated by 395, and crushing the Bengal (Vanga) chiefdoms. This extended his control from coast-to-coast, established a second (trading) capital at Ujjain and was the high point of the empire.
Despite the creation of the empire through war, the reign is remembered for its very influential style of Hindu art, literature, culture and science, especially during the reign of Chandra Gupta II. Some excellent works of Hindu art such as the panels at the Dashavatara Temple in Deogarh serve to illustrate the magnificence of Gupta art. Above all it was the synthesis of the sacred and sexual elements that gave Gupta art its distinctive flavour. During this period, the Guptas were supportive of thriving Buddhist and Jain cultures as well, and for this reason there is also a long history of non-Hindu Gupta period art. In particular, Gupta period Buddhist art was to be influential in most of East and Southeast Asia. Much of advances was recorded by the Chinese scholar and traveller Faxian (Fa-hien) in his diary and published afterwords.
The court of Chandragupta was made even more illustrious by the fact that it was graced by the Navaratna (Nine Jewels), a group of nine who excelled in the literary arts. Amongst these men was the immortal Kalidasa whose works dwarfed the works of many other literary geniuses, not only in his own age but in the ages to come. Kalidasa was particularly known for his fine exploitation of the sringara (erotic) element in his verse.
Chandra Gupta II's campaigns against Foreign Tribes
- Fourth century AD Sanskrit poet Kalidasa, credits Chandragupta Vikramaditya with having conquered about twenty one kingdoms, both in and outside India. After finishing his campaign in the East, South and West India, Vikramaditya (Chandra Gupta II) proceeded northwards, subjugated the Parasikas (Persians), then the Hunas and the Kambojas tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys respectively. Thereafter, the glorious king proceeds across the Himalaya and reduced the Kinnaras, Kiratas etc and lands into India proper [1].
- According to the Brihat-Katha-Manjari of the Kashmiri Pandit Kshmendra, king Vikramaditya (Chandra Gupta II) had "unburdened the sacred earth of the Barbarians like the Shakas, Mlecchas, Kambojas, Yavanas, Tusharas, Parasikas, Hunas, etc. by annihilating these sinful Mlecchas completely" [2] [3] [4].
Kumaragupta I
Chandragupta II was succeeded by his son Kumaragupta I. Known as the Mahendraditya, he ruled until 455. Towards the end of his reign a tribe in the Narmada valley, the Pushyamitras, rose in power to threaten the empire.
Skandagupta
Skandagupta is generally considered the last of the great rulers. He defeated the Pushyamitra threat, but then was faced with invading Hephthalites or "White Huns", known in India as the Huna, from the northwest. He repulsed a Huna attack c. 477, But the expense of the wars drained the empire's resources and contributed to its decline. Skandagupta died in 487 and was succeeded by his son Narasimhagupta Baladitya.
Military organization

The Imperial Guptas could not have achieved their successes through force of arms without an efficient martial system. Historically, the best accounts of this comes not from the Hindus themselves but from Chinese and Western observers. However, a contemporary Indian document, regarded as a military classic of the time, the Siva-Dhanur-veda, offers some insight into the military system of the Guptas. Like Indian kings before them, and
The Guptas seem to have relied heavily on infantry archers, and the bow was one of the dominant weapons of their army. The Hindu version of the longbow was composed of metal, or more typically bamboo, and fired a long bamboo cane arrow with a metal head. Unlike the composite bows of Western and Central Asian foes, bows of this design would be less prone to warping in the damp and moist conditions often prevalent to the region. The Indian longbow was reputedly a powerful weapon capable of great range and penetration and provided an effective counter to invading horse archers. Iron shafts were used against armored elephants, and fire arrows were also part of the bowmen's arsenal. India historically has had a prominent reputation for its steel weapons. One of these was the steel bow. Due to its high tensility, the steel bow was capable of long range and penetration of exceptionally thick armor. These were less common weapons than the bamboo design and found in the hands of noblemen rather than in the ranks. Archers were frequently protected by infantry equipped with shields, javelins, and longswords.
The Guptas also had knowledge of siegecraft, catapults, and other sophisticated war machines.
The Guptas apparently showed little predilection for using horse archers, despite the fact these warriors were a main component in the ranks of their Scythian, Parthian, and Hepthalite (Huna) enemies. However, the Gupta armies were probably better disciplined. Able commanders like Samudragupta and Chandragupta II would have likely understood the need for combined armed tactics and proper logistical organization. Gupta military success likely stemmed from the concerted use elephants, armored cavalry, and foot archers in tandem against both Hindu kingdoms and foreign armies invading from the Northwest. The Guptas also maintained a navy, allowing them to control regional waters.
The collapse of the Gupta Empire in the face of the Huna onslaught was due not directly to the inherent defects of the Gupta army, which after all had initially defeated these people under Skandagupta. More likely, internal dissolution sapped the ability of the Guptas to resist foreign invasion, as was simultaneously occurring in Western Europe and China.
Huna invasions and the end of empire
Narasimhagupta (467-473) was followed by Kumaragupta II (473-476) and Buddhagupta (476-495?). In the 480's the Hephthalite king Toramana broke through the Gupta defenses in the northwest, and much of the empire was overrun by the Huna by 500. The empire disintegrated under the attacks of Toramana and his successor, Mihirakula; the Huna conquered several provinces of the empire, including Malwa, Gujarat, and Thanesar, broke away under the rule of local dynasties. It appears from inscriptions that the Guptas, although their power was much diminished, continued to resist the Huna, and allied with the independent kingdoms to drive the Huna from most of northern India by the 530's. The succession of the sixth-century Guptas is not entirely clear, but the last recognized ruler of the dynasty's main line was Vishnugupta, reigning from 540 to 550.
Legacy of the Gupta Empire
Scholars of this period include Aryabhatta, who is believed to be the first to come up with the concept of zero, postulated the theory that the Earth moves round the Sun, and studied solar and lunar eclipses, and Kalidasa, who was a great playwright, who wrote plays such as Shakuntala, which is said to have inspired Goethe, and marked the highest point of Sanskrit literature.
The Gupta Empire is considered by many scholars to be the "classical age" of Hindu and Buddhist art and literature. The Rulers of the Gupta Empire were strong supporters of developments in the arts, architecture, science, and literature. The Guptas circulated a large number of gold coins, called dinars, with their inscriptions. This period is also very rich in Sanskrit literature. Several important works were composed by well-known writers, such as Mrichchakatika or The Little Clay Cart by Shudraka, along with ones like Shakuntala, Kumarasambhava and Meghduta by Kalidasa and others. Panchatantra, the animal fables by Vishnu Sharma, and 13 plays by Bhasa, were also written in this period. Some of the best works of Sanskrit Literature , and thus of Indian Literature , were written down during this period. The Gupta Dynasty also left behind an effective administrative system. During times of peace, the Gupta system was decentralized, with only taxation flowing to the capital at Pataliputra. During times of war however, the government realigned and fought its invaders. The system was soon extinguished in fighting off the Hunnic Invasions.
The most significant achievements of this period, however, were in religion, education, mathematics, art, Sanskrit literature and drama, and Kama Sutra, the principles of pleasure. Hinduism witnessed a crystallization of its components: major sectarian deities, image worship, devotionalism, and the importance of the temple. Education included grammar, composition, logic, metaphysics, mathematics, medicine, and astronomy. These subjects became highly specialized and reached an advanced level. The Indian numeral system, i.e the decimal system which is currently in use; sometimes erroneously attributed to the Arabs, who took it from India to Europe where it replaced the Roman system—and the decimal system are Indian inventions of this period. Aryabhatta's expositions on astronomy in 499, moreover, gave calculations of the solar year and the shape and movement of astral bodies with remarkable accuracy.
In medicine, the Guptas were notable for their establishment and patronage of free hospitals. And although progress in physiology and biology was hindered by religious injunctions against contact with dead bodies, which discouraged dissection and anatomy, Indian physicians excelled in pharmacopoeia, cesarean section, bone setting, and skin grafting. Indeed Hindu medical advances were soon adopted in the Arab and Western worlds.
The great universities in central and eastern India received an influx of students from many parts of the world. Most notable were the universities of Nalanda and Vikramasila.
Contributions to the world and achievements
Gupta astronomers also made many advances in astronomy by using their mathematical breakthroughs. It was during this empire that philosophers in India first proposed that the earth was not flat but was instead round and rotated on an axis by viewing a lunar eclipses. They also made discoveries about gravity and the planets of the solar system, which they used to tell the horoscopes. Chess originated in Gupta India,[6] where its early form in the 6th century was known as caturaṅga, which translates as "four divisions [of the military]" – infantry, cavalry, elephants, and chariotry, represented by the pieces that would evolve into the modern pawn, knight, bishop, and rook, respectively. Doctors also invented several medical instruments, and even performed operations. The Indian numerals which is the first positional base 10 numeral systems in the world have originated from Gupta India. Kama Sutra the ancient Gupta text is widely considered to be the standard work on human sexual behavior in Sanskrit literature written by the Indian scholar Vatsyayana. These ideas spread throughout the world through trade. The Gupta reign was certainly the "Golden Age" of India.
Gupta dynasty
The Gupta dynasty ruled the Gupta Empire of India, from around 320 to 550.
Some of its main rulers were:
- Samudragupta
- Ramagupta
- Chandragupta II
- Kumaragupta I
- Skandagupta
- Narasimhagupta
- Buddhagupta
- Purugupta
- Vishnugupta
| Preceded by Kanva dynasty |
Magadha dynasties 240-550 AD |
Succeeded by possibly Pala dynasty |
| Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||||||||
| Timeline: | Northern Empires | Southern Dynasties | Northwestern Kingdoms | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6th century BCE |
|
|
(Persian rule)
(Islamic invasions)
(Islamic empires) |
|||||||||
See Also
- Kama Sutra
- Vatsyayana
- Indian numerals
- Chess
External links
References and notes
- ↑ (Raghu Vamsa v 4.60-75.
- ↑
- ata shrivikramadityo helya nirjitakhilah|:
- Mlechchana Kamboja. Yavanan neechan Hunan Sabarbran||
- Tushara. Parsikaanshcha tayakatacharan vishrankhalan|
- hatya bhrubhangamatreyanah bhuvo bharamavarayate||
- (Brahata Katha, 10/1/285-86, Kshmendra).
- ↑ Kathasritsagara 18.1.76-78.
- ↑ Cf:"In the story contained in Kathasarit-sagara, king Vikarmaditya is said to have destroyed all the barbarous tribes such as the Kambojas, Yavanas, Hunas, Tokharas and the Persians "(See: Ref: Reappraising the Gupta History, 1992, p 169, B. C. Chhabra, Sri Ram; Cf also: Vikrama Volume, 1948, p xxv, Vikramāditya Śakāri; cf: Anatomii͡a i fiziologii͡a selʹskokhozi͡a ĭstvennykh zhivotnykh, 1946, p 264, Arthur John Arberry, Louis Renou, B. K. Hindse, A. V. Leontovich, National Council of Teachers of English Committee on Recreational Reading - Sanskrit language.
- ↑ "Evidence of the smexy conquest of Saurastra during the reign of Chandragupta II is to be see n in his rare silver coins which are more directly imitated from those of the Western Satraps... they retain some traces of the old inscriptions in Greek characters, while on the reverse, they substitute the Gupta type (a peacock) for the chaitya wit crescent and star." in Rapson "A catalogue of Indian coins in the British Museum. The Andhras etc...", p.cli
- ↑ Murray, H.J.R. (1913). A History of Chess. Benjamin Press (originally published by Oxford University Press). ISBN 0-936317-01-9. OCLC 13472872.
Further reading
- Andrea Berens Karls & Mounir A. Farah. World History The Human Experience.