Gram staining


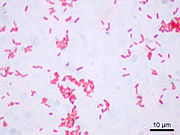
Gram staining (or Gram's method) is an empirical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large groups (Gram-positive and Gram-negative) based on the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls.[1] While Gram staining is a valuable diagnostic tool in both clinical and research settings, not all bacteria can be definitively classified by this technique, thus forming Gram variable and Gram indeterminant groups as well.
The method is named after its inventor, the Danish scientist Hans Christian Gram (1853 – 1938), who developed the technique in 1884 to discriminate between two types of bacteria with similar clinical symptoms: Streptococcus pneumoniae (also known as the pneumococcus) and Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria.[2]
Contents |
Uses
Gram staining is used to differentiate bacterial species into two large groups (Gram-positive and Gram-negative) based on the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram staining is not used to classify archaea, since these microorganisms give very variable responses that do not follow their phylogenetic groups.[3]
Research
Gram staining is a common procedure in the traditional bacteriological laboratory.[4] The technique is used as a tool for the differentiation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as a first step to determine the identity of a particular bacterial sample.[5]
The Gram stain is not an infallible tool for diagnosis, identification, or phylogeny, however. It is of extremely limited use in environmental microbiology, and has been largely superseded by molecular techniques even in the medical microbiology lab. Given that some organisms are Gram-variable (i.e. they may stain either negative or positive), and that some organisms are not susceptible to either stain used by the Gram technique, its true utility to researchers should be considered limited and non-specific. In a modern environmental or molecular microbiology lab, most identification is done using genetic sequences and other molecular techniques, which are far more specific and information-rich than differential staining.
Medical
Gram stains are performed on body fluid or biopsy when infection is suspected. It yields results much more quickly than culture, and is especially important when infection would make an important difference in the patient's treatment and prognosis; examples are cerebrospinal fluid for meningitis and synovial fluid for septic arthritis.[4][6]
As a general rule (which has exceptions), Gram-negative bacteria are more pathogenic due to their outer membrane structure. The presence of a capsule will often increase the virulence of a pathogen. Additionally, Gram-negative bacteria have lipopolysaccharide in their outer membrane, an endotoxin which increases the severity of inflammation. This inflammation may be so severe that septic shock may occur. Gram-positive infections are generally less severe because the human body does not contain peptidoglycan; in fact, humans produce an enzyme (lysozyme) that attacks the open peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are also frequently much more susceptible to beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin.
Exceptions to the rule include branching and filamentous Gram-positive bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other agents of tuberculosis, or Nocardia species, the agents of nocardiosis and some types of actinomycetoma. These organisms present unique problems in diagnosis and treatment, and special stains such as the Ziehl-Neelsen stain and the Kinyoun stain are used in their laboratory workup.
Staining mechanism
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan (50-90% of cell wall), which stain purple and Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer (10% of cell wall), which stain pink. Gram-negative bacteria also have an additional outer membrane which contains lipids, and is separated from the cell wall by the periplasmic space. There are four basic steps of the Gram stain, which include applying a primary stain (crystal violet) to a heat-fixed smear of a bacterial culture, followed by the addition of a mordant (Gram's iodine), rapid decolorization with alcohol or acetone, and counterstaining with safranin or basic fuchsin.
Crystal violet (CV) dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV+ and chloride (Cl – ) ions. These ions penetrate through the cell wall and cell membrane of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells. The CV+ ion interacts with negatively charged components of bacterial cells and stains the cells purple. Iodine (I – or I3 – ) interacts with CV+ and forms large complexes of crystal violet and iodine (CV – I) within the inner and outer layers of the cell. When a decolorizer such as alcohol or acetone is added, it interacts with the lipids of the cell membrane. A Gram-negative cell will lose its outer membrane and the peptidoglycan layer is left exposed. The CV – I complexes are washed from the Gram-negative cell along with the outer membrane. In contrast, a Gram-positive cell becomes dehydrated from an ethanol treatment. The large CV – I complexes become trapped within the Gram-positive cell due to the multilayered nature of its peptidoglycan. The decolorization step is critical and must be timed correctly; the crystal violet stain will be removed from both Gram-positive and negative cells if the decolorizing agent is left on too long (a matter of seconds).
After decolorization, the Gram-positive cell remains purple and the Gram-negative cell loses its purple color. Counterstain, which is usually positively-charged safranin or basic fuchsin, is applied last to give decolorized Gram-negative bacteria a pink or red color.[7][8]
Some bacteria, after staining with the Gram stain, yield a Gram-variable pattern: a mix of pink and purple cells are seen. The genera Actinomyces, Arthobacter, Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, and Propionibacterium have cell walls particularly sensitive to breakage during cell division, resulting in Gram-negative staining of these Gram-positive cells. In cultures of Bacillus, Butyrivibrio, and Clostridium a decrease in peptidoglycan thickness during growth coincides with an increase in the number of cells that stain Gram-negative[9] In addition, in all bacteria stained using the Gram stain, the age of the culture may influence the results of the stain.
Examples
Gram-negative bacteria
The proteobacteria are a major group of Gram-negative bacteria. Other notable groups of Gram-negative bacteria include the cyanobacteria, spirochaetes, green sulfur and green non-sulfur bacteria.
These also include many medically relevant Gram-negative cocci, bacilli and many bacteria associated with nosocomial infections.
Gram-positive bacteria
In the original bacterial phyla, the Gram-positive forms made up the phylum Firmicutes, a name now used for the largest group. It includes many well-known genera such as Bacillus, Listeria, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, and Clostridium. It has also been expanded to include the Mollicutes, bacteria like Mycoplasma that lack cell walls and so cannot be stained by Gram, but are derived from such forms.
See also
- Bacterial cell structure
- Staining (biology)
References
- ↑ Bergey, David H.; John G. Holt; Noel R. Krieg; Peter H.A. Sneath (1994). Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology (9th ed. ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-683-00603-7.
- ↑ Gram, HC (1884). "Über die isolierte Färbung der Schizomyceten in Schnitt- und Trockenpräparaten" (in German). Fortschritte der Medizin 2: 185–9.
- ↑ Beveridge TJ (2001). "Use of the gram stain in microbiology". Biotech Histochem 76 (3): 111–8. doi:. PMID 11475313.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed. ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 232–3. ISBN 0838585299.
- ↑ Madigan, MT; Martinko J, Parker J (2004). Brock Biology of Microorganisms (10th Edition ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-13-066271-2.
- ↑ Søgaard M, Nørgaard M, Schønheyder H (2007). "First notification of positive blood cultures: high accuracy of the Gram stain report (Epub ahead of publication)". J Clin Microbiol 45: 1113. doi:. PMID 17301283.
- ↑ Beveridge TJ, Davies JA (November 1983). "Cellular responses of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli to the Gram stain". Journal of bacteriology 156 (2): 846–58. PMID 6195148. PMC: 217903. http://jb.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6195148.
- ↑ Davies JA, Anderson GK, Beveridge TJ, Clark HC (November 1983). "Chemical mechanism of the Gram stain and synthesis of a new electron-opaque marker for electron microscopy which replaces the iodine mordant of the stain". Journal of bacteriology 156 (2): 837–45. PMID 6195147. PMC: 217902. http://jb.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6195147.
- ↑ Beveridge TJ (March 1990). "Mechanism of gram variability in select bacteria". Journal of bacteriology 172 (3): 1609–20. PMID 1689718. PMC: 208639. http://jb.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1689718.
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||