Geography of Sweden
|
||
| Continent | Europe | |
| Subregion | Scandinavia | |
| Geographic coordinates | ||
| Area - Total - Water |
Ranked 55th 449,964 km² 39,03- km² (8.69%) |
|
| Coastline | 3,218 km (2,000 mi) | |
| Land boundaries | 2,333 km (1,550 mi) | |
| Countries bordered | Norway 1,169 km Finland 614 km |
|
| Highest point | Kebnekaise, 2,111 m / 6,926 ft | |
| Lowest point | Kristianstad, -2.41 m | |
| Longest river | Torne River, 521.63 km (324.14 mi) | |
| Largest inland body of water | Vänern 5,648 km² (3,510 sq mi) | |
| Land Use - Arable land - Permanent crops - Other |
5.93 % 0.01 % 94.06 % (2005 est.) |
|
| Irrigated Land | 1,150 km² | |
| Climate: | Temperate to subarctic | |
| Terrain: | flat lowlands, mountains | |
| Natural resources | iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, gold, silver, tungsten, uranium, arsenic, feldspar, timber, hydropower | |
| Natural hazards | ice flow | |
| Environmental issues | acid rains | |
Sweden is a country in Northern Europe.
Contents |
Location
Northern Europe, Scandinavian Peninsula, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway. Strategic location along Öresund and the Danish Straits linking the Baltic and North Seas.
- Climate: temperate in the south with cold, cloudy Winters and cool, partly cloudy Summers; subarctic in the north
- Terrain: Mountains and hills in the west. Plains and agricultural land in the south. The mountains field are in the north together with plains and lakes and a lot of snow in the winter. More than 50% of Sweden is forests, dominant in the central parts, comparable to the terrain of Canada.
- Geographic coordinates:
The two largest islands are Gotland and Öland in the south-east. They each have their own culture, most notably Gotland with the old, largely intact and heritage-filled city Visby.
Lands of Sweden
Sweden is traditionally divided into three Lands or landsdelar without any administrative function:
- Götaland
- Svealand
- Norrland
Provinces
The lands are further divided into 25 provinces or landskap, which are also without administrative function.
Counties

Administratively Sweden is divided into 21 counties or län. In each county there is a County Administrative Board or länsstyrelse which is appointed by the Government.
In each county there is also a separate County Council or landsting, which is the municipal representation appointed by the county electorate.
- K = Blekinge County
- W = Dalarna County
- I = Gotland County
- X = Gävleborg County
- N = Halland County
- Z = Jämtland County
- F = Jönköping County
- H = Kalmar County
- G = Kronoberg County
- BD = Norrbotten County
- M = Skåne County
- AB = Stockholm County
- D = Södermanland County
- C = Uppsala County
- S = Värmland County
- AC = Västerbotten County
- Y = Västernorrland County
- U = Västmanland County
- O = Västra Götaland County
- T = Örebro County
- E = Östergötland County
The letters shown were on the vehicle registration plates until 1973 .
Municipalities
Each county is further divided into municipalities or kommuner, ranging from only one (in Gotland County) to forty-nine (in Västra Götaland County). The total number of municipalities is 290.
The northern municipalities are often large in size, but have small populations – the largest municipality is Kiruna with an area as large as the three southern provinces in Sweden (Scania, Blekinge and Halland) combined, but it only has a population of 25,000, and its density is about 1 / km².
Cities
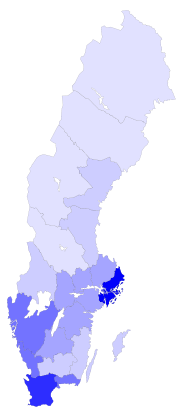
people/km²
0-9.9 10-24.9 25-49.9 50-99.9 100-199.9 200+
Cities and towns in Sweden are not political or administrative entities, but localities or urban areas, independent of the municipal subdivision.
The largest city, in terms of population, is the capital Stockholm, in the east, the dominant city for culture and media, with a population of 1,250,000. The second largest city is Gothenburg, with 510,500, in the west. The third largest is Malmö in the south, with 258,000.
The north is less populated than the southern and central parts, mostly because of its colder climate. The largest city is Umeå with 75,000 inhabitants.
There are 1,940 localities with more than 200 inhabitants in the country.
Area
- Total: 449,964 km² (slightly larger than California, USA)
- where of land: 410,934 km²
- and water: 39,030 km²
The water area consists of around 95,700 lakes [1], and the area taken up by lakes are close to 10%. They are extensively used for water power plants, especially the large northern rivers and lakes. Sweden is the biggest Scandinavian country as well as the third largest West-European country.
Land boundaries
Maritime claims
- continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- exclusive economic zone: agreed boundaries or midlines
- territorial sea: 12 nautical miles (22 km) (adjustments made to return a portion of straits to high seas)
Elevation extremes
- lowest point: in the city of Kristianstad in southern Sweden, −2.41 m
- highest point: Kebnekaise, 2,104 m
Railways
- Main line railways of Sweden (Stambanor) were built between 1860-1930.
Natural resources
Land use

- arable land: 7%
- permanent crops: 0%
- permanent pastures: 1%
- forests and woodland: 78%
- other: 14% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land: 1,150 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards

Ice floes in the surrounding waters, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia, can interfere with maritime traffic.
Environment
- current issues: acid rain damaging soils and lakes; pollution of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. The HBV hydrology transport model has been used to analyze nutrient discharge to the Baltic from tributary watersheds.
- international agreements: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change,Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78), Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
- signed, but not ratified:none of the selected agreements
See also
- List of islands of Sweden
- List of lakes in Sweden
- List of rivers in Sweden
- List of national parks of Sweden
- List of municipalities of Sweden
- List of cities in Sweden
- Provinces of Sweden
- Counties of Sweden
- Geographical center of Sweden
References
- CIA World Factbook 2001
- CIA World Factbook 2006
|
|||||||||||