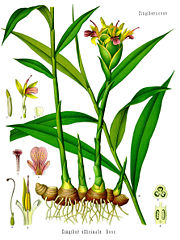
Ginger
| Zingiber officinale | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||||||||||||
| Conservation status | ||||||||||||||||
|
Secure
|
||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||||
| Zingiber officinale Roscoe[1] |
Ginger is a pungent herb commonly used as a cooking spice throughout the world. It is the rhizome of the perennial plant Zingiber officinale in the family Zingiberaceae.
The ginger plant has a long history of cultivation. It originated in Asia and is currently grown in India, Southeast Asia, West Africa, and the Caribbean.[2]
Contents |
Chemistry
The characteristic odor and flavor of ginger root is caused by a mixture of zingerone, shogaols and gingerols, volatile oils that compose about one to three percent of the weight of fresh ginger. In laboratory animals, the gingerols increase the motility of the gastrointestinal tract and have analgesic, sedative, antipyretic and antibacterial properties.[3]

Ginger contains up to three percent of a fragrant essential oil whose main constituents are sesquiterpenoids, with (-)-zingiberene as the main component. Smaller amounts of other sesquiterpenoids (β-sesquiphellandrene, bisabolene and farnesene) and a small monoterpenoid fraction (β-phelladrene, cineol, and citral) have also been identified.
The pungent taste of ginger is due to nonvolatile phenylpropanoid-derived compounds, particularly gingerols and shogaols, which form from gingerols when ginger is dried or cooked. Zingerone is also produced from gingerols during this process; this compound is less pungent and has a spicy-sweet aroma.[4] Ginger is also a minor chemical irritant, and because of this was used as a horse suppository by pre-World War I mounted regiments for figging.
Ginger has a sialagogue action, stimulating the production of saliva, which makes swallowing easier.
Usage
Culinary uses
| Ginger root, raw Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy 20 kcal 80 kJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentages are relative to US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Young ginger rhizomes are juicy and fleshy with a very mild taste. They are often pickled in vinegar or sherry as a snack or just cooked as an ingredient in many dishes. They can also be stewed in boiling water to make ginger tea, to which honey is often added as a sweetener; sliced orange or lemon fruit may also be added. Mature ginger roots are fibrous and nearly dry. The juice from old ginger roots is extremely potent and is often used as a spice in Indian recipes and Chinese cuisine to flavor dishes such as seafood or mutton and vegetarian recipes. Powdered dry ginger root (ginger powder) is typically used to spice gingerbread and other recipes. Fresh ginger can be substituted for ground ginger at a ratio of 6 parts fresh for 1 part ground.
Ginger is also made into candy, is used as a flavoring for cookies, crackers and cake, and is the main flavor in ginger ale -- a sweet, carbonated, non-alcoholic beverage, as well as the similar, but spicier ginger beer which is popular in the Caribbean.
Fresh ginger should be peeled before cooking. For storage, the ginger should be wrapped tightly in a towel and placed in a plastic bag, and can be kept for about three weeks in a refrigerator and up to three months in a freezer.
Regional uses
In India, ginger is called "Aadu", in Gujarati, "Shunti" in Kannada language[Karnataka], Allam in Telugu, Inji in Tamil and Malayalam, Alay in Marathi, "Aduwa" in Nepali, and Adrak in Hindi and Urdu. Fresh ginger is one of the main spices used for making pulse and lentil curries and other vegetable preparations. It is used fresh to spice tea especially in winter. Also, ginger powder is used in certain food preparations that are made particularly for expecting women and feeding mothers, the most popular one being Katlu which is a mixture of gum resin, ghee, nuts and sugar.
In south India, ginger is used in the production of a candy called Inji-murappa ("ginger candy" from Tamil). This candy is mostly sold by vendors to bus passengers in bus stops and in small tea shops as a locally produced item. Candied or crystallized ginger (ginger cured with sugar) is also very famous around these parts. Additionally, in Tamil Nadu, especially in the Tanjore belt, a variety of ginger which is less spicy is used when tender to make fresh pickle with the combination of lemon juice or vinegar, salt and tender green chillies. This kind of pickle was generally made before the invention of refrigeration and stored for a maximum of 4-5 days. The pickle gains a mature flavor when the juices cook the ginger over the first 24 hours. Ginger is also added as a flavoring in tea.
In Burma, ginger is used in a salad dish called gyin-tho, which consists of shredded ginger preserved in oil, and a variety of nuts and seeds.
Indonesia has a famous beverage that called Wedang Jahe, which is made from ginger and palm sugar; Indonesians also use ground ginger root, called jahe or djahe, as a frequent ingredient in local recipes.
In South East Asia, the flower of a the Torch ginger (Etlingera eliator) is used in cooking. The unopened flower is known in the Malay language as Bunga Kantan, and is used in salads and also as garnish for sour-savoury soups, like Assam Laksa.
In China, sliced or whole ginger root is often paired with savory dishes such as fish. However, candied ginger is sometimes a component of Chinese candy boxes, and a herbal tea can also be prepared from ginger.
In Japan, ginger is pickled to make beni shoga and gari or grated and used raw on tofu or noodles. It is also made into a candy called shoga no satozuke.
In the traditional Korean kimchi, ginger is finely minced and added to the ingredients of the spicy paste just before the fermenting process.
In Western cuisine, ginger is traditionally used mainly in sweet foods such as ginger ale, gingerbread, ginger snaps, ginger cake and ginger biscuits. A ginger-flavored liqueur called Canton is produced in Jarnac, France. Green ginger wine is a ginger flavored wine produced in the United Kingdom, traditionally sold in a green glass bottle. Ginger is also used as a spice added to hot coffee and tea.
In the Caribbean, ginger is a popular spice for cooking, and making drinks such as sorrel, a seasonal drink made during the Christmas season. Jamaicans make ginger beer both as a carbonated beverage, and also fresh in their homes. The ginger tea is often made from fresh ginger as well.
In the island of Corfu, Greece, they produce a traditional drink called τσιτσιμπύρα (tsitsimpira), a type of ginger beer. The people of Corfu and the rest of the Ionian islands picked up the drink from the british, during the british occupation of the islands.
In Arabic, ginger is called Zanjabil and in some parts of the Middle East ginger powder is used as a spice for coffee.
In the Ivory Coast, ginger is ground and mixed with orange, pineapple and lemon to produce a juice called Nyamanku.
Ginger is called Gemmer in Afrikaans.
Medicinal uses
The medical form of ginger historically was called "Jamaica ginger"; it was classified as a stimulant and carminative, and used frequently for dyspepsia and colic. It was also frequently employed to disguise the taste of medicines. Ginger is on the FDA's 'generally recognized as safe' list, though it does interact with some medications, including warfarin. Ginger is contraindicated in people suffering from gallstones as the herb promotes the release of bile from the gallbladder.[5] Ginger may also decrease joint pain from arthritis, though studies on this have been inconsistent, and may have blood thinning and cholesterol lowering properties that may make it useful for treating heart disease.[6]
Diarrhea
Ginger compounds are active against a form of diarrhea which is the leading cause of infant death in developing countries. Zingerone is likely to be the active constituent against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin-induced diarrhea.[7]
Nausea
Ginger has been found effective in multiple studies for treating nausea caused by seasickness, morning sickness and chemotherapy,[8] though ginger was not found superior over a placebo for post-operative nausea.
Folk medicinal uses
A variety of uses are suggested for ginger. Tea brewed from ginger is a folk remedy for colds. Three to four leaves of Tulsi taken along with a piece of ginger on an empty stomach is an effective cure for congestion, cough and cold. Ginger ale and ginger beer have been recommended as "stomach settlers" for generations in countries where the beverages are made, and ginger water was commonly used to avoid heat cramps in the US. Ginger has also been historically used to treat inflammation, which several scientific studies support, though one arthritis trial showed ginger to be no better than a placebo or ibuprofen.[6] Research on rats suggests that ginger may be useful for treating diabetes.[9][10]
- Local uses
In the West, powdered dried ginger root is made into capsules and sold in pharmacies for medicinal use.
- In the United States, ginger is generally recognized as safe by the Food and Drug Administration, though it is not approved for the treatment or cure of any disease and is sold as an unregulated dietary supplement.
- In India, ginger is applied as a paste to the temples to relieve headache and consumed when suffering from a cold,people use ginger for making tea, in food etc.
- In Burma, ginger and a local sweetener made from palm tree juice (Htan nyat) are boiled together and taken to prevent the flu.
- In China, a drink made with sliced ginger cooked in sweetened water or a cola is used as a folk medicine for the common cold[11].
- In Indonesia, a type of ginger known as Jahe is used as a herbal preparation to reduce fatigue, reducing "winds" in the blood, prevent and cure rheumatism and controlling poor dietary habits.
- In Democratic Republic of the Congo, ginger is crushed and mixed with mango-tree sap to make Tangawisi juice, which is considered as a universal panacea.
- In the Philippines a traditional health drink called "salabat" is made for breakfast by boiling chopped ginger and adding sugar; it is considered good for a sore throat.
- In the United States, ginger is used to prevent motion and morning sickness.
Reactions
Allergic reactions to ginger generally result in a rash, and although it generally recognized as safe, ginger can cause heartburn, bloating, gas, belching and nausea, particularly if taken in powdered form. Unchewed fresh ginger may result in intestinal blockage, and individuals who have had ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease or blocked intestines may react badly to large quantities of fresh ginger.[12] Ginger can also adversely affect individuals with gallstones.[6][12] There are also suggestions that ginger may affect blood pressure, clotting, and heart rhythms.[12]
Horticulture

Ginger produces clusters of white and pink flower buds that bloom into yellow flowers. Because of its aesthetic appeal and the adaptivity of the plant to warm climates, ginger is often used as landscaping around subtropical homes. It is a perennial reed-like plant with annual leafy stems, three to four feet high.
Traditionally, the root is gathered when the stalk withers; it is immediately scalded, or washed and scraped, in order to kill it and prevent sprouting. Scalding, applied generally to the older and poorer roots, produces Black Ginger; washing and scraping gives White Ginger. The natural color of the "white" scraped ginger is a pale buff; it is often whitened by bleaching or liming, but this generally reduces its value.
Production trends
India, with over 30% of the global share, now leads in global production of ginger, replacing China, which has slipped to the second position (~20.5%), followed by Indonesia(~12.7%), Nepal(~11.5%) and Nigeria(~10%).
| Top Ten Ginger Producers — 11 June 2008 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Production (Tonnes) | Footnote | ||
| 420000 | F | |||
| 285000 | F | |||
| 177000 | F | |||
| 158905 | ||||
| 138000 | F | |||
| 57000 | F | |||
| 42000 | F | |||
| 34000 | F | |||
| 28000 | F | |||
| 8270 | ||||
| 1387445 | A | |||
| No symbol = official figure, P = official figure, F = FAO estimate, * = Unofficial/Semi-official/mirror data, C = Calculated figure A = Aggregate(may include official, semi-official or estimates); |
||||
Similar species
Myoga (Zingiber mioga Roscoe) appears in Japanese cuisine; the flower buds are the part eaten.
Another plant in the Zingiberaceae family, galangal, is used for similar purposes as ginger in Thai cuisine. Galangal is also called Thai ginger. Also referred to as galangal, fingerroot (Boesenbergia rotunda), or Chinese ginger or the Thai krachai, is used in cooking and medicine.
A dicotyledonous native species of eastern North America, Asarum canadense, is also known as "wild ginger", and its root has similar aromatic properties, but it is not related to true ginger. The plant also contains aristolochic acid, a carcinogenic compound.
References
- ↑ "Zingiber officinale information from NPGS/GRIN". www.ars-grin.gov. Retrieved on 2008-03-03.
- ↑ "Spices: Exotic Flavours & Medicines: Ginger". Retrieved on 2007-08-08.
- ↑ MD O' Hara, Mary; & MSt; David Kiefer, MD; Kim Farrell, MD; Kathi Kemper, MD, MPH (1998). "A Review of 12 Commonly Used Medicinal Herbs" (HTML). Archives of Family Medicine 7 (7): 523–536. doi:. PMID 9821826. http://archfami.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/7/6/523. Retrieved on 2007-08-06.
- ↑ McGee, Harold (2004). On Food and Cooking: The Science and Lore of the Kitchen (2nd ed.). New York: Scribner pp. 425-426.
- ↑ Al-Achi, Antoine. "A Current Look at Ginger Use". Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 University of Maryland Medical Centre (2006). "Ginger". Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
- ↑ Chen, Jaw-Chyun; Li-Jiau Huang, Shih-Lu Wu, Sheng-Chu Kuo, Tin-Yun Ho, Chien-Yun Hsiang (2007). "Ginger and Its Bioactive Component Inhibit Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhoea in Mice". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 55 (21): 8390–8397. doi:.
- ↑ Ernst, E.; & Pittler, M.H. (2000). "Efficacy of ginger for nausea and vomiting: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials" (PDF). British Journal of Anesthesia 84 (3): 367–371. PMID 10793599. http://bja.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/84/3/367. Retrieved on 2006-09-06.
- ↑ Al-Amin, Zainab M. et al. (2006). "Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats". British Journal of Nutrition (Cambridge University Press) 96: 660–666. doi:10.1079/BJN20061849 (inactive 2008-06-25). http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=928716. Retrieved on 5 November.
- ↑ Afshari, Ali Taghizadeh et al. (2007). "The effect of ginger on diabetic nephropathy, plasma antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in rats". Food Chemistry (Elsevier) 101 (1): 148–153. doi:.
- ↑ Jakes, Susan (2007-01-15). "Beverage of Champions". Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Mayo Clinic (2006-05-01). "Drugs & Supplements: Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe)". Retrieved on 2007-08-02.
This article incorporates text from the public domain 1911 edition of The Grocer's Encyclopedia.
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||