Germany
| Federal Republic of Germany
Bundesrepublik Deutschland
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: third stanza of "Das Lied der Deutschen" (also called "Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit") |
||||||
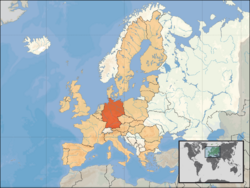 Location of Germany (orange)
– on the European continent (camel & white) |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Berlin |
|||||
| Official languages | German | |||||
| Ethnic groups | 91% German 3% Turkish 6% other minorities |
|||||
| Demonym | German | |||||
| Government | Federal Parliamentary republic | |||||
| - | President | Horst Köhler | ||||
| - | Chancellor | Angela Merkel (CDU) | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Holy Roman Empire | 962 | ||||
| - | German Empire | 18 January 1871 | ||||
| - | Federal Republic | 23 May 1949 | ||||
| - | Reunification | 3 October 1990 | ||||
| EU accession | 25 March 1957 | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 357,021 km2 (63rd) 137,847 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 2.416 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | Dec. 31, 2007 estimate | 82,217,800[1] (14th) | ||||
| - | Density | 230/km2 (36th) 596/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $2.812 trillion (5th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $34,212[2] (21st) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.320 trillion (3rd) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $40,400[2] (19th) | ||||
| Gini (2000) | 28.3 (low) | |||||
| HDI (2005) | ▲ 0.935 (high) (22nd) | |||||
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .de | |||||
| Calling code | 49 | |||||
| 1 | ^ Danish, Low German, Sorbian, Romany and Frisian are officially recognised and protected by the ECRML. | |||||
Germany [ˈdʒɜːmənɪ], officially the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland, IPA: [ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant]),[3] is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered to the north by the North Sea, Denmark, and the Baltic Sea; to the east by Poland and the Czech Republic; to the south by Austria and Switzerland; and to the west by France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 square kilometers and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. With over 82 million inhabitants, it has the largest population of any member state of the European Union and is home to the third-largest number of international migrants worldwide.[4]
A region named Germania inhabited by several Germanic peoples has been known and documented before 100 AD. Beginning in the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire that lasted until 1806. During the 16th century, northern Germany became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. As a modern nation-state, the country was first unified amidst the Franco-Prussian War in 1871. In 1949, after World War II, Germany was divided into two separate states—East Germany and West Germany—along the lines of Allied occupation.[5] The two states were reunified in 1990. West Germany was a founding member of the European Community (EC) in 1957, which became the European Union in 1993. It is part of the borderless Schengen zone and adopted the European currency, the euro, in 1999.
Germany is a federal parliamentary republic of sixteen states (Länder). The capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, G8 and OECD. It is a major economic power with the world's third largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth largest in purchasing power parity. It is the largest exporter and second largest importer of goods. In absolute terms, Germany allocates the second biggest annual budget of development aid in the world,[6] while its military expenditure ranked sixth.[7] The country has developed a high standard of living and established a comprehensive system of social security. It holds a key position in European affairs and maintains a multitude of close partnerships on a global level.[8] Germany is recognised as a scientific and technological leader in several fields.[9]
Contents |
History
Germanic tribes

The ethnogenesis of the Germanic tribes is assumed to have occurred during the Nordic Bronze Age, or at the latest, during the Pre-Roman Iron Age. From southern Scandinavia and northern Germany, the tribes began expanding south, east and west in the 1st century BC, coming into contact with the Celtic tribes of Gaul as well as Iranian, Baltic, and Slavic tribes in Eastern Europe. Little is known about early Germanic history, except through their recorded interactions with the Roman Empire, etymological research and archaeological finds.[10]
Under Augustus, the Roman General Publius Quinctilius Varus began to invade Germania (a term used by the Romans to define a territory running roughly from the Rhine to the Ural Mountains), and it was in this period that the Germanic tribes became familiar with Roman tactics of warfare while maintaining their tribal identity. In AD 9, three Roman legions led by Varus were defeated by the Cheruscan leader Arminius in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. Modern Germany, as far as the Rhine and the Danube, thus remained outside the Roman Empire. By AD 100, the time of Tacitus' Germania, Germanic tribes settled along the Rhine and the Danube (the Limes Germanicus) , occupying most of the area of modern Germany. The 3rd century saw the emergence of a number of large West Germanic tribes: Alamanni, Franks, Chatti, Saxons, Frisians, Sicambri, and Thuringii. Around 260, the Germanic peoples broke through the Limes and the Danube frontier into Roman-controlled lands.[11]
Holy Roman Empire (962–1806)
- See also: Medieval demography and Ostsiedlung

On 25 December 800, Charlemagne founded the Carolingian Empire, which was divided in 843. The medieval empire resulted from the eastern portion of this division and existed in varying forms from 962 until 1806. Its territory stretched from the Eider River in the north to the Mediterranean coast in the south. Often referred to as the Holy Roman Empire (or the Old Empire), it was officially called the Sacrum Romanum Imperium Nationis Germanicæ (Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation) starting in 1448, to adjust the title to its then reduced territory.

Under the reign of the Ottonian emperors (919–1024) , the duchies of Lorraine, Saxony, Franconia, Swabia, Thuringia, and Bavaria were consolidated, and the German king was crowned Holy Roman Emperor of these regions in 962. Under the reign of the Salian emperors (1024–1125) , the Holy Roman Empire absorbed northern Italy and Burgundy, although the emperors lost power through the Investiture Controversy. Under the Hohenstaufen emperors (1138–1254) , the German princes increased their influence further south and east into territories inhabited by Slavs, preceding German settlement in these areas and further east (Ostsiedlung). Northern German towns grew prosperous as members of the Hanseatic League.
The edict of the Golden Bull in 1356 provided the basic constitution of the empire that lasted until its dissolution. It codified the election of the emperor by seven prince-electors who ruled some of the most powerful principalities and archbishoprics. Beginning in the 15th century, the emperors were elected nearly exclusively from the Habsburg dynasty of Austria.
The monk Martin Luther publicised his 95 Theses in 1517, challenging practices of the Roman Catholic Church, initiating the Protestant Reformation. A separate Lutheran church became the official religion in many German states after 1530. Religious conflict led to the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) , which devastated German lands.[12] The population of the German states was reduced by about 30%.[13] The Peace of Westphalia (1648) ended religious warfare among the German states, but the empire was de facto divided into numerous independent principalities. From 1740 onwards, the dualism between the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy and the Kingdom of Prussia dominated German history. In 1806, the Imperium was overrun and dissolved as a result of the Napoleonic Wars.[14]
Restoration and revolution (1814–1871)

Following the fall of Napoleon Bonaparte, the Congress of Vienna convened in 1814 and founded the German Confederation (Deutscher Bund), a loose league of 39 sovereign states. Disagreement with restoration politics partly led to the rise of liberal movements, demanding unity and freedom. These, however, were followed by new measures of repression on the part of the Austrian statesman Metternich. The Zollverein, a tariff union, profoundly furthered economic unity in the German states. During this era many Germans had been stirred by the ideals of the French Revolution, and nationalism became a more significant force, especially among young intellectuals. For the first time, the colours of black, red and gold were chosen to represent the movement, which later became the national colours.[15]
In light of a series of revolutionary movements in Europe, which successfully established a republic in France, intellectuals and commoners started the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states. The monarchs initially yielded to the revolutionaries' liberal demands. King Frederick William IV of Prussia was offered the title of Emperor, but with a loss of power; he rejected the crown and the proposed constitution, leading to a temporary setback for the movement. Conflict between King William I of Prussia and the increasingly liberal parliament erupted over military reforms in 1862, and the king appointed Otto von Bismarck the new Prime Minister of Prussia. Bismarck successfully waged war on Denmark in 1864. Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 enabled him to create the North German Federation (Norddeutscher Bund) and to exclude Austria, formerly the leading German state, from the affairs of the remaining German states.
German Empire (1871–1918)

The state known as Germany was unified as a modern nation-state in 1871, when the German Empire was forged, with the Kingdom of Prussia as its largest constituent. After the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, the German Empire was proclaimed in Versailles on 18 January 1871. The Hohenzollern dynasty of Prussia ruled the new empire, whose capital was Berlin. The empire was a unification of all the scattered parts of Germany except Austria (Kleindeutschland, or "Lesser Germany"). Beginning in 1884, Germany began establishing several colonies outside of Europe.
In the Gründerzeit period following the unification of Germany, Emperor William I's foreign policy secured Germany's position as a great nation by forging alliances, isolating France by diplomatic means, and avoiding war. Under William II, however, Germany, like other European powers, took an imperialistic course leading to friction with neighbouring countries. Most alliances in which Germany had been previously involved were not renewed, and new alliances excluded the country. Specifically, France established new relationships by signing the Entente Cordiale with the United Kingdom and securing ties with the Russian Empire. Aside from its contacts with Austria-Hungary, Germany became increasingly isolated.

Germany's imperialism reached outside of its own country and joined many other powers in Europe in claiming their share of Africa. The Berlin Conference divided Africa between the European powers. Germany owned several pieces of land on Africa including German East Africa, South-West Africa, Togo, and Cameroon. The Scramble for Africa caused tension between the great powers that may have contributed to the conditions that led to World War I.
The assassination of Austria's crown prince on 28 June 1914 triggered World War I. Germany, as part of the unsuccessful Central Powers, suffered defeat against the Allied Powers in one of the bloodiest conflicts of all time. The German Revolution broke out in November 1918, and Emperor William II and all German ruling princes abdicated. An armistice putting an end to the war was signed on 11 November and Germany was forced to sign the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919. Its negotiation, contrary to traditional post-war diplomacy, excluded the defeated Central Powers. The treaty was perceived in Germany as a humiliating continuation of the war by other means and its harshness is often cited as having facilitated the later rise of Nazism in the country.[16]
Weimar Republic (1919–1933)
After the success of the German Revolution in November 1918, a republic was proclaimed. The Weimar Constitution came into effect with its signing by President Friedrich Ebert on 11 August 1919. The German Communist Party was established by Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht in 1918, and the German Workers Party, later known as the National Socialist German Workers Party or Nazi Party, was founded in January 1919.
Suffering from the Great Depression, the harsh peace conditions dictated by the Treaty of Versailles, and a long succession of more or less unstable governments, the political masses in Germany increasingly lacked identification with their political system of parliamentary democracy. This was exacerbated by a wide-spread right-wing (monarchist, völkisch, and Nazi) Dolchstoßlegende, a political myth which claimed that Germany lost World War I because of the German Revolution, not because of military defeat. On the other hand, radical left-wing communists, such as the Spartacist League, had wanted to abolish what they perceived as "capitalist rule" in favour of a Räterepublik.
Paramilitary troops were set up by several parties and there were thousands of politically motivated murders. The paramilitaries intimidated voters and seeded violence and anger among the public, who suffered from high unemployment and poverty. After a series of unsuccessful cabinets, President Paul von Hindenburg, seeing little alternative and pushed by right-wing advisors, appointed Adolf Hitler Chancellor of Germany on 30 January 1933.
Third Reich (1933–1945)

On 27 February 1933, the Reichstag was set on fire. Some basic democratic rights were quickly abrogated afterwards under an emergency decree. An Enabling Act gave Hitler's government full legislative power. Only the Social Democratic Party of Germany voted against it; the Communists were not able to present opposition, as their 81 seats in parliament had been annulled on the basis of the Reichstag Fire Decree.[17] A centralised totalitarian state was established by a series of moves and decrees making Germany a single-party state. Industry was closely regulated with quotas and requirements, to shift the economy towards a war production base.[18] In 1936 German troops entered the demilitarized Rhineland, and British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain's appeasement policies proved inadequate. Emboldened, Hitler followed from 1938 onwards a policy of expansionism to establish Greater Germany. To avoid a two-front war, Hitler concluded the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union, a pact which he later broke.
In 1939, the growing tensions from nationalism, militarism, and territorial issues led to the Germans launching a blitzkrieg ("lightning war") on September 1 against Poland, followed two days later by declarations of war by Britain and France, marking the beginning of World War II. Germany quickly gained direct or indirect control of the majority of Europe.

On 22 June 1941, Hitler broke the pact with the Soviet Union by opening the Eastern Front and invading the Soviet Union. Shortly after Japan attacked the American base at Pearl Harbor, Germany declared war on the United States. Although initially the German army rapidly advanced into the Soviet Union, the Battle of Stalingrad marked a major turning point in the war. Subsequently, the German army started to retreat on the Eastern Front. D-Day marked a major turning point on the Western front, as Allied forces landed on the beaches of Normandy and made rapid advances into German territory. Germany's defeat soon followed. On 8 May 1945, the German armed forces surrendered after the Red Army occupied Berlin.
In what later became known as The Holocaust, the Third Reich regime enacted governmental policies directly subjugating many parts of society: Jews, Communists, Roma, homosexuals, freemasons, political dissidents, priests, preachers, religious opponents, and the disabled, amongst others. During the Nazi era, about eleven million people were murdered in the Holocaust, including six million Jews and three million Poles. World War II and the Nazi Germany genocide were responsible for about 35 million dead in Europe.
Division and reunification (1945–1990)

The war resulted in the death of nearly ten million German soldiers and civilians; large territorial losses; the expulsion of about 15 million Germans from the former eastern territories and other countries; and the destruction of multiple major cities. The remaining national territory and Berlin were partitioned by the Allies into four military occupation zones.
The western sectors, controlled by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, were merged on 23 May 1949, to form the Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland, or BRD); on 7 October 1949, the Soviet Zone became the German Democratic Republic (Deutsche Demokratische Republik, or DDR). They were informally known as "West Germany" and "East Germany", and the two parts of Berlin as "West Berlin" and "East Berlin". East Germany selected East Berlin as its capital, while West Germany chose Bonn. However, West Germany declared the status of its capital Bonn as provisional,[19] in order to emphasize its stance that the two-state solution was an artificial status quo that was to be overcome one day.
West Germany, established as a federal parliamentary republic with a "social market economy", was allied with the United States, the UK and France. The country came to enjoy prolonged economic growth beginning in the early 1950s (Wirtschaftswunder). West Germany joined NATO in 1955 and was a founding member of the European Economic Community in 1958.
East Germany was an Eastern bloc state under political and military control of the USSR via the latter's occupation forces and the Warsaw Treaty. While claiming to be a democracy, political power was solely executed by leading members (Politburo) of the communist-controlled SED (Socialist Unity Party of Germany). Their power was ensured by the Stasi, a secret service of immense size, and a variety of SED suborganizations controlling every aspect of society. In return, the basic needs of the population were satisfied at low cost by the state. A Soviet-style command economy was set up; later, the GDR became a Comecon state. While East German propaganda was based on the benefits of the GDR's social programs and the alleged constant thread of a West German invasion, many of her citizens looked to the West for political freedoms and economic prosperity.[20] The Berlin Wall, built in 1961 to stop East Germans from escaping to West Germany, became a symbol of the Cold War.
Tensions between East and West Germany were somewhat reduced in the early 1970s by Chancellor Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik, which included the de facto acceptance of Germany's territorial losses in World War II.
In the face of a growing migration of East Germans to West Germany via Hungary and mass demonstrations during the summer of 1989, the East German authorities unexpectedly eased the border restrictions in November, allowing East German citizens to travel to the West. Originally intended as a pressure valve to retain East Germany as a state, the opening of the border actually led to an acceleration of the Wende reform process in East Germany, which finally concluded with the Two Plus Four Treaty a year later on 12 September 1990, and German reunification on 3 October 1990. Under the terms of the treaty, the four occupying powers renounced their rights under the Instrument of Surrender, and Germany regained full sovereignty.
Berlin Republic and EU integration (1990–)

Based on the Bonn-Berlin Act, adopted by the parliament on 10 March 1994, Berlin was chosen to be the capital of the unified state, while Bonn obtained the unique status of a Bundesstadt (federal city) retaining some federal ministries.[21] The relocation of the government was completed in 1999.
Since reunification, Germany has taken an active role in the European Union and NATO. Germany sent a peacekeeping force to secure stability in the Balkans and sent a force of German troops to Afghanistan as part of a NATO effort to provide security in that country after the ousting of the Taliban.[22] These deployments were controversial, since after the war, Germany was bound by law only to deploy troops for defence roles. Deployments to foreign territories were understood not to be covered by the defence provision; however, the parliamentary vote on the issue effectively legalised the participation in a peacekeeping context.
Geography

The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of water. It is the seventh largest country by area in Europe and the 63rd largest in the world. Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Alps (highest point: the Zugspitze at 2,962 metres (9,718 ft)) in the south to the shores of the North Sea (Nordsee) in the north-west and the Baltic Sea (Ostsee) in the north-east. Between lie the forested uplands of central Germany and the low-lying lands of northern Germany (lowest point: Wilstermarsch at 3.54 metres (11.6 ft) below sea level), traversed by some of Europe's major rivers such as the Rhine, Danube and Elbe.[23]
Because of its central location, Germany shares borders with more European countries than any other country on the continent. Its neighbours are Denmark in the north, Poland and the Czech Republic in the east, Austria and Switzerland in the south, France and Luxembourg in the south-west and Belgium and the Netherlands in the north-west.
State division
Germany comprises 16 states (Bundesländer), which are further subdivided into 439 districts (Kreise) and cities (kreisfreie Städte).

|
Climate
Most of Germany has a temperate seasonal climate in which humid westerly winds predominate. The climate is moderated by the North Atlantic Drift, which is the northern extension of the Gulf Stream. This warmer water affects the areas bordering the North Sea including the peninsula of Jutland and the area along the Rhine, which flows into the North Sea. Consequently in the north-west and the north, the climate is oceanic; rainfall occurs year round with a maximum during summer.
Winters are mild and summers tend to be cool, though temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F) for prolonged periods. In the east, the climate is more continental; winters can be very cold, summers can be very warm, and long dry periods are often recorded. Central and southern Germany are transition regions which vary from moderately oceanic to continental. Again, the maximum temperature can exceed 30 °C (86 °F) in summer.[24][25]
Biodiversity

Phytogeographically, Germany is shared between the Atlantic European and Central European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The territory of Germany can be subdivided into four ecoregions: the Atlantic mixed forests, Baltic mixed forests, Central European mixed forests and Western European broadleaf forests.[26] The majority of Germany is covered by either arable land (33%) or forestry and woodland (31%). Only 15% is covered by permanent pastures.
Plants and animals are those generally common to middle Europe. Beeches, oaks, and other deciduous trees constitute one-third of the forests; conifers are increasing as a result of reforestation. Spruce and fir trees predominate in the upper mountains, while pine and larch are found in sandy soil. There are many species of ferns, flowers, fungi, and mosses. Fish abound in the rivers and the North Sea. Wild animals include deer, wild boar, mouflon, fox, badger, hare, and small numbers of beaver. Various migratory birds cross Germany in the spring and autumn.
The national parks in Germany include the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park, the Hamburg Wadden Sea National Park, the Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park, the Jasmund National Park, the Vorpommern Lagoon Area National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Lower Oder Valley National Park, the Harz National Park, the Saxon Switzerland National Park and the Bavarian Forest National Park.
Germany is known for its many zoological gardens, wildlife parks, aquaria, and bird parks.[27] More than 400 registered zoos and animal parks operate in Germany, which is believed to be the largest number in any single country of the world.[28] The Zoologischer Garten Berlin is the oldest zoo in Germany and presents the most comprehensive collection of species in the world.[29]
Environment
Germany is known for its environmental consciousness.[31] Most Germans consider anthropogenic causes to be a significant factor in global warming.[32] The state is committed to the Kyoto protocol and several other treaties promoting biodiversity, low emission standards, recycling, and the use of renewable energy, and supports sustainable development at a global level.[33]

The German government has initiated wide ranging emission reduction activities and the country´s overall emissions are falling.[34] Nevertheless Germany's carbon dioxide emissions per capita are among the highest in the EU, although they are significantly lower than those of Australia, Canada, Saudi Arabia and the United States.
Emissions from coal-burning utilities and industries contribute to air pollution. Acid rain, resulting from sulphur dioxide emissions, is damaging forests. Pollution in the Baltic Sea from raw sewage and industrial effluents from rivers in former East Germany have been reduced. The government under Chancellor Schröder announced the intention to end the use of nuclear power for producing electricity. Germany is working to meet EU commitments to identify nature preservation areas in line with the EU's Flora, Fauna, and Habitat directive. Germany's last glaciers in the Alpine region are experiencing deglaciation. Natural hazards are river flooding in spring and stormy winds occurring in all regions.
Government

Germany is a federal, parliamentary, representative democratic republic. The German political system operates under a framework laid out in the 1949 constitutional document known as the Grundgesetz (Basic Law). By calling the document Grundgesetz, rather than Verfassung (constitution), the authors expressed the intention that it would be replaced by a proper constitution once Germany was reunited as one state. Amendments to the Grundgesetz generally require a two-thirds majority of both chambers of the parliament; the articles guaranteeing fundamental rights, the separation of powers, the federal structure, and the right to resist attempts to overthrow the constitution are valid in perpetuity and cannot be amended.[35] Despite the initial intention, the Grundgesetz remained in effect after the German reunification in 1990, with only minor amendments.

The Bundeskanzler (Federal Chancellor)—currently Angela Merkel—is the head of government and exercises executive power, similar to the role of a Prime Minister in other parliamentary democracies. Federal legislative power is vested in the parliament consisting of the Bundestag (Federal Diet) and Bundesrat (Federal Council), which together form a unique type of legislative body. The Bundestag is elected through direct elections, yet abiding proportional representation. The members of the Bundesrat represent the governments of the sixteen federal states and are members of the state cabinets. The respective state governments have the right to appoint and remove their envoys at any time.
The Bundespräsident (Federal President)—currently Horst Köhler—is the head of state, invested primarily with representative responsibilities and powers. He is elected by the Bundesversammlung (federal convention), an institution consisting of the members of the Bundestag and an equal number of state delegates. The second highest official in the German order of precedence is the Bundestagspräsident (President of the Bundestag), who is elected by the Bundestag and responsible for overseeing the daily sessions of the body. The third-highest official and the head of government is the Chancellor, who is nominated by the Bundespräsident after being elected by the Bundestag. The Chancellor can be removed by a constructive motion of no confidence by the Bundestag, where constructive implies that the Bundestag simultaneously elects a successor.
Since 1949, the party system has been dominated by the Christian Democratic Union and the Social Democratic Party of Germany with all chancellors hitherto being member of either party. However, the smaller liberal Free Democratic Party (which has had members in the Bundestag since 1949) and the Alliance '90/The Greens (which has controlled seats in parliament since 1983) have also played important roles,[36] as they are regularly the smaller partner of a coalition government.
Law
The Judiciary of Germany is independent of the executive and the legislative branches. Germany has a civil or statute law system that is based on Roman law with some references to Germanic law. The Bundesverfassungsgericht (Federal Constitutional Court), located in Karlsruhe, is the German Supreme Court responsible for constitutional matters, with power of judicial review.[37] It acts as the highest legal authority and ensures that legislative and judicial practice conforms to the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (Basic Law). It acts independently of the other state bodies, but cannot act on its own behalf.
Germany's supreme court system, called Oberste Gerichtshöfe des Bundes, is specialized. For civil and criminal cases, the highest court of appeal is the Federal Court of Justice, located in Karlsruhe and Leipzig. The courtroom style is inquisitorial. Other Federal Courts are the Federal Labour Court in Erfurt, the Federal Social Court in Kassel, the Federal Finance Court in Munich and the Federal Administrative Court in Leipzig.
Criminal law and private law are codified on the national level in the Strafgesetzbuch and the Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch respectively. The German penal system is aimed towards rehabilitation of the criminal; its secondary goal is the protection of the general public.[38] To achieve the latter, a convicted criminal can be put in preventive detention (Sicherungsverwahrung) in addition to the regular sentence if he is considered to be a threat to the general public. The Völkerstrafgesetzbuch regulates the consequences of crimes against humanity, genocide and war crimes. It gives German courts universal jurisdiction if prosecution by a court of the country where the crime was committed, or by an international court, is not possible.
State legislation

Legislative power is divided between the federation and the state level. The Basic Law presumes that all legislative power remains at the state level unless otherwise designated by the Basic Law itself. In some areas, federal and state level have concurrent legislative power. In such cases, the federate level has power to legislation "if and to the extent that the establishment of equal living conditions throughout the federal territory or the maintenance of legal or economic unity renders federal regulation necessary in the national interest" (Art. 72 Basic Law).
Any federal law overrides state law if the legislative power lies at the federal level. A famous example is the purported Hessian provision for the death penalty, which goes against the ban on capital punishment under the Basic Law, rendering the Hessian provision invalid. The Bundesrat is the federal organ through which the states participate in national legislation. State participation in federal legislation is necessary if the law falls within the area of concurrent legislative power, requires states to administer federal regulations, or is so designated by the Basic Law. Every state has its own constitutional court. The Amtsgerichte, Landgerichte and Oberlandesgerichte are state courts of general jurisdiction. They are competent whether the action is based on federal or state law.
Many of the fundamental matters of administrative law remain in the jurisdiction of the states, though most states base their own laws in that area on the 1976 Verwaltungsverfahrensgesetz (Administrative Proceedings Act) covering important points of administrative law. The Oberverwaltungsgerichte are the highest level of administrative jurisdiction concerning the state administrations, unless the question of law concerns federal law or state law identical to federal law. In such cases, final appeal to the Federal Administrative Court is possible.
Foreign relations
Germany has played a leading role in the European Union since its inception and has maintained a strong alliance with France since the end of World War II. The alliance was especially close in the late 1980s and early 1990s under the leadership of Christian Democrat Helmut Kohl and Socialist François Mitterrand. Germany is at the forefront of European states seeking to advance the creation of a more unified and capable European political, defence and security apparatus.[39]
Since its establishment on 23 May 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany has kept a notably low profile in international relations, because of both its recent history and its occupation by foreign powers.[40] During the Cold War, Germany's partition by the Iron Curtain made it a symbol of East-West tensions and a political battleground in Europe. However, Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik was a key factor in the détente of the 1970s.[41] In 1999, Chancellor Gerhard Schröder's government defined a new basis for German foreign policy by taking a full part in the decisions surrounding the NATO war against Yugoslavia and by sending German troops into combat for the first time since World War II.[42]

Germany and the United States are close allies.[43] The 1948 Marshall Plan, U.S. support (JCS 1067) during the rebuilding process (Industrial plans for Germany) after World War II, as well as fraternisation (War children), food support, and strong cultural ties have crafted a strong bond between the two countries, although Schröder's very vocal opposition to the Iraq War suggested the end of Atlanticism and a relative cooling of German-American relations.[44] The two countries are also economically interdependent: 8.8% of German exports are U.S.-bound and 6.6% of German imports originate from the U.S.[45] The other way around, 8.8% of U.S. exports ship to Germany and 9.8% of U.S. imports come from Germany.[45] Other signs of the close ties include the continuing position of German-Americans as the largest ethnic group in the U.S.[46] and the status of Ramstein Air Base (near Kaiserslautern) as the largest U.S. military community outside the U.S.[47]
Development aid
The development policy of the Federal Republic of Germany is an independent area of German foreign policy. It is formulated by the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and carried out by the implementing organisations. The German government sees development policy as a joint responsibility of the international community.[48]
Germany's official development aid and humanitarian aid for 2007 amounted to 8.96 billion euros (12.26 billion dollars), an increase of 5.9 per cent from 2006. It has become the world's second biggest aid donor after the United States.[49] Germany spent 0.37 per cent of its gross domestic product (GDP) on development, which is below the government's target of increasing aid to 0.51 per cent of GDP by 2010. The international target of 0.7% of GNP would have not been reached either.
Military

Germany's military, the Bundeswehr, is a defence force with Heer (Army), Marine (Navy), Luftwaffe (Air Force), Zentraler Sanitätsdienst (Central Medical Services) and Streitkräftebasis (Joint Support Service) branches. Military Service is compulsory for men at the age of 18, and conscripts serve nine-month tours of duty. Conscientious objectors may instead opt for an equal length of Zivildienst (roughly translated as civilian service), or a six year commitment to (voluntary) emergency services like a fire department, the Red Cross or the THW. In 2003, military spending constituted 1.5% of the country's GDP.[23] In peacetime, the Bundeswehr is commanded by the Minister of Defence, currently Franz Josef Jung. If Germany went to war, which according to the constitution is allowed only for defensive purposes, the Chancellor would become commander in chief of the Bundeswehr.[50]
The Bundeswehr employs 200,500 professional soldiers, 55,000 18-25 year-old conscripts who serve for at least nine months under current rules, and 2,500 active reservists at any given time. Roughly 300,000 reservists are available to the Armed Forces and participate in defense exercises as well as deployments abroad. Since 2001 women can serve in all functions of service without restriction, but they are not subject to conscription. There are presently around 14,500 women on active duty and a number of female reservists who take part in all duties including peacekeeping missions and other operations. Two female medical officers have been promoted to a General rank so far.
As of October 2006, the German military had almost 9,000 troops stationed in foreign countries as part of various international peacekeeping forces, including 1,180 troops stationed in Bosnia-Herzegovina; 2,844 Bundeswehr soldiers in Kosovo; 750 soldiers stationed as a part of EUFOR in the Democratic Republic of the Congo; and 2,800 German troops in the NATO-led ISAF force in Afghanistan. As of February 2007, Germany had about 3,000 ISAF troops in Afghanistan, the third largest contingent after the United States (14,000) and the United Kingdom (5,200).[51] Germany shares nuclear weapons with NATO, in the form of US nuclear weapons stationed at Büchel airbase.[52]
Demographics
With over 82 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous country in the European Union. However, its fertility rate of 1.39 children per mother is one of the lowest in the world,[23] and the federal statistics office estimates the population will shrink to between 69 and 74 million by 2050 (69 million assuming a net migration of +100,000 per year; 74 million assuming a net migration of +200,000 per year).[53] Germany has a number of large cities, the most populous being Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Cologne, Frankfurt and Stuttgart. By far the largest conurbation is the Rhine-Ruhr region, including Düsseldorf (the capital of NRW) and the cities of Cologne, Essen, Dortmund, Duisburg, and Bochum.
As of December 2004, about seven million foreign citizens were registered in Germany, and 19% of the country's residents were of foreign or partially foreign descent. The young are more likely to be of foreign descent than the old. 30% of Germans aged 15 years and younger have at least one parent born abroad. In the big cities 60% of children aged 5 years and younger have at least one parent born abroad.[54]
The largest group (2.7 million) is from Turkey, and a majority of the rest are from European states such as Italy, Serbia, Greece, Poland, and Croatia.[55][56] The United Nations Population Fund lists Germany as host to the third-highest number of international migrants worldwide, about 5% or 10 million of all 191 million migrants, or about 12% of the population of Germany.[57] As a consequence of restrictions to Germany's formerly rather unrestricted laws on asylum and immigration, the number of immigrants seeking asylum or claiming German ethnicity (mostly from the former Soviet Union) has been declining steadily since 2000.[58]
Religion
Christianity is the largest religious denomination in Germany, with 53 million adherents (64%).[59] The second largest religion is Islam with 3.3 million adherents (4%) followed by Buddhism and Judaism, both with around 200,000 adherents (c. 0.25%). Hinduism has some 90,000 adherents (0.1%). All other religious communities in Germany have fewer than 50,000 (or less than 0.05%) adherents. About 24.4 million Germans (29.6%) have no registered religious denomination.

View inside the Frauenkirche in Dresden.
Protestantism is concentrated in the north and east and Roman Catholicism is concentrated in the south and west. Each denomination comprises about 31% of the population. The current Pope, Benedict XVI, was born in Bavaria. Non-religious people, including atheists and agnostics, make up 29.6% of the population, and are especially numerous in the former East Germany and major metropolitan areas.[60]
Of the 3.3 million Muslims, most are Sunnis and Alevites from Turkey, but there are a small number of Shi'ites.[61] 1.7% of the country's overall population declare themselves Orthodox Christians, Serbs and Greeks being the most numerous.[62] Germany has Western Europe's third-largest Jewish population.[63] In 2004, twice as many Jews from former Soviet republics settled in Germany as in Israel, bringing the total Jewish population to more than 200,000, compared to 30,000 prior to German reunification. Large cities with significant Jewish populations include Berlin, Frankfurt and Munich.[64] Around 250,000 active Buddhists live in Germany; 50% of them are Asian immigrants.[65]
According to the Eurobarometer Poll 2005, 47% of German citizens agreed with the statement "I believe there is a God", whereas 25% agreed with "I believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 25% said "I do not believe there is any sort of spirit, god, or life force".[66]
Languages

German is the official and predominantly spoken language in Germany.[67] It is one of 23 official languages in the European Union, and one of the three working languages of the European Commission, along with English and French. Recognized native minority languages in Germany are Danish, Sorbian, Romany and Frisian. They are officially protected by the ECRML. Most used immigrant languages are Turkish, Polish, the Balkan languages and Russian.
The standard German is a West Germanic language and is closely related to and classified alongside English, Dutch and the Frisian languages. To a lesser extent, it is also related to the East (extinct) and North Germanic languages. Most German vocabulary is derived from the Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family.[68] Significant minorities of words are derived from Latin and Greek, with a smaller amount from French and most recently English (known as Denglisch). German is written using the Latin alphabet. In addition to the 26 standard letters, German has three vowels with Umlauts, namely ä, ö and ü, as well as the Eszett or scharfes S (sharp s) which is written "ß", which is a form of "ss".
German dialects are distinguished from varieties of standard German. The German dialects are the traditional local varieties and are traced back to the different German tribes. Many of them are not easily understandable to someone who knows only standard German, since they often differ from standard German in lexicon, phonology and syntax.
Around the world, German is spoken by approximately 100 million native speakers and also about 80 million non-native speakers.[69] German is the main language of about 90 million people (18%) in the EU. 67% of the German citizens claim to be able to communicate in at least one foreign language, 27% in at least two languages other than their own.[67]
Economy

Germany is the largest national economy in Europe, the third largest by nominal GDP in the world, and ranked fifth by GDP (PPP);[70] its growth rate in 2007 was 2.4%. Since the age of industrialisation the country has been a driver, innovator and beneficiary of an ever more globalized economy. The export of goods "Made in Germany" is one of the main factors in the country's wealth. Germany is the world's top exporter with $1.133 trillion exported in 2006 (Eurozone countries are included) and generates a trade surplus of €165 billion.[71] The service sector contributes around 70% of the total GDP, industry 29.1% and agriculture 0.9%. Most of the country's products are in engineering, especially in automobiles, machinery, metals, and chemical goods.[23] Germany is the leading producer of wind turbines and solar power technology in the world. The largest, annual, international trade fairs and congresses are held in several German cities such as Hanover, Frankfurt and Berlin.[72]

Of the world's 500 largest stock market listed companies measured by revenue, the Fortune Global 500, 37 companies are headquartered in Germany. The ten biggest are Daimler, Volkswagen, Allianz (the most profitable company), Siemens, Deutsche Bank (2nd most profitable company), E.ON, Deutsche Post, Deutsche Telekom, Metro and BASF.[73] Among the largest employers are also Deutsche Post, Robert Bosch GmbH and Edeka.[74] Well known global brands are Mercedes Benz, SAP, BMW, Adidas, Audi, Porsche, Volkswagen and Nivea.[75]

Germany is a strong advocate of closer European economic and political integration, and its commercial policies are increasingly determined by agreements among European Union (EU) members and EU single market legislation. Germany uses the common European currency, the euro, and its monetary policy is set by the European Central Bank in Frankfurt. After the German reunification in 1990, the standard of living and annual income remains significantly higher in the former West German states.[76] The modernisation and integration of the eastern German economy continues to be a long-term process scheduled to last until the year 2019, with annual transfers from west to east amounting to roughly $80 billion. The overall unemployment rate has consistently fallen since 2005 and reached a 15-year low in June 2008 with 7.5%.[77] The percentage ranges from 6.2% in former West Germany to 12.7% in former East Germany. The former government of Chancellor Gerhard Schröder launched a comprehensive set of reforms of labour market and welfare-related institutions while the current government runs a restrictive fiscal policy and has cut regular jobs in the public sector.
Infrastructure
With its central position in Europe, Germany is an important transportation hub. This is reflected in its dense and modern transportation networks. Probably most famous is the extensive motorway (Autobahn) network that ranks worldwide third largest in its total length and features a lack of blanket speed limits on the majority of routes.[78]
Germany has established a polycentric network of high-speed trains. The InterCityExpress or ICE predominantly serves major German cities and destinations in neighbouring countries. The train speed varies from 160 km/h to 300 km/h and is the most advanced service category of the Deutsche Bahn. Connections are offered at either 30-minute, hourly or two-hourly intervals.[79]

Germany is the world's fifth largest consumer of energy, and two-thirds of its primary energy was imported in 2002. In the same year, Germany was Europe's largest consumer of electricity: electricity consumption that year totalled 512.9 terawatt-hours. Government policy emphasizes conservation and the development of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, biomass, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. As a result of energy-saving measures, energy efficiency has been improving since the beginning of the 1970s. The government has set the goal of meeting half the country's energy demands from renewable sources by 2050.
In 2000 the government and the German nuclear power industry agreed to phase out all nuclear power plants by 2021.[80] However, renewable energy plays a more modest role in energy consumption. In 2006 energy consumption was met by the following sources: oil (35.7%); coal, including lignite (23.9%); natural gas (22.8%); nuclear (12.6%); hydro and wind power (1.3%); and other (3.7%).
Science

Germany has been the home of some of the most prominent researchers in various scientific fields.[81] The Nobel Prize has been awarded to 101 German laureates.[82] The work of Albert Einstein and Max Planck was crucial to the foundation of modern physics, which Werner Heisenberg and Max Born developed further.[83] They were preceded by physicists such as Hermann von Helmholtz, Joseph von Fraunhofer, and Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit. Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays, which are called Röntgenstrahlen (Röntgen-rays) in German and many other languages. This accomplishment made him the first winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.[84]
Aerospace engineer Wernher von Braun developed the first space rocket and later on was a prominent member of NASA and developed the Saturn V Moon rocket, which paved the way for the success of the US Apollo program. Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's work in the domain of electromagnetic radiation was pivotal to the development of modern telecommunication.[85] Through his construction of the first laboratory at the University of Leipzig in 1879, Wilhelm Wundt is credited with the establishment of psychology as an independent empirical science.[86] Alexander von Humboldt's work as a natural scientist and explorer was foundational to biogeography.[87]

Numerous significant mathematicians were born in Germany, including Carl Friedrich Gauss, David Hilbert, Bernhard Riemann, Gottfried Leibniz, Karl Weierstrass and Hermann Weyl. Germany has been the home of many famous inventors and engineers, such as Johannes Gutenberg, who is credited with the invention of movable type printing in Europe; Hans Geiger, the creator of the Geiger counter; and Konrad Zuse, who built the first fully automatic digital computer.[88] German inventors, engineers and industrialists such as Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, Otto Lilienthal, Gottlieb Daimler, Rudolf Diesel, Hugo Junkers and Karl Benz helped shape modern automotive and air transportation technology.[89][90]
Important research institutions in Germany are the Max Planck Society, the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft and the Fraunhofer Society. They are independently or externally connected to the university system and contribute to a considerable extent to the scientific output. The prestigious Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize is granted to ten scientists and academics every year. With a maximum of €2.5 million per award it is one of highest endowed research prizes in the world.[91]
Education

Responsibility for educational oversight in Germany lies primarily with the federal states individually, whilst the federal government only has a minor role. Optional kindergarten education is provided for all children between three and six years old, after which school attendance is compulsory for at least nine years. Primary education usually lasts for four years and public schools are not stratified at this stage.[92] In contrast, secondary education includes four types of schools based on a pupil's ability as determined by teacher recommendations: the Gymnasium enrols the most gifted children and prepares students for university studies, and attendance lasts eight or nine years depending on the state; the Realschule has a broader range of emphasis for intermediate students and lasts six years; the Hauptschule prepares pupils for vocational education, and the Gesamtschule or comprehensive school combines the three approaches.[92]

The Programme for International Student Assessment, coordinated by the OECD, assesses the skills of 15-year-olds in OECD countries and a number of partner countries. In 2006, German schoolchildren improved their position compared to previous years, being ranked (statistically) significantly above average (rank 13) in science skills and statistically not significantly above or below average in mathematical skills (rank 20) and reading skills (rank 18).[93][94] The socio-economic gradient was very high in Germany, the pupils' performance in Germany being more dependent on socio-economic factors than in most other countries.[93][94]
To enter a university, high school students are required to take the Abitur examination, similar to A-levels in the UK; however, students possessing a diploma from a vocational school may also apply to enter. A special system of apprenticeship called Duale Ausbildung allows pupils in vocational training to learn in a company as well as in a state-run school.[92] Most German universities are state-owned and charge tuition fees ranging from €50–500 per semester for each student.[95]
Germany's universities are recognised internationally, indicating the high education standards in the country. In the THES - QS World University Rankings 2007, 3 German universities were ranked amongst the top 100 in the world, and 11 in the top 200.[96]
Culture

Germany is historically called Das Land der Dichter und Denker (the land of poets and thinkers).[97] Since 2006 it has called itself the Land of ideas.[98] German culture began long before the rise of Germany as a nation-state and spanned the entire German-speaking world. From its roots, culture in Germany has been shaped by major intellectual and popular currents in Europe, both religious and secular. As a result, it is difficult to identify a specific German tradition separated from the larger framework of European high culture.[99] Another consequence of these circumstances is the fact that some historical figures, such as Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Franz Kafka and Paul Celan, though not citizens of Germany in the modern sense, must be considered in the context of the German cultural sphere in order to understand their historical situation, work and social relations.

In Germany, the Federal States are in charge of the cultural institutions. There are 240 subsidised theatres, hundreds of symphonic orchestras, thousands of museums and over 25,000 libraries spread over the 16 states. These cultural opportunities are enjoyed by many millions: there are over 91 million German museum visits every year; annually, 20 million go to theatres and operas; while 3.6 million listen to the great symphonic orchestras.[100]
Germany claims some of the world's most renowned classical music composers, including Ludwig van Beethoven, Johann Sebastian Bach, Johannes Brahms and Richard Wagner. As of 2006, Germany is the fifth largest music market in the world and has influenced pop and rock music through artists such as Kraftwerk, Scorpions and Rammstein.[101]
Numerous German painters have enjoyed international prestige through their work in diverse artistic styles. Hans Holbein the Younger, Matthias Grünewald, and Albrecht Dürer were important artists of the Renaissance, Caspar David Friedrich of Romanticism, and Max Ernst of Surrealism. Architectural contributions from Germany include the Carolingian and Ottonian styles, which were important precursors of Romanesque. The region later became the site of significant works in styles such as Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque. Germany was particularly important in the early modern movement, especially through the Bauhaus movement founded by Walter Gropius. Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, also from Germany, became one of world's most renowned architects in the second half of the 20th century. The glass façade skyscraper was his idea.[102]
Philosophy

Germany's influence on philosophy is historically significant and many notable German philosophers have helped shape western philosophy since the Middle Ages. Gottfried Leibniz's contributions to rationalism; the establishment of classical German idealism by Immanuel Kant, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling and Johann Gottlieb Fichte; Karl Marx's and Friedrich Engels' formulation of Communist theory; Arthur Schopenhauer's composition of metaphysical pessimism; Friedrich Nietzsche's development of Perspectivism; Martin Heidegger's works on Being; and the social theories of Jürgen Habermas were especially influential.
German literature can be traced back to the Middle Ages and the works of writers such as Walther von der Vogelweide and Wolfram von Eschenbach. Various German authors and poets have won great renown, including Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller. The collections of folk tales published by the Brothers Grimm popularized German folklore on an international level. Influential authors of the 20th century include Thomas Mann, Berthold Brecht, Hermann Hesse, Heinrich Böll, and Günter Grass.[103]
Media
Germany's television market is the largest in Europe, with some 34 million TV households. The many regional and national public broadcasters are organised in line with the federal political structure. Around 90% of German households have cable or satellite TV, and viewers can choose from a variety of free-to-view public and commercial channels. Pay-TV services have not become popular or successful while public TV broadcasters ZDF and ARD offer a range of digital-only channels.[104]
Germany is home to some of the world's largest media conglomerates, including Bertelsmann and the Axel Springer AG. Some of Germany's top free-to-air commercial TV networks are owned by ProSiebenSat1.
The German book market produces around 60,000 new publications every year. It represents 18% of all the books published worldwide and puts Germany in third place among the world’s book producers.[105] The Frankfurt Book Fair is considered to be the most important book fair in the world for international deals and trading and has a tradition that spans over 500 years.
The country's news is provided in English by news magazine Der Spiegel, state broadcaster Deutsche Welle and news site The Local.
In November 2007 the top visited websites by German internet users were Google, eBay, YouTube, Yahoo, studiVZ and Wikipedia.[106]
Cinema

German cinema dates back to the very early years of the medium with the work of Max Skladanowsky. It was particularly influential during the years of the Weimar Republic with German expressionists such as Robert Wiene and Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau. Austrian-based director Fritz Lang, who became a German citizen in 1926 and whose career flourished in the pre-war German film industry, is said to have been a major influence on Hollywood cinema. His silent movie Metropolis (1927) is referred to as the birth of modern Science Fiction movies.
In 1930 Austrian-American Josef von Sternberg directed The Blue Angel, which was the first major German sound film and it brought world fame to actress Marlene Dietrich.[107] Impressionist documentary Berlin: Symphony of a Great City, directed by Walter Ruttmann, is a prominent example of the city symphony genre. The Nazi era produced mostly propaganda films although the work of Leni Riefenstahl still introduced new aesthetics to film.[108]
During the 1970s and 80s, New German Cinema directors such as Volker Schlöndorff, Werner Herzog, Wim Wenders and Rainer Werner Fassbinder put West German cinema back on the international stage with their often provocative films.[109]
More recently, films such as Das Boot (1981), Lola rennt (Run Lola Run) (1998), Das Experiment (2001), Good Bye Lenin! (2003), Gegen die Wand (Head-on) (2004) and Der Untergang (Downfall) (2004) have enjoyed international success. The Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film went to the German production Die Blechtrommel (The Tin Drum) in 1979, to Nowhere in Africa in 2002, and to Das Leben der Anderen (The Lives of Others) in 2007.[110] Among the most famous German actors are Marlene Dietrich, Klaus Kinski, Hanna Schygulla, Armin Mueller-Stahl, Jürgen Prochnow and Thomas Kretschmann.
The Berlin Film Festival, held annually since 1951, is one of the world's foremost film festivals. An international jury places emphasis on representing films from all over the world and awards the winners with the Golden and Silver Bears.[111] The annual European Film Awards ceremony is held every second year in the city of Berlin, where the European Film Academy (EFA) is located. The Babelsberg Studios in Potsdam are the oldest large-scale film studios in the world and a centre for international film production.
Sports

Sport forms an integral part of German life. Twenty-seven million Germans are members of a sports club and an additional twelve million pursue such an activity individually.[112] Association football is the most popular sport. With more than 6.3 million official members, the German Football Association (Deutscher Fußball-Bund) is the largest sports organisation of its kind worldwide.[112] The Bundesliga attracts the second highest average attendance of any professional sports league in the world. The German national football team won the FIFA World Cup in 1954, 1974 and 1990 and the European Football Championship in 1972, 1980 and 1996. Germany has hosted the FIFA World Cup in 1974 and 2006 and the UEFA European Football Championship in 1988. Among the most successful and renowned footballers are Franz Beckenbauer, Gerd Müller, Jürgen Klinsmann, Lothar Matthäus, and Oliver Kahn. Other popular spectator sports include handball, volleyball, basketball, ice hockey, and tennis.[112]

Germany is one of the leading motorsports countries in the world. Race winning cars, teams and drivers have come from Germany. The most successful Formula One driver in history, Michael Schumacher, has set the most significant motorsport records during his career and won more Formula One championships and races than any other driver since Formula One's debut season in 1946. He is one of the highest paid sportsmen in history and became a billionaire athlete.[113] Constructors like BMW and Mercedes are among the leading teams in motorsport sponsorship. Porsche has won the 24 hours of Le Mans, a prestigious annual race held in France, 16 times. The Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters is a popular series in Germany.
Historically, German sportsmen have been some of the most successful contenders in the Olympic Games, ranking third in an all-time Olympic Games medal count, combining East and West German medals. In the 2008 Summer Olympics, Germany finished fifth in the medal count,[114] while in the 2006 Winter Olympics they finished first.[115] Germany has hosted the Summer Olympic Games twice, in Berlin in 1936 and in Munich in 1972. The Winter Olympic Games took place in Germany once in 1936 when they were staged in the Bavarian twin towns of Garmisch and Partenkirchen.
Cuisine

German cuisine varies from region to region. The southern regions of Bavaria and Swabia, for instance, share a culinary culture with Switzerland and Austria. Pork, beef, and poultry are the main varieties of meat consumed in Germany, with pork being the most popular.[116] Throughout all regions, meat is often eaten in sausage form. More than 1500 different types of sausage are produced in Germany. The most popular vegetables are potatoes, cabbage, carrots, turnips, spinach and beans.[117] Organic food has gained a market share of around 3.0% and this is predicted to be an increasing trend.[118]
A popular saying in Germany is: "Breakfast like an emperor, lunch like a king, and dine like a beggar." Breakfast is usually a selection of cereals and jam or honey with bread or rolls. Some Germans eat cold meats or cheese with bread for breakfast.[119] More than 300 types of bread are sold in bakery shops in the country.[120]

As a country with many immigrants, Germany has adopted many international dishes into its cuisine and daily eating habits. Italian dishes like Pizza and Pasta, Turkish and Arab dishes like Döner Kebab and Falafel are well established, especially in bigger cities. International burger chains, as well as Chinese and Greek restaurants, are widespread. Indian, Thai, Japanese, and other Asian cuisines have gained popularity in recent decades. Among high-profile restaurants in Germany the Michelin guide has awarded three stars, the highest designation, to nine restaurants; 15 more received two stars.[121] German restaurants have become the world's second most decorated after eateries in France.[122]
Although wine is becoming more popular in many parts of Germany, the national drink is beer. German beer consumption per person is declining but at 116 litres annually it is still among the highest in the world.[123] Beer varieties include Alt, Bock, Dunkel, Kölsch, Lager, Malzbier, Pils, and Weizenbier. Among 18 surveyed western countries, Germany ranked 14th in the list of per capita consumption of soft drinks in general, while it ranked third in the consumption of fruit juices.[124] Furthermore, sparkling mineral water and Schorle (its mixture with fruit juice) are extremely popular in Germany.
Society
Since the 2006 World Cup celebrations the internal and external perception of Germany's national image has changed.[125] In annually conducted global surveys known as Nation Brands Index, Germany became significantly and repeatedly higher ranked after the tournament. People in 20 different states were asked to assess the country's reputation in terms of culture, politics, exports, its people and its attractiveness to tourists, immigrants and investments. Germany has been named the world's most valued nation among 50 countries.[126] Another global opinion poll for the BBC revealed that Germany is recognized for the most positive influence in the world, leading 22 investigated countries. A majority of 56% have a positive view of the country, while 18% have a negative view.[127][128]

Germany is a legally and socially tolerant country towards homosexuals. Civil unions have been permitted since 2001.[129] Gays and lesbians can legally adopt their partner's biological children (stepchild adoption). The mayors of the two largest German cities, Berlin and Hamburg, are openly gay.[130]
During the last decade of the 20th century Germany has transformed its attitude towards immigrants considerably. Until the mid-nineties the opinion was widespread that Germany is not a country of immigration, even though about 10% of the population were of non-German origin. After the end of the influx of so-called Gastarbeiter (blue-collar guest-workers), refugees were a tolerated exception to this point of view. Today the government and German society are acknowledging the opinion that controlled immigration should be allowed based on the qualification of immigrants.[131]
With an expenditure of €58 billion on international travel in 2005, Germans invested more money in travel than any other country. Most popular destinations were Austria, Spain, Italy and France.[132]
References
- ↑ (German) Destatis. "Bevölkerungsstand am 31.12. ... nach Geschlecht - in 1 000". Retrieved on 2008-06-28.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". World Economic Outlook Database, October 2008. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved on 2008-10-09.
- ↑ Max Mangold (ed.), ed. (1995) (in German). Duden, Aussprachewörterbuch (Duden Pronunciation Dictionary) (6th ed. ed.). Mannheim: Dudenverlag (Bibliographisches Institut & F.A. Brockhaus AG. pp. 271, 53f. ISBN 3-411-04066-1.
- ↑ Germany: Inflow of foreign population by country of nationality, 1994 to 2003
- ↑ Federal Constitutional Court of Germany (2 BvF 1/73; BVerfGE 36, 1) : The German Reich as the German state is identically the very same to the Federal Republic of Germany [because it exists as a nation-state and international legal personality (public international law) since 1871]. In 1949, at East – West Germany division there was no foundation of a new West German state and no successor of the German Reich, instead of that a part of Germany was reorganized.
- ↑ Germany world's second biggest aid donor after US TopNews, India, Retrieved 2008, 04-10.
- ↑ "The fifteen major spenders in 2006" (PDF). Recent trends in military expenditure. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (2007). Retrieved on 2007-08-23.
- ↑ The leader of Europe? Answers an ocean apart International Herald Tribune. April 4, 2008. Retrieved 2008, 04-04.
- ↑ Confidently into the Future with Reliable Technology www.innovations-report.de. May 7, 2008. Retrieved 2008, 04-04.
- ↑ Jill N. Claster: Medieval Experience: 300–1400. NYU Press 1982, p. 35. ISBN 0814713815.
- ↑ The Cambridge Ancient History, vol. 12, p. 442. ISBN 0521301998.
- ↑ The Thirty-Years-War, Gerhard Rempel, Western New England College.
- ↑ The Thirty Years War (1618–48), Alan McFarlane, The Savage Wars of Peace: England, Japan and the Malthusian Trap (2003)
- ↑ Fulbrook, Mary: A Concise History of Germany, Cambridge University Press 1991, p. 97. ISBN 0521540712
- ↑ Martin, Norman. German Confederation 1815–1866 (Germany) Flags of the World. Oct. 5, 2000. Retrieved 2006, 12-07.
- ↑ Stephen J. Lee: Europe, 1890–1945. Routledge 2003, p. 131. ISBN 0415254558.
- ↑ Deutsches Historisches Museum. "Das Ermächtigungsgesetz 1933" (in German). Deutsches Historisches Museum. Retrieved on 2008-09-12. "An der Abstimmung nicht teilnehmen konnten die 81 Abgeordneten der Kommunistischen Partei Deutschlands (KPD). Ihre Mandate waren auf Basis der Reichstagsbrandverordnung bereits am 8. März 1933 annulliert worden."
Roderick Stackelberg, Hitler's Germany: origins, interpretations, legacies. Routledge 1999, p. 103. ISBN 0415201144.
Scheck, Raffael. Establishing a Dictatorship: The Stabilization of Nazi Power Colby College. Retrieved 2006, 07-12. - ↑ Deutsches Historisches Museum. "Industrie und Wirtschaft" (in German). Deutsches Historisches Museum. Retrieved on 2008-09-12. "Der Vierjahresplan sollte ab 1936 die wirtschaftliche Kriegsfähigkeit Deutschlands herbeiführen. . . .Bereits im Februar 1933 erklärte Hitler, dass alle öffentlichen Maßnahmen zur Arbeitsbeschaffung zugleich der "Wehrhaftmachung" zu dienen hätten und den Interessen des Staates untergeordnet seien. . . ."
- ↑ Britannica http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9080620/Bonn
- ↑ Colchester, Nico. D-mark day dawns Financial Times. January 1, 2001. Retrieved 2006, 12-07
- ↑ WDR http://www.wdr.de/themen/kultur/stichtag/2004/03/10.jhtml Eine "faire Arbeitsteilung" Vor 10 Jahren: Bundestag beschließt Bonn-Berlin-Gesetz . 10 March 04.
- ↑ Dempsey, Judy. Germany is planning a Bosnia withdrawal International Herald Tribune. Oct. 31, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 11-30
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 Germany CIA Factbook. November 14, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 11-29.
- ↑ Olson, Donald (May 2007). Germany For Dummies, 3rd Edition. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-08956-9. http://www.dummies.com/WileyCDA/DummiesArticle/id-5361.html.
- ↑ German Climate and Weather World Travels. Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ The Ecoregions WWF, Retrieved 2008, 12-28.
- ↑ List of famous Zoological gardens in European countries www.eupedia.com, Retrieved 2008, 10-17.
- ↑ Some interesting zoo facts www.americanzoos.info/, Retrieved 2008, 10-17.
- ↑ Tierstatistik 2007(German), Zoo Berlin, Accessed August 5, 2008
- ↑ German lessons, The Economist, Retrieved 2008, 11-29.
- ↑ Starting points and focus of environmental communication German Federal Environmental Foundation, Retrieved 2007, 12-28.
- ↑ PIPA (2007-09-24). "All Countries Need to Take Major Steps on Climate Change: Global Poll" (PDF). BBC World service Poll, carried out by Globescan. Program on International Policy Attitudes at the University of Maryland, College Park. Retrieved on 2008-02-11. "Eighty-seven percent of German respondents agree that human activity is a significant cause of climate change and 95 percent think it is necessary to take measures to deal with the problem."
- ↑ Reinforcing Germany's environmental protection industry Umweltbundesamt, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
- ↑ Germany greenest country in the world Times of India, Retrieved 2008, 11-25
- ↑ [www.gesetze-im-internet.de/gg/art_79.html Article 79 of the Grundgesetz] (German) Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 2008, 12-07.
- ↑ Christian Democratic Union/Christian Social Union U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2006, 12-07.
- ↑ Federal Constitutional Court, Bundesverfassungsgericht.de, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ § 2, StVllzg, gesetze-im-internet.de, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ Declaration by the Franco-German Defence and Security Council Elysee.fr May 13, 3004. Retrieved 2006, 12-03.
- ↑ Glaab, Manuela. German Foreign Policy: Book Review Internationale Politik. Spring 2003. Retrieved 2007, 01-03.
- ↑ Harrison, Hope. The Berlin Wall, Ostpolitik and DétentePDF (91.1 KB) GERMAN HISTORICAL INSTITUTE, WASHINGTON, DC, BULLETIN SUPPLEMENT 1, 2004, "AMERICAN DÉTENTE AND GERMAN OSTPOLITIK, 1969–1972".
- ↑ Germany's New Face Abroad Deutsche Welle. Oct. 14, 2005. Retrieved 2006, 12-03.
- ↑ Background Note: Germany U.S. Department of State. July 6, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 12-03.
- ↑ Ready for a Bush hug?, The Economist, July 6 2006. Retrieved 2006, 12-31.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 U.S.-German Economic Relations FactsheetPDF (32.8 KB) U.S. Embassy in Berlin. May 2006. Retrieved 2006, 12-03.
- ↑ German Still Most Frequently Reported Ancestry U.S. Census Bureau June 30, 2004. Retrieved 2006, 12-03
- ↑ Kaiserslautern, Germany Overview U.S. Military. Retrieved 2006, 12-03.
- ↑ Aims of German development policy Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development April 10, 2008. Retrieved 2008, 12-07.
- ↑ Germany is a leader in development funding www.young-germany.de April 17, 2008. Retrieved 2008, 12-07.
- ↑ Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland Bundestag.de Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ "NATO International Security Assistance Force Placemat" (PDF) (Current as of 2007-02-07). Retrieved on 2007-02-12.
- ↑ Hans Kristensen (2007-07-09). "United States Removes Nuclear Weapons From German Base, Documents Indicate". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved on 2008-07-26.
- ↑ Destatis. "Im Jahr 2050 doppelt so viele 60-Jährige wie Neugeborene". Retrieved on 2007-06-20. (German)
- ↑ BiBB: Menschen mit Migrationshintergrund - neue Definition, alte Probleme retrieved 25 of May 2008
- ↑ Foreign population on 31 December 2004 by country of origin Federal Statistical Office Germany January 24, 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-01.
- ↑ "Germany: Stock of foreign population by country of nationality (table available by menu selection)". Migration Policy Institute (2008).
- ↑ State of World Population 2006 United Nations Population Fund. 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-01.
- ↑ Erstmals seit 1990 weniger als 600 000 Ausländer zugezogen, German Federal Statistics Bureau (Statistiches Bundesamt Deutschland) , July 6 2006. Retrieved on 2007, 01-01. (German)
- ↑ Christen in Deutschland 2005(German), EKD, Retrieved 2007, November 11-25.
- ↑ Religionen in Deutschland: Mitgliederzahlen Religionswissenschaftlicher Medien- und Informationsdienst. November 4, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 11-30. (German)
- ↑ Germany Euro-Islam.info. Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ "EKD: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland - Christen in Deutschland 2006". Ekd.de. Retrieved on 2008-11-04.
- ↑ Blake, Mariah. In Nazi cradle, Germany marks Jewish renaissance Christian Science Monitor. November 10,2006. Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ The Jewish Community of Germany European Jewish Congress. Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ Die Zeit 12/07, page 13
- ↑ "Eurobarometer on Social Values, Science and technology 2005 (page 11)" (PDF). Retrieved on 2007-05-05.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 European Commission (2006). "Special Eurobarometer 243: Europeans and their Languages (Survey)" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved on 2007-02-03.
European Commission (2006). "Special Eurobarometer 243: Europeans and their Languages (Executive Summary)" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved on 2007-02-03. - ↑ European Commission (2004). "Many tongues, one family. Languages in the European Union" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved on 2007-02-03.
- ↑ National Geographic Collegiate Atlas of the World. Willard, Ohio: R.R Donnelley & Sons Company. April 2006. pp. 257–270. ISBN Regular:0-7922-3662-9, 978-0-7922-3662-7. Deluxe:0-7922-7976-X, 978-0-7922-7976-1.
- ↑ Rank Order - GDP (purchasing power parity) CIA Factbook 2005. Retrieved 2006, 12-31.
- ↑ German trade surplus hits record BBC, . Retrieved 2007, 01-03.
- ↑ Wind Power Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology (Germany) Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ Global 500 Germany, CNN Money, Retrieved 2007, 11-26.
- ↑ Global 500 Biggest Employers, CNN Money, Retrieved 2007, 11-26.
- ↑ The 100 Top Brands 2006, Businessweek, Retrieved 2007, 11-26.
- ↑ Berg, S., Winter, S., Wassermann, A. The Price of a Failed Reunification Spiegel Online International. Sep. 5, 2005. Retrieved 2006, 11-28.
- ↑ Arbeitslosenzahl unter 3,2 Millionen gesunken(German) Tagesschau, . Retrieved 2008, 07-01.
- ↑ "Autobahn-Temporegelung" (PDF). ADAC (October 2007). Retrieved on 2008-11-15. (German)
- ↑ Geschäftsbericht 2006 der Deutschen Bahn AG, Deutsche Bahn, Retrieved 2007, October 19.
- ↑ Germany split over green energy, BBC, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ Back to the Future: Germany - A Country of Research German Academic Exchange Service (2005, 02-23). Retrieved 2006, 12-08.
- ↑ Nobel Prize, nobelprize.org, Retrieved 2008, July 5.
- ↑ Roberts, J. M. The New Penguin History of the World, Penguin History, 2002. Pg. 1014. ISBN 0141007230.
- ↑ The Alfred B. Nobel Prize Winners, 1901–2003 History Channel from The World Almanac and Book of Facts 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Historical figures in telecommunications. International Telecommunication Union. January 14, 2004. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Kim, Alan. Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Jun. 16, 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ The Natural History Legacy of Alexander von Humboldt (1769 to 1859), Humboldt Field Research Institute and Eagle Hill Foundation. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Horst, Zuse. The Life and Work of Konrad Zuse Everyday Practical Electronics (EPE) Online. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Automobile. Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ The Zeppelin U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize, DFG, Accessed March 12, 2007
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 92.2 COUNTRY PROFILE: GERMANYPDF (177 KB) U.S. Library of Congress. Dec. 2005. Retrieved 2006, 12-04.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 Programme for International Student Assessment (2007) (PDF). Executive Summary, PISA 2006: Science Competencies for Tomorrow’s World Volume 1: Analysis. France: OECD. ISBN 978-92-64-04000-7. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/15/13/39725224.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-12-15.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Programme for International Student Assessment (2007) (PDF). PISA 2006: Science Competencies for Tomorrow’s World Volume 1: Analysis. France: OECD. ISBN 978-92-64-04000-7. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/30/17/39703267.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-12-15.
- ↑ Tuition Fees in Germany German Academic Exchange Service. Retrieved 2006, 11-30.
- ↑ "Times Higher Education - QS World University Rankings 2007 - Top 400 Universities". Quacquarelli Symonds. Retrieved on 2008-08-11.
- ↑ Wasser, Jeremy. Spätzle Westerns Spiegel Online International. Apr. 6, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 12-06.
- ↑ "Land of Ideas" campaign www.land-of-ideas.org, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
- ↑ Federal Republic of Germany: Culture. Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. Retrieved 2007, 01-02.
- ↑ Unbelievable Multitude www.study-in-germany.de Retrieved 2008, 10-17.
- ↑ Music market worth US$ 32 billion P2pnet.net Apr. 7, 2004. Retrieved 2006, 12-07.
- ↑ 2006 A Dictionary of Architecture and Landscape Architecture (Paperback) , Second (in English) , Oxford University Press, 880. ISBN 0198606788
- ↑ Kjell Espmark (1999-12-03). "The Nobel Prize in Literature". Nobelprize.org. Retrieved on 2006-08-14.
- ↑ Country profile: Germany, BBC News, Retrieved 2007, 12-07.
- ↑ German literature German Embassy London, Retrieved 2008, 10-22.
- ↑ Top Sites Germany Alexa, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
- ↑ Bordwell, David; Kristin Thompson (2003) [1994]. "The Introduction of Sound". Film History: An Introduction (2nd Edition ed.). New York City: McGraw-Hill. pp. 204. ISBN 978-0071151412.
- ↑ Leni Riefenstahl, FILMBUG, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ Rainer Werner Fassbinder, Fassbinder Foundation, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ Awards:Das Leben der Anderen, IMDb, Accessed April 13, 2007
- ↑ 2006 FIAPF accredited Festivals Directory, International Federation of Film Producers Associations, retrieved on December 11, 2006.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 112.2 Germany Info: Culture & Life: Sports Germany Embassy in Washington, D.C. Retrieved 2006, 12-28.
- ↑ What we will miss about Michael Schumacher, Guardian Unlimited, Retrieved 2007, October 19
- ↑ Beijing 2008 Medal Table The Official Website of the Beijing 2008 Olympic Games. Retrieved 2008, 9-8.
- ↑ Turin 2006 Medal Table International Olympic Committee. Retrieved 2006, 12-28.
- ↑ GERMAN FOOD STATS, www.nationmaster.com, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ German cuisine, www.cuisineeurope.com, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ Organic Agriculture in Germany, organic-Europe, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ EATING THE GERMAN WAY, Cultural Profiles Project, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ 300 Types of Bread, /www.germany-tourism.de, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ Schnitzel Outcooks Spaghetti in Michelin Guide, Deutsche Welle, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ German cuisine beats Italy, Spain in gourmet stars, Reuters India, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ Europe's largest beer market, royalunibrew.com, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ Soft drink consumption, www.nationmaster.com, Retrieved 2007, November 26
- ↑ How Germany won the World Cup of Nation Branding BrandOvation, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
- ↑ 2008 Anholt-GfK Roper Nation Brands IndexSM Ranking GfK Custom Research North America, Retrieved 2008, 10-03.
- ↑ World views US 'more positively BBC NEWS, Retrieved 2008, 04-02
- ↑ Germany gets the most positive ratings of all countries Globescan, Retrieved 2008, 04-04.
- ↑ Germany extends gay rights News24.com, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
- ↑ Weinthal, Benjamin (2006-08-31). "He’s Gay, and That’s Okay". Gay City News. Retrieved on 2008-11-13.
- ↑ From ethnic nation to universalistic immigrant integration: Germany The Integration of Immigrants in European Societies, Retrieved 2008, 11-25.
- ↑ The Germans are world champions in travelling Goethe Institut Singapore, Retrieved 2007, 11-25.
External links
General
- Deutschland.de — Official Germany portal (non-profit)
- Deutsche Welle — Germany's international broadcaster
- Germany entry at The World Factbook
- Germany at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Germany at the Open Directory Project
Facts and figures
- Facts about Germany — by the German Federal Foreign Office
- Destatis.de — Federal Statistical Office Germany (English)
Travel
- Germany Travel Info — Official Germany tourism portal (non-profit)
- Germany travel guide from Wikitravel
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
||||||||
|
|||||